Splunk splk-1002 practice test
Splunk Core Certified Power User
Question 1
Which of the following Statements about macros is true? (select all that apply)
- A. Arguments are defined at execution time.
- B. Arguments are defined when the macro is created.
- C. Argument values are used to resolve the search string at execution time.
- D. Argument values are used to resolve the search string when the macro is created.
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
A macro is a way to save a commonly used search string as a variable that you can reuse in other
searches1
.
When you create a macro, you can define arguments that are placeholders for values that
you specify at execution time1
.
The argument values are used to resolve the search string when the
macro is invoked, not when it is created1
. Therefore, statements B and C are true, while statements
A and D are false.
Question 2
What is required for a macro to accept three arguments?
- A. The macro's name ends with (3).
- B. The macro's name starts with (3).
- C. The macro's argument count setting is 3 or more.
- D. Nothing, all macros can accept any number of arguments.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To create a macro that accepts arguments, you must include the number of arguments in
parentheses at the end of the macro name1
. For example, my_macro(3) is a macro that accepts three
arguments.
The number of arguments in the macro name must match the number of arguments in
the definition1
. Therefore, option A is correct, while options B, C and D are incorrect.
Question 3
Which of the following statements describes POST workflow actions?
- A. POST workflow actions are always encrypted.
- B. POST workflow actions cannot use field values in their URI.
- C. POST workflow actions cannot be created on custom sourcetypes.
- D. POST workflow actions can open a web page in either the same window or a new .
Answer:
D
Explanation:
A workflow action is a link that appears when you click an event field value in your search results1
.
A
workflow action can open a web page or run another search based on the field value1
.
There are two
types of workflow actions: GET and POST1
.
A GET workflow action appends the field value to the end
of a URI and opens it in a web browser1
.
A POST workflow action sends the field value as part of an
HTTP request to a web server1
.
You can configure a workflow action to open a web page in either the
same window or a new window1
. Therefore, option D is correct, while options A, B and C are
incorrect.
Question 4
Which of the following searches show a valid use of macro? (Select all that apply)
- A. index=main source=mySource oldField=* |'makeMyField(oldField)'| table _time newField
- B. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | stats if('makeMyField(oldField)') | table _time newField
- C. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | eval newField='makeMyField(oldField)'| table _time newField
- D. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | "'newField('makeMyField(oldField)')'" | table _time newField
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
Reference:
https://answers.splunk.com/answers/574643/field-showing-an-additional-and-not-visible-value-1.html
To use a macro in a search, you must enclose the macro name and any arguments in single quotation
marks1
. For example, 'my_macro(arg1,arg2)' is a valid way to use a macro with two arguments.
You
can use macros anywhere in your search string where you would normally use a search command or
expression1
. Therefore, options A and C are valid searches that use macros, while options B and D
are invalid because they do not enclose the macros in single quotation marks.
Question 5
Which of the following workflow actions can be executed from search results? (select all that apply)
- A. GET
- B. POST
- C. LOOKUP
- D. Search
Answer:
A, B, D
Explanation:
As mentioned before, there are two types of workflow actions: GET and POST1
.
Both types of
workflow actions can be executed from search results by clicking on an event field value that has a
workflow action configured for it1
.
Another type of workflow action is Search, which runs another
search based on the field value1
. Therefore, options A, B and D are correct, while option C is
incorrect because LOOKUP is not a type of workflow action.
Question 6
Which of the following is the correct way to use the data model command to search field in the data
model within the web dataset?
- A. | datamodel web search | filed web *
- B. | Search datamodel web web | filed web*
- C. | datamodel web web field | search web*
- D. Datamodel=web | search web | filed web*
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The data model command allows you to run searches on data models that have been
accelerated1
.
The syntax for using the data model command is | datamodel <model_name>
<dataset_name> [search <search_string>]1
. Therefore, option A is the correct way to use the data
model command to search fields in the data model within the web dataset. Options B and C are
incorrect because they do not follow the syntax for the data model command. Option D is incorrect
because it does not use the data model command at all.
