Snowflake dea-c01 practice test
SnowPro Advanced: Data Engineer Certification Exam
Question 1
Given the table sales which has a clustering key of column CLOSED_DATE which table function will
return the average clustering depth for the SALES_REPRESENTATIVE column for the North American
region?
A)
B)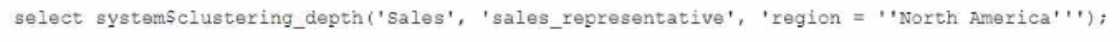
C)
D)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The table function SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_DEPTH returns the average clustering depth for a specified
column or set of columns in a table. The function takes two arguments: the table name and the
column name(s). In this case, the table name is sales and the column name is
SALES_REPRESENTATIVE. The function also supports a WHERE clause to filter the rows for which the
clustering depth is calculated. In this case, the WHERE clause is REGION = ‘North America’.
Therefore, the function call in Option B will return the desired result.
Question 2
What is the purpose of the BUILD_FILE_URL function in Snowflake?
- A. It generates an encrypted URL foe accessing a file in a stage.
- B. It generates a staged URL for accessing a file in a stage.
- C. It generates a permanent URL for accessing files in a stage.
- D. It generates a temporary URL for accessing a file in a stage.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The BUILD_FILE_URL function in Snowflake generates a temporary URL for accessing a file in a stage.
The function takes two arguments: the stage name and the file path. The generated URL is valid for
24 hours and can be used to download or view the file contents. The other options are incorrect
because they do not describe the purpose of the BUILD_FILE_URL function.
Question 3
A Data Engineer has developed a dashboard that will issue the same SQL select clause to Snowflake
every 12 hours.
---will Snowflake use the persisted query results from the result cache provided that the underlying
data has not changed^
- A. 12 hours
- B. 24 hours
- C. 14 days
- D. 31 days
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Snowflake uses the result cache to store the results of queries that have been executed recently. The
result cache is maintained at the account level and is shared across all sessions and users. The result
cache is invalidated when any changes are made to the tables or views referenced by the query.
Snowflake also has a retention policy for the result cache, which determines how long the results are
kept in the cache before they are purged. The default retention period for the result cache is 24
hours, but it can be changed at the account, user, or session level. However, there is a maximum
retention period of 14 days for the result cache, which cannot be exceeded. Therefore, if the
underlying data has not changed, Snowflake will use the persisted query results from the result cache
for up to 14 days.
Question 4
A Data Engineer ran a stored procedure containing various transactions During the execution, the
session abruptly disconnected preventing one transaction from committing or rolling hark. The
transaction was left in a detached state and created a lock on resources
...must the Engineer take to immediately run a new transaction?
- A. Call the system function SYSTEM$ABORT_TRANSACTION.
- B. Call the system function SYSTEM$CANCEL_TRANSACTION.
- C. Set the LOCK_TIMEOUT to FALSE in the stored procedure
- D. Set the transaction abort on error to true in the stored procedure.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The system function SYSTEM$ABORT_TRANSACTION can be used to abort a detached transaction
that was left in an open state due to a session disconnect or termination. The function takes one
argument: the transaction ID of the detached transaction. The function will abort the transaction and
release any locks held by it. The other options are incorrect because they do not address the issue of
a detached transaction. The system function SYSTEM$CANCEL_TRANSACTION can be used to cancel
a running transaction, but not a detached one. The LOCK_TIMEOUT parameter can be used to set a
timeout period for acquiring locks on resources, but it does not affect existing locks. The
TRANSACTION_ABORT_ON_ERROR parameter can be used to control whether a transaction should
abort or continue when an error occurs, but it does not affect detached transactions.
Question 5
The following code is executed in a Snowflake environment with the default settings:
What will be the result of the select statement?
- A. SQL compilation error object CUSTOMER' does not exist or is not authorized.
- B. John
- C. 1
- D. 1John
Answer:
C
Question 6
Which output is provided by both the SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_DEPTH function and the
SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_INFORMATION function?
