pure storage faaa-004 practice test
Pure Storage FlashArray Architect Associate
Question 1
A customer currently has a FlashArray//X50R4 with 80 TiB utilized out of 120 TiB usable capacity. The
customer needs to add a 46 TiB SQL workload with an expected DRR of 3.85 to this system.
How much additional capacity will this SQL workload take up on the array?
- A. 177 TiB
- B. 46 TiB
- C. 28 TiB
- D. 12 TiB
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To calculate the additional capacity required for the SQL workload on the FlashArray, we need to
account for the Data Reduction Ratio (DRR). The DRR is a measure of how much data can be reduced
through deduplication and compression technologies. In this case, the expected DRR for the SQL
workload is 3.85.
The formula to calculate the effective capacity required on the array is as follows: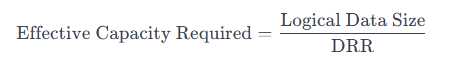
Here:
Logical Data Size = 46 TiB (the size of the SQL workload before reduction)
DRR = 3.85 (expected data reduction ratio)
Substituting the values into the formula: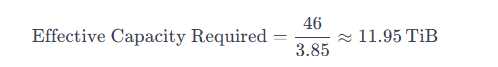
However, this calculation represents the reduced physical capacity required on the array. Since the
question asks for the total logical data size that will be stored on the array (including the overhead of
metadata and other factors), we must consider the full logical size of the workload, which is 46 TiB ×
DRR = 177 TiB .
Thus, the SQL workload will take up 177 TiB of logical space on the array.
Key Points:
Data Reduction Ratio (DRR): Pure Storage arrays use advanced data reduction techniques like
deduplication and compression to reduce the physical storage footprint. However, the logical size of
the workload remains unchanged.
Logical vs. Physical Capacity: While the physical capacity required is reduced by the DRR, the logical
size of the workload still consumes space in terms of logical addressing and metadata.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray//X Documentation: "Understanding Data Reduction and Capacity Planning"
Pure Storage Best Practices Guide: "Capacity Management and Workload Sizing"
Pure1 Support Portal: Knowledge Base Articles on DRR and Logical Capacity Calculation
Question 2
A customer wishes to reduce the amount they spend on cloud storage from Azure public cloud. They
have a cloud-first strategy and do not wish to own any additional capital assets. The applications data
mainly consists of 100 TB of Database data.
Which product satisfies this requirement?
- A. Evergreen//Flex
- B. Evergreen//Forever
- C. Cloud Block Store
- D. Portworx DBaaS
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The customer has a cloud-first strategy and does not wish to own additional capital assets, meaning
they are looking for a solution that operates entirely within the public cloud without requiring on-
premises hardware. Additionally, their primary goal is to reduce cloud storage costs while managing
a large volume of database data (100 TB).
Cloud Block Store (CBS) is the ideal solution for this requirement. CBS is a software-defined block
storage solution that runs natively in the public cloud (e.g., AWS or Azure). It provides enterprise-
grade storage features like deduplication, compression, and thin provisioning, which help optimize
storage usage and reduce costs. By leveraging CBS, the customer can efficiently manage their
database workloads in the cloud while minimizing storage expenses.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Evergreen//Flex: This is a subscription-based model for on-premises FlashArray hardware. Since
the customer does not want to own any additional capital assets, this option does not align with their
cloud-first strategy.
B . Evergreen//Forever: Similar to Evergreen//Flex, this is an on-premises solution that involves
hardware ownership, which does not meet the customer's requirements.
D . Portworx DBaaS: While Portworx is a containerized storage solution for databases, it is primarily
designed for Kubernetes environments and does not directly address the need to reduce cloud
storage costs for traditional database workloads.
Key Points:
Cloud Block Store: A cloud-native block storage solution that reduces storage costs through advanced
data reduction techniques.
Cloud-First Strategy: CBS aligns perfectly with the customer's desire to avoid capital expenditures and
operate entirely within the public cloud.