Question 7
Which of the following searches will return events contains a tag name Privileged?
- A. Tag= Priv
- B. Tag= Pri*
- C. Tag= Priv*
- D. Tag= Privileged
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Reference:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/PCI/4.1.0/Install/PrivilegedUserActivity
A tag is a descriptive label that you can apply to one or more fields or field values in your
events1
.
You can use tags to simplify your searches by replacing long or complex field names or
values with short and simple tags1
.
To search for events that contain a tag name, you can use the tag
keyword followed by an equal sign and the tag name1
.
You can also use wildcards (*) to match partial
tag names1
. Therefore, option B is correct because it will return events that contain a tag name that
starts with Pri. Options A and D are incorrect because they will only return events that contain an
exact tag name match. Option C is incorrect because it will return events that contain a tag name that
starts with Priv, not Privileged.
Question 8
Which of the following statements describes this search?
sourcetype=access_combined I transaction JSESSIONID | timechart avg (duration)
- A. This is a valid search and will display a timechart of the average duration, of each transaction event.
- B. This is a valid search and will display a stats table showing the maximum pause among transactions.
- C. No results will be returned because the transaction command must include the startswith and endswith options.
- D. No results will be returned because the transaction command must be the last command used in the search pipeline.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This search uses the transaction command to group events that share a common value for
JSESSIONID into transactions1
.
The transaction command assigns a duration field to each transaction,
which is the difference between the latest and earliest timestamps of the events in the
transaction1
.
The search then uses the timechart command to create a time-series chart of the
average duration of each transaction1
. Therefore, option A is correct because it describes the search
accurately. Option B is incorrect because the search does not use the stats command or the pause
field.
Option C is incorrect because the transaction command does not require the startswith and
endswith options, although they can be used to specify how to identify the beginning and end of a
transaction1
.
Option D is incorrect because the transaction command does not have to be the last
command in the search pipeline, although it is often used near the end of a search1
.
Question 9
Calculated fields can be based on which of the following?
- A. Tags
- B. Extracted fields
- C. Output fields for a lookup
- D. Fields generated from a search string
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Reference:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.0.3/Knowledge/definecalcfields
A calculated field is a field that you create based on the value of another field or fields1
.
You can use
calculated fields to enrich your data with additional information or to transform your data into a
more useful format1
.
Calculated fields can be based on extracted fields, which are fields that are
extracted from your raw data using various methods such as regular expressions, delimiters, or key-
value pairs1
. Therefore, option B is correct, while options A, C and D are incorrect because tags,
output fields for a lookup, and fields generated from a search string are not types of extracted fields.
Question 10
Based on the macro definition shown below, what is the correct way to execute the macro in a search
string?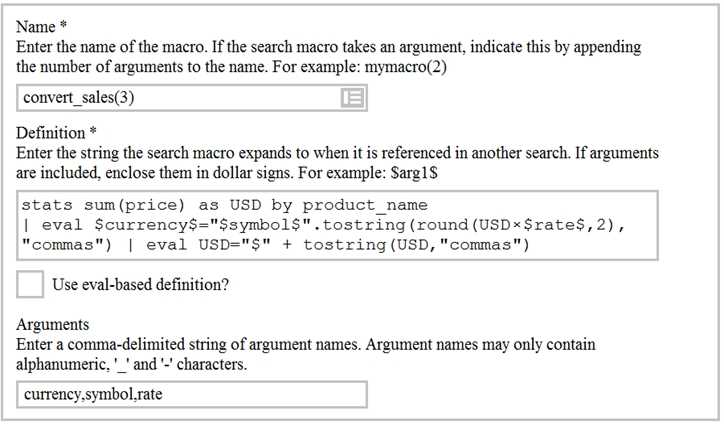
- A. Convert_sales (euro, €, 79)”
- B. Convert_sales (euro, €, .79)
- C. Convert_sales ($euro,$€$,s79$
- D. Convert_sales ($euro, $€$,S,79$)
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Reference:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.0.3/Knowledge/Usesearchmacros
The correct way to execute the macro in a search string is to use the format macro_name($arg1$,
$arg2$, ...) where $arg1$, $arg2$, etc. are the arguments for the macro. In this case, the macro name
is convert_sales and it takes three arguments: currency, symbol, and rate. The arguments are
enclosed in dollar signs and separated by commas. Therefore, the correct way to execute the macro
is convert_sales($euro$, $€$, .79).
