palo alto networks sse-engineer practice test
Palo Alto Networks Security Service Edge Engineer
Question 1
A customer is implementing Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) to connect mobile
users, branch locations, and business-to- business (B2B) partners to their data centers.
The solution must meet these requirements:
The mobile users must have internet filtering, data center connectivity, and remote site connectivity
to the branch locations.
The branch locations must have internet filtering and data center connectivity.
The B2B partner connections must only have access to specific data center internally developed
applications running on non-standard ports.
The security team must have access to manage the mobile user and access to branch locations.
The network team must have access to manage only the partner access.
How should Prisma Access be implemented to meet the customer requirements?
- A. Deploy two Prisma Access instances - the first with mobile users, remote networks, and private access for all internal connection types, and the second with remote networks and private application access for B2B connections - and use the Strata Multitenant Cloud Manager Prisma Access configuration scope to manage access.
- B. Deploy a Prisma Access instance with mobile users, remote networks, and private access for all connection types, and use the Prisma Access Configuration scope to manage all access.
- C. Deploy two Prisma Access instances - the first with mobile users, remote networks, and private access for all internal connection types, and the second with remote networks and private application access for B2B connections - and use the specific configuration scope for the connection type to manage access.
- D. Deploy a Prisma Access instance with mobile users, remote networks, and private access for all connection types, and use the specific configuration scope for the connection type to manage access.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To meet the customer’s requirements, two separate Prisma Access instances should be deployed:
Instance 1 should include mobile users, remote networks, and private access for internal
connectivity. This ensures that mobile users can access the internet, data centers, and remote branch
locations while enforcing security policies.
Instance 2 should be configured with remote networks and private application access for B2B
connections. This instance will restrict access to only the required internally developed applications
using non-standard ports, ensuring that partners cannot access other corporate resources.
By using specific configuration scopes for different connection types, the security team can manage
access to mobile users and branch locations, while the network team can manage B2B partner
connections. This ensures proper segmentation of management responsibilities while maintaining
security and compliance.
Question 2
A customer is implementing Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) to connect mobile
users, branch locations, and business-to- business (B2B) partners to their data centers.
The solution must meet these requirements:
The mobile users must have internet filtering, data center connectivity, and remote site connectivity
to the branch locations.
The branch locations must have internet filtering and data center connectivity.
The B2B partner connections must only have access to specific data center internally developed
applications running on non-standard ports.
The security team must have access to manage the mobile user and access to branch locations.
The network team must have access to manage only the partner access.
How can the engineer configure mobile users and branch locations to meet the requirements?
- A. Use GlobalProtect and Remote Networks to filter internet traffic and provide access to data center resources using service connections.
- B. Use Explicit Proxy to filter internet traffic and provide access to data center resources using service connections.
- C. Use GlobalProtect to filter internet traffic and provide access to data center resources using service connections.
- D. Use Explicit Proxy and Remote Networks to filter internet traffic and provide access to data center resources using service connections.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To meet the customer’s requirements, GlobalProtect and Remote Networks should be used as
follows:
GlobalProtect: This enables secure access for mobile users, ensuring internet filtering, data center
connectivity, and access to branch locations.
Remote Networks: This is used to provide security and connectivity for branch locations, ensuring
internet filtering and data center access.
Service Connections: These allow both mobile users and branch locations to securely connect to the
data center for internal resources.
This configuration ensures that mobile users and branch locations can securely access the internet
while maintaining a segregated and secure connection to internal resources. It also aligns with
Prisma Access's best practices for security enforcement, traffic filtering, and centralized
management.
Question 3
A customer is implementing Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) to connect mobile
users, branch locations, and business-to- business (B2B) partners to their data centers.
The solution must meet these requirements:
The mobile users must have internet filtering, data center connectivity, and remote site connectivity
to the branch locations.
The branch locations must have internet filtering and data center connectivity.
The B2B partner connections must only have access to specific data center internally developed
applications running on non-standard ports.
The security team must have access to manage the mobile user and access to branch locations.
The network team must have access to manage only the partner access.
Which two options will allow the engineer to support the requirements? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure the CPE with Static Routes pointing to Prisma Access Infrastructure and Mobile User routes.
- B. Enable eBGP for dynamic routing and configure RemoteNetworks.
- C. Configure Remote Networks and define the branch IP subnets using Static Routes.
- D. Enable Remote Networks Advertise Default Route.
