python institute pcpp-32-101 practice test
Certified Professional in Python Programming 1
Question 1
Select the true statement about composition
- A. Composition extends a class's capabilities by adding new components and modifying the existing ones.
- B. Composition allows a class to be projected as a container of different classes
- C. Composition is a concept that promotes code reusability while inheritance promotes encapsulation.
- D. Composition is based on the has a relation: so it cannot be used together with inheritance.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Composition is an object-oriented design concept that models a has-a relationship. In composition, a
class known as composite contains an object of another class known as component. In other words, a
composite class has a component of another class
.
1. Composition allows a class to be projected as a container of different classes.
Composition is a concept in Python that allows for building complex objects out of simpler objects,
by aggregating one or more objects of another class as attributes. The objects that are aggregated
are generally considered to be parts of the whole object, and the containing object is often viewed as
a container for the smaller objects.
In composition, objects are combined in a way that allows for greater flexibility and modifiability
than what inheritance can offer. With composition, it is possible to create new objects by combining
existing objects, by using a container object to host other objects. By contrast, with inheritance, new
objects extend the behavior of their parent classes, and are limited by that inheritance hierarchy.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
Composition:
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/classes.html#composition
GeeksforGeeks article on Composition vs Inheritance:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/composition-
vs-inheritance-python/
Real Python article on Composition and Inheritance:
https://realpython.com/inheritance-
composition-python/
Question 2
Analyze the following snippet and select the statement that best describes it.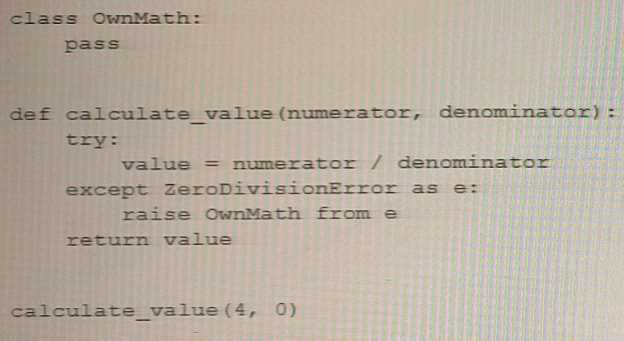
- A. The code is an example of implicitly chained exceptions.
- B. The code is erroneous as the OwnMath class does not inherit from any Exception type class
- C. The code is fine and the script execution is not interrupted by any exception.
- D. The code is an example of explicitly chained exceptions.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In the given code snippet, an instance of OwnMath exception is raised with an explicitly
specified __cause__ attribute that refers to the original exception (ZeroDivisionError). This is an
example of explicitly chaining exceptions in Python.
Question 3
Analyze the following snippet and choose the best statement that describes it.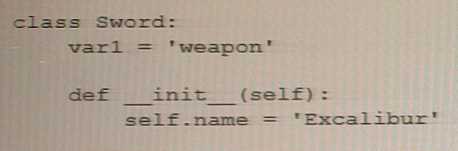
- A. self. name is the name of a class variable.
- B. varl is the name of a global variable
- C. Excalibur is the value passed to an instance variable
- D. Weapon is the value passed to an instance variable
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. Excalibur is the value passed to an instance variable. In the given code
snippet, self.name is an instance variable of the Sword class. When an instance of the Sword class is
created with varl = Sword('Excalibur'), the value 'Excalibur' is passed as an argument to
the __init__ method and assigned to the name instance variable of the varl object.
The code defines a class called Sword with an __init__ method that takes one parameter name.
When a new instance of the Sword class is created with varl = Sword('Excalibur'), the value of
the 'Excalibur' string is passed as an argument to the __init__ method, and assigned to
the self.name instance variable of the varl object.
Reference:
Official Python documentation on Classes:
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/classes.html
Question 4
The following snippet represents one of the OOP pillars Which one is that?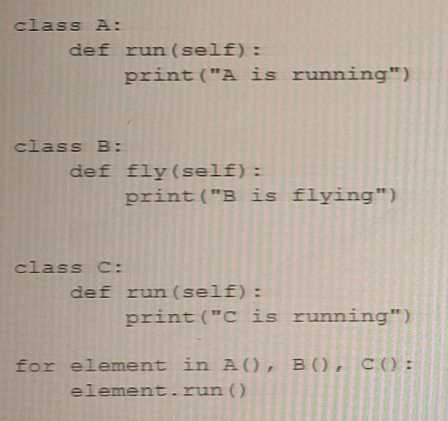
- A. Serialization
- B. Inheritance
- C. Encapsulation
- D. Polymorphism
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The given code snippet demonstrates the concept of encapsulation in object-oriented programming.
