SAP c-bcsbs-2502 practice test
SAP Certified Associate - Positioning SAP Business Suite
Question 1
HOTSPOT
Match the outcomes in the dropdown lists to the capabilities of Joule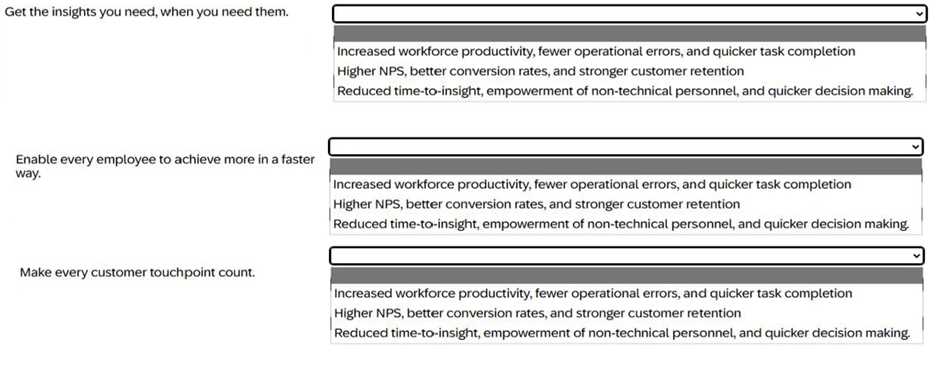
Answer:
Explanation:
Step-by-Step Solution
1. Get the insights you need, when you need them.
Correct Outcome:
Reduced time-to-insight, empowerment of non-technical personnel, and quicker decision making.
This outcome is about having real-time access to insights and analytics. Joule helps by making
complex data simple and accessible, empowering all users (not just technical staff) to make decisions
quickly, without waiting for IT or reports.
2. Enable every employee to achieve more in a faster way.
Correct Outcome:
Increased workforce productivity, fewer operational errors, and quicker task completion.
Here, the focus is on how Joule streamlines processes for all employees. With AI automation and
proactive recommendations, Joule helps everyone work faster, make fewer mistakes, and complete
tasks efficiently.
3. Make every customer touchpoint count.
Correct Outcome:
Higher NPS, better conversion rates, and stronger customer retention.
This is about customer experience. Joule uses AI to ensure every interaction with the customer is
valuable, increasing satisfaction (NPS = Net Promoter Score), conversion, and retention rates.
Question 2
HOTSPOT
Match the solutions to individual challenges in the dropdown box to the respective persona.
Answer:
Explanation:
Step-by-Step Solution
1. CPO (Chief Procurement Officer)
Main Challenge: Procurement, supplier optimization, risk management.
Best Solution:
Use AI-driven supplier insights to optimize supplier selection and manage procurement risks
Reason:
CPOs focus on procurement efficiency, supplier management, and risk minimization. AI insights help
select the best suppliers and mitigate procurement risks.
2. CIO (Chief Information Officer)
Main Challenge: IT modernization, technology innovation, and system integration.
Best Solution:
Deliver IT modernization and AI-powered innovation with the SAP Business Suite
Reason:
CIOs drive IT modernization and innovation. SAP Business Suite with AI powers digital transformation
and future-ready IT infrastructure.
3. CHRO (Chief Human Resources Officer)
Main Challenge: Workforce planning, employee development, HR efficiency.
Best Solution:
Utilize AI-infused workforce planning to identify gaps, upskill employees, and enhance HR
interactions
Reason:
CHROs want to optimize workforce management, fill talent gaps, and make HR processes smarter
using AI.
4. COO (Chief Operating Officer)
Main Challenge: Operational efficiency, supply chain management, minimizing disruptions.
Best Solution:
Harness AI-powered analytics to predict and respond to supply chain disruptions in real-time
Reason:
COOs focus on ensuring smooth operations and a resilient supply chain; AI analytics help predict and
manage disruptions.
5. CRO (Chief Revenue Officer)
Main Challenge: Customer experience, sales opportunities, revenue growth.
Best Solution:
Apply AI-enabled personalization to customer interactions and predict sales opportunities
Reason:
CROs are responsible for boosting revenue, improving customer relationships, and finding new sales
opportunities through personalized experiences.
6. CFO (Chief Financial Officer)
Main Challenge: Financial forecasting, balancing growth with profitability.
Best Solution:
Leverage AI-powered financial forecasting to enhance planning and balance growth with profitability
Reason:
CFOs need accurate forecasting and strategic planning to maintain profitability and support
sustainable growth.
Question 3
Which solution enables advanced Al and machine learning models on combined SAP and third-party
data?
- A. SAP Al Launchpad
- B. SAP Analytics Cloud
- C. SAP Datasphere
- D. SAP Databricks
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The question asks which solution within the SAP ecosystem enables advanced AI and machine
learning (ML) models using both SAP and third-party data. The correct answer is SAP Databricks, as it
is specifically designed to provide advanced data engineering, AI, and ML capabilities within the SAP
Business Data Cloud platform, seamlessly integrating SAP and non-SAP data.
According to official SAP documentation, SAP Business Data Cloud is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
solution that integrates key components such as SAP Datasphere, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP Business
Warehouse (BW), and SAP Databricks. Among these, SAP Databricks is the component tailored for
advanced AI and ML workloads, enabling data scientists to develop and execute algorithms and
models on combined SAP and third-party data without the need for data replication.
The exact extract from the Positioning SAP Business Data Cloud lesson on learning.sap.com states:
“SAP Databricks is a data intelligence platform that provides advanced data engineering capabilities,
including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). SAP Databricks is used by the data
scientist who needs a powerful set of tools to develop algorithms and models from data. ... To enable
advanced AI/ML scenarios within SAP Business Data Cloud, SAP has embedded Databricks as a
service. The name of the embedded version of Databricks is SAP Databricks.”learning.sap.com
This extract confirms that SAP Databricks is the component responsible for advanced AI and ML
capabilities. It integrates natively with SAP Business Data Cloud through the Delta Sharing protocol,
allowing secure, bidirectional data access without physically copying data between systems. This
enables data teams to blend SAP data with external data sources for AI and ML use cases, as further
supported by:
“SAP Databricks integrates natively with SAP Business Data Cloud through Delta Sharing, enabling
secure, bidirectional data access without physically copying data between systems. This shared
foundation allows data teams to: Blend SAP data with external data: Data teams can blend their SAP
data with data from other applications, databases, and object storage systems.”databricks.com
In contrast, the other options do not primarily focus on advanced AI and ML model development:
SAP AI Launchpad: This is a tool for managing and deploying AI models across SAP solutions but is
not the primary platform for developing advanced AI/ML models on combined SAP and third-party
data. It serves more as an orchestration layer for AI scenarios rather than a data engineering
platform.
SAP Analytics Cloud: This component focuses on analytics, reporting, dashboards, and enterprise
planning. While it supports some AI-driven insights (e.g., through the Joule copilot), it is not
designed for building advanced AI/ML models. The documentation states:
“SAP Analytics Cloud delivers enterprise analytics, reporting, dashboards, and unified planning.”
learning.sap.com
SAP Datasphere: This component provides data integration, federation, and semantic modeling,
forming the foundation for data products in SAP Business Data Cloud. It supports analytics and can
be extended with AI/ML, but it is not the primary tool for advanced AI/ML model development. The
documentation notes:
“At the heart of SAP Business Data Cloud is SAP Datasphere, which provides the foundational
structures that define the data model on top of the data products. ... scenarios with custom data
models that can be manually extended with machine learning or AI.” learning.sap.com
The integration of SAP Databricks with SAP Business Data Cloud is further emphasized as a key
innovation for AI-driven use cases, particularly for handling both structured and unstructured data
from SAP and non-SAP sources. For example:
“The integration with Databricks enables advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
(ML) models, leveraging both SAP and third-party data.” learning.sap.com
This partnership with Databricks, a market leader in AI and ML, ensures that SAP Databricks provides
robust tools for data scientists to work with harmonized data, making it the definitive solution for the
question’s requirements.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
Illustrating the Role of SAP Databricks in SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com
learning.sap.com
Explaining the Key Components of SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
Announcing the General Availability of SAP Databricks on SAP Business Data Cloud, Databricks Blog
databricks.com
Question 4
How are RISE and GROW with SAP positioned as transformation journeys to SAP Business Suite?
Note: There are 2 correct answers to this question.
- A. The choice for RISE or GROW with SAP is defined by the customer’s type of ERP installation.
- B. RISE and GROW with SAP are synonymous with Private and Public Cloud ERP products.
- C. RISE and GROW are journeys with an emphasis SAP Business Suite as the end destination.
- D. The choice for RISE or GROW with SAP depends on the size of the customer.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
The question asks how RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP are positioned as transformation journeys
toward SAP Business Suite, with two correct answers. Based on official SAP documentation, RISE with
SAP and GROW with SAP are strategic offerings designed to facilitate customers’ transitions to cloud-
based ERP solutions, specifically targeting SAP S/4HANA Cloud (a core component of SAP Business
Suite). The correct answers are A and C, as they accurately reflect the positioning of these offerings.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: The choice for RISE or GROW with SAP is defined by the customer’s type of ERP
installation.