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
Enabling eBGP for dynamic routing and configuring Remote Networks ensures seamless connectivity
between branch locations, mobile users, and the data center. eBGP allows Prisma Access to
dynamically exchange routes with the Customer Premises Equipment (CPE), optimizing path
selection without requiring manual updates. Configuring Remote Networks and defining branch IP
subnets using static routes ensures controlled and segmented routing, aligning with security policies.
This setup provides proper internet filtering, data center connectivity, and restricted access for B2B
partners while keeping management responsibilities aligned.
Question 4
A customer is implementing Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) to connect mobile
users, branch locations, and business-to- business (B2B) partners to their data centers.
* The solution must meet these requirements:
* The mobile users must have internet filtering, data center connectivity, and remote site
connectivity to the branch locations.
* The branch locations must have internet filtering and data center connectivity.
* The B2B partner connections must only have access to specific data center internally developed
applications running on non-standard ports.
* The security team must have access to manage the mobile user and access to branch locations.
* The network team must have access to manage only the partner access.
Which two components can be provisioned to enable data center connectivity over the internet?
(Choose two.)
- A. ZTNA Connector
- B. SD-WAN Connector
- C. Service connections
- D. Colo-Connect
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
Service connections enable secure connectivity between Prisma Access and on-premises data
centers, allowing mobile users and branch locations to access internal applications. They facilitate
seamless integration of internal networks with Prisma Access while maintaining security policies.
Colo-Connect provides a dedicated and optimized pathway for traffic between Prisma Access and
data centers, ensuring stable performance and reduced latency over the internet. Both components
together support secure and efficient data center connectivity while aligning with the customer's
access control and filtering requirements.
Question 5
Which two actions can a company with Prisma Access deployed take to use the Egress IP API to
automate policy rule updates when the IP addresses used by Prisma Access change? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure a webhook to receive notifications of IP address changes.
- B. Copy the Egress IP API Key in the service infrastructure settings.
- C. Enable the Egress IP API endpoint in Prisma Access.
- D. Download a client certificate to authenticate to the Egress IP API.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Configuring a webhook allows the company to receive real-time notifications when Prisma Access
changes its egress IP addresses, ensuring that policy rules are updated automatically. Downloading a
client certificate is necessary for authentication to the Egress IP API, allowing secure API access for
retrieving updated IP addresses. These actions ensure that security policies remain effective without
manual intervention.
Question 6
How can an engineer verify that only the intended changes will be applied when modifying Prisma
Access policy configuration in Strata Cloud Manager (SCM)?
- A. Review the SCM portal for blue circular indicators next to each configuration menu item and ensure only the intended areas of configuration have this indicator.
- B. Compare the candidate configuration and the most recent version under "Config Version Snapshots/
- C. Select the most recent job under Operations > Push Status to view the pending changes that would apply to Prisma Access.
- D. Open the push dialogue in SCM to preview all changes which would be pushed to Prisma Access.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Palo Alto Networks documentation explicitly states that the "Preview Changes" functionality within
the Strata Cloud Manager (SCM) push dialogue allows engineers to review a detailed summary of all
modifications that will be applied to the Prisma Access configuration before committing the changes.
This is the primary and most reliable method to ensure only the intended changes are deployed.
Let's analyze why the other options are incorrect based on official documentation:
A . Review the SCM portal for blue circular indicators next to each configuration menu item and
ensure only the intended areas of configuration have this indicator. While blue circular indicators
might signify unsaved changes within a specific configuration section, they do not provide a
comprehensive, consolidated view of all pending changes across different policy areas. This method
is insufficient for verifying the entirety of the intended modifications.
B . Compare the candidate configuration and the most recent version under "Config Version
Snapshots". While comparing configuration snapshots is a valuable method for understanding
historical changes and potentially identifying unintended deviations after a push, it does not provide
a real-time preview of the pending changes before they are applied during the current modification
session
C . Select the most recent job under Operations > Push Status to view the pending changes that
would apply to Prisma Access. The "Push Status" section primarily displays the status and details of
completed or in-progress push operations. It does not offer a preview of the changes before a push is
initiated.
Therefore, the "Preview Changes" feature within the push dialogue is the documented and
recommended method for an engineer to verify that only the intended changes will be applied when
modifying Prisma Access policy configuration in Strata Cloud Manager (SCM).
Question 7
When using the traffic replication feature in Prisma Access, where is the mirrored traffic directed for
analysis?
