Splunk splk-1005 practice test
Splunk Cloud Certified Admin
Question 1
At what point in the indexing pipeline set is SEDCMD applied to data?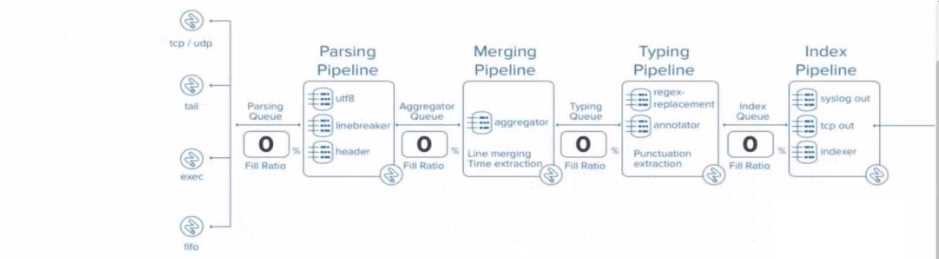
- A. In the aggregator queue
- B. In the parsing queue
- C. In the exec pipeline
- D. In the typing pipeline
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Splunk, SEDCMD (Stream Editing Commands) is applied during the Typing Pipeline of the data
indexing process. The Typing Pipeline is responsible for various tasks, such as applying regular
expressions for field extractions, replacements, and data transformation operations that occur after
the initial parsing and aggregation steps.
Here’s how the indexing process works in more detail:
Parsing Pipeline: In this stage, Splunk breaks incoming data into events, identifies timestamps, and
assigns metadata.
Merging Pipeline: This stage is responsible for merging events and handling time-based operations.
Typing Pipeline: The Typing Pipeline is where SEDCMD operations occur. It applies regular
expressions and replacements, which is essential for modifying raw data before indexing. This
pipeline is also responsible for field extraction and other similar operations.
Index Pipeline: Finally, the processed data is indexed and stored, where it becomes available for
searching.
Splunk Cloud Reference: To verify this information, you can refer to the official Splunk documentation
on the data pipeline and indexing process, specifically focusing on the stages of the indexing pipeline
and the roles they play. Splunk Docs often discuss the exact sequence of operations within the
pipeline, highlighting when and where commands like SEDCMD are applied during data processing.
Source:
Splunk Docs: Managing Indexers and Clusters of Indexers
Splunk Answers: Community discussions and expert responses frequently clarify where specific
operations occur within the pipeline.
Question 2
When monitoring directories that contain mixed file types, which setting should be omitted from
inputs, conf and instead be overridden in propo.conf?
- A. sourcetype
- B. host
- C. source
- D. index
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When monitoring directories containing mixed file types, the sourcetype should typically be
overridden in props.conf rather than defined in inputs.conf. This is because sourcetype is meant to
classify the type of data being ingested, and when dealing with mixed file types, setting a single
sourcetype in inputs.conf would not be effective for accurate data classification. Instead, you can use
props.conf to define rules that apply different sourcetypes based on the file path, file name patterns,
or other criteria. This allows for more granular and accurate assignment of sourcetypes, ensuring the
data is properly parsed and indexed according to its type.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For further clarification, refer to Splunk's official documentation on
configuring inputs and props, especially the sections discussing monitoring directories and
configuring sourcetypes.
Source:
Splunk Docs: Monitor files and directories
Splunk Docs: Configure event line breaking and input settings with props.conf
Question 3
How are HTTP Event Collector (HEC) tokens configured in a managed Splunk Cloud environment?
- A. Any token will be accepted by HEC, the data may just end up in the wrong index.
- B. A token is generated when configuring a HEC input, which should be provided to the application developers.
- C. Obtain a token from the organization's application developers and apply it in Settings > Data Inputs > HTTP Event Collector > New Token.