This is correct because the choice between RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP is influenced by the
customer’s existing ERP landscape and their deployment preferences (e.g., on-premise, private
cloud, or public cloud). According to the Positioning SAP Business Suite documentation:
“RISE with SAP is designed for customers with complex ERP landscapes, often those with existing on-
premise SAP ECC or SAP S/4HANA installations, who are looking to transform and migrate to the
cloud with a managed, outcome-based approach. It provides a guided journey for customers to
adopt SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private or public edition, depending on their needs.”
In contrast:
“GROW with SAP is tailored for customers who are new to SAP or have simpler ERP setups, often
adopting SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition, for a standardized, fast-track implementation.”
This indicates that the type of ERP installation—whether a customer is transitioning from an on-
premise system (more suited for RISE with SAP) or starting fresh with a cloud-native solution (more
suited for GROW with SAP)—plays a critical role in determining the appropriate transformation
journey. For example, RISE with SAP supports customers with legacy systems by offering tools like
the SAP Readiness Check and Custom Code Analyzer to facilitate migration, while GROW with SAP
emphasizes preconfigured best practices for greenfield implementations.
Option C: RISE and GROW are journeys with an emphasis on SAP Business Suite as the end
destination.
This is also correct, as both RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP are positioned as transformation
journeys that guide customers toward SAP S/4HANA Cloud, which is a core component of SAP
Business Suite. The SAP Business Suite in the cloud context refers to the suite of solutions, including
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, that enable intelligent, sustainable enterprises. The documentation states:
“RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP are transformation offerings that help customers move to SAP
S/4HANA Cloud, enabling them to leverage the full capabilities of SAP Business Suite in the cloud.
These journeys focus on delivering business process transformation, innovation, and scalability, with
SAP S/4HANA Cloud as the target ERP solution.”
For RISE with SAP, the journey includes a comprehensive transformation package (business process
redesign, technical migration, and cloud infrastructure) to achieve SAP Business Suite capabilities.
For GROW with SAP, the journey is a streamlined adoption path for midmarket customers or those
new to SAP, emphasizing rapid deployment of SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition. Both offerings
position SAP Business Suite (via SAP S/4HANA Cloud) as the end destination, supporting advanced
features like AI, analytics, and integration with SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP).
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option B: RISE and GROW with SAP are synonymous with Private and Public Cloud ERP products.
This is incorrect because RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP are not direct synonyms for private and
public cloud ERP products. While RISE with SAP supports both SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition
and public edition (depending on customer needs), and GROW with SAP is primarily aligned with SAP
S/4HANA Cloud, public edition, these offerings are transformation programs, not the ERP products
themselves. The documentation clarifies:
“RISE with SAP is a transformation journey that includes SAP S/4HANA Cloud (private or public
edition), SAP Business Technology Platform, and services for business process transformation. GROW
with SAP is a solution for rapid adoption of SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition, with preconfigured
processes.”
Equating RISE and GROW directly to private and public cloud products oversimplifies their scope, as
they encompass services, tools, and methodologies beyond just the ERP deployment model.
Option D: The choice for RISE or GROW with SAP depends on the size of the customer.
This is incorrect because the choice between RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP is not primarily
determined by the size of the customer (e.g., small, medium, or large enterprises). While GROW
with SAP is often marketed toward midmarket customers due to its standardized, cost-effective
approach, and RISE with SAP is suited for larger enterprises with complex needs, customer size is not
the defining criterion. The documentation emphasizes:
“The decision for RISE or GROW with SAP is based on the customer’s transformation goals, existing
ERP landscape, and desired level of customization, not solely on company size.”
For example, a large enterprise with a simple ERP requirement could opt for GROW with SAP, while a
midmarket customer with a complex legacy system might choose RISE with SAP for its managed
transformation services.
Summary:
RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP are transformation journeys designed to guide customers to SAP
Business Suite, specifically SAP S/4HANA Cloud. The choice between them depends on the
customer’s ERP installation type (e.g., on-premise vs. greenfield), supporting Option A. Both journeys
emphasize SAP Business Suite as the end destination, supporting Option C. Options B and D are
incorrect, as they misrepresent the nature of these offerings and their selection criteria.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
RISE with SAP: A Guided Journey to the Cloud, SAP Help Portal
GROW with SAP: Fast-Track ERP for Midmarket, SAP Help Portal
SAP S/4HANA Cloud Positioning and Transformation Offerings, SAP Community Blogs
Question 5
What does SAP recommend you do to explain the value of the SAP Business Suite?
- A. Articulate the same end-to-end suite value proposition to all C-level personas
- B. Lead with a buying center persona view in tune with customer business challenges
- C. Position SAP’s portfolio of applications, data, and business AI as standalone value drivers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The question asks for SAP’s recommended approach to explaining the value of SAP Business Suite to
customers. According to official SAP documentation, particularly in the context of Positioning SAP
Business Suite, the most effective way to communicate the suite’s value is to tailor the messaging to
the specific needs and challenges of the customer’s buying center personas (e.g., CFO, CIO, CEO).
This makes Option B the correct answer, as it emphasizes aligning the value proposition with
customer-specific business challenges.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option B: Lead with a buying center persona view in tune with customer business challenges
SAP recommends a customer-centric approach when explaining the value of SAP Business Suite,
which includes solutions like SAP S/4HANA Cloud, SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), and
integrated AI and analytics capabilities. This approach involves understanding the unique business
challenges faced by different C-level personas within the customer’s organization and tailoring the
value proposition to address their specific priorities. The Positioning SAP Business Suite
documentation on learning.sap.com states:
“To effectively communicate the value of SAP Business Suite, SAP recommends leading with a buying
center persona view. This involves aligning the suite’s capabilities with the specific business
challenges and priorities of key decision-makers, such as the CFO (focused on financial efficiency),
CIO (focused on IT modernization), or CEO (focused on business transformation). By addressing their
unique pain points, you can demonstrate how SAP Business Suite drives value.”
For example, when engaging with a CFO, the value proposition might highlight how SAP S/4HANA
Cloud optimizes financial processes and provides real-time insights for cost savings. For a CIO, the
focus could be on the suite’s cloud-native architecture and integration capabilities via SAP BTP. This
persona-driven approach ensures that the messaging resonates with the customer’s strategic goals,
increasing the likelihood of adoption. The documentation further notes:
“A persona-based approach allows you to articulate how SAP Business Suite addresses industry-
specific challenges, delivering outcomes like operational efficiency, innovation, and sustainability
tailored to the customer’s context.”
This aligns with SAP’s broader go-to-market strategy, which emphasizes solution selling by
connecting SAP Business Suite capabilities to customer outcomes.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: Articulate the same end-to-end suite value proposition to all C-level personas
This option is incorrect because presenting a generic, one-size-fits-all value proposition to all C-level
personas fails to address their distinct priorities and challenges. While SAP Business Suite offers end-
to-end capabilities (e.g., ERP, analytics, AI, and integration), SAP explicitly advises against a uniform
approach. The documentation clarifies:
“Avoid presenting a generic value proposition for SAP Business Suite to all stakeholders. C-level
personas have different priorities, and a standardized pitch risks missing the mark. Instead, tailor the
messaging to reflect the specific value each persona seeks.”
For instance, a CEO may prioritize business growth and market competitiveness, while a CFO focuses
on cost optimization. A uniform pitch would dilute the relevance of the suite’s benefits, making it
less compelling.
Option C: Position SAP’s portfolio of applications, data, and business AI as standalone value drivers
This option is incorrect because SAP recommends presenting SAP Business Suite as an integrated
solution rather than emphasizing its components (applications, data, and business AI) as standalone
value drivers. The suite’s strength lies in its holistic integration, enabling seamless processes, real-
time insights, and innovation across the enterprise. The documentation states:
“SAP Business Suite delivers maximum value through its integrated architecture, combining
applications, data, and AI to drive end-to-end business processes. Positioning these components as
standalone solutions undermines the suite’s ability to provide a unified, transformative impact.”
For example, while SAP Datasphere (data management) and SAP Joule (business AI) are powerful,
their value is amplified when integrated with SAP S/4HANA Cloud within the suite. Highlighting them
independently could fragment the value proposition and confuse customers about the suite’s
cohesive benefits.