Encapsulation refers to the practice of keeping the internal state and behavior of an object hidden
from the outside world and providing a public interface for interacting with the object. In the given
code snippet, the __init__ and get_balance methods provide a public interface for interacting with
instances of the BankAccount class, while the __balance attribute is kept hidden from the outside
world by using a double underscore prefix.
Question 5
Analyze the following function and choose the statement that best describes it.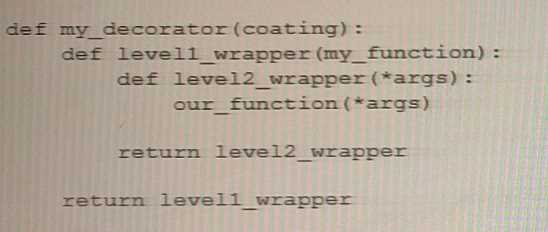
- A. It is an example of a decorator that accepts its own arguments.
- B. It is an example of decorator stacking.
- C. It is an example of a decorator that can trigger an infinite recursion.
- D. The function is erroneous.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In the given code snippet, the repeat function is a decorator that takes an
argument num_times specifying the number of times the decorated function should be called.
The repeat function returns an inner function wrapper_repeat that takes a function func as an
argument and returns another inner function wrapper that calls func num_times times.
The provided code snippet represents an example of a decorator that accepts its own arguments.
The @decorator_function syntax
is
used
to
apply
the decorator_function to
the some_function function. The decorator_function takes an argument arg1 and defines an inner
function wrapper_function that
takes
the
original
function func as
its
argument.
The wrapper_function then returns the result of calling func, along with the arg1 argument passed to
the decorator_function.
Here is an example of how to use this decorator with some_function:
@decorator_function("argument 1")
def some_function():
return "Hello world"
When some_function is called, it will first be passed as an argument to the decorator_function.
The decorator_function then
adds
the
string "argument
1" to
the
result
of
calling some_function() and returns the resulting string. In this case, the final output would be "Hello
world argument 1".
Reference:
Official Python documentation on Decorators:
https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-
decorator
Question 6
Analyze the following snippet and select the statement that best describes it.
- A. The code is syntactically correct despite the fact that the names of the function parameters do not follow the naming convention
- B. The *arg parameter holds a list of unnamed parameters
- C. The code is missing a placeholder for unnamed parameters.
- D. The code is syntactically incorrect - the function should be defined as def f1 (*args, **kwargs) :
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The provided code snippet defines a function f1 that accepts variable-length arguments using
the *args and **kwargs syntax. The *args parameter allows for an arbitrary number of unnamed
arguments to be passed to the function as a tuple, while the **kwargs parameter allows for an
arbitrary number of named arguments to be passed to the function as a dictionary.
Therefore, the correct statement that best describes the code is:
1. The *args parameter holds a list of unnamed parameters, while the **kwargs parameter holds a
dictionary of named parameters.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
Function
definitions:
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/controlflow.html#defining-functions
The arg parameter holds a list of unnamed parameters. In the given code snippet, the f1 function
takes two arguments: *arg and **kwarg. The *arg syntax in the function signature is used to pass a
variable number of non-keyword (positional) arguments to the function. Inside the function, arg is a
tuple containing the positional arguments passed to the function. The **kwarg syntax in the function
signature is used to pass a variable number of keyword arguments to the function. Inside the
function, kwarg is a dictionary containing the keyword arguments passed to the function.