- D. Open a support case for each new data input and a token will be provided.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In a managed Splunk Cloud environment, HTTP Event Collector (HEC) tokens are configured by an
administrator through the Splunk Web interface. When setting up a new HEC input, a unique token is
automatically generated. This token is then provided to application developers, who will use it to
authenticate and send data to Splunk via the HEC endpoint.
This token ensures that the data is correctly ingested and associated with the appropriate inputs and
indexes. Unlike the other options, which either involve external tokens or support cases, option B
reflects the standard procedure for configuring HEC tokens in Splunk Cloud, where control over
tokens remains within the Splunk environment itself.
Splunk Cloud Reference: Splunk's documentation on HEC inputs provides detailed steps on creating
and managing tokens within Splunk Cloud. This includes the process of generating tokens,
configuring data inputs, and distributing these tokens to application developers.
Source:
Splunk Docs: HTTP Event Collector in Splunk Cloud Platform
Splunk Docs: Create and manage HEC tokens
Question 4
Which of the following statements regarding apps in Splunk Cloud is true?
- A. Self-service install of premium apps is possible.
- B. Only Cloud certified and vetted apps are supported.
- C. Any app that can be deployed in an on-prem Splunk Enterprise environment is also supported on Splunk Cloud.
- D. Self-service install is available for all apps on Splunkbase.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Splunk Cloud, only apps that have been certified and vetted by Splunk are supported. This is
because Splunk Cloud is a managed service, and Splunk ensures that all apps meet specific security,
performance, and compatibility requirements before they can be installed. This certification process
guarantees that the apps won’t negatively impact the overall environment, ensuring a stable and
secure cloud service.
Self-service installation is available, but it is limited to apps that are certified for Splunk Cloud. Non-
certified apps cannot be installed directly; they require a review and approval process by Splunk
support.
Splunk Cloud Reference: Refer to Splunk’s documentation on app installation and the list of Cloud-
vetted apps available on Splunkbase to understand which apps can be installed in Splunk Cloud.
Source:
Splunk Docs: About apps in Splunk Cloud
Splunkbase: Splunk Cloud Apps
Question 5
When using Splunk Universal Forwarders, which of the following is true?
- A. No more than six Universal Forwarders may connect directly to Splunk Cloud.
- B. Any number of Universal Forwarders may connect directly to Splunk Cloud.
- C. Universal Forwarders must send data to an Intermediate Forwarder.
- D. There must be one Intermediate Forwarder for every three Universal Forwarders.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Universal Forwarders can connect directly to Splunk Cloud, and there is no limit on the number of
Universal Forwarders that may connect directly to it. This capability allows organizations to scale
their data ingestion easily by deploying as many Universal Forwarders as needed without the
requirement for intermediate forwarders unless additional data processing, filtering, or load
balancing is required.
Splunk Documentation Reference: Forwarding Data to Splunk Cloud
Question 6
In which of the following situations should Splunk Support be contacted?
- A. When a custom search needs tuning due to not performing as expected.
- B. When an app on Splunkbase indicates Request Install.
- C. Before using the delete command.
- D. When a new role that mirrors sc_admin is required.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Splunk Cloud, when an app on Splunkbase indicates "Request Install," it means that the app is not
available for direct self-service installation and requires intervention from Splunk Support. This could
be because the app needs to undergo an additional review for compatibility with the managed cloud
environment or because it requires special installation procedures.
In these cases, customers need to contact Splunk Support to request the installation of the app.
Support will ensure that the app is properly vetted and compatible with Splunk Cloud before
proceeding with the installation.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For further details, consult Splunk’s guidelines on requesting app
installations in Splunk Cloud and the processes involved in reviewing and approving apps for use in
the cloud environment.
Source:
Splunk Docs: Install apps in Splunk Cloud Platform
Splunkbase: App request procedures for Splunk Cloud
Question 7
The following Apache access log is being ingested into Splunk via a monitor input: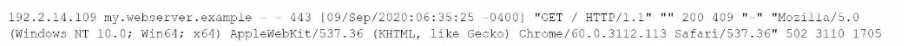
How does Splunk determine the time zone for this event?