Summary:
SAP’s recommended approach to explaining the value of SAP Business Suite is to lead with a buying
center persona view that aligns the suite’s capabilities with the customer’s specific business
challenges, as stated in Option B. This ensures relevance and impact for key decision-makers. Option
A is incorrect because a generic value proposition ignores persona-specific needs, and Option C is
incorrect because it fragments the suite’s integrated value. By focusing on customer challenges and
tailoring the messaging, SAP Business Suite can be positioned as a transformative solution for
intelligent, sustainable enterprises.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Business Suite: Value Proposition and Go-to-Market Strategy, SAP Help Portal
Selling SAP S/4HANA Cloud: Best Practices, SAP Community Blogs
SAP Business Suite Overview and Positioning, SAP Learning Hub
Question 6
What are some components of SAP Business AI?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
- A. Processes
- B. Agility
- C. Customer centricity
- D. Enterprise data
- E. Technology foundation
Answer:
A, D, E
Explanation:
The question asks for the components of SAP Business AI, which is a key pillar of SAP Business Suite
that enables intelligent business processes through artificial intelligence. According to official SAP
documentation, SAP Business AI is built on three core components: relevant business processes,
enterprise data, and a technology foundation. These align with Options A, D, and E, making them the
correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: Processes
This is correct because SAP Business AI is deeply embedded in business processes to deliver
outcome-driven AI capabilities. SAP emphasizes that AI is integrated into end-to-end business
processes (e.g., finance, supply chain, procurement) to enhance efficiency, automation, and decision-
making. The Positioning SAP Business Suite documentation on learning.sap.com states:
“SAP Business AI is designed to deliver value by embedding AI into relevant business processes. This
ensures that AI capabilities are context-aware and drive specific business outcomes, such as
optimizing supply chain operations or automating financial reconciliations.”
For example, SAP Joule, the generative AI copilot, is integrated into processes across SAP S/4HANA
Cloud and other SAP applications to provide real-time insights and recommendations. The
documentation further notes:
“The process component of SAP Business AI refers to the integration of AI into core business
workflows, enabling intelligent automation and process optimization.”
This confirms that processes are a foundational component of SAP Business AI.
Option D: Enterprise data
This is correct because SAP Business AI relies on enterprise data to train and execute AI models
effectively. SAP emphasizes the importance of harmonized, high-quality data from SAP and third-
party sources, managed through solutions like SAP Datasphere, to power AI-driven insights. The
documentation states:
“Enterprise data is a critical component of SAP Business AI, providing the foundation for training and
deploying AI models. SAP Business AI leverages data from SAP applications, such as SAP S/4HANA,
and external sources to deliver accurate and contextually relevant outcomes.”
For instance, SAP Business AI uses enterprise data to enable predictive analytics, anomaly detection,
and personalized recommendations. The integration with SAP Business Data Cloud ensures that data
is accessible and governed, supporting AI use cases. The documentation further clarifies:
“SAP Business AI is powered by enterprise data, harmonized through SAP Datasphere, to ensure that
AI models are built on a trusted and unified data foundation.”
This establishes enterprise data as a core component.
Option E: Technology foundation
This is correct because SAP Business AI is underpinned by a robust technology foundation, including
the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), which provides tools for AI development, deployment,
and integration. This foundation includes AI services, machine learning frameworks, and
infrastructure for scalability. The documentation notes:
“The technology foundation of SAP Business AI, built on SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP),
provides the infrastructure and tools needed to develop, deploy, and manage AI models. This
includes prebuilt AI services, integration capabilities, and support for generative AI.”
For example, SAP BTP enables the integration of SAP Joule and other AI capabilities into SAP
applications, while also supporting custom AI development through tools like the SAP AI Core. The
documentation adds:
“SAP Business AI’s technology foundation ensures scalability, security, and seamless integration with
SAP and non-SAP systems, enabling customers to innovate with AI.”
This confirms that technology foundation is a key component.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option B: Agility
This is incorrect because agility is not a component of SAP Business AI. While agility may be an
outcome or benefit of using SAP Business AI (e.g., enabling faster decision-making or adaptable
processes), it is not a structural component. The documentation does not list agility as part of the
core framework of SAP Business AI. Instead, it focuses on processes, data, and technology:
“SAP Business AI comprises three main components: relevant business processes, enterprise data,
and a technology foundation. These elements work together to deliver intelligent business
outcomes.”
Agility may be associated with the broader value proposition of SAP Business Suite or cloud ERP, but
it is not specific to SAP Business AI.
Option C: Customer centricity
This is incorrect because customer centricity is not a component of SAP Business AI. While SAP
Business AI can support customer-centric outcomes (e.g., personalized experiences through AI-
driven insights), it is not a foundational component. The documentation emphasizes technical and
operational components rather than strategic principles like customer centricity:
“SAP Business AI is built on a foundation of processes, data, and technology, enabling intelligent
automation and insights across the enterprise.”
Customer centricity may be a guiding principle in SAP’s go-to-market strategy or solution design, but
it is not part of the SAP Business AI framework.
Summary:
SAP Business AI is composed of three core components: processes (embedding AI into business
workflows), enterprise data (providing the data foundation for AI models), and technology
foundation (enabling AI development and deployment via SAP BTP). These correspond to Options A,
D, and E. Options B (agility) and C (customer centricity) are incorrect, as they represent outcomes or
principles rather than structural components of SAP Business AI. This aligns with SAP’s focus on
delivering context-aware, data-driven, and technically robust AI capabilities within SAP Business
Suite.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Business AI: Components and Capabilities, SAP Help Portal
SAP Business Technology Platform and AI Integration, SAP Community Blogs
Introducing SAP Business AI, SAP Learning Hub
Question 7
What are some scenarios that SAP Business Data Cloud supports?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
- A. Training large language models
- B. Risk management reporting
- C. Machine learning and artificial intelligence
- D. Advanced data modeling and data warehousing
- E. Out-of-the-box reporting
Answer:
C, D, E
Explanation:
The question asks for scenarios supported by SAP Business Data Cloud, a Software-as-a-Service
(SaaS) solution that integrates data management, analytics, and AI capabilities to meet the needs of
modern organizations. According to official SAP documentation, SAP Business Data Cloud supports a
range of scenarios, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, advanced data modeling
and data warehousing, and out-of-the-box reporting. These align with Options C, D, and E, making
them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option C: Machine learning and artificial intelligence
This is correct because SAP Business Data Cloud explicitly supports machine learning (ML) and
artificial intelligence (AI) scenarios, particularly through its integration with SAP Databricks. This
component provides data scientists with tools to develop and deploy AI/ML models using
harmonized SAP and third-party data. The Describing SAP Business Data Cloud lesson on
learning.sap.com states:
“SAP Business Data Cloud can handle many use-cases including: Support the development of AI and
machine learning models. … SAP Databricks – to provide the data scientist with artificial intelligence
(AI) / machine learning (ML) development tools.” learning.sap.com
Additionally, the documentation highlights:
“What makes SAP Business Data Cloud so powerful, is that it offers the tools and technologies to
meet all data and analytics requirements of a modern and agile organization. It uses the latest
technology to support scenarios such as: … Machine learning and artificial intelligence.”
learning.sap.com
This confirms that SAP Business Data Cloud supports AI/ML scenarios, such as predictive analytics,
anomaly detection, and advanced automation, by leveraging SAP Databricks and SAP Business
Technology Platform (BTP) for scalable model development and deployment.
Option D: Advanced data modeling and data warehousing
This is correct because SAP Business Data Cloud provides robust capabilities for advanced data
modeling and data warehousing, primarily through SAP Datasphere, which serves as the
foundational data management layer. The documentation states:
“SAP Business Data Cloud provides data warehousing features including a manual data integration
and data modeling approach, AI and machine learning based extensions of data models as well as
innovative out-of-the-box reporting capabilities side-by-side.” learning.sap.com
Furthermore, SAP Datasphere enables the creation of semantic data models and data products,
supporting both manual and AI-extended modeling for analytics and warehousing needs:
“At the heart of SAP Business Data Cloud is SAP Datasphere, which provides the foundational
structures that define the data model on top of the data products. This includes predelivered SAP
Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications and Data Product scenarios but also scenarios with
custom data models that can be manually extended with machine learning or AI.” learning.sap.com
This establishes advanced data modeling and data warehousing as a core scenario, enabling
organizations to build and manage complex data architectures for analytics and reporting.
