VMware 5v0-23-20 practice test
VMware vSphere with Tanzu Specialist
Question 1
An administrator working in a vSphere with Tanzu environment wants to ensure that all persistent
volumes configured by developers within a namespace are placed on a defined subset of datastores
The administrator has applied tags to the required datastores in the vSphere Client
Which action should the administrator take next to meet the requirement?
- A. Create a storage policy containing the tagged datastores. and apply it to the vSphere Namespace.
- B. Create a storage class containing the tagged datastores. and apply it to the Supervisor Cluster
- C. Create a persistent volume claim containing the tagged datastores, and apply it to the vSphere Namespace.
- D. Create a storage Policy containing the tagged datastores. and apply it to the Supervisor Cluster.
Answer:
A
Explanation: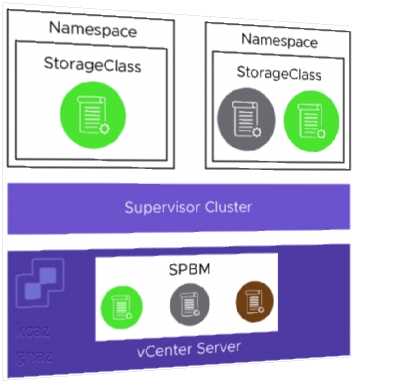
The vSphere administrator defines and assigns VM storage policies to a namespace:
• VM storage policies are translated into Kubernetes storage classes.
• Developers can access all assigned VM storage policies in the form of storage classes.
• Developers cannot manage storage classes.
Storage class names are created in the following way:
• Spaces in VM Storage Policy names are replaced with hyphens (-).
• Special characters are replaced with a digit. A VM Storage Policy called My Gold Policy $ is called
my-gold-policy-0 as a storage class.
Question 2
Which three roles does the Spherelet perform? (Choose three )
- A. Determines placement of vSphere pods
- B. Manages node configuration
- C. Starts vSphere pods
- D. Provides a key-value store for pod configuration
- E. Communicates with Kubernetes API
- F. Provisions Tanzu Kubernetes clusters
Answer:
BCE
Explanation: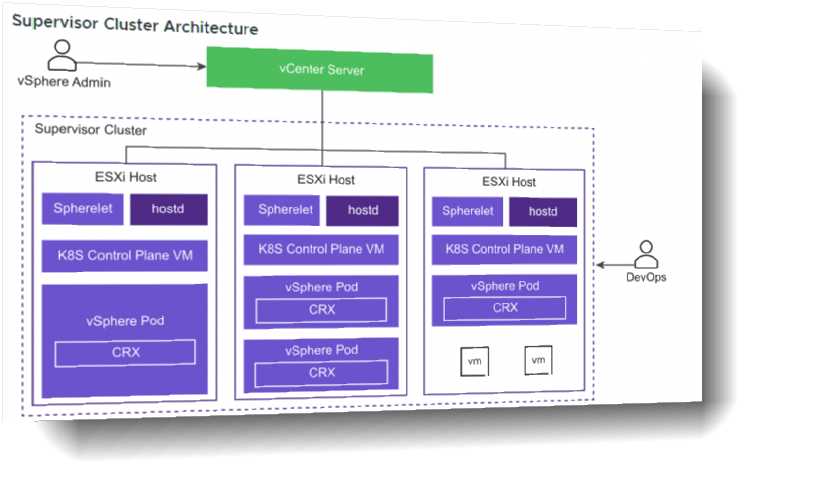
Spherelet is a kubelet that is ported natively to ESXi. It allows the ESXi host to become part of a
Kubernetes cluster. Spherelet performs the following functions:
• Communicates with the control plane VMs
• Manages node configuration
• Starts vSphere Pods
• Monitors vSphere Pods
Question 3
Why would developers choose to deploy an application as a vSphere Pod instead of a Tanzu
Kubernetes cluster?
- A. They need the application to run as privileged pods.
- B. The application works with sensitive customer data, and they want strong resource and security isolation.
- C. They want to have root level access to the control plane and worker nodes in the Kubernetes cluster.
- D. The application requires a version of Kubernetes that is above the version running on the supervisor cluster.