- A. The value of the TZ attribute in props. cont for the a :ces3_ccwbined sourcetype.
- B. The value of the TZ attribute in props, conf for the my.webserver.example host.
- C. The time zone of the Heavy/Intermediate Forwarder with the monitor input.
- D. The time zone indicator in the raw event data.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Splunk, when ingesting logs such as an Apache access log, the time zone for each event is typically
determined by the time zone indicator present in the raw event data itself. In the log snippet you
provided, the time zone is indicated by -0400, which specifies that the event's timestamp is 4 hours
behind UTC (Coordinated Universal Time).
Splunk uses this information directly from the event to properly parse the timestamp and apply the
correct time zone. This ensures that the event's time is accurately reflected regardless of the time
zone in which the Splunk instance or forwarder is located.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For further details, you can review Splunk documentation on timestamp
recognition and time zone handling, especially in relation to log files and data ingestion
configurations.
Source:
Splunk Docs: How Splunk software handles timestamps
Splunk Docs: Configure event timestamp recognition
Question 8
What syntax is required in inputs.conf to ingest data from files or directories?
- A. A monitor stanza, sourcetype, and Index is required to ingest data.
- B. A monitor stanza, sourcetype, index, and host is required to ingest data.
- C. A monitor stanza and sourcetype is required to ingest data.
- D. Only the monitor stanza is required to ingest data.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Splunk, to ingest data from files or directories, the basic configuration in inputs.conf requires at
least the following elements:
monitor stanza: Specifies the file or directory to be monitored.
sourcetype: Identifies the format or type of the incoming data, which helps Splunk to correctly parse
it.
index: Determines where the data will be stored within Splunk.
The host attribute is optional, as Splunk can auto-assign a host value, but specifying it can be useful
in certain scenarios. However, it is not mandatory for data ingestion.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For more details, you can consult the Splunk documentation on inputs.conf
file configuration and best practices.
Source:
Splunk Docs: Monitor files and directories
Splunk Docs: Inputs.conf examples
Question 9
A user has been asked to mask some sensitive data without tampering with the structure of the file
/var/log/purchase/transactions. log that has the following format: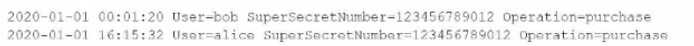
A)
B)
C)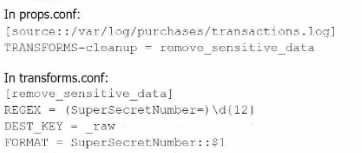
D)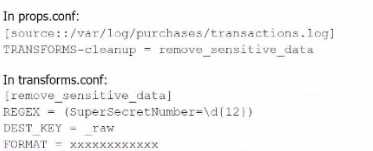
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Option B is the correct approach because it properly uses a TRANSFORMS stanza in props.conf to
reference the transforms.conf for removing sensitive data. The transforms stanza in transforms.conf
uses a regular expression (REGEX) to locate the sensitive data (in this case, the SuperSecretNumber)
and replaces it with a masked version using the FORMAT directive.
In detail:
props.conf refers to the transforms.conf stanza remove_sensitive_data by setting TRANSFORMS-
cleanup = remove_sensitive_data.
transforms.conf defines the regular expression that matches the sensitive data and specifies how the
sensitive data should be replaced in the FORMAT directive.
This approach ensures that sensitive information is masked before indexing without altering the
structure of the log files.
Splunk Cloud Reference: For further reference, you can look at Splunk's documentation regarding
data masking and transformation through props.conf and transforms.conf.
Source:
Splunk Docs: Anonymize data
Splunk Docs: Props.conf and Transforms.conf
Question 10
Which of the following are valid settings for file and directory monitor inputs?