- A. average_depth
- B. notes
- C. average_overlaps
- D. total_partition_count
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The output that is provided by both the SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_DEPTH function and the
SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_INFORMATION function is average_depth. This output indicates the average
number of micro-partitions that contain data for a given column value or combination of column
values. The other outputs are not common to both functions. The notes output is only provided by
the SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_INFORMATION function and it contains additional information or
recommendations about the clustering status of the table. The average_overlaps output is only
provided by the SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_DEPTH function and it indicates the average number of
micro-partitions that overlap with other micro-partitions for a given column value or combination of
column values. The total_partition_count output is only provided by the
SYSTEM$CLUSTERING_INFORMATION function and it indicates the total number of micro-partitions
in the table.
Question 7
A Data Engineer needs to ingest invoice data in PDF format into Snowflake so that the data can be
queried and used in a forecasting solution.
..... recommended way to ingest this data?
- A. Use Snowpipe to ingest the files that land in an external stage into a Snowflake table
- B. Use a COPY INTO command to ingest the PDF files in an external stage into a Snowflake table with a VARIANT column.
- C. Create an external table on the PDF files that are stored in a stage and parse the data nto structured data
- D. Create a Java User-Defined Function (UDF) that leverages Java-based PDF parser libraries to parse PDF data into structured data
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The recommended way to ingest invoice data in PDF format into Snowflake is to create a Java User-
Defined Function (UDF) that leverages Java-based PDF parser libraries to parse PDF data into
structured data. This option allows for more flexibility and control over how the PDF data is extracted
and transformed. The other options are not suitable for ingesting PDF data into Snowflake. Option A
and B are incorrect because Snowpipe and COPY INTO commands can only ingest files that are in
supported file formats, such as CSV, JSON, XML, etc. PDF files are not supported by Snowflake and
will cause errors or unexpected results. Option C is incorrect because external tables can only query
files that are in supported file formats as well. PDF files cannot be parsed by external tables and will
cause errors or unexpected results.
Question 8
Which methods will trigger an action that will evaluate a DataFrame? (Select TWO)
- A. DataFrame.random_split ( )
- B. DataFrame.collect ()
- C. DateFrame.select ()
- D. DataFrame.col ( )
- E. DataFrame.show ()
Answer:
B, E
Explanation:
The methods that will trigger an action that will evaluate a DataFrame are DataFrame.collect() and
DataFrame.show(). These methods will force the execution of any pending transformations on the
DataFrame and return or display the results. The other options are not methods that will evaluate a
DataFrame. Option A, DataFrame.random_split(), is a method that will split a DataFrame into two or
more DataFrames based on random weights. Option C, DataFrame.select(), is a method that will
project a set of expressions on a DataFrame and return a new DataFrame. Option D, DataFrame.col(),
is a method that will return a Column object based on a column name in a DataFrame.
Question 9
Which Snowflake objects does the Snowflake Kafka connector use? (Select THREE).
- A. Pipe
- B. Serverless task
- C. Internal user stage
- D. Internal table stage
- E. Internal named stage
- F. Storage integration
Answer:
A, D, E
Explanation:
The Snowflake Kafka connector uses three Snowflake objects: pipe, internal table stage, and internal
named stage. The pipe object is used to load data from an external stage into a Snowflake table using
COPY statements. The internal table stage is used to store files that are loaded from Kafka topics into
Snowflake using PUT commands. The internal named stage is used to store files that are rejected by
the COPY statements due to errors or invalid data. The other options are not objects that are used by
the Snowflake Kafka connector. Option B, serverless task, is an object that can execute SQL
statements on a schedule without requiring a warehouse. Option C, internal user stage, is an object
that can store files for a specific user in Snowflake using PUT commands. Option F, storage
integration, is an object that can enable secure access to external cloud storage services without
exposing credentials.
Question 10
A new customer table is created by a data pipeline in a Snowflake schema where MANAGED ACCESS
enabled.
…. Can gran access to the CUSTOMER table? (Select THREE.)