Question 7
Analyze the following snippet and decide whether the code is correct and/or which method should
be distinguished as a class method.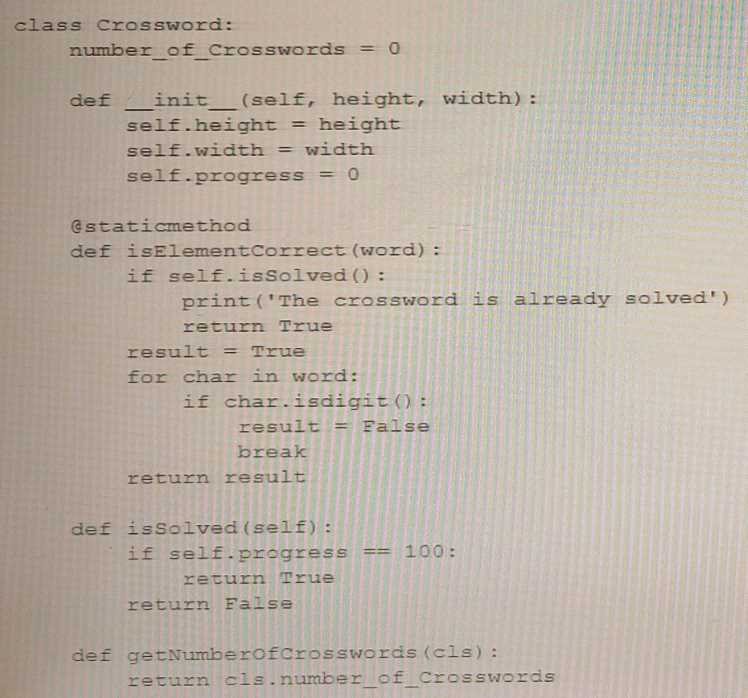
- A. There is only one initializer, so there is no need for a class method.
- B. The getNumberofCrosswords () method should be decorated With @classmethod.
- C. The code is erroneous.
- D. The gexNumberOfcrosswords () and issrived methods should be decorated with @classzoechod.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The correct answer is B. The getNumberofCrosswords() method should be decorated with
@classmethod. In the given code snippet, the getNumberofCrosswords method is intended to be a
class method that returns the value of the numberofcrosswords class variable. However, the method
is not decorated with the @classmethod decorator and does not take a cls parameter representing
the class itself. To make getNumberofCrosswords a proper class method, it should be decorated
with @classmethod and take a cls parameter as its first argument.
B. The getNumberofCrosswords() method should be decorated with @classmethod.
This is because the getNumberofCrosswords() method is intended to access the class-level
variable numberofcrosswords, but it is defined as an instance method, which requires an instance of
the class to be created before it can be called. To make it work as a class-level method, you can
define it as a class method by adding the @classmethod decorator to the function.
Here's an example of how to define getNumberofCrosswords() as a class method:
class Crossword:
numberofcrosswords = 0
def __init__(self, author, title):
self.author = author
self.title = title
Crossword.numberofcrosswords += 1
@classmethod
def getNumberofCrosswords(cls):
return cls.numberofcrosswords
In
this
example, getNumberofCrosswords() is
defined
as
a
class
method
using
the @classmethod decorator, and the cls parameter is used to access the class-level
variable numberofcrosswords.
Reference:
Official Python documentation on Classes:
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/classes.html
Question 8
Analyze the code and choose the best statement that describes it.
- A. ___ne___() is not a built-in special method
- B. The code is erroneous
- C. The code is responsible for the support of the negation operator e.g. a = - a.
- D. The code is responsible for the support of the inequality operator i.e. i =
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The correct answer is D. The code is responsible for the support of the inequality operator i.e. i != j.
In the given code snippet, the __ne__ method is a special method that overrides the behavior of the
inequality operator != for instances of the MyClass class. When the inequality operator is used to
compare two instances of MyClass, the __ne__ method is called to determine whether the two
instances are unequal.
Question 9
Which function or operator should you use to obtain the answer True or False to the question: "Do
two variables refer to the same object?"
- A. The = operator
- B. The isinstanceO function
- C. The id () function
- D. The is operator
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To test whether two variables refer to the same object in memory, you should use the is operator.
The is operator returns True if the two variables point to the same object in memory,
and False otherwise.
For example:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = a
c = [1, 2, 3]
print(a is b) # True
print(a is c) # False
In this example, a and b refer to the same list object in memory, so a is b returns True. On the other
hand, a and c refer to two separate list objects with the same values, so a is c returns False.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
Comparisons:
https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html#not-in
Official
Python
documentation
on
Identity
comparisons:
https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html#is
The is operator is used to test whether two variables refer to the same object in memory. If two
variables x and y refer to the same object, the expression x is y will evaluate to True. Otherwise, it
will evaluate to False.
Question 10
Which sentence about the ©property decorator is false?
- A. The ©property decorator should be defined after the method that is responsible for setting an encapsulated attribute.