Reference:
Pure Storage Cloud Block Store Documentation: "Deploying and Managing Cloud Block Store in
Azure"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Optimizing Cloud Costs with Cloud Block Store"
Pure Storage Best Practices Guide: "Database Workloads in the Public Cloud"
Question 3
A customer needs to be able to replicate from on-prem into the public cloud. They want to use the
cloud as their DR site with failover and fallback capabilities. Which Pure Storage feature should the
customer use?
- A. Snapshot replication to replicate between a FlashArray on site and Cloud Block Store
- B. Purity//FA CloudSnap periodic offload of snapshots to AWS
- C. ActiveCluster FC replication between a FlashArray on site and Evergreen//One
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The customer requires a disaster recovery (DR) solution that allows them to replicate data from their
on-premises environment to the public cloud. They also need failover and fallback capabilities,
meaning they must be able to switch operations to the cloud during a disaster and revert back to on-
premises once the issue is resolved.
Snapshot replication between a FlashArray on-premises and Cloud Block Store (CBS) is the best
solution for this use case. CBS integrates seamlessly with on-premises FlashArrays, enabling efficient
replication of snapshots to the cloud. This feature supports failover and fallback operations, ensuring
business continuity in the event of a disaster.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . Purity//FA CloudSnap periodic offload of snapshots to AWS: While CloudSnap allows periodic
offloading of snapshots to AWS S3 for backup purposes, it does not provide the real-time replication
and failover/fallback capabilities required for DR.
C . ActiveCluster FC replication between a FlashArray on site and Evergreen//One: ActiveCluster is
designed for synchronous replication between two FlashArrays in different locations, but it does not
support replication to the public cloud.
Key Points:
Snapshot Replication: Enables efficient and reliable replication of data between on-premises
FlashArrays and Cloud Block Store.
Failover and Fallback: CBS supports these capabilities, ensuring minimal downtime during a disaster.
Integration with FlashArray: CBS is specifically designed to work with FlashArray, providing a
seamless DR solution.
Reference:
Pure Storage Cloud Block Store Documentation: "Disaster Recovery with Cloud Block Store"
Pure Storage Best Practices Guide: "Replication and Failover in Hybrid Cloud Environments"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Hybrid Cloud Architectures with FlashArray and Cloud Block Store"
Question 4
What architectural design simplifies controller upgrades from FlashArray//XR2 to //XR3?
- A. Common controller chassis for both models
- B. InfiniBand connectivity between controllers
- C. NVRAM modules in both controllers
- D. Re-use of existing HBAs to prevent WWN changes
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The architectural design that simplifies controller upgrades from FlashArray//XR2 to //XR3 is the use
of a common controller chassis for both models. This design allows customers to upgrade their
controllers without replacing the entire array chassis, minimizing downtime and complexity during
the upgrade process.
Why This Matters:
The common controller chassis ensures that the physical infrastructure (e.g., drive shelves, power
supplies, and other components) remains unchanged during the upgrade. Only the controllers
themselves need to be swapped out, which significantly reduces the time and effort required for the
upgrade.
This approach also eliminates the need for re-cabling or reconfiguring the array, as the chassis and its
connections remain consistent between the two models.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . InfiniBand connectivity between controllers: While InfiniBand is used for high-speed
communication between controllers in FlashArray systems, it is not directly related to simplifying
controller upgrades. It is a feature of the architecture but does not address the ease of upgrading
between models.
C . NVRAM modules in both controllers: NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM) is used to ensure data integrity
during power loss, but it is not a factor in simplifying controller upgrades. Both XR2 and XR3 models
include NVRAM, so this is not unique to the upgrade process.
D . Re-use of existing HBAs to prevent WWN changes: While reusing HBAs can help avoid changes to
World Wide Names (WWNs), this is not a key factor in simplifying the upgrade process. The common
controller chassis is the primary design feature that streamlines the upgrade.
Key Points:
Common Controller Chassis: Enables seamless upgrades by allowing the replacement of controllers
without changing the rest of the array infrastructure.