A)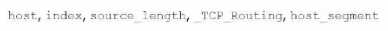
B)
C)
D)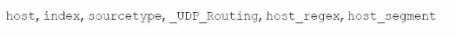
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Splunk, when configuring file and directory monitor inputs, several settings are available that
control how data is indexed and processed. These settings are defined in the inputs.conf file. Among
the given options:
host: Specifies the hostname associated with the data. It can be set to a static value, or dynamically
assigned using settings like host_regex or host_segment.
index: Specifies the index where the data will be stored.
sourcetype: Defines the data type, which helps Splunk to correctly parse and process the data.
TCP_Routing: Used to route data to specific indexers in a distributed environment based on TCP
routing rules.
host_regex: Allows you to extract the host from the path or filename using a regular expression.
host_segment: Identifies the segment of the directory structure (path) to use as the host.
Given the options:
Option B is correct because it includes host, index, sourcetype, TCP_Routing, host_regex, and
host_segment. These are all valid settings for file and directory monitor inputs in Splunk.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
Monitor Inputs (inputs.conf)
Host Setting in Inputs
TCP Routing in Inputs
By referring to the Splunk documentation on configuring inputs, it's clear that Option B aligns with
the valid settings used for file and directory monitoring, making it the correct choice.
Question 11
Which of the following is not a path used by Splunk to execute scripts?
- A. SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/bin
- B. SPLUNK HOME/etc/appa/<app name>/bin
- C. SPLUNKHOMS/ctc/scripts/local
- D. SPLUNK_HOME/bin/scripts
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Splunk executes scripts from specific directories that are structured within its installation paths.
These directories typically include:
SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/bin: This directory is used to store scripts that are part of the core Splunk
system configuration.
SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/<app name>/bin: Each Splunk app can have its own bin directory where
scripts specific to that app are stored.
SPLUNK_HOME/bin/scripts: This is a standard directory for storing scripts that may be globally
accessible within Splunk's environment.
However, C. SPLUNKHOMS/ctc/scripts/local is not a recognized or standard path used by Splunk for
executing scripts. This path does not adhere to the typical directory structure within the
SPLUNK_HOME environment, making it the correct answer as it does not correspond to a valid script
execution path in Splunk.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
Using Custom Scripts in Splunk
Directory Structure of SPLUNK_HOME
Question 12
Which of the following are features of a managed Splunk Cloud environment?
- A. Availability of premium apps, no IP address whitelisting or blacklisting, deployed in US East AWS region.
- B. 20GB daily maximum data ingestion, no SSO integration, no availability of premium apps.
- C. Availability of premium apps, SSO integration, IP address whitelisting and blacklisting.
- D. Availability of premium apps, SSO integration, maximum concurrent search limit of 20.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a managed Splunk Cloud environment, several features are available to ensure that the platform is
secure, scalable, and meets enterprise requirements. The key features include:
Availability of premium apps: Splunk Cloud supports the installation and use of premium apps such
as Splunk Enterprise Security, IT Service Intelligence, etc.
SSO Integration: Single Sign-On (SSO) integration is supported, allowing organizations to leverage
their existing identity providers for authentication.
IP address whitelisting and blacklisting: To enhance security, managed Splunk Cloud environments
allow for IP address whitelisting and blacklisting to control access.
Given the options:
Option C correctly lists these features, making it the accurate choice.
Option A incorrectly states "no IP address whitelisting or blacklisting," which is indeed available.
Option B mentions "no SSO integration" and "no availability of premium apps," both of which are
inaccurate.
Option D talks about a "maximum concurrent search limit of 20," which does not represent the
standard limit settings and may vary based on the subscription level.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
Splunk Cloud Features and Capabilities
Single Sign-On (SSO) in Splunk Cloud
Security and Access Control in Splunk Cloud
Question 13
Which of the following statements is true about data transformations using SEDCMD?
- A. Can only be used to mask or truncate raw data.
- B. Configured in props.conf and transform.conf.