- A. Specified internal security appliance
- B. Dedicated cloud storage location
- C. Panorama
- D. Strata Cloud Manager (SCM)
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Palo Alto Networks documentation clearly states that when configuring the traffic replication feature
in Prisma Access, you must specify an internal security appliance as the destination for the mirrored
traffic. This appliance, typically a Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewall or a third-party security
tool, is responsible for receiving and analyzing the replicated traffic for various purposes like threat
analysis, troubleshooting, or compliance monitoring.
Let's analyze why the other options are incorrect based on official documentation:
B . Dedicated cloud storage location: While Prisma Access logs and other data might be stored in the
cloud, the mirrored traffic for real-time analysis is directly streamed to a designated security
appliance, not a passive storage location.
C . Panorama: Panorama is the centralized management system for Palo Alto Networks firewalls.
While Panorama can receive logs and manage the configuration of Prisma Access, it is not the direct
destination for real-time mirrored traffic intended for immediate analysis.
D . Strata Cloud Manager (SCM): Strata Cloud Manager is the platform used to configure and manage
Prisma Access. It facilitates the setup of traffic replication, including specifying the destination
appliance, but it does not directly receive or analyze the mirrored traffic itself.
Therefore, the mirrored traffic from the traffic replication feature in Prisma Access is directed to a
specified internal security appliance for analysis.
Question 8
When a review of devices discovered by IoT Security reveals network routers appearing multiple
times with different IP addresses, which configuration will address the issue by showing only unique
devices?
- A. Add the duplicate entries to the ignore list in IoT Security.
- B. Merge individual devices into a single device with multiple interfaces.
- C. Create a custom role to merge devices with the same hostname and operating system.
- D. Delete all duplicate devices, keeping only those discovered using their management IP addresses.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When network routers appear multiple times with different IP addresses in IoT Security, it is likely
because they have multiple interfaces with separate IPs. Merging these entries into a single device
with multiple interfaces ensures that the system correctly identifies each router as a unique entity
while maintaining visibility across all its interfaces. This approach prevents unnecessary duplicates,
improves asset management, and enhances security monitoring.
Question 9
What is the impact of selecting the “Disable Server Response Inspection” checkbox after confirming
that a Security policy rule has a threat protection profile configured?
- A. Only HTTP traffic from the server to the client will bypass threat inspection.
- B. The threat protection profile will override the 'Disable Server Response Inspection1 only for HTTP traffic from the server to the client.
- C. All traffic from the server to the client will bypass threat inspection.
- D. The threat protection profile will override the 'Disable Server Response Inspection1 for all traffic from the server to the client.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Selecting the “Disable Server Response Inspection” checkbox means that traffic flowing from the
server to the client will not be inspected for threats, even if a threat protection profile is applied to
the Security policy rule. This setting can reduce processing overhead but may expose the network to
threats embedded in server responses, such as malware or exploits.
Question 10
A company has a Prisma Access deployment for mobile users in North America and Europe. Service
connections are deployed to the data centers on these continents, and the data centers are
connected by private links.
With default routing mode, which action will verify that traffic being delivered to mobile users
traverses the service connection in the appropriate regions?
- A. Configure BGP on the customer premises equipment (CPE) to prefer the assigned community string attribute on the mobile user prefixes in its respective Prisma Access region.
- B. Configure each service connection to filter out the mobile user pool prefixes from the other region in the advertisements to the data center.
- C. Configure BGP on the customer premises equipment (CPE) to prefer the MED attribute on the mobile user prefixes in its respective Prisma Access region.
- D. Configure each service connection to prepend the BGP ASN five times for mobile user pool prefixes originating from the other region.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Prisma Access's default routing mode, the service connections establish BGP sessions with the
customer premises equipment (CPE) in the data centers. To ensure traffic destined for mobile users
in a specific region (e.g., North America) traverses the service connection in that same region, you
need to control the route advertisements.
Filtering out the mobile user pool prefixes from the other region on each service connection achieves
this by:
Preventing the data center in one region from learning the specific mobile user prefixes of the other
region. For example, the North American service connection would filter out the mobile user pool
prefixes allocated to European users.
Ensuring that when a data center needs to send traffic to a mobile user, it will only see and use the
route advertised by the service connection in the appropriate geographical region. This forces the
traffic to enter the Prisma Access infrastructure through the intended regional service connection.