Answer:
B
Explanation: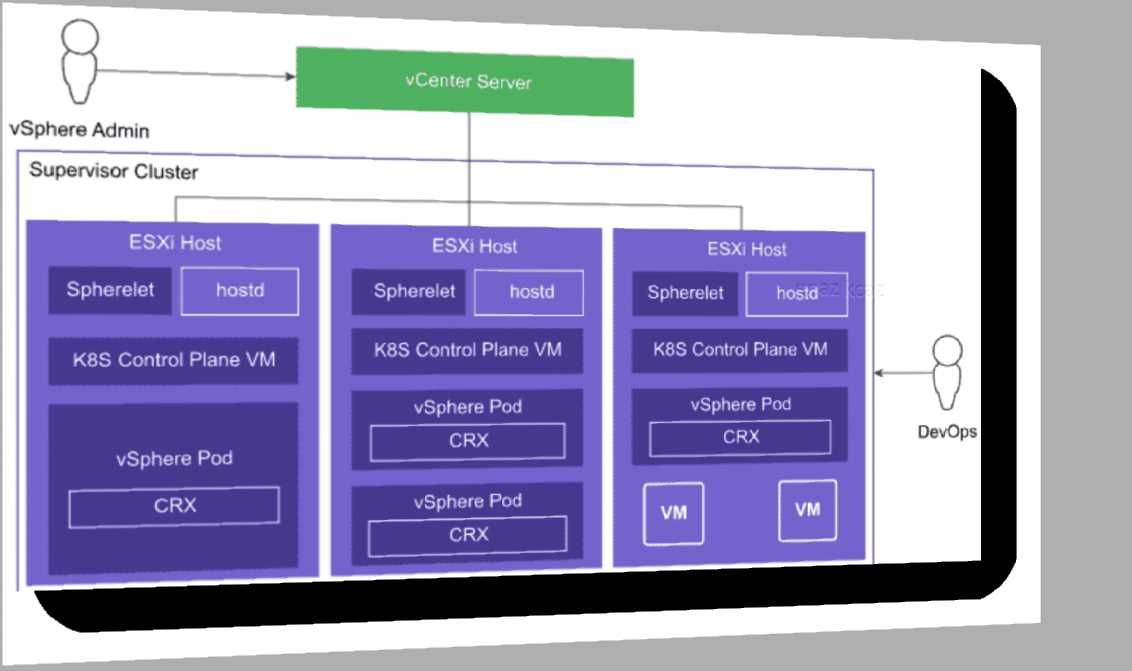
A vSphere Pod is a VM with a small footprint that runs one or more Linux containers. With vSphere
Pods, workloads have the following capabilities:
• Strong isolation from a Linux kernel based on Photon OS
• Resource management using DRS
• Same level of resource isolation as VMs
• Open Container Initiative (OCI) compatible
• Equivalent to a Kubernetes Container Host
vSphere Pods are not compatible with vSphere vMotion. When an ESXi host is placed into
maintenance mode, running vSphere Pods are drained and redeployed on another ESXi host, but
only if the vSphere Pod is part of a ReplicaSet.
Question 4
A company needs to provide global visibility and consistent policy management across multiple
Tanzu Kubernetes Clusters, namespaces, and clouds Which VMvare solution will meet these
requirements'?
- A. vSphere with Tanzu Supervisor Cluster
- B. vCenter Server
- C. Tanzu Mission Control
- D. Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service
Answer:
C
Explanation: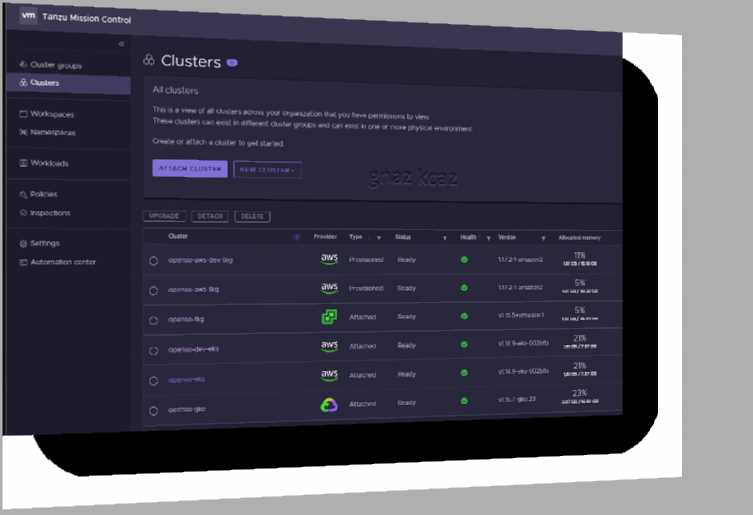
VMware Tanzu Mission Control™ is a centralized management platform for consistently operating
and securing your Kubernetes infrastructure and modern applications across multiple teams and
clouds.
