VMware 2v0-72-22 practice test
Professional Develop VMware Spring
Question 1
If a class is annotated with @Component, what should be done to have Spring automatically detect
the annotated class and load it as a bean? (Choose the best answer.)
- A. Ensure a valid bean name in the @Component annotation is specified.
- B. Ensure a valid @ComponentScan annotation in the Java configuration is specified.
- C. Ensure a valid @Scope for the class is specified.
- D. Ensure a valid @Bean for the class is specified.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The @Component annotation indicates that a class is a candidate for auto-detection by Spring and
can be registered as a bean in the application context. However, to enable this feature, the Java
configuration class must also have the @ComponentScan annotation, which tells Spring where to
look for annotated components.
Reference: : https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#beans-stereotype-annotations
Question 2
Which two options will inject the value of the daily.limit system property? (Choose two.)
- A. @Value(“#{daily.limit}”)
- B. @Value(“$(systemProperties.daily.limit)”)
- C. @Value(“$(daily.limit)”)
- D. @Value(“#{systemProperties[‘daily.limit’]}”)
- E. @Value(“#{systemProperties.daily.limit}”)
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
The @Value annotation can be used to inject values from external sources into fields, constructor
parameters, or method parameters. To inject a system property, the annotation can use either the
${…} placeholder syntax or the #{…} SpEL expression syntax. The former is simpler and more concise,
while the latter is more powerful and flexible. Both syntaxes can access the systemProperties map,
which contains all the system properties as key-value pairs.
Reference: : https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#beans-value-annotations:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#expressions :
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#expressions-
beandef-xml-based
Question 3
Which two options are REST principles? (Choose two.)
- A. RESTful applications use a stateless architecture.
- B. RESTful application use HTTP headers and status codes as a contract with the clients.
- C. RESTful applications cannot use caching.
- D. RESTful application servers keep track of the client state.
- E. RESTful applications favor tight coupling between the clients and the servers.
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
REST stands for Representational State Transfer, which is an architectural style for designing web
services that adhere to certain principles. One of these principles is statelessness, which means that
each request from a client to a server must contain all the information necessary to understand the
request, and that no session state is maintained on the server side. Another principle is uniform
interface, which means that clients and servers communicate using a standardized protocol, such as
HTTP, and use its features, such as headers and status codes, to exchange information about the
resources and their representations.
Reference: : https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/rest : https://restfulapi.net/statelessness/ :
https://restfulapi.net/uniform-interface/
Question 4
Which option is true about use of mocks in a Spring Boot web slice test? (Choose the best answer.)
- A. Mocking a Spring Bean requires annotating it with @MockBean annotation.
- B. If a Spring Bean already exists in the web slice test spring context, it cannot be mocked.
- C. Mocks cannot be used in a Spring Boot web slice test.
- D. Mocking a Spring Bean requires annotating it with @Mock annotation.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A web slice test is a type of test in Spring Boot that focuses on testing only the web layer of an
application, without starting a full server or requiring a real database. To isolate the web layer from
other dependencies, such as services or repositories, mocks can be used to simulate their behavior
and return predefined responses. To create and inject a mock for an existing bean in the application
context, the @MockBean annotation can be used on a field or a parameter in the test class. This
annotation will replace any existing bean of the same type with a mock created by Mockito.
Reference: : https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/features.html#features.testing.spring-boot-applications.testing-
autoconfigured-web-test : https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/api/org/springframework/boot/test/mock/mockito/MockBean.html:
https://site.mockito.org/
Reference: https://tanzu.vmware.com/developer/guides/spring-boot-testing/
Question 5
Which two statements are true regarding Spring Security? (Choose two.)
- A. Access control can be configured at the method level.
- B. A special Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) policy file needs to be configured.
- C. Authentication data can be accessed using a variety of different mechanisms, including databases and LDAP.
- D. In the authorization configuration, the usage of permitAll () allows bypassing Spring security completely.
- E. It provides a strict implementation of the Java EE Security specification.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
Spring Security is a framework that provides comprehensive security services for Java applications,
such as authentication, authorization, encryption, session management, and more. One of its
features is method security, which allows applying access control rules at the method level using
annotations or XML configuration. Another feature is authentication, which is the process of verifying
the identity of a user or a system. Spring Security supports various authentication mechanisms, such
as username and password, tokens, certificates, etc., and can access authentication data from
different sources, such as databases, LDAP directories, in-memory stores, etc.