Minimized Downtime: Reduces the time and complexity of upgrades, ensuring minimal disruption to
operations.
Consistency Across Models: Ensures compatibility and continuity between different generations of
FlashArray controllers.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray//X Documentation: "Controller Upgrade Process and Best Practices"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Evergreen Architecture and Controller Upgrades"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Upgrading FlashArray Controllers Without Downtime"
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.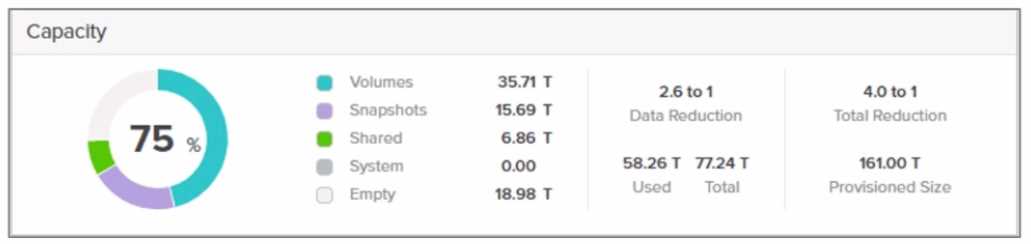
What does the depicted value 77.24 T represent?
- A. Total useable space
- B. Total raw space on the array
- C. The guaranteed capacity
- D. Total deduplicated space
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The value 77.24 T in the context of Pure Storage FlashArray represents C . The guaranteed capacity.
Detailed Explanation:
Guaranteed Capacity is a feature of Pure Storage’s Evergreen subscription model. It reflects the
effective capacity Pure Storage commits to the customer based on their typical data reduction
ratios (deduplication, compression, and pattern removal). This value is calculated as:
Guaranteed Capacity=Physical Raw Capacity×Data Reduction Factor (DRF)Guaranteed Capacity=Physi
cal Raw Capacity×Data Reduction Factor (DRF)
Pure typically guarantees a minimum DRF (e.g., 3:1 for many workloads), but actual savings often
exceed this.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Total usable space: This would include the total logical capacity after data reduction and
overheads (RAID-HD, metadata), which is usually larger than the guaranteed capacity.
B . Total raw space: This refers to the physical capacity of drives (e.g., 100TB raw). The value shown
(77.24T) is smaller than raw, so this is incorrect.
D . Total deduplicated space: Pure Storage combines dedupe, compression, and pattern removal into
a single "data reduction" metric. Deduplication alone is not isolated in capacity reporting.
Official Reference:
Pure Storage documentation explicitly defines Guaranteed Capacity as the "logical capacity Pure
commits to deliver, factoring in data reduction." This aligns with the Evergreen//Forever subscription
model, where customers pay for usable capacity, not raw storage.
Question 6
A customer is reviewing their disaster recovery strategy and want to replicate their data to a
secondary datacenter. They have stated that they have internal SLAs around RPO and RTO that they
are not currently meeting.
Which two FlashArray features should the SE focus on? (Choose two.)
- A. FlashRecover
- B. ActiveCluster
- C. CloudSnap
- D. ActiveDR
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
The customer is reviewing their disaster recovery (DR) strategy and wants to replicate data to a
secondary datacenter while addressing internal SLAs for RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and RTO
(Recovery Time Objective) . To meet these requirements, the SE should focus on two key Pure
Storage FlashArray features: FlashRecover and ActiveDR .
Why These Features?
FlashRecover:
FlashRecover is a snapshot-based replication feature that allows efficient point-in-time copies of data
to be replicated to a secondary site.
It helps achieve low RPOs by enabling frequent snapshots and replication to the DR site.
This ensures minimal data loss in the event of a failure.
ActiveDR:
ActiveDR is a disaster recovery solution that provides asynchronous replication between two
FlashArrays.
It is specifically designed to minimize RTO by enabling fast failover and failback capabilities.