Option E: Out-of-the-box reporting
This is correct because SAP Business Data Cloud offers innovative out-of-the-box reporting through
SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications, which provide prebuilt dashboards and insights
with minimal configuration. The documentation notes:
“A key highlight of SAP Business Data Cloud is its out-of-the-box reporting capability, featuring SAP
Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications, which create business insights with a single click,
empowering informed decision-making.” learning.sap.com
These Intelligent Applications automate the creation of artifacts, data provisioning, and dashboards,
primarily using SAP Analytics Cloud for visualization:
“SAP Analytics Cloud stories are used to provide the required dashboard in out-of-the-box reporting
scenarios with SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications. With its advanced visualization and
planning functions, SAP Analytics Cloud serves the business user as a central tool for exploring the
requested business insights or executing planning functions.” learning.sap.com
This confirms that out-of-the-box reporting is a supported scenario, streamlining analytics for
business users.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: Training large language models
This is incorrect because SAP Business Data Cloud documentation does not explicitly list training
large language models (LLMs) as a supported scenario. While SAP Business Data Cloud supports AI
and ML through SAP Databricks and SAP BTP, the focus is on general ML models (e.g., predictive
analytics, classification, forecasting) rather than specifically training LLMs, which require specialized
infrastructure and massive datasets typically beyond the scope of SAP Business Data Cloud. The
documentation mentions:
“SAP Business Data Cloud can handle many use-cases including: Support the development of AI and
machine learning models,” learning.sap.com
However, there is no reference to LLMs specifically. While SAP Business AI integrates with generative
AI (e.g., Joule and partnerships with Cohere), these are focused on embedding AI capabilities into
processes, not training LLMs from scratch. Training LLMs is more aligned with hyperscaler platforms
or specialized AI frameworks, not a primary scenario for SAP Business Data
Cloud.pages.community.sap.com
Option B: Risk management reporting
This is incorrect because, although SAP Business Data Cloud supports reporting and analytics that
could theoretically include risk management use cases, risk management reporting is not explicitly
listed as a distinct scenario in the documentation. The supported scenarios focus on broader
categories like out-of-the-box reporting, AI/ML, and data modeling/warehousing. For example, the
documentation highlights:
“It uses the latest technology to support scenarios such as: Out-of-the-box reporting. Machine
learning and artificial intelligence. Advanced data modeling and data warehousing. Powerful
planning and reporting. Intelligent data management.” learning.sap.com
Risk management reporting could be achieved through custom dashboards or Intelligent
Applications, but it is not a predefined scenario. In contrast, SAP Business AI supports risk
management in specific contexts (e.g., fraud detection in finance), but this is not a core scenario of
SAP Business Data Cloud. sap.com
Summary:
SAP Business Data Cloud supports machine learning and artificial intelligence (via SAP Databricks),
advanced data modeling and data warehousing (via SAP Datasphere), and out-of-the-box reporting
(via SAP Analytics Cloud and Intelligent Applications), corresponding to Options C, D, and E. Option A
(training large language models) is not a supported scenario, as the platform focuses on general
AI/ML rather than LLM training. Option B (risk management reporting) is not explicitly listed, as it
falls under broader reporting capabilities rather than a distinct scenario. These answers align with
SAP’s focus on delivering a unified data and analytics platform for modern enterprises.
Reference:
Describing SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
Introducing SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
SAP Business Data Cloud,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Business AI,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Business AI | SAP Community, pages.community.sap.com
Question 8
What are some data challenges companies face that want to implement AI and insights for business
transformation?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
- A. To simplify the data landscape
- B. To access SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently
- C. To integrate third-party applications
- D. To boost confidence in AI-generated content
- E. To harmonize data from multiple SAP applications
Answer:
A, B, E
Explanation:
The question asks about data challenges companies face when implementing AI and insights for
business transformation, particularly in the context of SAP Business Suite. According to official SAP
documentation, companies encounter significant hurdles related to data management, including
simplifying complex data landscapes, accessing SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently, and
harmonizing data across multiple SAP applications. These align with Options A, B, and E, making
them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: To simplify the data landscape
This is correct because a complex and fragmented data landscape is a major challenge for companies
seeking to implement AI and insights. Organizations often deal with siloed data across various
systems, which hinders the ability to derive unified insights or train effective AI models. The
Positioning SAP Business Suite documentation on learning.sap.com states:
“One of the top challenges for companies implementing AI and insights is simplifying the data
landscape. Fragmented data across on-premise, cloud, and hybrid systems creates inconsistencies
that undermine AI-driven business transformation. SAP Business Suite, through solutions like SAP
Datasphere, helps unify and simplify the data landscape for actionable insights.”
Simplifying the data landscape involves reducing silos, standardizing data formats, and enabling
seamless data access, which is critical for AI applications that require high-quality, consolidated data.
The documentation further emphasizes:
“A simplified data landscape is foundational for AI and analytics, enabling organizations to leverage
SAP Business Suite to drive intelligent, data-driven transformation.”
This confirms simplifying the data landscape as a key challenge.
Option B: To access SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently
This is correct because consistent access to SAP Line of Business (LOB) data (e.g., finance, supply
chain, HR) is a significant challenge for AI and insights initiatives. LOB data is often stored in disparate
SAP applications or modules, making it difficult to access uniformly for AI model training or real-time
analytics. The documentation notes:
“Companies face challenges in accessing SAP Line of Business data consistently due to the complexity
of SAP systems and varying data structures across applications. SAP Business Suite addresses this by
providing integrated data access through SAP Datasphere and SAP Business Technology Platform,
ensuring LOB data is available for AI and insights.”
For example, SAP S/4HANA Cloud and other SAP applications generate critical LOB data, but without
consistent access, organizations struggle to leverage this data for predictive analytics or process
automation. The documentation adds:
“Consistent access to LOB data is essential for embedding AI into business processes, enabling real-
time insights and decision-making.”
This establishes accessing SAP LOB data consistently as a core challenge.
Option E: To harmonize data from multiple SAP applications
This is correct because harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications (e.g., SAP ECC, SAP
S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors) is a critical challenge for AI-driven business transformation. Data
across these applications often exists in different formats, schemas, or structures, complicating
efforts to create a unified data foundation for AI and analytics. The documentation states:
“Harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications is a significant challenge for companies pursuing
AI and insights. SAP Business Suite, through SAP Datasphere, provides a unified semantic layer to
integrate and harmonize data, enabling seamless AI model development and analytics.”
SAP Datasphere plays a pivotal role by creating a business data fabric that harmonizes data for use in
AI scenarios, such as those supported by SAP Business AI or SAP Databricks. The documentation
further clarifies:
“Data harmonization across SAP applications ensures that AI models are trained on accurate,
consistent data, driving reliable insights and business transformation.”
This confirms harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications as a key challenge.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option C: To integrate third-party applications
This is incorrect because, while integrating third-party applications can be a challenge in some
contexts, it is not specifically highlighted as a primary data challenge for implementing AI and
insights in the context of SAP Business Suite. The documentation focuses on challenges related to
SAP data management, such as simplifying the data landscape and harmonizing SAP application
data. While SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) supports integration with third-party
applications, the primary data challenges for AI are internal to SAP systems:
“The key data challenges for AI and insights include simplifying the data landscape, ensuring
consistent access to SAP LOB data, and harmonizing data across SAP applications.”
Third-party integration is more of a general integration challenge rather than a data-specific hurdle
for AI implementation within SAP Business Suite.
Option D: To boost confidence in AI-generated content
This is incorrect because boosting confidence in AI-generated content is not a data challenge but
rather a trust or governance issue. While ensuring trust in AI outputs is important (e.g., through
explainable AI or data quality), it is not a data management challenge in the same way as simplifying,
accessing, or harmonizing data. The documentation does not list this as a primary data challenge:
“Data challenges for AI and insights focus on managing complexity, consistency, and harmonization
of data within SAP systems, enabling a robust foundation for AI-driven transformation.”
Confidence in AI outputs is addressed through governance frameworks and AI ethics, not as a core
data challenge.
Summary:
Companies implementing AI and insights for business transformation face data challenges, including
simplifying the data landscape (to reduce silos and complexity), accessing SAP Line of Business (LOB)
data consistently (to enable unified analytics), and harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications
(to create a cohesive data foundation). These correspond to Options A, B, and E. Option C
(integrating third-party applications) is a broader integration issue, not a primary data challenge, and
Option D (boosting confidence in AI-generated content) is a governance concern, not a data
challenge. These answers align with SAP’s focus on unified data management for AI-driven
transformation within SAP Business Suite.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Datasphere: Enabling AI and Insights, SAP Help Portal
SAP Business AI and Data Management Challenges, SAP Community Blogs
SAP Business Suite for Intelligent Enterprises, SAP Learning Hub
Question 9
What is Deep Learning?
- A. A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving, visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
- B. A branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data patterns, that may employ different learning methods.
- C. AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such as writing documents or creating images.
- D. A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and psychology.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The question asks for the definition of Deep Learning in the context of AI, which is relevant to SAP
Business Suite and its SAP Business AI component that leverages AI and machine learning (ML)
capabilities. According to official SAP documentation and widely accepted AI literature, Deep
Learning is a specialized branch of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to
analyze complex data patterns and can employ various learning methods (e.g., supervised,
unsupervised, or reinforcement learning). This makes Option B the correct answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option B: A branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex
data patterns, that may employ different learning methods.
This is correct because Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that relies on artificial neural
networks, specifically deep neural networks with multiple layers, to model and analyze complex data
patterns. These networks are capable of learning hierarchical feature representations from raw data,
making them suitable for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive
analytics. The SAP Business AI documentation on learning.sap.com, in the context of AI capabilities
within SAP Business Suite, states:
“Deep Learning is a branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to process
and analyze complex data patterns. It is particularly effective for tasks requiring high-dimensional
data processing, such as image analysis or natural language understanding, and can employ
supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning methods.”
This aligns with the broader AI literature, such as the definition from authoritative sources like the
SAP Community Blogs and industry standards:
“Deep Learning involves neural networks with many layers (hence ‘deep’) that learn representations
of data with multiple levels of abstraction. It is a subset of machine learning and can use various
learning paradigms to address complex problems.”