- A. The role that owns the schema
- B. The role that owns the database
- C. The role that owns the customer table
- D. The SYSADMIN role
- E. The SECURITYADMIN role
- F. The USERADMIN role with the manage grants privilege
Answer:
ABE
Explanation:
The roles that can grant access to the CUSTOMER table are the role that owns the schema, the role
that owns the database, and the SECURITYADMIN role. These roles have the ownership or the
manage grants privilege on the schema or the database level, which allows them to grant access to
any object within them. The other options are incorrect because they do not have the necessary
privilege to grant access to the CUSTOMER table. Option C is incorrect because the role that owns
the customer table cannot grant access to itself or to other roles. Option D is incorrect because the
SYSADMIN role does not have the manage grants privilege by default and cannot grant access to
objects that it does not own. Option F is incorrect because the USERADMIN role with the manage
grants privilege can only grant access to users and roles, not to tables.
Question 11
Which stages support external tables?
- A. Internal stages only; within a single Snowflake account
- B. internal stages only from any Snowflake account in the organization
- C. External stages only from any region, and any cloud provider
- D. External stages only, only on the same region and cloud provider as the Snowflake account
Answer:
C
Explanation:
External stages only from any region, and any cloud provider support external tables. External tables
are virtual tables that can query data from files stored in external stages without loading them into
Snowflake tables. External stages are references to locations outside of Snowflake, such as Amazon
S3 buckets, Azure Blob Storage containers, or Google Cloud Storage buckets. External stages can be
created from any region and any cloud provider, as long as they have a valid URL and credentials. The
other options are incorrect because internal stages do not support external tables. Internal stages are
locations within Snowflake that can store files for loading or unloading data. Internal stages can be
user stages, table stages, or named stages.
Question 12
A Data Engineer wants to check the status of a pipe named my_pipe. The pipe is inside a database
named test and a schema named Extract (case-sensitive).
Which query will provide the status of the pipe?
- A. SELECT FROM SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS (''test.'extract'.my_pipe"i:
- B. SELECT FROM SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS (,test.,,Extracr,,.ny_pipe, i I
- C. SELE2T * FROM SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS < ' test. "Extract", my_pipe');
- D. SELECT * FROM SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS ("test. 'extract' .my_pipe"};
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The query that will provide the status of the pipe is SELECT * FROM
SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS(‘test.“Extract”.my_pipe’);. The SYSTEM$PIPE_STATUS function returns
information about a pipe, such as its name, status, last received message timestamp, etc. The
function takes one argument: the pipe name in a qualified form. The pipe name should include the
database name, the schema name, and the pipe name, separated by dots. If any of these names are
case-sensitive identifiers, they should be enclosed in double quotes. In this case, the schema name
Extract is case-sensitive and should be quoted. The other options are incorrect because they do not
follow the correct syntax for the pipe name argument. Option A and B use single quotes instead of
double quotes for case-sensitive identifiers. Option D uses double quotes instead of single quotes for
non-case-sensitive identifiers.
Question 13
A Data Engineer is investigating a query that is taking a long time to return The Query Profile shows
the following: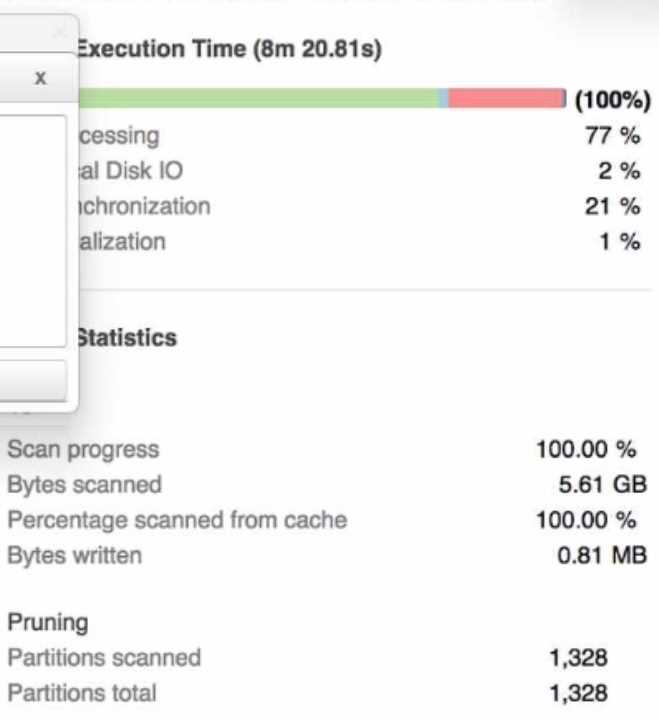
What step should the Engineer take to increase the query performance?