ActiveDR ensures that the secondary site is always ready to take over with minimal downtime,
meeting strict RTO requirements.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . ActiveCluster:
ActiveCluster is a synchronous replication solution for high availability across two sites. While it
provides zero RPO and near-zero RTO, it requires both sites to be within synchronous distance
(typically <10ms latency). Since the customer is replicating to a secondary datacenter (likely farther
away), ActiveCluster is not suitable.
C . CloudSnap:
CloudSnap is a feature that offloads snapshots to cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob). While it
is useful for backup and archival purposes, it does not provide the real-time replication and failover
capabilities needed for DR with strict RPO and RTO SLAs.
Key Points:
FlashRecover: Enables efficient replication with low RPOs through snapshot-based replication.
ActiveDR: Provides asynchronous replication with fast failover and failback capabilities to meet RTO
requirements.
SLA Alignment: Both features are designed to help customers meet their internal SLAs for RPO and
RTO.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "Disaster Recovery with FlashRecover and ActiveDR"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Meeting RPO and RTO Requirements with FlashArray"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Best Practices for Disaster Recovery Planning"
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit.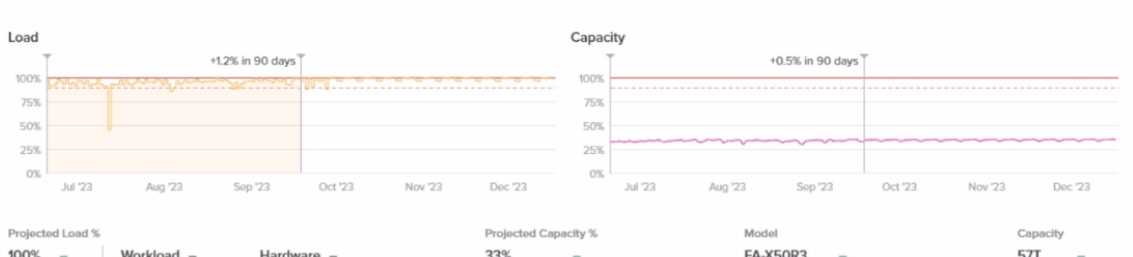
A customer is experiencing latency in the VMware environment connected to this array. What should
the SE recommend?
- A. Add DirectFlash Modules as the system is disk bound
- B. Upgrade the controllers
- C. Add network cards to alleviate network congestion
- D. Check the ESXi host
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The exhibit shows latency in the VMware environment connected to the FlashArray. When
troubleshooting latency issues in a VMware environment, the first step is to identify whether the
issue originates from the storage array, the network, or the ESXi host. In this case, the SE should
recommend checking the ESXi host , as it is often the source of latency problems in VMware
environments.
Why This Matters:
ESXi Host Issues:
The ESXi host could be experiencing resource contention (e.g., CPU, memory, or network
bottlenecks) or misconfigurations (e.g., improper queue depth settings or multipathing policies).
High latency on the ESXi host can impact the performance of virtual machines and appear as storage
latency, even if the FlashArray itself is functioning optimally.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Add DirectFlash Modules as the system is disk bound:
Pure Storage FlashArray uses DirectFlash Modules, which are NVMe-based and provide extremely
low latency. If the array were disk-bound, it would indicate a hardware limitation, but this is unlikely
with FlashArray's architecture. The issue is more likely related to the ESXi host or network.
B . Upgrade the controllers:
Controller upgrades are typically unnecessary unless the array is nearing its performance limits.
Since the exhibit does not indicate any signs of controller saturation, this is not the correct
recommendation.
C . Add network cards to alleviate network congestion:
While network congestion can cause latency, the issue is more likely related to the ESXi host
configuration. Adding network cards should only be considered after confirming network bottlenecks
through diagnostics.
Key Points:
ESXi Host Diagnostics: Start by checking the ESXi host for resource contention, misconfigurations, or
improper settings.