Question 5
A developer is connecting to a Tanzu Kubernetes Cluster using the kubectl vsphere login command
Which information must be specified, in addition to both the name of the cluster and the Supervisor
Cluster Control Wane IP?
- A. The path to the existing kubeconfig file and the SSO Username
- B. The path to the existing kubeconfig file and the Token D for the SSO credentials
- C. The name of the Supervisor Namespace and the Token ID for the SSO credentials
- D. The name of the Supervisor Namespace and the SSO Username
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To connect to the Supervisor Cluster, run the following command.
kubectl vsphere login --server=SUPERVISOR-CLUSTER-CONTROL-PLANE-IP
--tanzu-kubernetes-cluster-name TANZU-KUBERNETES-CLUSTER-NAME
--tanzu-kubernetes-cluster-namespace
SUPERVISOR-NAMESPACE-WHERE-THE-CLUSTER-IS-
DEPLOYED
--vsphere-username VCENTER-SSO-USER-NAME
For example:
kubectl vsphere login --server=10.92.42.137
--tanzu-kubernetes-cluster-name tanzu-kubernetes-cluster-01
--tanzu-kubernetes-cluster-namespace tanzu-ns-1
--vsphere-username [email protected]
Question 6
Which value must be increased or decreased to horizontally scale a Tanzu Kubernetes cluster?
- A. Namespaces
- B. etcd instance
- C. Worker node count
- D. ReplicaSets
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Scale a Cluster Horizontally With the Tanzu CLI
To horizontally scale a Tanzu Kubernetes cluster, use the tanzu cluster scale command. You change
the number of control plane nodes by specifying the --controlplane-machine-count option. You
change the number of worker nodes by specifying the --worker-machine-count option.
Question 7
Which two container network interfaces (CNIs) are supported with Tanzu Kubernetes clusters created
by the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service? (Choose two )
- A. NSX-T
- B. Weave Net
- C. Flannel
- D. Antrea
- E. Calico
Answer:
DE
Explanation:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-vSphere/7.0/vmware-vsphere-with-tanzu/GUID-A7756D67-0B95-447D-A645-E2A384BF8135.html
A Tanzu Kubernetes cluster provisioned by the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service supports two CNI
options: Antrea (default) and Calico. Both are open-source software that provide networking for
cluster pods, services, and ingress.
Tanzu Kubernetes clusters provisioned by the Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service support the
following
Container Network Interface
(CNI) options:
Antrea
Calico
Explanation
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service CNI
Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service supports Antrea and Calico as container network interfaces (CNI).
The default CNI in vSphere 7 Update 1 is Antrea.
Antrea is a VMware-supported, open source, Kubernetes-native project that implements the
container network interface (CNI) and Kubernetes network policy, providing network connectivity
and security for pod workloads. Antrea extends the benefit of programmable networks from Open
vSwitch (OVS) to Kubernetes.
For more information about Antrea, see https://antrea.io/
Question 8
Where are the virtual machine images stored that are used to deploy Tanzu Kubernetes clusters?
- A. Content Library
- B. Supervisor Cluster
- C. Harbor Image Registry
- D. Namespace
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The vSphere administrator configures a Subscribed Content Library on the Supervisor Cluster. The
virtual machine image that is used for the Tanzu Kubernetes cluster nodes is pulled from this library.
A Subscribed Content Library originates from a Published Content Library. After the subscription is
created, the system synchronizes it with the published library. To create the Tanzu Kubernetes cluster
nodes, VMware publishes a Photon OS OVA library to which you subscribe. After the subscriber is
synchronized with the publisher, you associate the content library with the Supervisor Cluster.