- A. Add additional virtual warehouses.
- B. increase the size of the virtual warehouse.
- C. Rewrite the query using Common Table Expressions (CTEs)
- D. Change the order of the joins and start with smaller tables first
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The step that the Engineer should take to increase the query performance is to increase the size of
the virtual warehouse. The Query Profile shows that most of the time was spent on local disk IO,
which indicates that the query was reading a lot of data from disk rather than from cache. This could
be due to a large amount of data being scanned or a low cache hit ratio. Increasing the size of the
virtual warehouse will increase the amount of memory and cache available for the query, which
could reduce the disk IO time and improve the query performance. The other options are not likely
to increase the query performance significantly. Option A, adding additional virtual warehouses, will
not help unless they are used in a multi-cluster warehouse configuration or for concurrent queries.
Option C, rewriting the query using Common Table Expressions (CTEs), will not affect the amount of
data scanned or cached by the query. Option D, changing the order of the joins and starting with
smaller tables first, will not reduce the disk IO time unless it also reduces the amount of data
scanned or cached by the query.
Question 14
What is a characteristic of the use of binding variables in JavaScript stored procedures in Snowflake?
- A. All types of JavaScript variables can be bound
- B. All Snowflake first-class objects can be bound
- C. Only JavaScript variables of type number, string and sf Date can be bound
- D. Users are restricted from binding JavaScript variables because they create SQL injection attack vulnerabilities
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A characteristic of the use of binding variables in JavaScript stored procedures in Snowflake is that
only JavaScript variables of type number, string and sf Date can be bound. Binding variables are a
way to pass values from JavaScript variables to SQL statements within a stored procedure. Binding
variables can improve the security and performance of the stored procedure by preventing SQL
injection attacks and reducing the parsing overhead. However, not all types of JavaScript variables
can be bound. Only the primitive types number and string, and the Snowflake-specific type sf Date,
can be bound. The other options are incorrect because they do not describe a characteristic of the
use of binding variables in JavaScript stored procedures in Snowflake. Option A is incorrect because
authenticator is not a type of JavaScript variable, but a parameter of the
snowflake.connector.connect function. Option B is incorrect because arrow_number_to_decimal is
not a type of JavaScript variable, but a parameter of the snowflake.connector.connect function.
Option D is incorrect because users are not restricted from binding JavaScript variables, but
encouraged to do so.
Question 15
Which use case would be BEST suited for the search optimization service?
- A. Analysts who need to perform aggregates over high cardinality columns
- B. Business users who need fast response times using highly selective filters
- C. Data Scientists who seek specific JOIN statements with large volumes of data
- D. Data Engineers who create clustered tables with frequent reads against clustering keys
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The use case that would be best suited for the search optimization service is business users who
need fast response times using highly selective filters. The search optimization service is a feature
that enables faster queries on tables with high cardinality columns by creating inverted indexes on
those columns. High cardinality columns are columns that have a large number of distinct values,
such as customer IDs, product SKUs, or email addresses. Queries that use highly selective filters on
high cardinality columns can benefit from the search optimization service because they can quickly
locate the relevant rows without scanning the entire table. The other options are not best suited for
the search optimization service. Option A is incorrect because analysts who need to perform
aggregates over high cardinality columns will not benefit from the search optimization service, as
they will still need to scan all the rows that match the filter criteria. Option C is incorrect because
data scientists who seek specific JOIN statements with large volumes of data will not benefit from the
search optimization service, as they will still need to perform join operations that may involve
shuffling or sorting data across nodes. Option D is incorrect because data engineers who create
clustered tables with frequent reads against clustering keys will not benefit from the search
optimization service, as they already have an efficient way to organize and access data based on
clustering keys.