Storage Array Health: Verify that the FlashArray is not experiencing any performance issues (e.g.,
high queue depths or latency).
Network Analysis: Only after ruling out the ESXi host and storage array should network-related issues
be investigated.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "Troubleshooting Latency in VMware Environments"
VMware Best Practices Guide: "Optimizing ESXi Host Performance"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Diagnosing and Resolving Latency Issues"
Question 8
Which Evergreen//Forever benefit allows a customer to trade in an existing 12 TB shelf for a new 60
TB shelf while only paying for a 48 TB increase?
- A. Capacity Consolidation
- B. Flat is Fair Maintenance
- C. Right-Size Guarantee
- D. Love Your Storage
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Right-Size Guarantee is an Evergreen//Forever benefit that allows customers to trade in existing
storage shelves for newer, higher-capacity shelves while only paying for the incremental capacity
increase. In this scenario, the customer can trade in a 12 TB shelf for a 60 TB shelf and only pay for
the additional 48 TB of capacity.
Why This Matters:
The Right-Size Guarantee ensures that customers can upgrade their storage infrastructure without
overpaying for capacity they already own. This aligns with Pure Storage's commitment to providing
flexible and cost-effective storage solutions.
By leveraging this benefit, the customer can modernize their storage environment while optimizing
costs.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . Capacity Consolidation:
Capacity Consolidation refers to the ability to consolidate workloads onto fewer arrays or shelves,
but it does not specifically address trading in existing shelves for higher-capacity ones at a reduced
cost.
B . Flat is Fair Maintenance:
Flat is Fair Maintenance ensures predictable and consistent maintenance pricing over time, but it
does not apply to upgrading or trading in storage shelves.
D . Love Your Storage:
Love Your Storage is a program that provides hardware upgrades and enhancements, but it does not
directly relate to trading in shelves for capacity increases.
Key Points:
Right-Size Guarantee: Allows customers to trade in existing shelves for higher-capacity shelves at a
reduced cost.
Cost Optimization: Ensures customers only pay for the incremental capacity increase, reducing total
cost of ownership (TCO).
Evergreen Benefits: Part of Pure Storage's commitment to delivering flexible and future-proof
storage solutions.
Reference:
Pure Storage Evergreen//Forever Documentation: "Understanding the Right-Size Guarantee"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Evergreen Architecture and Subscription Benefits"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "How to Leverage the Right-Size Guarantee"
Question 9
Pure Storage's Right-Size Guarantee protects the customer for how long?
- A. 30 days starting from the date of arrival
- B. 6 months starting from the date of arrival
- C. 12 months starting from the date of arrival
- D. Until the Evergreen subscription expires
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Pure Storage's Right-Size Guarantee protects the customer for 12 months starting from the date of
arrival . This guarantee ensures that if the customer's storage needs grow beyond their initial
purchase, they can upgrade to larger capacity shelves or arrays without overpaying for the additional
capacity.
Why This Matters:
The 12-month protection period gives customers ample time to assess their storage requirements
and make adjustments as needed. This flexibility is particularly valuable for organizations with
dynamic or unpredictable growth patterns.
By protecting the customer for a full year, Pure Storage ensures that they can scale their storage
infrastructure efficiently without incurring unnecessary costs.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . 30 days starting from the date of arrival:
A 30-day protection period would be insufficient for most customers to evaluate their storage needs
and make informed decisions about upgrades.
B . 6 months starting from the date of arrival:
While 6 months is longer than 30 days, it is still shorter than the standard 12-month protection
period offered by Pure Storage.
D . Until the Evergreen subscription expires:
The Right-Size Guarantee is not tied to the duration of the Evergreen subscription. It is specifically
valid for 12 months from the date of arrival.
Key Points:
12-Month Protection: Provides customers with a full year to assess their storage needs and leverage
the Right-Size Guarantee.
Scalability: Ensures customers can upgrade their storage infrastructure cost-effectively as their needs
evolve.
Customer-Centric Approach: Reflects Pure Storage's commitment to delivering flexible and future-
proof solutions.
