oracle 1z0-580 practice test
Solaris 11 Installation and Configuration Essentials Exam
Question 1
Which two actions are used to permanently configure a new interface?
- A. dladm set-linkprop mtu=1500 net2
- B. ipadm create-addr –T static –a 10.2.3.5/24 net2/v4static
- C. ipadm create-addr –a local=2ff0::f3ad/64 –T static –t net2/v6dhcp
- D. ipadm create-ip net2
Answer:
B, D
Question 2
Which Oracle Solaris 1l milestone is equivalent to run level 2 on an Oracle Solaris 10 or earlier
system?
- A. svc:/milestone/single-user:default
- B. svc:/milestone/multi-user:default
- C. svc:/milestone/multi-user-server:default
- D. svc:/milestone/network:default
- E. svc:/milestone/self-assembly-complete:default
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Note:
* The services started by svc.startd are referred to as milestones. The milestone concept replaces the
traditional run levels that were used in previous versions of Solaris. A milestone is a special type of
service that represents a group of services. A milestone is made up of several SMF services. For
example, the services that instituted run levels S, 2, and 3 in previous version of Solaris are now
represented by milestone services named:
milestone/single-user (equivalent to run level S)
milestone/multi-user (equivalent to run level 2)
milestone/multi-user-server (equivalent to run level 3)
* Shut down the system.
# shutdown -iinit-state -ggrace-period -y
-iinit-state
Brings the system to an init state that is different from the default of S. The choices are 0, 1, 2, 5, and
6.
Run levels 0 and 5 are states reserved for shutting the system down. Run level 6 reboots the system.
Run level 2 is available as a multiuser operating state.
Question 3
The command "pkg list n *mysql-5?" produced the following output: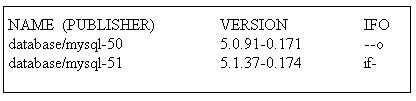
The IFO column of this output indicates that_______.
- A. both versions of mysql are installed and version 5.0.91-0.171 is older
- B. neither version of mysql is installed but either one can be selected for installation
- C. version 5.0-91-0.171 is obsolete and cannot be selected for installation
- D. version 5.1.37-0.1/4 is installed and can be updated
- E. either version of mysql can be updated
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Version 5.1.37-0.1/4 is installed (see note 1 below) and this version can be updated (see note 2
below).
Note:
* 1 The i in the I column indicates that these packages are installed in this image.
2 An f in the F column indicates the package is frozen. If a package is frozen, you can only install or
update to packages that match the frozen version.
* The pkg list command tells you whether a package is installed in the current image and whether an
update is available. With no options or operands, this command lists all packages that are installed in
the current image. To narrow your results, provide one or more package names. You can use
wildcards in the package names. Package variants for an architecture or zone type that does not
match this image are not listed.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Showing Package Install State Information
Question 4
Which IPS task requires special privileges?
- A. Determine if a package is installed or can be updated.
- B. Identify the group to which a package belongs.
- C. Determine if a package is in a particular category.
- D. Determine if a package delivers a specified file.
- E. Create a copy of an existing IPS package repository.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Tasks such as installing and updating IPS packages, setting publishers, and modifying images require
more privilege.
Incorrect answers:
Getting Information About Software Packages
No special privileges are needed to run any of the following commands.
Commands that give you the following kinds of information about packages:
(not A) Whether the package is installed or can be updated
The description, size, and version of the package
(not B) Which packages are part of a group package
(not C) Which packages are in a particular category
(not D) Which package delivers a specified file
No special privileges are needed to run any of these commands.
Reference: Adding and Updating Oracle Solaris 11 Software Packages, Installation Privileges
Question 5
You have just completed a default Oracle Solaris 11 installation of a new server system. While testing
network connectivity from your desktop to the server, you find that you are not able to communicate
with the "sendmail" service from your desktop. Why is this?
- A. By default, the "sendmail" software is not installed.
- B. By default, "sendmail" is not enabled on the system.
- C. By default, "sendmail'' access is blocked by TCP Wrappers.
- D. By default, "sendmail" responds to local requests only.
- E. By default, "sendmail" is running on its encrypted port.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Note:
* sendmail
* Enabling Access to Remote Clients
On an unmodified system, access to sendmail by remote clients is enabled and disabled through the
service management facility (see smf(5)). In particular, remote access is determined by the value of
the local_only SMF property:
svc:/network/smtp:sendmail/config/local_only = true
A setting of true, as above, disallows remote access; false allows remote access. The default value is
true.