Question 11
When multiple event types with different color values are assigned to the same event, what
determines the color displayed for the events?
- A. Rank
- B. Weight
- C. Priority
- D. Precedence
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Reference:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/SplunkCloud/8.0.2003/Knowledge/Defineeventtypes
When multiple event types with different color values are assigned to the same event, the color
displayed for the events is determined by the priority of the event types. The priority is a numerical
value that indicates how important an event type is. The higher the priority, the more important the
event type. The event type with the highest priority will determine the color of the event.
Question 12
Which of the following statements describes the command below (select all that apply)
Sourcetype=access_combined | transaction JSESSIONID
- A. An additional filed named maxspan is created.
- B. An additional field named duration is created.
- C. An additional field named eventcount is created.
- D. Events with the same JSESSIONID will be grouped together into a single event.
Answer:
B, C, D
Explanation:
The command sourcetype=access_combined | transaction JSESSIONID does three things:
It filters the events by the sourcetype access_combined, which is a predefined sourcetype for Apache
web server logs.
It groups the events by the field JSESSIONID, which is a unique identifier for each user session.
It creates a single event from each group of events that share the same JSESSIONID value. This single
event will have some additional fields created by the transaction command, such
as duration, eventcount, and startime.
Therefore, the statements B, C, and D are true.
Question 13
Which of the following can be used with the eval command tostring function (select all that apply)
- A. ‘’hex’’
- B. ‘’commas’’
- C. ‘’Decimal’’
- D. ‘’duration’’
Answer:
A, B, D
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.1.0/SearchReference/ConversionFunctions#tostri
ng.28X.2CY.29
The tostring function in the eval command converts a numeric value to a string value. It can take an
optional second argument that specifies the format of the string value. Some of the possible formats
are:
hex: converts the numeric value to a hexadecimal string.
commas: adds commas to separate thousands in the numeric value.
duration: converts the numeric value to a human-readable duration string, such as “2h 3m 4s”.
Therefore, the formats A, B, and D can be used with the tostring function.
Question 14
Which of the following statements about tags is true?
- A. Tags are case insensitive.
- B. Tags are created at index time.
- C. Tags can make your data more understandable.
- D. Tags are searched by using the syntax tag: : <fieldneme>
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Tags are aliases or alternative names for field values in Splunk. They can make your data more
understandable by using common or descriptive terms instead of cryptic or technical terms. For
example, you can tag a field value such as “200” with “OK” or “success” to indicate that it is a HTTP
status code for a successful request. Tags are case sensitive, meaning that “OK” and “ok” are different
tags. Tags are created at search time, meaning that they are applied when you run a search on your
data. Tags are searched by using the syntax tag::<tagname>, where <tagname> is the name of the tag
you want to search for.
Question 15
Which of the following statements about data models and pivot are true? (select all that apply)
- A. They are both knowledge objects.
- B. Data models are created out of datasets called pivots.
- C. Pivot requires users to input SPL searches on data models.
- D. Pivot allows the creation of data visualizations that present different aspects of a data model.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Data models and pivot are both knowledge objects in Splunk that allow you to analyze and visualize
your data in different ways. Data models are collections of datasets that represent your data in a
structured and hierarchical way. Data models define how your data is organized into objects and
fields. Pivot is a user interface that allows you to create data visualizations that present different
aspects of a data model. Pivot does not require users to input SPL searches on data models, but
rather lets them select options from menus and forms. Data models are not created out of datasets
called pivots, but rather pivots are created from datasets in data models.