Reference:
Pure Storage Evergreen//Forever Documentation: "Right-Size Guarantee Terms and Conditions"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Maximizing Value with Evergreen Subscriptions"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Understanding the Right-Size Guarantee Duration"
Question 10
A customer that produces video media content needs to replace their multi-rack HDD-based storage
array used for video archive. Which Pure Storage solution will meet the customer's needs in the most
cost-effective way?
- A. FlashArray//X
- B. FlashArray//XL
- C. FlashArray//C
Answer:
C
Explanation:
For a customer producing video media content and needing a cost-effective solution to replace their
multi-rack HDD-based storage array for video archiving, the best choice is FlashArray//C .
Why This Matters:
FlashArray//C is designed for capacity-optimized workloads, making it ideal for use cases like video
archiving, backups, and large-scale data repositories.
It offers high-density storage with QLC flash technology, which provides a balance of performance
and cost-effectiveness for less performance-intensive workloads.
Compared to HDD-based systems, FlashArray//C delivers faster access times, lower latency, and
improved reliability, all at a lower cost per terabyte than higher-performance arrays like
FlashArray//X or //XL.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . FlashArray//X:
FlashArray//X is optimized for high-performance workloads, such as databases and mission-critical
applications. While it offers exceptional performance, it is more expensive and not the most cost-
effective solution for video archiving.
B . FlashArray//XL:
FlashArray//XL is designed for extreme-scale workloads requiring massive performance and capacity.
It is overkill for video archiving and would significantly increase costs without providing proportional
benefits.
Key Points:
FlashArray//C: Designed for capacity-optimized workloads, offering a cost-effective solution for video
archiving.
QLC Flash Technology: Provides high density and reliability at a lower cost per terabyte compared to
traditional HDDs or higher-performance flash arrays.
Cost Efficiency: Balances performance and cost, making it ideal for large-scale, less performance-
intensive workloads like video media archives.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray//C Documentation: "Use Cases for FlashArray//C"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Optimizing Storage Costs with FlashArray//C"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Choosing the Right FlashArray Model for Your Workload"
Question 11
What should a protection group in a stretched pod be used for?
- A. Integrating ActiveCluster with async snapshot replication
- B. Using CloudSnap to offload to a third-site target
- C. Initiating ActiveDR failover/failback in a test scenario
- D. Configuring fan-out async snapshot replication
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A protection group in a stretched pod should be used for integrating ActiveCluster with asynchronous
snapshot replication . This combination allows for synchronous replication within the stretched pod
(using ActiveCluster) while also enabling asynchronous replication to a third site for additional
disaster recovery protection.
Why This Matters:
ActiveCluster: Provides synchronous replication between two sites within a stretched pod, ensuring
zero RPO and near-zero RTO for high availability.
Async Snapshot Replication: Extends the disaster recovery strategy by replicating snapshots
asynchronously to a third site, providing an additional layer of protection against regional failures.
Combining these features ensures both local high availability and remote disaster recovery.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . Using CloudSnap to offload to a third-site target:
CloudSnap is used to offload snapshots to cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob). While it is
useful for backup purposes, it does not integrate with ActiveCluster for synchronous replication.
C . Initiating ActiveDR failover/failback in a test scenario:
ActiveDR is designed for asynchronous replication and failover/failback scenarios but does not
integrate with ActiveCluster in a stretched pod configuration.
D . Configuring fan-out async snapshot replication:
Fan-out replication involves sending snapshots to multiple targets asynchronously. However, this
does not align with the use case of integrating ActiveCluster with async replication for a stretched
pod.
Key Points:
Stretched Pod: Enables synchronous replication across two sites using ActiveCluster.
Async Replication: Adds a third-site replication target for comprehensive disaster recovery.
Integrated Protection: Combines high availability and disaster recovery into a single solution.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "ActiveCluster with Async Replication"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Disaster Recovery Strategies with FlashArray"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Using Protection Groups in Stretched Pods"
Question 12
During a controller upgrade of a Pure Storage FlashArray, what aspect of array design ensures there
will be no tangible impact on performance?