The following example shows the sequence of SMF commands used to enable sendmail to allow
access to remote systems:
# svccfg -s svc:/network/smtp:sendmail setprop config/local_only = false
# svcadm refresh svc:/network/smtp:sendmail
# svcadm restart svc:/network/smtp:sendmail
Reference:
man pages section 1M: System Administration Commands, sendmail
Question 6
Which line would you remove in the GRUB's menu to prevent an automatic installation from
commencing when booting from CD or DVD, but without intentions of installing?
- A. install=default
- B. install=true
- C. install=always
- D. install=yes
- E. install=now
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To ensure the system boots without starting the installation, make sure the entry you choose to boot
does not have the install=true boot property specified in its kernel line.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Express Automated Installer Guide, Boot the Install Environment
Without Starting an Installation
Question 7
Which command would be used to restore the gedit package to its original as-delivered state?
- A. pkg revert gedit
- B. pkg restore gedit
- C. pkg update gedit@original
- D. pkg reinstall gedit
- E. pkg reset gedit
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Use the pkg revert command to restore files to their as-delivered condition.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library, Fixing Package Problems
Question 8
Which resource controls should you use to maximize consistency of CPU performance? Select all that
apply.
- A. CPU share
- B. CPU cap
- C. RAM cap
- D. Dedicated CPUs
- E. Locked memory cap
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
A: project.cpu-shares
Number of CPU shares granted to this project for use with the fair share scheduler
B: project.cpu-cap
Absolute limit on the amount of CPU resources that can be consumed by a project. A value of 100
means 100% of one CPU as the project.cpu-cap setting. A value of 125 is 125%, because 100%
corresponds to one full CPU on the system when using CPU caps.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Configuring Resource Controls and Attributes
Question 9
In planning a system's initial configuration, you realize that you may not have disk space to complete
an installation that contains all of Oracle Solaris 11 software. Which installation method would be
your safest bet to begin the interactive installation process?
- A. Automated installer
- B. Text based installer
- C. LiveMedia, or LiveDVD image
- D. Distribution constructor
- E. USB-based installer
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Live Media provides administrators with an opportunity to explore the Oracle Solaris 11.1
environment without installing it on a system. The system boots off the media directly allowing
administrators to start the installer should they choose to install it to a system.
Note:
* You have several alternatives for where to install Oracle Solaris 11:
Inside a virtual machine on top of your existing operating system
On the bare metal as a standalone operating system
On the bare metal alongside your existing operating system(s) (multiboot scenario)
Question 10
You are attempting to create an iSCSI LUN on your Oracle Solaris 11 server. You type m the following
command to enable the storage server / COMSTAR package and you receive the following output.
What is the problem?
- A. The correct package name is COMSTAR.
- B. You have not installed the storage-server package from your IPS repository
- C. You have mistyped the service name. It is called stmfadm.
- D. The Oracle Solaris 11 software repository is missing.
- E. You need to install the stmf command first by typing root@solaris:~# svcadm install stamf.
Answer:
E
Explanation:
'stamf' doesn't match any instances
Note:
* Enabling the COMSTAR service
COMSTAR runs as a SMF-managed service and enabling is no different than usual. First of all, check if
the service is running:
# svcs \*stmf\*
STATE
STIME FMRI
disabled
11:12:50 svc:/system/stmf:default
If the service is disable, enable it:
# svcadm enable svc:/system/stmf:default
After that, check that the service is up and running:
# svcs \*stmf\*
STATE
STIME FMRI
online
11:12:50 svc:/system/stmf:default
# stmfadm list-state
Operational Status: online
Config Status : initialized
ALUA Status
: disabled
ALUA Node
: 0
Question 11
The Oracle Solaris Image Packaging System (IPS) ________.
- A. requires the administrator to create software repositories
- B. requires a network connection to the Oracle software repositories
- C. automatically includes and installs required software dependence
- D. can be used on Oracle Solaris 10 with SVR4 packages
- E. can be used to manage remote systems' repositories
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Note:
* In many cases, one software package depends on another package. For example, one package
might require functionality that is in a second package in order to function or install correctly. These
relationships, or dependencies, between packages are important for automating package installation
operations and for upgrading system software to known and well-tested states. IPS supports a
number of different relationships between packages.
Incorrect:
Not B: IPS relies on network-accessible or locally available software repositories as a delivery
mechanism.
Not D:
Table, SVR4 and IPS Package Command Equivalents
SVR4 Package Command
IPS Package Command Equivalent
pkgadd
pkg install
patchadd
pkg update
pkgrm
pkg uninstall
pkgadm addcert, pkgadm removecert
pkg set-publisher -k, -c, --approve-ca-cert, --revoke-ca-cert, unset-ca-cert
pkginfo, pkgchk -l
pkg info, pkg list, pkg contents, pkg search
pkgchk
pkg verify, pkg fix, pkg revert
Question 12
The Oracle Solaris Image Packaging System (IPS) cannot be used to_____.