Question 9
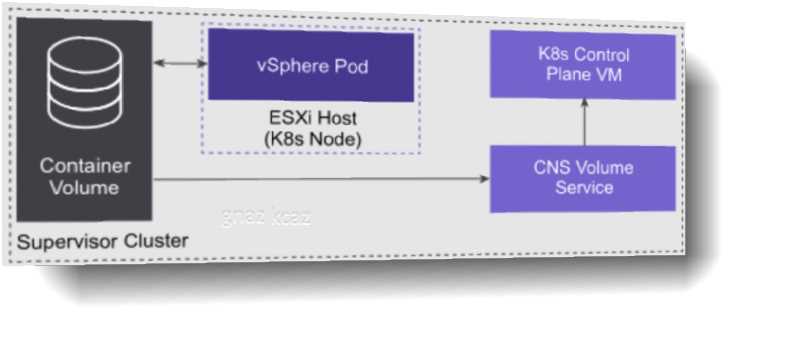
Which capability do persistent volumes provide to containerized applications?
- A. Automated disk archival
- B. Support for in-memory databases
- C. Support for ephemeral workloads
- D. Retention of application state and data
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Certain Kubernetes workloads require persistent storage to store data permanently. To provision
persistent storage for Kubernetes workloads, vSphere with Tanzu integrates with Cloud Native
Storage (CNS), a vCenter Server component that manages persistent volumes.
Persistent storage is used by vSphere Pods, Tanzu Kubernetes clusters, and VMs. The following
example illustrates how persistent storage is used by a vSphere Pod.
vSphere Pods use different types of storage depending on the objects that are stored. The types of
storage are ephemeral virtual machine disks (VMDKs), persistent volume VMDKs, and containers
image VMDKs:
• Storage policies for container image and ephemeral disks are defined at the cluster level.
• Storage policies for persistent volumes are defined at the namespace level.
• Networking for vSphere Pods uses the topology provided by NSX.
Question 10
What is the proper way to delete a Persistent Volume Claim?
- A. By using the kubectl delete persistentvolumeclaim command
- B. By using the kubectl remove pvc command
- C. Through the SPBM policy engine using the vSphere Client
- D. By unmounting the volume from the VM and deleting it from the vSphere datastore
Answer:
A
Explanation: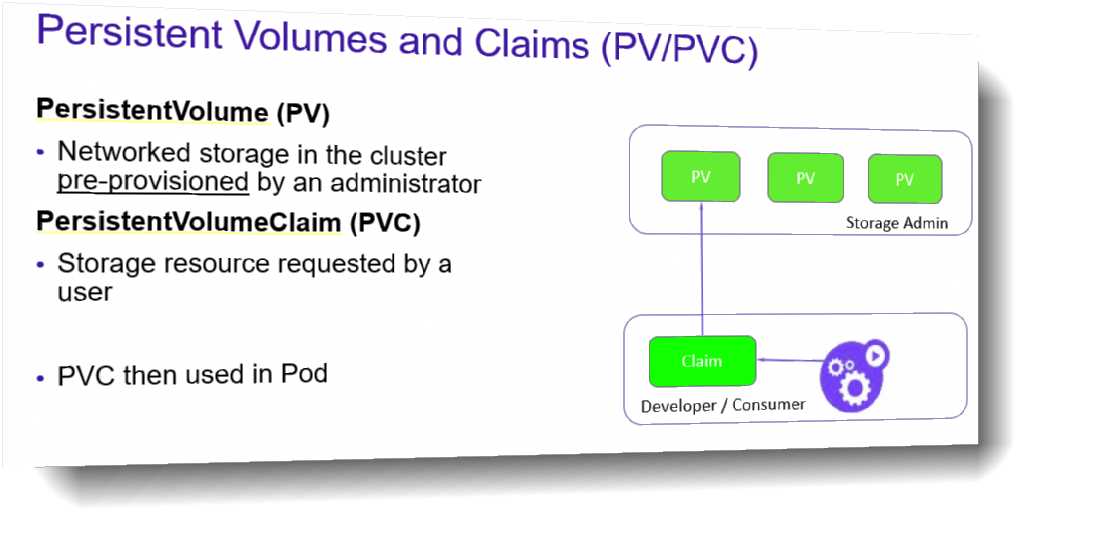
Also, kubectl delete pvc, which is much shorter.