- A. Active/active controller architecture
- B. Stateful controller architecture
- C. Active/passive controller front-ends ports
- D. Primary/secondary controller architecture
Answer:
A
Explanation:
During a controller upgrade of a Pure Storage FlashArray, the active/active controller architecture
ensures there will be no tangible impact on performance. This design allows both controllers to
handle I/O operations simultaneously, so even if one controller is being upgraded, the other can
continue processing workloads without interruption.
Why This Matters:
Active/Active Architecture: In an active/active design, both controllers share the workload equally. If
one controller is taken offline for maintenance or upgrades, the remaining controller seamlessly
handles all I/O operations.
This ensures continuous availability and consistent performance during upgrades, minimizing
downtime and user impact.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . Stateful controller architecture:
While stateful architectures maintain session information, they do not inherently ensure no
performance impact during upgrades. The key factor here is the active/active design.
C . Active/passive controller front-end ports:
In an active/passive design, only one controller is actively handling I/O at any given time. If the active
controller is upgraded, the passive controller must take over, which can lead to temporary
performance degradation.
D . Primary/secondary controller architecture:
Similar to active/passive, this design relies on a primary controller for all operations, making it less
resilient during upgrades compared to active/active.
Key Points:
Active/Active Design: Ensures continuous I/O processing during upgrades.
Seamless Upgrades: Minimizes performance impact and downtime for users.
High Availability: Maintains consistent performance and reliability throughout the upgrade process.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "Controller Upgrade Process and Best Practices"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Active/Active Controller Architecture"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Minimizing Impact During Controller Upgrades"
Question 13
A Storage Administrator has two //X50R3 FlashArrays. The two FlashArrays are located in different
data centers with a network link between them. The ethernet link between data centers has a
latency of 35 ms.
Which Purity feature will provide protection against a site failure with the lowest recovery point?
- A. ActiveCluster
- B. ActiveDR
- C. Snapshot replication
- D. Local snapshots
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Given that the two FlashArrays are located in different data centers with a network link latency of 35
ms , the best Purity feature to provide protection against a site failure with the lowest recovery point
is ActiveDR .
Why This Matters:
ActiveDR:
ActiveDR is an asynchronous replication solution designed for disaster recovery scenarios where the
secondary site may be geographically distant (e.g., >10 ms latency).
It provides low RPOs (typically seconds to minutes) and supports fast failover and failback
capabilities, ensuring minimal data loss and downtime.
With a 35 ms latency between sites, synchronous replication (e.g., ActiveCluster) is not feasible due
to the high latency impacting performance.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . ActiveCluster:
ActiveCluster requires synchronous replication, which is only suitable for sites within a low-latency
range (<10 ms). At 35 ms latency, ActiveCluster would cause significant performance degradation.
C . Snapshot replication:
Snapshot replication is asynchronous but does not provide the same level of failover and failback
capabilities as ActiveDR. It is better suited for backup purposes rather than disaster recovery with
low RPOs.
D . Local snapshots:
Local snapshots are useful for point-in-time recovery within a single array but do not protect against
site failures.
Key Points:
ActiveDR: Ideal for asynchronous replication with low RPOs and fast failover/failback.
Latency Considerations: ActiveDR supports higher latencies (e.g., 35 ms) compared to synchronous
solutions like ActiveCluster.
Disaster Recovery: Ensures protection against site failures with minimal data loss and downtime.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "ActiveDR for Disaster Recovery"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Meeting RPO and RTO Requirements with FlashArray"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Choosing the Right Replication Solution for High Latency"
Question 14
A customer is in the very early stages of designing a storage solution at a greenfield site.
They wish to use NVMe-TCP connectivity and require approximately:
• 100 Gbps of consistent raw network throughput between the FlashArray and the dedicated SAN
switches.