Let's analyze why the other options are incorrect based on official documentation regarding default
routing mode:
A . Configure BGP on the customer premises equipment (CPE) to prefer the assigned community
string attribute on the mobile user prefixes in its respective Prisma Access region. While BGP
communities can be used for influencing routing decisions, in the context of default routing mode
and ensuring regional traffic flow, relying solely on the CPE to prefer community strings might not be
the most robust or direct method to guarantee traffic traverses the correct regional service
connection. The service connection itself needs to control the advertisement of prefixes.
C . Configure BGP on the customer premises equipment (CPE) to prefer the MED attribute on the
mobile user prefixes in its respective Prisma Access region. The BGP MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator)
attribute is primarily used to influence the path selection between autonomous systems (AS) or
within the same AS at different entry points. In this scenario, where service connections are
advertising prefixes, filtering at the source (service connection) is a more direct and reliable way to
ensure regional traffic flow than relying on the MED attribute on the CPE.
D . Configure each service connection to prepend the BGP ASN five times for mobile user pool
prefixes originating from the other region. BGP AS path prepending is a mechanism to make a path
less desirable. While this could influence routing, it doesn't guarantee that traffic will always take the
intended regional path. Filtering provides a more definitive control over which routes are advertised
and learned.
Therefore, configuring each service connection to filter out the mobile user pool prefixes from the
other region in the advertisements to the data center is the verified method to ensure traffic
destined for mobile users traverses the service connection in the appropriate region when using
Prisma Access in default routing mode.
Question 11
Based on the image below, which two statements describe the reason and action required to resolve
the errors? (Choose two.)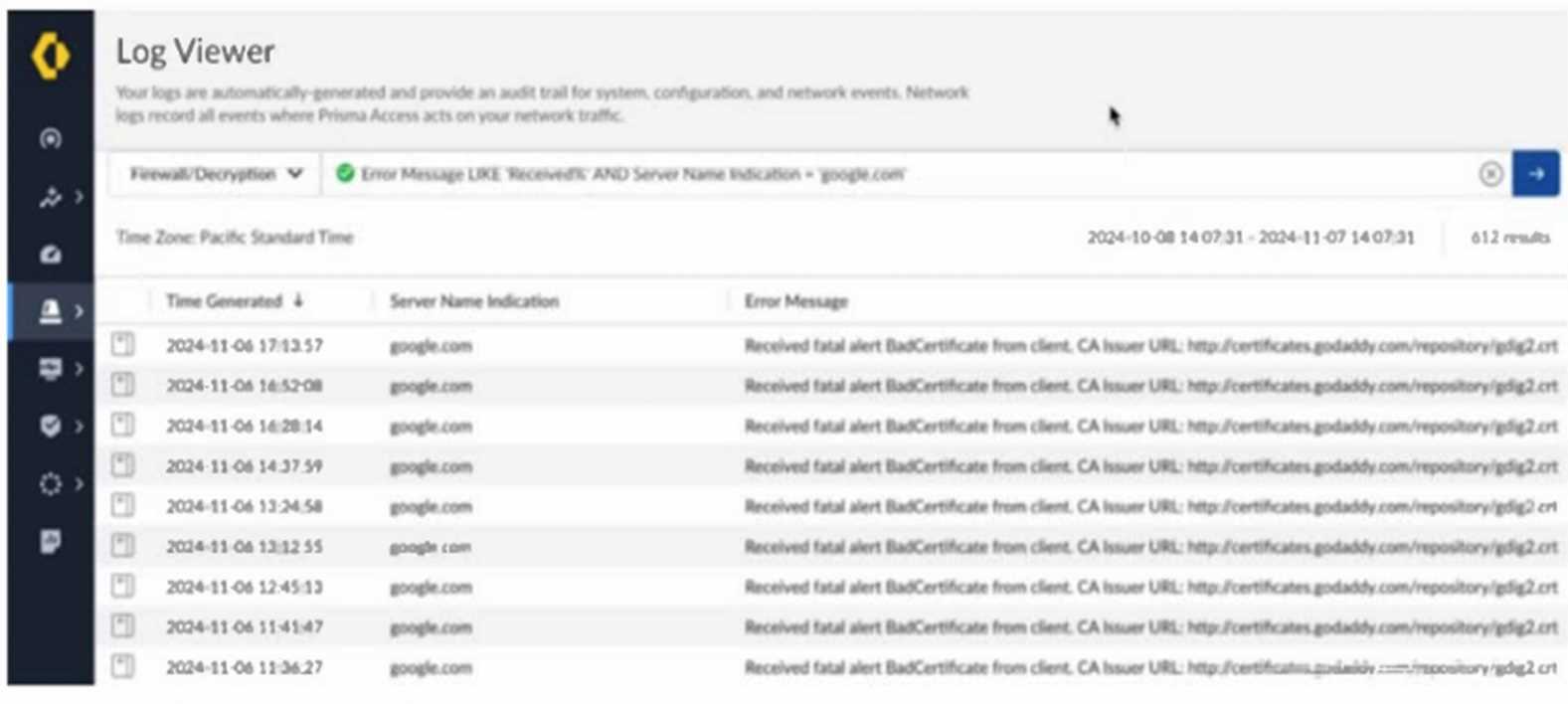
- A. The client is misconfigured.