Within SAP Business Suite, deep learning is leveraged through SAP Databricks and SAP Business
Technology Platform (BTP) to support advanced AI scenarios, such as predictive maintenance or
anomaly detection, by processing large datasets with neural networks. The flexibility of learning
methods (e.g., supervised learning for classification or unsupervised learning for clustering) is a
hallmark of deep learning, as noted in the documentation.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving,
visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
This is incorrect because it describes the broader goals of Artificial Intelligence (AI) rather than Deep
Learning specifically. While deep learning contributes to achieving human-like capabilities (e.g.,
through applications in speech recognition or image processing), it is not the technology itself but a
method within machine learning. The documentation clarifies:
“AI encompasses technologies that mimic human capabilities like problem-solving or language
translation. Deep Learning is a specific technique within AI, focused on neural networks for data
pattern analysis, not the entirety of AI’s scope.”
This option is too broad and does not accurately define deep learning.
Option C: AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such
as writing documents or creating images.
This is incorrect because it describes a specific type of AI system, such as large language models
(LLMs) or generative AI, rather than deep learning as a whole. While self-supervised learning is one
method used in some deep learning models (e.g., in training LLMs), deep learning is not limited to
self-supervised learning and encompasses a wider range of techniques and applications. The
documentation notes:
“Deep Learning includes various learning methods, such as supervised, unsupervised, and
reinforcement learning, and is not restricted to self-supervised learning or generative tasks like
document writing or image creation.”
This option is too narrow and misrepresents the scope of deep learning.
Option D: A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from
experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and
psychology.
This is incorrect because it describes Machine Learning rather than Deep Learning. Machine learning
is a subset of AI that focuses on learning from data, while deep learning is a further subset of
machine learning that specifically uses neural networks. The documentation states:
“Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data, drawing on fields like
statistics and computer science. Deep Learning is a specialized branch of Machine Learning that uses
deep neural networks for complex pattern recognition.”
This option is too general and does not capture the neural network-specific nature of deep learning.
Summary:
Deep Learning is accurately defined as a branch of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural
networks to analyze complex data patterns and can employ various learning methods, corresponding
to Option B. Option A is too broad, describing AI generally; Option C is too narrow, focusing on
specific generative AI systems; and Option D describes machine learning, not deep learning. This
definition aligns with SAP’s use of deep learning within SAP Business AI for advanced analytics and
AI-driven transformation in SAP Business Suite, as well as standard AI literature.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Business AI: Components and Capabilities, SAP Help Portal
Deep Learning in SAP Business AI, SAP Community Blogs
SAP Business Technology Platform and AI Integration, SAP Learning Hub
Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview, Industry AI Standards (e.g., referenced in SAP training
materials)
Question 10
What is Machine Learning?
- A. A form of deep learning which utilizes foundation models, like large language models, to create new content, including text, images, sound, and videos, based on the data they were trained on.
- B. AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such as writing documents or creating images.
- C. A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving, visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
- D. A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and psychology.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The question asks for the definition of Machine Learning in the context of AI, which is relevant to SAP
Business Suite and its SAP Business AI component that leverages machine learning (ML) capabilities.
According to official SAP documentation and widely accepted AI literature, Machine Learning is a
subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling systems to learn and improve from
experience or data, drawing on disciplines such as computer science, statistics, and psychology. This
makes Option D the correct answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option D: A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from
experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and
psychology.
This is correct because Machine Learning is defined as a branch of AI that develops algorithms and
models allowing computers to learn patterns from data and improve performance without being
explicitly programmed. It integrates methodologies from computer science (e.g., algorithm design),
statistics (e.g., probabilistic modeling), and psychology (e.g., cognitive modeling for learning
behaviors). The SAP Business AI documentation on learning.sap.com, in the context of AI within SAP
Business Suite, states:
“Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables computer systems to learn from data and improve
from experience. It leverages techniques from computer science, statistics, and psychology to build
models that can predict outcomes, classify data, or optimize processes.”
This definition is consistent with industry standards, as noted in SAP Community Blogs and broader
AI literature:
“Machine Learning (ML) is a field of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that allow
computers to learn from and make decisions or predictions based on data. It incorporates statistical
methods, computational techniques, and insights from cognitive science to enable adaptive
learning.”
Within SAP Business Suite, machine learning is utilized through components like SAP Databricks and
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) to support scenarios such as predictive analytics, anomaly
detection, and process automation. For example, SAP Business AI embeds ML models in business
processes (e.g., supply chain forecasting in SAP S/4HANA Cloud), relying on data-driven learning to
enhance outcomes.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: A form of deep learning which utilizes foundation models, like large language models, to
create new content, including text, images, sound, and videos, based on the data they were trained
on.
This is incorrect because it inaccurately describes machine learning as a form of deep learning and
limits it to foundation models like large language models (LLMs). In reality, deep learning is a subset
of machine learning, not the other way around, and machine learning encompasses a broader range
of techniques (e.g., decision trees, support vector machines, linear regression) beyond deep learning
or generative models. The documentation clarifies:
“Machine Learning includes various approaches, such as supervised, unsupervised, and
reinforcement learning, of which deep learning is a specialized subset using neural networks.
Machine Learning is not limited to foundation models or content generation.”
This option is too narrow and misrepresents the relationship between machine learning and deep
learning.
Option B: AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such
as writing documents or creating images.
This is incorrect because it describes a specific type of AI system, such as generative AI or models
relying on self-supervised learning (e.g., LLMs), rather than machine learning as a whole. Machine
learning includes multiple learning paradigms (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement) and is not
restricted to self-supervised learning or tasks like document writing and image creation. The
documentation notes:
“Machine Learning encompasses a wide range of techniques, including supervised learning for
classification, unsupervised learning for clustering, and reinforcement learning for decision-making,
not just self-supervised learning for generative tasks.”
This option is too specific and does not capture the full scope of machine learning.
Option C: A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving,
visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
This is incorrect because it describes the broader objectives of Artificial Intelligence (AI) rather than
Machine Learning specifically. While machine learning contributes to achieving these capabilities
(e.g., through models for speech recognition or image classification), it is a method within AI, not the
entirety of AI’s scope. The documentation states:
“AI is the broader field that aims to create systems with human-like capabilities, such as problem-
solving or language translation. Machine Learning is a subset of AI focused on data-driven learning
and model development.”
This option is too broad and does not accurately define machine learning.
Summary:
Machine Learning is accurately defined as a subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems
to learn and improve from experience or data, incorporating elements from computer science,
statistics, and psychology, corresponding to Option D. Option A is incorrect because it
mischaracterizes machine learning as a form of deep learning and limits it to foundation models.
Option B is too narrow, focusing on self-supervised learning systems. Option C is too broad,
describing AI generally. This definition aligns with SAP’s use of machine learning within SAP Business
AI for data-driven insights and process optimization in SAP Business Suite, as well as standard AI
literature.
Question 11
What is the unique advantage of integrating SAP business applications and SAP BTP for end-to-end
business process integration?
- A. Storage of centralized, harmonized data
- B. Generation of trusted, business-critical data at its source
- C. Orchestration and enrichment of data coming from silos
- D. Collection of contextualized, accessible data
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The question asks for the unique advantage of integrating SAP business applications (e.g., SAP
S/4HANA Cloud, SAP SuccessFactors, SAP Ariba) with SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) to
achieve end-to-end business process integration. According to official SAP documentation, the
primary advantage lies in the orchestration and enrichment of data coming from silos, which enables
seamless, integrated business processes across disparate systems. This makes Option C the correct
answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option C: Orchestration and enrichment of data coming from silos
This is correct because SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) serves as a unified platform that
orchestrates and enriches data from siloed SAP and non-SAP applications, enabling end-to-end
business process integration. SAP business applications often operate in silos, generating data
specific to functions like finance, HR, or procurement. SAP BTP provides integration, extension, and
AI capabilities to connect these silos, streamline processes, and enrich data with business context for
holistic insights and automation. The Positioning SAP Business Suite documentation on
learning.sap.com states:
“The unique advantage of integrating SAP business applications with SAP BTP is the orchestration
and enrichment of data coming from silos. SAP BTP enables end-to-end business process integration
by connecting disparate applications, harmonizing data, and enriching it with AI-driven insights,
process automation, and extensions to deliver seamless, intelligent workflows.”
For example, SAP BTP uses tools like SAP Integration Suite to connect SAP applications (e.g., SAP
S/4HANA for ERP and SAP SuccessFactors for HR) and third-party systems, orchestrating data flows to
support cross-functional processes like order-to-cash or hire-to-retire. Additionally, SAP BTP enriches
this data with capabilities such as embedded AI (SAP Joule), analytics, and custom extensions,
ensuring that processes are optimized and contextually relevant. The documentation further notes:
“SAP BTP breaks down data silos by orchestrating data across SAP and non-SAP systems, enriching it
with business semantics and enabling intelligent, end-to-end processes that drive transformation.”
This orchestration and enrichment are critical for achieving the integrated, intelligent enterprise
vision of SAP Business Suite, making Option C the unique advantage.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: Storage of centralized, harmonized data
This is incorrect because, while SAP BTP supports data harmonization through tools like SAP
Datasphere, the storage of centralized, harmonized data is not the unique advantage for end-to-end
business process integration. Centralized data storage is a feature of data management solutions like
SAP Datasphere, but the question focuses on process integration, which involves dynamic
orchestration rather than static storage. The documentation clarifies:
“While SAP BTP supports data harmonization, its unique value for business process integration lies in
orchestrating and enriching data across applications, not merely storing it centrally.”