Reference: : https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/ :
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/#jc-method :
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/#servlet-authentication
Reference: https://www.baeldung.com/security-none-filters-none-access-permitAll
Question 6
Which two statements are true regarding a Spring Boot-based Spring MVC application? (Choose
two.)
- A. The default embedded servlet container can be replaced with Undertow.
- B. Jetty is the default servlet container.
- C. Spring Boot starts up an embedded servlet container by default.
- D. The default port of the embedded servlet container is 8088.
- E. Spring MVC starts up an in-memory database by default.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
Spring Boot provides a convenient way to create Spring MVC applications with minimal
configuration. By default, it uses Tomcat as the embedded servlet container, but it also supports
other containers such as Jetty and Undertow. To use a different container, we just need to exclude
the spring-boot-starter-tomcat dependency and include the corresponding starter for the desired
container. For example, to use Undertow, we can add the following dependencies in our pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-
web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-
undertow</artifactId> </dependency>
Reference: https://www.javatpoint.com/spring-vs-spring-boot-vs-spring-mvc
Question 7
Which two statements are true regarding Spring and Spring Boot Testing? (Choose two.)
- A. EasyMock is supported out of the box.
- B. @SpringBootTest or @SpringJUnitConfig can be used for creating an ApplicationContext.
- C. Mockito spy is not supported in Spring Boot testing by default.
- D. The spring-test dependency provides annotations such as @Mock and @MockBean.
- E. Integration and slice testing are both supported.
Answer:
BE
Explanation:
Spring and Spring Boot provide various annotations and utilities to support testing of different layers
of the application. To create an ApplicationContext for integration tests, we can use either
@SpringBootTest or @SpringJUnitConfig annotations. The former is a specialized annotation that
also provides additional features such as auto-configuration, web environment emulation, and test
properties management. The latter is a general-purpose annotation that combines
@ContextConfiguration and @ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class) annotations.
To perform slice testing, which focuses on testing a specific layer or feature of the application in
isolation, we can use annotations such as @WebMvcTest, @DataJpaTest, @RestClientTest, etc. These
annotations will only load the relevant beans for the tested slice and mock or stub the other
dependencies.
Reference: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.5.RELEASE/reference/html/boot-features-testing.html
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.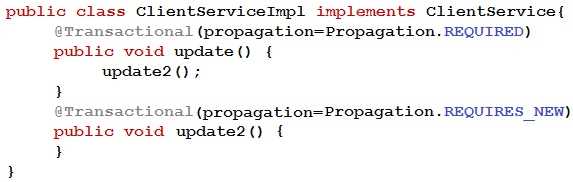
Assume that the application is using Spring transaction management which uses Spring AOP
internally.
Choose the statement that describes what is happening when the update1 method is called?
(Choose the best answer.)
- A. There are 2 transactions because REQUIRES_NEW always runs in a new transaction.
- B. An exception is thrown as another transaction cannot be started within an existing transaction.
- C. There is only one transaction because REQUIRES_NEW will use an active transaction if one already exists.
- D. There is only one transaction initiated by update1() because the call to update2() does not go through the proxy.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When using Spring transaction management with annotation-driven mode, the @Transactional
annotation will be processed by a TransactionInterceptor that implements the AOP advice interface.
This interceptor will be applied to the target bean through a proxy that implements the same
interface as the target bean. Therefore, when a method of the target bean is called from outside, it
will actually invoke the proxy method, which will delegate to the interceptor and then to the actual
target method.
However, when a method of the target bean is called from within the same bean, it will not go
through the proxy and thus bypass the interceptor logic. In this case, when update1() calls update2(),
it will not start a new transaction as specified by REQUIRES_NEW propagation level, but rather join
the existing transaction initiated by update1() itself.
Question 9
Which two statements are true concerning constructor injection? (Choose two.)
- A. If there is only one constructor the @Autowired annotation is not required.
- B. Constructor injection only allows one value to be injected.
- C. Constructor injection is preferred over field injection to support unit testing.
- D. Construction injection can be used with multiple constructors without @Autowired annotation.
- E. Field injection is preferred over constructor injection from a unit testing standpoint.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
Constructor injection is one of the ways to inject dependencies into a bean using its constructor
parameters. Since Spring 4.3, if a bean has only one constructor, the @Autowired annotation can be
omitted and Spring will use that constructor by default.
Constructor injection is generally recommended over field injection because it makes the
dependencies of a bean explicit and immutable. It also facilitates unit testing because it allows us to
easily provide mock dependencies through constructor arguments.