DevOps engineers create persistent volume claims to request persistent storage resources. The
request provisions a persistent volume object and a matching virtual disk. In the vSphere Client, the
persistent volume claim manifests as an FCD virtual disk that can be monitored by vSphere
administrators.
The claim is bound to the persistent volume. The workloads can use the claim to mount the
persistent volumes and access storage.
When the DevOps engineers delete the claim, the corresponding persistent volume object and the
provisioned virtual disk are also deleted.
Question 11
Which command will show the Tanzu Kubernetes cluster versions available in the vSphere content
library?
- A. kubect1 get rc,services
- B. kubect1 get contentlibrary
- C. kubect1 get tanzukubernetesreleases
- D. kubect1 get tanzuimages
Answer:
C
Explanation:
kubectl get tanzukubernetesreleases
List available Tanzu Kubernetes releases.
kubectl get tkr
Short form version of the preceding command.
kubectl get tkr v1.17.8---vmware.1-tkg.1.5417466 -o yaml
Provides details on the named Tanzu Kubernetes release.
VMware Tanzu distributes Kubernetes software versions as Tanzu Kubernetes releases. To consume
these releases, you configure a vSphere Content Library and synchronize the available releases. You
can do so using a subscription-based model, or on-demand. If you want to provision Tanzu
Kubernetes in an internet restricted environment, you can create a local library and manually import
the releases.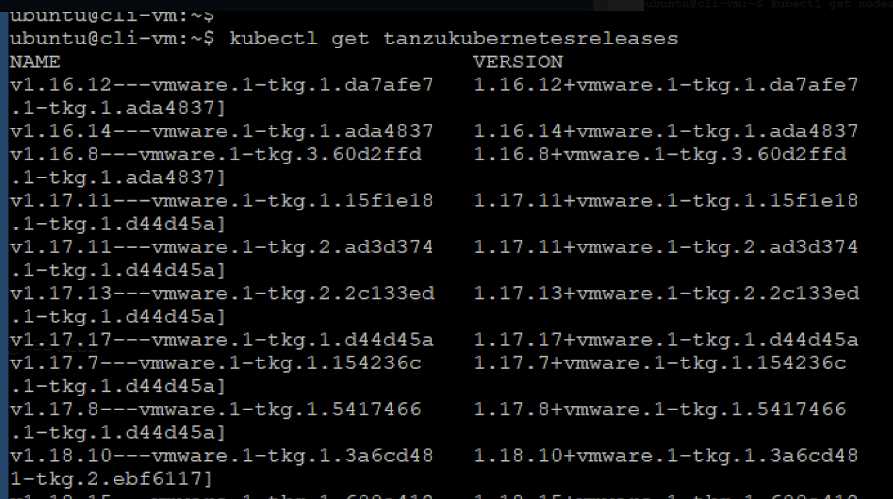
Question 12
Which object helps maintain copies of a vSphere pod?
- A. ReplicaSets
- B. Network Policies
- C. Namespaces
- D. Persistent Volume
Answer:
A
Explanation: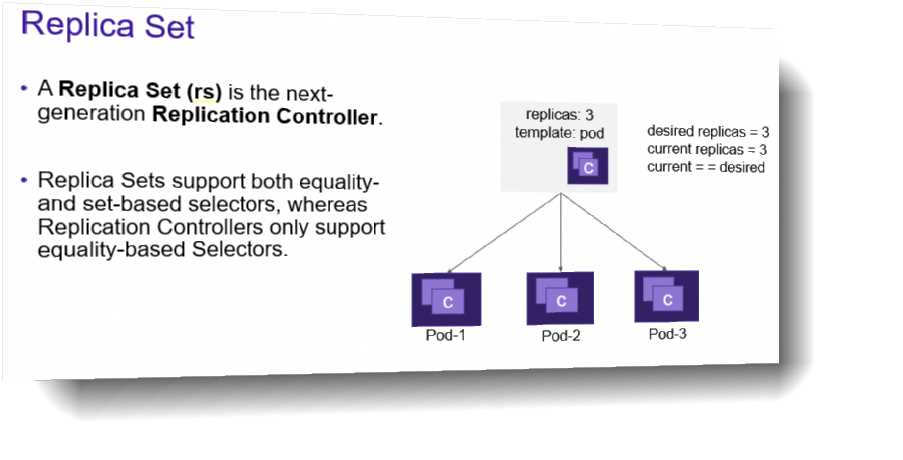
A ReplicaSet declares how the functionality of a pod is made scalable and resilient through
redundancy. The ReplicaSet ensures that a specified number of pods is kept running. Example:
Deploy a ReplicaSet. • The ReplicaSet name is nginx-replica-demo. • Two replicas are expected to be
running. • The ReplicaSet applies to pods with label nginx.