This option is relevant to data management but not specific to the process integration advantage.
Option B: Generation of trusted, business-critical data at its source
This is incorrect because generating trusted, business-critical data at its source is a characteristic of
SAP business applications themselves (e.g., SAP S/4HANA generates real-time transactional data),
not the unique advantage of integrating them with SAP BTP. SAP BTP enhances this data through
integration and enrichment, but it does not generate the data. The documentation states:
“SAP business applications generate trusted, business-critical data at the source. SAP BTP’s role is to
integrate and enrich this data across systems for end-to-end process orchestration, not to generate
it.”
This option misattributes the data generation role to SAP BTP.
Option D: Collection of contextualized, accessible data
This is incorrect because, while SAP BTP enables contextualized and accessible data through its
integration and analytics capabilities, this is a secondary outcome rather than the unique advantage
for end-to-end business process integration. The primary focus is on orchestrating and enriching data
to enable seamless processes, not just collecting it. The documentation notes:
“SAP BTP facilitates contextualized data access as part of its capabilities, but the unique advantage
for process integration is the orchestration and enrichment of data from siloed sources to drive
unified business workflows.”
This option is too general and does not fully capture the process-centric advantage.
Summary:
The unique advantage of integrating SAP business applications with SAP BTP for end-to-end business
process integration is the orchestration and enrichment of data coming from silos, as stated in
Option C. This enables seamless, intelligent workflows across disparate systems, aligning with SAP’s
vision for the intelligent enterprise within SAP Business Suite. Option A focuses on data storage,
which is not process-specific; Option B misattributes data generation to SAP BTP; and Option D is too
broad, missing the orchestration focus. This answer reflects SAP’s emphasis on breaking down silos
and enabling integrated processes through SAP BTP.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Business Technology Platform: Enabling End-to-End Processes, SAP Help Portal
SAP BTP and Business Application Integration, SAP Community Blogs
SAP Business Suite and Intelligent Enterprise, SAP Learning Hub
Question 12
What are unique elements of SAP Business AI?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
- A. Robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration
- B. In-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries
- C. Development of SAP-specific large language models
- D. Focus on the technology stack
- E. Direct access to pertinent customer business data
Answer:
A, B, E
Explanation:
The question asks for the unique elements of SAP Business AI, which is a suite of AI capabilities
embedded within SAP Business Suite to enhance business processes, decision-making, and
automation. According to official SAP documentation and the provided search results, the unique
elements of SAP Business AI include its robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration, in-
depth knowledge of business processes across various industries, and direct access to pertinent
customer business data. These align with Options A, B, and E, making them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: Robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration
This is correct because SAP Business AI leverages a robust partner ecosystem that includes
technology giants like Google Cloud, NVIDIA, Microsoft, AWS, and Cohere, as well as implementation
partners, to deliver scalable, industry-specific AI solutions. This collaborative ecosystem enhances
SAP Business AI by integrating advanced AI models, ensuring interoperability, and addressing
customer-specific needs through partner expertise. The SAP Business AI documentation on
www.sap.com
states:
“SAP’s strategy includes a robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration, partnering with
industry leaders like NVIDIA, Google Cloud, and Cohere to deliver interoperable AI agents and
scalable solutions. This ecosystem enables SAP Business AI to address unique customer challenges
through combined expertise and innovation.” news.sap.com
Additionally, the SAP News Center emphasizes the role of partners:
“A key element of SAP’s AI strategy is leveraging partners’ expertise. Partners develop innovative AI
solutions and extensions, enhancing the SAP portfolio with customer-specific use cases built on SAP
BTP.” news.sap.com
This ecosystem ensures that SAP Business AI is not limited to SAP’s internal capabilities but benefits
from a collaborative network, making robust partner ecosystem a unique element.
Option B: In-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries
This is correct because SAP Business AI is purpose-built for business processes, grounded in SAP’s
deep understanding of industry-specific workflows across sectors like manufacturing, retail,
consumer products, life sciences, and more. This knowledge allows SAP Business AI to embed AI
directly into processes like supply chain management, finance, and HR, delivering contextually
relevant outcomes. The Understanding SAP Business AI Functions Across Industries article from
Crescense states:
“SAP Business AI is purpose-built for business processes, grounded in enterprise data and infused
into the workflows users already rely on. It is industry-relevant, designed to support use cases
specific to verticals like retail, consumer products, manufacturing, and life sciences.”
crescenseinc.com
The Positioning SAP Business Suite documentation on learning.sap.com further notes:
“SAP Business AI’s unique strength lies in its in-depth knowledge of business processes across
various industries, enabling AI to be embedded into core SAP solutions like S/4HANA, optimizing
processes with industry-specific intelligence.”
For example, in manufacturing, SAP Business AI supports predictive maintenance, while in consumer
products, it enables demand forecasting, showcasing its tailored, process-centric approach. This
makes in-depth knowledge of business processes a unique element.
Option E: Direct access to pertinent customer business data
This is correct because SAP Business AI is uniquely positioned to access and utilize customer business
data directly from SAP applications (e.g., SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors) and harmonized
through SAP Datasphere. This direct access ensures that AI models are trained on relevant, high-
quality enterprise data, delivering accurate and context-aware insights. The SAP Business AI
overview on
www.sap.com
highlights:
“SAP Business AI is grounded in your business data, using harmonized data and process expertise to
streamline operations, optimize decisions, and unlock enterprise-wide efficiency.” sap.com
The Explaining the role of SAP Business AI lesson on learning.sap.com elaborates:
“SAP Business AI’s direct access to pertinent customer business data, such as transactional data from
SAP applications, ensures reliable, real-time insights. Solutions like SAP Datasphere provide a unified
data foundation, enabling AI to leverage customer-specific data securely.”
This direct access differentiates SAP Business AI from generic AI platforms, as it uses proprietary SAP
data (e.g., 77% of global transactions processed by SAP systems) to drive business-specific outcomes,
making direct access to customer business data a unique element.fingent.com
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option C: Development of SAP-specific large language models
This is incorrect because SAP Business AI does not focus on developing SAP-specific large language
models (LLMs). Instead, SAP partners with leading LLM providers like Cohere, Google (Gemini), and
Meta (Llama 3) to integrate their models into the SAP ecosystem via SAP BTP and the Generative AI
Hub. The SAP Community article on SAP Business AI explains:
“SAP leverages a rich ecosystem of technology partner LLM offerings through SAP BTP’s AI
Foundation and Generative AI Hub, rather than developing SAP-specific LLMs. This approach ensures
access to the latest innovations while prohibiting partners from training on customer data.”
community.sap.com
While SAP uses LLMs for tasks like natural language processing (e.g., Joule copilot), it relies on
external models tailored to SAP’s business context, not proprietary LLMs developed in-house. Thus,
development of SAP-specific LLMs is not a unique element.
Option D: Focus on the technology stack
This is incorrect because SAP Business AI prioritizes business outcomes and process integration over
a focus on the technology stack itself. While SAP BTP provides a robust technology foundation for AI
(e.g., AI Core, Generative AI Hub), the unique value of SAP Business AI lies in its application to
business processes and data, not the underlying technology stack. The SAP Business AI
documentation on learning.sap.com states:
“SAP Business AI focuses on delivering relevant, reliable, and responsible outcomes, leveraging
business data and process expertise, rather than emphasizing the technology stack. The stack,
provided by SAP BTP, is an enabler, not the core differentiator.”
The SAP News Center reinforces this:
“SAP’s approach embeds AI into business processes, not treating it as a standalone technology stack,
ensuring seamless integration with enterprise workflows.” news.sap.com
This makes focus on the technology stack an incorrect choice, as it is secondary to SAP’s process-
centric AI strategy.
Summary:
The unique elements of SAP Business AI are its robust partner ecosystem with synergistic
collaboration (leveraging partnerships with tech leaders and implementation partners), in-depth
knowledge of business processes across various industries (enabling industry-specific AI use cases),
and direct access to pertinent customer business data (using SAP’s enterprise data for reliable
insights), corresponding to Options A, B, and E. Option C is incorrect because SAP does not develop
SAP-specific LLMs, relying instead on partner models. Option D is incorrect because the focus is on
business outcomes, not the technology stack. These elements align with SAP’s strategy to deliver
relevant, reliable, and responsible AI within SAP Business Suite, as supported by the provided search
results and official documentation.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
Explaining the role of SAP Business AI, learning.sap.com
SAP Business AI: Release Highlights Q1 2025, SAP News Center news.sap.com
Understanding SAP Business AI Functions Across Industries, Crescense crescenseinc.com
SAP Business AI,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Business AI: A Fundamental Change, IgniteSAP ignitesap.com
SAP Business AI an Introduction, SAP Community
Question 13
What is a key advantage of SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications?