Question 10
Given an ApplicationContext containing three bean definitions of type Foo with bean ids foo1, foo2,
and foo3, which three @Autowired scenarios are valid and will allow the ApplicationContext to
initialize successfully? (Choose three.)
- A. @Autowired public void setFoo (Foo foo) {…}
- B. @Autowired @Qualifier (“foo3”) Foo foo;
- C. @Autowired public void setFoo (@Qualifier (“foo1”) Foo foo) {…}
- D. @Autowired private Foo foo;
- E. @Autowired private Foo foo2;
- F. @Autowired public void setFoo(Foo foo2) {…}
Answer:
BCF
Explanation:
The @Autowired annotation can be used to inject a dependency into a field, a constructor, or a
setter method. However, if there are multiple beans of the same type in the application context,
Spring will not be able to determine which one to inject by default. To resolve this ambiguity, we can
use the @Qualifier annotation to specify the bean id of the desired dependency. Alternatively, we
can use the bean id as the name of the field or the parameter of the setter method, and Spring will
match it with the corresponding bean.
Question 11
Which dependency enables an automatic restart of the application as code is changed during
development of a Spring boot configuration on a web application? (Choose the best answer.)
- A. spring-boot-devtools
- B. spring-boot-initializr
- C. spring-boot-starter-devtools
- D. spring-boot-restart
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Spring Boot provides a set of tools for improving the development experience, such as automatic
restart, live reload, remote debugging, etc. These tools are included in the spring-boot-starter-
devtools dependency, which can be added to the project’s pom.xml or build.gradle file. The
automatic restart feature will monitor the classpath for changes and trigger a restart of the
application when necessary.
Question 12
Spring puts each bean instance in a scope. What is the default scope? (Choose the best answer.)
- A. prototype
- B. singleton
- C. request
- D. session
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Spring supports different scopes for bean instances, such as singleton, prototype, request, session,
etc. The scope determines how many instances of a bean are created and how they are shared
among other components. The default scope is singleton, which means that only one instance of a
bean is created per application context and it is shared by all components that depend on it.
Reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17599216/spring-bean-scopes
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit.
Which option is a valid way to retrieve the account id? (Choose the best answer.)
- A. Add @PathVariable(“id”) String accountId argument to the update() handler method.
- B. Add @PathVariable long accountId argument to the update() handler method.
- C. Add @RequestParam long accountId argument to the update() handler method.
- D. Add @RequestParam(“id”) String accountId argument to the update() handler method.
Answer:
B
Question 14
Which strategy is correct for configuring Spring Security to intercept particular URLs? (Choose the
best answer.)
- A. The URLs can be specified via configuration (using authorizeRequests () and request matchers), with the most specific rule first and the least specific last.
- B. Spring Security can obtain URLs from Spring MVC controllers, the Spring Security configuration just needs a reference to the controller to be protected.
- C. The URLs are specified in a special properties file, used by Spring Security.
- D. The URLs can be specified via configuration (using authorizeRequests () and request matchers), with the least specific rule first and the most specific last.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Spring Security provides a fluent API for configuring web security based on URL patterns and request
matchers. The authorizeRequests() method returns an expression that allows specifying access rules
for different URLs using methods such as antMatchers(), regexMatchers(), mvcMatchers(), etc. The
order of these rules matters, as they are evaluated from top to bottom. Therefore, it is
recommended to put the most specific rules first and the least specific ones last.
Reference: https://www.baeldung.com/security-none-filters-none-access-permitAll
Question 15
In which three ways are Security filters used in Spring Security? (Choose three.)
- A. To provide risk governance.
- B. To drive authentication.
- C. To manage application users.
- D. To provide a logout capability.
- E. To enforce authorization (access control).
- F. To encrypt data.
Answer:
BDE
Explanation:
Spring Security uses a filter-based architecture to provide security services for web applications. A
filter is an object that intercepts HTTP requests and responses and performs some logic before or
after the request is processed by the servlet. Spring Security provides a number of filters for different
purposes, such as:
Authentication: Filters that handle the authentication process, such as
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter, BasicAuthenticationFilter,
RememberMeAuthenticationFilter, etc.
User management: Filters that manage the user details and roles, such as
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter, AnonymousAuthenticationFilter, ConcurrentSessionFilter, etc.
Logout: Filters that handle the logout process, such as LogoutFilter and
SecurityContextLogoutHandler.
Authorization: Filters that enforce access control rules based on the user’s authentication and roles,
such as FilterSecurityInterceptor, ExceptionTranslationFilter, etc.
Reference: https://www.javadevjournal.com/spring-security/spring-security-filters/