- B. The @property decorator designates a method which is responsible for returning an attribute value
- C. The ©property decorator marks the method whose name will be used as the name of the instance attribute
- D. The ©property decorator should be defined before the methods that are responsible for setting and deleting an encapsulated attribute
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The @property decorator should be defined after the method that is responsible for setting an
encapsulated attribute is a false sentence. In fact, the @property decorator should be defined before
the method that is used to set the attribute value. The @property decorator and the setter and
deleter methods work together to create an encapsulated attribute, which is used to provide control
over the attribute's value.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
Property:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#property
The @property decorator is used to designate a method as a getter for an instance attribute. The
method decorated with @property should be defined before any setter or deleter methods for the
same attribute.
Question 11
Select the true statement about the___name___attribute.
- A. ___name___is a special attribute, which is inherent for both classes and instances, and it contains information about the class to which a class instance belongs.
- B. ___name is a special attribute, which is inherent for both classes and instances, and it contains a dictionary of object attributes.
- C. __name___is a special attribute, which is inherent for classes and it contains information about the class to which a class instance belongs.
- D. __name___is a special attribute, which is inherent for classes, and it contains the name of a class.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The true statement about the __name__ attribute is D. name is a special attribute, which is inherent
for classes, and it contains the name of a class. The __name__ attribute is a special attribute of
classes that contains the name of the class as a string.
The __name__ attribute is a special attribute in Python that is available for all classes, and it contains
the name of the class as a string. The __name__ attribute can be accessed from both the class and its
instances using the dot notation.
Reference:
Official Python documentation on Classes:
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/classes.html#class-
objects
Question 12
What is a static method?
- A. A method that works on the class itself
- B. A method decorated with the @method trait
- C. A method that requires no parameters referring to the class itself
- D. A method that works on class objects that are instantiated
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A static method is a method that belongs to a class rather than an instance of the class. It is defined
using the @staticmethod decorator and does not take a self or cls parameter. Static methods are
often used to define utility functions that do not depend on the state of an instance or the class itself.
Question 13
What is true about type in the object-oriented programming sense?
- A. It is the bottommost type that any object can inherit from.
- B. It is a built-in method that allows enumeration of composite objects
- C. It is the topmost type that any class can inherit from
- D. It is an object used to instantiate a class
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In Python, type is the built-in metaclass that serves as the base class for all new-style classes. All
new-style classes in Python, including built-in types like int and str, are instances of
the type metaclass and inherit from it.
Question 14
What does the term deserialization mean? Select the best answer.
- A. It is a process of creating Python objects based on sequences of bytes.
- B. It is a process of assigning unique identifiers to every newly created Python object
- C. It is another name for the data transmission process
- D. It is a process of converting the structure of an object into a stream of bytes
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Deserialization is the process of converting data that has been serialized
Explanation:or encoded in a specific format, back into its original form as an object or a data
structure in memory. In Python, this typically involves creating Python objects based on sequences of
bytes that have been serialized using a protocol such as JSON, Pickle, or YAML.
For example, if you have a Python object my_obj and you want to serialize it to a JSON string, you
might do something like this:
import json
serialized_obj = json.dumps(my_obj)
To deserialize the JSON string back into a Python object, you would use the json.loads() method:
deserialized_obj = json.loads(serialized_obj)
This would convert the JSON string back into its original Python object form.
Reference:
Official
Python
Documentation
on
Serialization:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html#module-pickle
Real Python Tutorial on Serialization and Deserialization in Python:
https://realpython.com/python-
serialization/
Deserialization is the process of converting a sequence of bytes, such as a file or a network message,
into a Python object. This is the opposite of serialization, which is the process of converting a Python
object into a sequence of bytes for storage or transmission.
Question 15
What is a___traceback___?
(Select two answers )
- A. An attribute owned by every exception object
- B. A special method delivered by the traceback module to retrieve a full list of strings describing the traceback
- C. An attribute that is added to every object when the traceback module is imported
- D. An attribute that holds interesting information that is particularly useful when the programmer wants to store exception details in other objects
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
The correct answers are A. An attribute owned by every exception object and D. An attribute that
holds interesting information that is particularly useful when the programmer wants to store
exception details in other objects. A traceback is an attribute of an exception object that contains a
stack trace representing the call stack at the point where the exception was raised. The traceback
attribute holds information about the sequence of function calls that led to the exception, which can
be useful for debugging and error reporting.