- C. Can be used to manipulate the sourcetype per event.
- D. Operates on a REGEX pattern match of the source, sourcetype, or host of an event.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
SEDCMD is a directive used within the props.conf file in Splunk to perform inline data
transformations. Specifically, it uses sed-like syntax to modify data as it is being processed.
A . Can only be used to mask or truncate raw data: This is the correct answer because SEDCMD is
typically used to mask sensitive data, such as obscuring personally identifiable information (PII) or
truncating parts of data to ensure privacy and compliance with security policies. It is not used for
more complex transformations such as changing the sourcetype per event.
B . Configured in props.conf and transform.conf: Incorrect, SEDCMD is only configured in props.conf.
C . Can be used to manipulate the sourcetype per event: Incorrect, SEDCMD does not manipulate the
s ourcetype.
D . Operates on a REGEX pattern match of the source, sourcetype, or host of an event: Incorrect,
while SEDCMD uses regex for matching patterns in the data, it does not operate on the source,
sourcetype, or host specifically.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
SEDCMD Usage
Mask Data with SEDCMD
Question 14
Which of the following is correct in regard to configuring a Universal Forwarder as an Intermediate
Forwarder?
- A. This can only be turned on using the Settings > Forwarding and Receiving menu in Splunk Web/UI.
- B. The configuration changes can be made using Splunk Web. CU, directly in configuration files, or via a deployment app.
- C. The configuration changes can be made using CU, directly in configuration files, or via a deployment app.
- D. It is only possible to make this change directly in configuration files or via a deployment app.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Configuring a Universal Forwarder (UF) as an Intermediate Forwarder involves making changes to its
configuration to allow it to receive data from other forwarders before sending it to indexers.
D . It is only possible to make this change directly in configuration files or via a deployment app: This
is the correct answer. Configuring a Universal Forwarder as an Intermediate Forwarder is done by
editing the configuration files directly (like outputs.conf), or by deploying a pre-configured app via a
deployment server. The Splunk Web UI (Management Console) does not provide an interface for
configuring a Universal Forwarder as an Intermediate Forwarder.
A . This can only be turned on using the Settings > Forwarding and Receiving menu in Splunk Web/UI:
Incorrect, as this applies to Heavy Forwarders, not Universal Forwarders.
B . The configuration changes can be made using Splunk Web, CLI, directly in configuration files, or
via a deployment app: Incorrect, the Splunk Web UI is not used for configuring Universal Forwarders.
C . The configuration changes can be made using CLI, directly in configuration files, or via a
deployment app: While CLI could be used for certain configurations, the specific Intermediate
Forwarder setup is typically done via configuration files or deployment apps.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
Universal Forwarder Configuration
Intermediate Forwarder Configuration
Question 15
What does the followTail attribute do in inputs.conf?
- A. Pauses a file monitor if the queue is full.
- B. Only creates a tail checkpoint of the monitored file.
- C. Ingests a file starting with new content and then reading older events.
- D. Prevents pre-existing content in a file from being ingested.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The followTail attribute in inputs.conf controls how Splunk processes existing content in a monitored
file.
D . Prevents pre-existing content in a file from being ingested: This is the correct answer. When
followTail = true is set, Splunk will ignore any pre-existing content in a file and only start monitoring
from the end of the file, capturing new data as it is added. This is useful when you want to start
monitoring a log file but do not want to index the historical data that might be present in the file.
A . Pauses a file monitor if the queue is full: Incorrect, this is not related to the followTail attribute.
B . Only creates a tail checkpoint of the monitored file: Incorrect, while a tailing checkpoint is created
for state tracking, followTail specifically refers to skipping the existing content.
C . Ingests a file starting with new content and then reading older events: Incorrect, followTail does
not read older events; it skips them.
Splunk Documentation Reference:
followTail Attribute Documentation
Monitoring Files
These answers align with Splunk's best practices and available documentation on managing and
configuring Splunk environments.