- A. manage local software repositories
- B. create new software repositories
- C. create new Oracle Solaris 11 boot environments
- D. restore an installed file to its original content
- E. manage permissions of installed software
Answer:
E
Explanation:
Incorrect:
not A: IPS relies on network-accessible or locally available software repositories as a delivery
mechanism, which is similar to how other operating systems (notably Oracle Linux) supply
software updates.
not D: can be done with the pkg command.
Note:
* Image Packaging System (IPS) is a new network based package management system included in
Oracle Solaris 11. It provides a framework for complete software lifecycle management such as
installation, upgrade and removal of software packages.
Safe system upgrades with ZFS boot environments
Network package repositories of software
Efficient downloads and automatic dependency checking
Support for disconnected data center environments
Extensive package publishing tools
Question 13
What physical devices will be used in sequence to boot the system, given the following output?
- A. disk then net
- B. /pci@780/pci@0/pci@1/network@0 then/pci@780/pci@0/pci@9/scsi@0/disk@0
- C. /pci@780/pci@0/pci@9/scsi@0 then/pci780/pci@0/pci@1/networking@0
- D. /pci@780/pci@0/pci@9/scsi@0/disk@1 then/pci780/pci@0/pci@1/networking@0,1
- E. /pci@780/pci@0/pci@9/scsi@0/disk@0 then/pci780/pci@0/pci@1/networking@0
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Note:
* second line in exhibit (minor typo):
boot-device = disk net
*The line starting with net is:
/pci@780/pci@0/pci@1/network@0
Question 14
Best practice for creating local IPS repositories recommends_______.
- A. avoiding the use of ZFS to host repositories
- B. creating a separate ZFS file system for each repository
- C. hosting local repositories on separate servers
- D. replicating all publishers across all repository servers
- E. creating one large repository for all required software
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Recommended best practice is to create a separate ZFS file system for your local package repository.
Using a separate ZFS file system enables you to take advantage of the following benefits:
Achieve better performance.
Set separate file system characteristics.
Directly snapshot and recover specified file systems.
If one system hosts more than one IPS repository, make each repository a separate ZFS file system so
that you can rollback and recover each repository separately.
Reference: Copying and Creating Oracle Solaris 11 Package Repositories, Prepare the Repository Host
System
Question 15
Three zones each need access to shared data. Which configuration method can be used to safely
achieve this goal?
- A. Put the data on an NFS server, and mount that share from each zone.
- B. Put the data on an NFS server, mount the share in the global zone, and configure a loopback mount from the global zone into each zone using zonecfg.
- C. Create an iSCSI LUN on a remote server, accessible to the global zone. Give each zone direct access to the LUN.
- D. Create a LUN on a SAN and give the global zone access to it. Give each zone direct device access to the LUN.
- E. Create a ZFS file system and utilize the cloning feature to replicate the data to the individual zones.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
How to Loopback Mount a File That Is Usually Not Visible in a Labeled Zone
This procedure enables a user in a specified labeled zone to view files that are not exported from the
global zone by default.
1. Halt the zone whose configuration you want to change.
# zoneadm -z zone-name halt
2. Loopback mount a file or directory.
For example, enable ordinary users to view a file in the /etc directory.
# zonecfg -z zone-name
add filesystem
set special=/etc/filename
set directory=/etc/filename
set type=lofs
add options [ro,nodevices,nosetuid]
end
exit
Note - Certain files are not used by the system, so that loopback mounting them has no effect. For
example, the /etc/dfs/dfstab file in a labeled zone is not checked by Trusted Extensions software. For
more information, see Sharing Files From a Labeled Zone.
3. Start the zone.
# zoneadm -z zone-name boot
Note:
* In this Solaris release, you create a ZFS file system share and publish the share as follows:
Create the file system share and define the NFS or SMB share properties by using the zfs share
command.
* ZFS File Sharing Within a Non-Global Zone
In previous Solaris releases, you could not create and publish NFS or SMB shares in a Oracle Solaris
non-global zone. In this Solaris release, you can create and publish NFS shares by using the zfs set
share command and the legacy share command with a non-global zone.
* If a ZFS file system is mounted and available in a non-global zone, it can be shared in that zone.
* A file system can be shared in the global zone if it is not mounted in a non-global zone or is not
shared to a non-global zone.
* If a ZFS file system's mountpoint property set to legacy, the file system can be shared by using the
legacy share command.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Express, Managing Zones
these 2 is correct