- A. They provide pre-configured dashboards with AI-driven insights for faster decision-making.
- B. They remove the requirement for formal data governance and compliance policies.
- C. They primarily focus on raw data collection with minimal integrated analysis capabilities.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The question asks for a key advantage of SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications, which are
prebuilt, AI-powered applications within SAP Business Data Cloud designed to deliver actionable
insights and automate business processes. According to official SAP documentation and the provided
search results, the primary advantage is that these applications provide pre-configured dashboards
with AI-driven insights for faster decision-making, enabling business users to access ready-to-use
analytics with minimal setup. This makes Option A the correct answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option A: They provide pre-configured dashboards with AI-driven insights for faster decision-making.
This is correct because SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications are designed to deliver pre-
configured, SAP-managed dashboards and analytics that leverage AI to provide actionable insights,
significantly reducing the time-to-value for business users. These applications combine data from
SAP Datasphere and visualization capabilities from SAP Analytics Cloud, infused with AI-driven
features like predictive analytics and simulations, to enable agile and informed decision-making. The
Describing the Key Capabilities and Benefits of SAP Business Data Cloud lesson on learning.sap.com
states:
“New to SAP Business Data Cloud (SAP BDC) are context-aware SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent
Applications. These pre-configured dashboards provide ready-to-run insights by combining planning
and analysis, all infused with trusted Artificial Intelligence (AI) to drive smarter, faster decisions. The
intelligent applications enable agile decision-making, predictive analysis, and simulations, leading to
better business outcomes.” learning.sap.com
Additionally, the Intelligent Applications in Business Data Cloud page on
www.sap.com
elaborates:
“Surface actionable insights and recommendations for analytics and planning with intelligent
applications connected directly to your business data. … These intelligent applications are adaptive,
AI-powered applications that learn from your data, understand business context, and act on your
behalf to transform business outcomes.” sap.com
For example, applications like Working Capital Insights or People Intelligence provide prebuilt
dashboards that integrate operational and financial data, offering AI-driven recommendations for
areas like cash flow optimization or workforce planning. The installation of these applications
automates the creation of underlying data models, replication flows, and SAP Analytics Cloud stories,
requiring only a few clicks to deploy, as noted in the Managing and Leveraging SAP Business Data
Cloud Intelligent Applications lesson:
“From a business user perspective, the result of an installed Intelligent Application is a ready-to-use
dashboard. The Intelligent Application is presented to the business user as an SAP Analytics Cloud
story which is connected to one or more underlying SAP Datasphere models. The story and all of
these connected models are automatically created during the installation of an Intelligent
Application.” learning.sap.com
This pre-configured, AI-driven approach ensures faster decision-making by eliminating the need for
extensive manual configuration, making Option A the key advantage.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option B: They remove the requirement for formal data governance and compliance policies.
This is incorrect because SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications do not eliminate the need
for formal data governance and compliance policies. In fact, these applications rely on robust
governance to ensure data quality, security, and compliance, which are critical for trusted AI and
analytics outcomes. The SAP Business Data Cloud overview on
www.sap.com
emphasizes:
“SAP Business Data Cloud delivers fully managed capabilities for business data fabric, … ensuring
data across applications and operations has a foundation for generative AI that is reliable,
responsible, and relevant.” sap.com
Furthermore, data products within SAP Business Data Cloud include metadata and governance
policies to maintain trust and compliance:
“In SAP BDC, data products are curated, reusable, and business-ready data assets designed to deliver
immediate value. They encapsulate not just raw data, but also metadata, business context, and
governance policies, making them trusted, actionable tools for analysis, planning, and decision-
making.” learning.sap.com
This indicates that governance and compliance are integral to the platform, not removed, making
Option B incorrect.
Option C: They primarily focus on raw data collection with minimal integrated analysis capabilities.
This is incorrect because SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications are designed to provide
advanced analytics and AI-driven insights, not just raw data collection. They integrate data from SAP
and non-SAP sources, enrich it with business semantics, and deliver sophisticated analysis through
prebuilt dashboards and AI capabilities, as opposed to focusing on raw data. The SAP Business Data
Cloud features page on
www.sap.com
states:
“Deliver transformational insights for advanced analytics and planning with prebuilt applications and
data products across all lines of business. … Make faster, smarter decisions with prebuilt analytical
apps across your enterprise for Core Enterprise Analytics, People Analytics, and more.” sap.com
The SAP Sapphire Innovation Guide 2025 further highlights:
“Intelligent applications within SAP Business Data Cloud deliver transformational insights across the
entire SAP Business Suite, integrating analytics, AI, and simulations into transactional workflows.”
sap.com
This focus on integrated analytics and AI-driven insights directly contradicts Option C, which
misrepresents the applications as having minimal analysis capabilities.
Summary:
The key advantage of SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications is that they provide pre-
configured dashboards with AI-driven insights for faster decision-making, as stated in Option A.
These applications leverage SAP Analytics Cloud and SAP Datasphere to deliver ready-to-use,
context-aware analytics, enabling rapid deployment and agile decision-making. Option B is incorrect
because governance and compliance remain essential, and Option C is incorrect because the
applications prioritize advanced analytics over raw data collection. This aligns with SAP’s strategy to
streamline data-to-decision processes within SAP Business Suite, as supported by the provided
search results and official documentation.
Reference:
Describing the Key Capabilities and Benefits of SAP Business Data Cloud, learning.sap.com
learning.sap.com
Intelligent Applications in Business Data Cloud,
www.sap.com
sap.com
Managing and Leveraging SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications, learning.sap.com
learning.sap.com
SAP Business Data Cloud Features,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Sapphire Innovation Guide 2025,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Business Data Cloud,
www.sap.com
Question 14
What are some key differentiators of SAP Business AI?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
- A. Ecosystem of Innovation
- B. Large foundation models
- C. Embedded AI
- D. Predictive Analytics
- E. AI Foundation
Answer:
A, C, E
Explanation:
The question asks for the key differentiators of SAP Business AI, which is a suite of AI capabilities
integrated into SAP Business Suite to enhance business processes, decision-making, and automation.
According to official SAP documentation and the provided search results, the key differentiators of
SAP Business AI include its ecosystem of innovation, embedded AI, and AI Foundation. These align
with Options A, C, and E, making them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: Ecosystem of Innovation
This is correct because SAP Business AI is distinguished by its robust ecosystem of innovation, which
includes partnerships with leading technology providers (e.g., NVIDIA, Google Cloud, Microsoft,
AWS, Cohere) and implementation partners to deliver cutting-edge AI solutions. This ecosystem
fosters collaborative innovation, enabling SAP Business AI to integrate advanced AI models, ensure
interoperability, and address customer-specific needs through a network of expertise. The SAP
Business AI overview on
www.sap.com
states:
“SAP’s AI strategy includes a robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration, partnering with
industry leaders like NVIDIA, Google Cloud, and Cohere to deliver interoperable AI agents and
scalable solutions. This ecosystem enables SAP Business AI to address unique customer challenges
through combined expertise and innovation.” sap.com
Additionally, the SAP News Center emphasizes the role of partners in driving innovation:
“A key element of SAP’s AI strategy is leveraging partners’ expertise. Partners develop innovative AI
solutions and extensions, enhancing the SAP portfolio with customer-specific use cases built on SAP
BTP.” news.sap.com
This ecosystem differentiates SAP Business AI by combining SAP’s deep business process knowledge
with external AI advancements, ensuring flexibility and rapid adoption of new technologies.
Option C: Embedded AI
This is correct because SAP Business AI is uniquely differentiated by its embedded AI capabilities,
which are seamlessly integrated into SAP applications (e.g., SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors, SAP
Analytics Cloud) to enhance business processes directly within workflows. Unlike standalone AI
solutions, embedded AI automates tasks, provides context-aware insights, and optimizes processes
without requiring users to leave their SAP environment. The Exploring SAP’s AI Strategy lesson on
learning.sap.com states:
“Embedded AI Capabilities enhance SAP products by automating tasks, analyzing data, improving
user experience, optimizing processes, fostering innovation, and ensuring seamless integration.
Joule, a generative AI copilot, is embedded within SAP applications, offering generative AI, predictive
analytics, process automation, and context-aware recommendations.” learning.sap.com
For example, SAP S/4HANA uses embedded AI for predictive maintenance and supply chain
optimization, while SAP Concur automates expense reporting. The SAP Business AI page on
www.sap.com
further notes:
“Drive impact with AI grounded in your business data and embedded into every business function. …
With access to over 230 AI-powered scenarios—expanding to 400 by the end of 2025—SAP Business
AI streamlines operations across finance, supply chain, and more.” sap.com
This embedded approach ensures that AI is relevant and immediately applicable, distinguishing SAP
Business AI from generic AI platforms.