For
more
information
about
Kubernetes
replica
sets,
see
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicaset/
Question 13
On which network are TKG clusters deployed in vSphere with Tanzu when using the vSphere
networking stack?
- A. Workload
- B. Backend
- C. Edge
- D. Frontend
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Workload Network, such as TKGS-VLAN1000, is where the Tanzu Kubernetes clusters run.
A workload network is a network construct that is used by supervisor control plane VMs and vSphere
namespaces:
• The workload network is supported by a vSphere Distributed Switch port group.
• An IP range is defined to allocate an IP address for VMs attached to the workload network.
• A primary workload network must be selected.
• The supervisor control plane VMs attach to the primary workload networks port group.
A workload network can be used by multiple namespaces. A namespace can be assigned only one
workload network.
Question 14
What is the correct process to store images in a project on the Registry Service?
- A. Use the kubect1 push command
- B. Use the docker push command
- C. Use the vSphere Client to upload the image the content library
- D. Use the vSphere Client to upload the image to the Registry Service
Answer:
B
Explanation:
https://docs.docker.com/docker-hub/repos/
• Registry Service: Developers can store and manage Docker and OCI images using Harbor. Harbor is
an open-source container image registry that secures images with role-based access control.
Procedure
Login to Harbor Registry with the vSphere Docker Credential Helper.
docker-credential-vsphere login <container-registry-IP> --user [email protected]
Note:While providing --user username is acceptable for login, you should use the UserPrincipalName
(UPN) syntax ( --user [email protected]) to login and use docker push commands.
Tag the image that you want to push to the project in Harbor Registry with same name as the
namespace, where you want to use it:
docker tag <image-name>[:TAG] <container-registry-IP>/<project-name>/<image-name>[:TAG]
For example:
docker tag hello-world:latest 10.179.145.77/tkgs-cluster-ns/hello-world:latest
docker images
REPOSITORY
TAG
IMAGE ID
CREATED
SIZE
10.179.145.77/tkgs-cluster-ns/hello-world
latest
bf756fb1ae65
10 months ago
13.3kB
hello-world
latest
bf756fb1ae65
10 months ago
13.3kB
To push an image to a project in Harbor, run the following command:Syntax:
docker push <container-registry-IP>/<namespace-name>/<image_name>
For example:
docker push 10.179.145.77/tkgs-cluster-ns/hello-world:latest
Expected result.
The push refers to repository [10.179.145.77/tkgs-cluster-ns/hello-world]
9c27e219663c: Pushed
latest: digest: sha256:90659bf80b44ce6be8234e6ff90a1ac34acbeb826903b02cfa0da11c82cbc042
size: 525
Question 15
Which functionality does the Cloud Native Storage (CNS) component take advantage of to support
the creation of container volumes?
- A. First Class Disk
- B. VMware Disk Encryption
- C. Virtual Disk
- D. Storage Based Policy Management
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Cloud Native Storage server resides in vCenter Server:
• Provisions and manages life cycle operations for container volumes
• Creates First Class Disks (FCDs) to support the container volumes
• First Class Disks exist as .vmdk and -flat.vmdk files on a vSphere datastore •
Integrates with storage policy based management (SPBM) for the placement of disks
A First Class Disk (FCD) is also called an improved virtual disk. It is a named virtual disk that is
unassociated with a VM. These disks reside on a VMFS, NFS, or vSAN datastore and support container
volumes.
Storage policy based management (SPBM) is a vCenter Server service that supports provisioning of
persistent volumes according to specified storage requirements. After provisioning, the service
monitors compliance of the volume with the required policy characteristics.