- B. Create a do not decrypt rule for the hostname “google.com.”
- C. The server has pinned certificates.
- D. Create a do not decrypt rule for the hostname “certificates.godaddy.com.”
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
The error messages indicate that Prisma Access is encountering certificate issues while attempting to
decrypt traffic to "google.com." This suggests that the server has pinned certificates, meaning it does
not allow man-in-the-middle (MITM) decryption by Prisma Access. Since pinned certificates prevent
traffic decryption, a solution is to create a "do not decrypt" rule for the hostname "google.com." This
will allow traffic to flow without triggering certificate errors while maintaining secure communication
with Google's servers.
Question 12
How can a network security team be granted full administrative access to a tenant's configuration
while restricting access to other tenants by using role-based access control (RBAC) for Panorama
Managed Prisma Access in a multitenant environment?
- A. Create an Access Domain and restrict access to only the Device Groups and Templates for the Target Tenant.
- B. Create a custom role enabling all privileges within the specific tenant's scope and assign it to the security team's user accounts.
- C. Create a custom role with Device Group and Template privileges and assign it to the security team's user accounts.
- D. Set the administrative accounts for the security team to the "Superuser" role.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In a Panorama Managed Prisma Access multitenant environment, Access Domains provide granular
role-based access control (RBAC). By defining an Access Domain, the network security team can be
granted full administrative privileges for a specific tenant's configuration while ensuring they cannot
access or modify other tenants. This method enforces proper segmentation and ensures compliance
with multitenant security policies.
Question 13
An engineer has configured a Web Security rule that restricts access to certain web applications for a
specific user group. During testing, the rule does not take effect as expected, and the users can still
access blocked web applications.
What is a reason for this issue?
- A. The rule was created with improper threat management settings.
- B. The rule was created in the wrong scope, affecting only GlobalProtect users instead of all users.
- C. The rule was created at a higher level in the rule hierarchy, giving priority to a lower-level rule.
- D. The rule was created at a lower level in the rule hierarchy, giving priority to a higher-level rule.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Prisma Access applies security rules in a hierarchical order, where rules at higher levels take
precedence over those at lower levels. If a more permissive rule is placed higher in the hierarchy, it
may allow traffic before the restrictive Web Security rule is evaluated. To resolve this, the engineer
should reorder the rules to ensure the restrictive Web Security rule is positioned higher in the
hierarchy so it is applied before any broader or conflicting rules.
Question 14
What will cause a connector to fail to establish a connection with the cloud gateway during the
deployment of a new ZTNA Connector in a data center?
- A. There is a misconfiguration in the DNS settings on the connector.
- B. The connector is deployed behind a double NAT.
- C. The connector is using a dynamic IP address.
- D. There is a high latency in the network connection.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A ZTNA Connector requires a stable and direct connection to the cloud gateway. When the connector
is deployed behind a double NAT (Network Address Translation), it can cause issues with reachability
and session establishment because the cloud gateway may not be able to properly identify and
communicate with the connector. Double NAT can interfere with secure tunneling, IP address
resolution, and authentication mechanisms, leading to connection failures. To resolve this, the
connector should be placed in a network segment with a single NAT or a public IP assignment.
Question 15
Which feature will fetch user and group information to verify whether a group from the Cloud
Identity Engine is present on a security processing node (SPN)?
- A. SASE Health Dashboard
- B. User Activity Insights
- C. Prisma Access Locations
- D. Region Activity Insights
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The SASE Health Dashboard provides visibility into user and group synchronization between the
Cloud Identity Engine and the Security Processing Nodes (SPNs). It allows administrators to verify
whether a group from the Cloud Identity Engine is properly fetched and available on the SPN for
policy enforcement. This feature helps in troubleshooting identity-based access control issues and
ensures that user group mappings are correctly applied within Prisma Access.