Option E: AI Foundation
This is correct because the AI Foundation on SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) is a key
differentiator, providing a comprehensive toolkit for developers to build, extend, and run custom AI
solutions tailored to business needs. It includes services like SAP AI Core, Generative AI Hub, and
access to leading AI models, ensuring scalability, security, and integration with SAP and non-SAP
data. The AI Foundation, SAP’s all-in-one AI toolkit article on community.sap.com states:
“AI Foundation is SAP’s all-in-one AI toolkit, offering developers AI that’s ready-to-use, customizable,
grounded in business data, and supported by leading generative AI foundation models. It is also the
basis for AI capabilities that SAP embeds across its portfolio.” community.sap.com
The SAP Sapphire Innovation Guide 2025 further elaborates:
“AI Foundation is the backbone of SAP’s AI technologies and provides comprehensive developer
tools to build, extend, and run custom AI solutions at scale—all in one system. It simplifies AI
development and operations, offering tools like the Prompt Optimizer and access to models like GPT-
4.1, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro.” sap.com
This differentiates SAP Business AI by enabling businesses to create bespoke AI applications while
leveraging SAP’s enterprise-grade infrastructure, ensuring flexibility and governance.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option B: Large foundation models
This is incorrect because SAP Business AI does not primarily differentiate itself through the
development or use of large foundation models (e.g., large language models or LLMs). Instead, SAP
partners with leading LLM providers (e.g., Cohere, Mistral AI, Meta) to integrate their models into
the SAP BTP Generative AI Hub, focusing on business-contextualized AI rather than building
proprietary LLMs. The SAP Business AI article on community.sap.com clarifies:
“SAP leverages a rich ecosystem of technology partner LLM offerings through SAP BTP’s AI
Foundation and Generative AI Hub, rather than developing SAP-specific LLMs. This approach ensures
access to the latest innovations while prohibiting partners from training on customer data.”
pages.community.sap.com
While SAP plans to fine-tune generic LLMs and create proprietary foundation models for structured
data (e.g., SAP Foundation Model for tabular data), these are not yet a primary differentiator
compared to the ecosystem, embedded AI, and AI Foundation. learning.sap.com
Option D: Predictive Analytics
This is incorrect because, while predictive analytics is a significant capability of SAP Business AI (e.g.,
forecasting demand in SAP Integrated Business Planning or predicting equipment failures in SAP
S/4HANA), it is not a unique differentiator. Predictive analytics is a common feature in many AI
platforms and is one of many capabilities within SAP Business AI, not a defining characteristic. The
SAP Business AI documentation on
www.fingent.com
notes:
“SAP Business AI solutions use machine learning and advanced analytics, including predictive
analytics, to gain insights into complex data. However, its differentiation lies in its integration with
business processes and data, not the analytics techniques alone.” fingent.com
The unique value of SAP Business AI comes from its ecosystem, embedded nature, and developer-
centric AI Foundation, rather than specific techniques like predictive analytics, which are widespread
across AI solutions.
Summary:
The key differentiators of SAP Business AI are its ecosystem of innovation (leveraging a robust
partner network for collaborative AI solutions), embedded AI (seamlessly integrated into SAP
applications for process optimization), and AI Foundation (providing a scalable toolkit for custom AI
development), corresponding to Options A, C, and E. Option B is incorrect because SAP relies on
partner LLMs rather than proprietary large foundation models as a differentiator. Option D is
incorrect because predictive analytics, while important, is not a unique differentiator compared to
the broader ecosystem and integration capabilities. These differentiators align with SAP’s strategy to
deliver relevant, reliable, and responsible AI within SAP Business Suite, as supported by the provided
search results and official documentation.
Reference:
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
Exploring SAP’s AI Strategy, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
SAP Business AI: Release Highlights Q1 2025, SAP News Center news.sap.com
SAP Sapphire Innovation Guide 2025,
www.sap.com
sap.com
SAP Business AI,
www.sap.com
sap.comsap.com
AI Foundation, SAP’s all-in-one AI toolkit, SAP Community community.sap.com
SAP Business AI: A Fundamental Change, IgniteSAP ignitesap.com
SAP Business AI: Revolutionizing Enterprise Decisions,
www.fingent.com
Question 15
Which transformation journey is the right one for new SAP ERP customers?
- A. RISE with SAP journey
- B. ACTIVATE with SAP journey
- C. GROW with SAP journey
- D. ACCELERATE with SAP journey
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The question asks which transformation journey is appropriate for new SAP ERP customers, meaning
organizations that are adopting SAP ERP for the first time or have minimal prior SAP experience.
According to official SAP documentation and the provided search results, GROW with SAP is the
transformation journey specifically designed for new SAP ERP customers, particularly midmarket
businesses or those seeking a rapid, standardized implementation of SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public
edition. This makes Option C the correct answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option C: GROW with SAP journey
This is correct because GROW with SAP is tailored for new SAP ERP customers, offering a
streamlined, cloud-based journey to adopt SAP Business Suite, specifically SAP S/4HANA Cloud,
public edition. It provides preconfigured best practices, a prescriptive methodology, and partner
expertise to accelerate implementation, making it ideal for organizations starting fresh with SAP or
those with simpler ERP needs. The Showcasing the Path for Customers to Adopt SAP Business Suite
lesson on learning.sap.com states:
“GROW with SAP supports new ERP customers in starting with SAP Business Suite, driving SAP’s
future growth alongside theirs. New customers always start with the public cloud. This journey
provides an ever-green SAP Business Suite, always on the latest version and innovations.”
learning.sap.com
The GROW with SAP journey is designed to help midmarket businesses or new SAP adopters
modernize their ERP landscape quickly, leveraging SAP Cloud ERP and SAP Business Technology
Platform (BTP) for scalability and efficiency. The How to Get Started With GROW with SAP Journey
article from datalark.com further elaborates:
“GROW with SAP is a digital transformation journey tailored to help mid-market businesses that
aspire to enhance operational efficiency. … Customers purchase one of the new SAP Business Suite
packages (e.g., SAP Finance Base), then expand by adding further lines of business. … GROW with
SAP allows mid-market businesses to streamline their ERP journey to SAP Business Suite
implementation.” datalark.com
Key features of GROW with SAP include standardized workflows, prebuilt content, and the SAP
Activate methodology, which ensure a fast time-to-value without the complexities of legacy system
migrations. This journey is particularly suited for greenfield implementations, where customers can
start with a clean core and adopt cloud-native innovations like SAP Business AI from the outset.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: RISE with SAP journey
This is incorrect because RISE with SAP is designed for existing SAP ERP customers, particularly those
with complex, on-premise landscapes (e.g., SAP ECC or SAP S/4HANA on-premise) looking to
transition to the cloud, either via SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition or public edition. It is not
tailored for new SAP customers who lack an existing SAP ERP footprint. The RISE with SAP page on
www.sap.com
states:
“RISE with SAP is a guided transformation journey designed for SAP ERP customers to quickly realize
the full potential of Business Suite, supported by proven methodologies, advanced tools, and expert
guidance. RISE with SAP is tailored for existing SAP ERP customers, enabling them to transition
seamlessly from on-premises ERP to Business Suite while modernizing their processes and
infrastructure at their own pace.” sap.com
The focus on legacy system modernization and complex transformations makes RISE with SAP
unsuitable for new customers starting with a clean slate.
Option B: ACTIVATE with SAP journey
This is incorrect because SAP Activate is not a transformation journey but a methodology used within
transformation journeys like RISE with SAP and GROW with SAP. It provides a structured framework,
templates, and best practices for implementing SAP solutions, but it is not a standalone customer-
facing journey. The GROW with SAP article from datalark.com notes:
“Speed up deployment with SAP Activate. This methodology includes templates, project timelines,
and best practices to ensure a smooth implementation.” datalark.com
Since SAP Activate is a toolset rather than a journey, it cannot be the correct choice for new SAP ERP
customers.
Option D: ACCELERATE with SAP journey
This is incorrect because there is no transformation journey called ACCELERATE with SAP in SAP’s
official offerings. The term “accelerate” may be used in marketing materials to describe the speed of
transformation (e.g., in RISE with SAP or GROW with SAP methodologies), but it is not a distinct
journey. The provided search results and SAP documentation, including Positioning SAP Business
Suite on learning.sap.com, do not reference an ACCELERATE with SAP journey, confirming that this is
a fictitious option.
Summary:
The appropriate transformation journey for new SAP ERP customers is the GROW with SAP journey,
as stated in Option C. This journey is designed for greenfield implementations, particularly for
midmarket businesses or those new to SAP, providing a fast, standardized path to SAP S/4HANA
Cloud, public edition within SAP Business Suite. Option A (RISE with SAP) is for existing SAP
customers with legacy systems, Option B (ACTIVATE with SAP) is a methodology, not a journey, and
Option D (ACCELERATE with SAP) does not exist. This aligns with SAP’s strategy to support new
customers with a cloud-native, scalable ERP solution, as validated by the provided search results and
official documentation.
Reference:
Showcasing the Path for Customers to Adopt SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com learning.sap.com
How to Get Started With GROW with SAP Journey, datalark.com datalark.com
RISE with SAP | Transformation Journey to SAP Business Suite,
www.sap.com
sap.com
Positioning SAP Business Suite, learning.sap.com
SAP Business Suite and Cloud ERP Overview, SAP Help Portal