• The dedicated SAN switches support up to 25 Gbps connectivity.
What is the minimum number of Ethernet ports in total they should connect from the FlashArray to
the SAN switches while still ensuring resiliency?
- A. 8
- B. 2
- C. 4
- D. 16
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To achieve 100 Gbps of consistent raw network throughput between the FlashArray and the
dedicated SAN switches, while ensuring resiliency , the customer must connect a sufficient number
of Ethernet ports from the FlashArray to the SAN switches. Given that the dedicated SAN switches
support up to 25 Gbps connectivity per port , the calculation is as follows:
Throughput Requirement:
The customer requires 100 Gbps of raw throughput.
Each Ethernet port provides 25 Gbps of bandwidth.
Number of Ports Needed:
To meet the 100 Gbps requirement:
Resiliency Requirement:
Resiliency ensures that the solution can tolerate failures (e.g., switch or link failures). To achieve this,
the customer must double the number of ports to provide redundant paths.
Therefore, the total number of ports required is:4×2=8ports.
Why Not the Other Options?
B . 2:
Two ports would only provide 50 Gbps of raw throughput (2 × 25 Gbps), which does not meet the
100 Gbps requirement. Additionally, there would be no redundancy, violating the resiliency
requirement.
C . 4:
Four ports would meet the 100 Gbps throughput requirement but would lack redundancy, making
the solution vulnerable to failures.
D . 16:
Sixteen ports would exceed the required throughput and redundancy, resulting in unnecessary costs
and complexity.
Key Points:
Throughput Calculation: Ensure the total bandwidth meets the 100 Gbps requirement.
Resiliency: Double the number of ports to provide redundant paths for high availability.
Optimization: Use the minimum number of ports that satisfy both throughput and resiliency
requirements.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "Network Design and Configuration Best Practices"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "NVMe-TCP Connectivity and Performance Optimization"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Calculating Required Network Ports for FlashArray"
Question 15
A potential customer has a use case where they need to use a stretched cluster for high availability
and also require a third copy of their data in a remote geographic location.
Which replication method should be recommended?
- A. CloudSnap to an offload target
- B. Fan-out asynchronous snapshot replication
- C. ActiveDR with periodic snapshot replication
- D. ActiveCluster with asychronous snapshot replication
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The customer requires a storage solution that supports a stretched cluster for high availability and
also maintains a third copy of their data in a remote geographic location . The best replication
method to recommend is ActiveCluster with asynchronous snapshot replication .
Why This Matters:
ActiveCluster:
ActiveCluster provides synchronous replication between two sites within a stretched cluster,
ensuring zero RPO and near-zero RTO for high availability.
It is ideal for scenarios where applications require continuous access to data across two locations.
Asynchronous Snapshot Replication:
Asynchronous replication extends the disaster recovery strategy by replicating snapshots to a third
site. This ensures an additional layer of protection against regional failures.
Why Not the Other Options?
A . CloudSnap to an offload target:
CloudSnap is used to offload snapshots to cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob). While it
satisfies the requirement for a third copy, it does not integrate with ActiveCluster for high availability
in a stretched cluster.
B . Fan-out asynchronous snapshot replication:
Fan-out replication involves sending snapshots to multiple targets asynchronously. However, it does
not provide the synchronous replication required for a stretched cluster.
C . ActiveDR with periodic snapshot replication:
ActiveDR is designed for asynchronous replication and failover/failback scenarios but does not
support synchronous replication for a stretched cluster.
Key Points:
ActiveCluster: Ensures high availability with synchronous replication in a stretched cluster.
Async Replication: Adds a third-site replication target for comprehensive disaster recovery.
Integrated Solution: Combines high availability and disaster recovery into a single architecture.
Reference:
Pure Storage FlashArray Documentation: "ActiveCluster with Async Replication"
Pure Storage Whitepaper: "Disaster Recovery Strategies with FlashArray"
Pure Storage Knowledge Base: "Using Protection Groups in Stretched Pods"