oracle 1z0-580 practice test
Oracle Solaris 11 Installation and Configuration Essentials
Question 1
What information would the "beadm list -ds" command output?
- A. a list of all Bes
- B. a list of the datasets and snapshot information for the active BE
- C. a list of the datasets and snapshot information for all Bes
- D. a list of the default sets
- E. a list of BEs in machine readable format
Answer:
C
Explanation:
You can display information about snapshots, boot environments, and datasets that were created by
the beadm command by using the beadm list subcommand. The beadm list command output also
displays boot environments that are created by the pkg command.
The beadm list command syntax is:
Syntax: beadm list [-a | [-ds] [-H] [BeName]
The command lists information about the existing boot environment. To view information for a
specific boot environment, replace BeName with a boot environment name. If a specific boot
environment is not specified, the command lists information about all boot environments. The
default is to list boot environments without additional information.
-a Lists all available information about the boot environment. This information includes
subordinate datasets and snapshots.
-d Lists information about all subordinate datasets that belong to the boot environment.
-s Lists information about the snapshots of the boot environment.
-H Prevents listing header information. Each field in the output is separated by a semicolon.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Listing Existing Boot Environments and Snapshots
Question 2
What two entries could complete the following command from the directory listing below?
- A. inetboot.SUN4U.Solaris_10-1
- B. inetboot.SUN4V.Solaris_l0-1
- C. nbp.
- D. pxegrub.I86PC.Solaris_10-1
- E. sllgrub.i86pc
Answer:
D, E
Explanation:
As per exhibit these are the two files in the netboot directory.
Note:
*Missing argument is:
file=wanbootCGI-URL
Specifies the URL of the wanboot-cgi program on the web server
* During the installation, WAN boot refers to the contents of the /etc/netboot hierarchy on the web
server for instructions about how to perform the installation. This directory contains the
configuration information, private key, digital certificate, and certificate authority required for a WAN
boot installation. During the installation, the wanboot-cgi program converts this information into the
WAN boot file system. The wanboot-cgi program then transmits the WAN boot file system to the
client.
Question 3
A developer wants to use DTrace in a zone to examine the kernel. What are his options?
- A. Modify the zone so that he can use DTrace to examine kennel data structures.
- B. All that’s required is to assume the "root" role.
- C. By using dtrace_proc and dtrace_user privileges he can examine his own code, but not the kernel.
- D. By adding ipc_dac_read and ipc_dac_write privileges to the zone.
- E. Change the zone's file-mac-profile from strict to none to enable the use of DTrace within the zone.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
How to Use DTrace in a Non-global Zone
1. Use the zonecfg limitpriv property to add the dtrace_proc and dtrace_user privileges.
global# zonecfg -z my-zone
zonecfg:my-zone> set limitpriv="default,dtrace_proc,dtrace_user"
zonecfg:my-zone> exit
Note
Depending on your requirements, you can add either privilege, or both privileges.
2. Boot the zone.
3. global# zoneadm -z my-zone boot
Log in to the zone.
global# zlogin my-zone
4. Run the DTrace program.
my-zone# dtrace -l
Note:
* Oracle Solaris DTrace is a comprehensive, advanced tracing tool for troubleshooting systemic
problems in real time.
* DTrace helps you understand a software system by enabling you to dynamically modify the
operating system kernel and user processes to record additional data that you specify at locations of
interest, called probes.
Reference: System Administration Guide: Oracle Solaris Containers-Resource Management and
Oracle Solaris Zones, Using DTrace in a Non-Global Zone
Question 4
Your system has two disk devices, c2t0d0 and c2t1d0, and two flash devices, c2t5d0 and c2t8d0.
Which command would you to create a storage pool named tank, which mirrors the disks and adds
the two flash devices as cache?
- A. zpool create tank mirror c2t0d0 c2t1d0 mirror c2t5d0 c2t8d0
- B. zpool create tank mirror c2t0d0 c2t1d0 log mirror c2t5d0 c2t8d0
- C. zpool c2t0d0 c2t1d0 cache c2t5d0 c2t8d0 mirror
- D. zpool create tank mirror c2t0d0 c2t1d0 cache c2t5d0 c2t8d0
- E. zpool create tank raidz2 c2t0d0 c2t1d0 c2t5d0 c2t8d0
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Creating a ZFS Storage Pool with Cache Devices
You can create a storage pool with cache devices to cache storage pool data. For example:
# zpool create tank mirror c2t0d0 c2t1d0 c2t3d0 cache c2t5d0 c2t8d0
Note:
* Creating a Basic Storage Pool
The following command creates a new pool named tank that consists of the disks c1t0d0 and c1t1d0: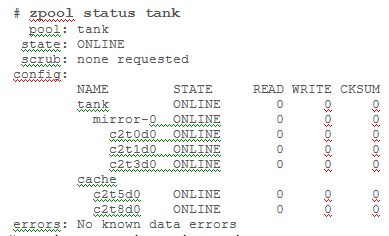
# zpool create tank c1t0d0 c1t1d0
These whole disks are found in the /dev/dsk directory and are labelled appropriately by ZFS to
contain a single, large slice. Data is dynamically striped across both disks.
* Creating a Mirrored Storage Pool
To create a mirrored pool, use the mirror keyword, followed by any number of storage devices that
will comprise the mirror. Multiple mirrors can be specified by repeating the mirror keyword on the
command line. The following command creates a pool with two, two-way mirrors:
# zpool create tank mirror c1d0 c2d0 mirror c3d0 c4d0
Reference: Solaris ZFS Administration Guide, Creating a ZFS Storage Pool with Cache Devices
Question 5
The "pkg update" command will ______.
- A. update all packages that have updates available including the kernel
- B. update all packages that have updates available excluding the kernel
- C. update only the kernel image
- D. update the global zone packages and non-global zone packages
- E. update all packages and the kernel, and then automatically reboot the system
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Updating all of the packages on your installed system To update all of the packages on your system
that have available updates, use the pkg update command, as follows:
# pkg update
Running this command updates packages that you might not otherwise consider updating, for
example, kernel components and other low-level system packages.
Question 6
What three items are true with regard to network planning in a Solaris 11 environment?
- A. Hardware and network topology should be planned in advance of installation.
- B. Subnetting needs to be considered when implementing IPv6 networks.
- C. IPv4 and IPv6 network addressing cannot co-exist on the same server.
- D. Solaris 11 enables the use of local files, NIS, DNS, or LDAP for name services.
- E. The physical network topology will determine if you need routers, not all networks require routers.
Answer:
A, C, D
Explanation:
The following table lists different tasks for planning the network configuration.
* (A) Identify the hardware requirements of your planned network topology.
Determine the types of equipment that you need for your network site.
*(C) Determine the type of IP addresses to use and obtain registered IP addresses.
Select whether you are deploying a purely IPv4 network, an IPv6 network, or a network that uses
both types of IP addresses. Obtain unique IP addresses to communicate to public networks in the
Internet.
* (D) Determine a naming scheme to identify the hosts in the network as well as the name service to
use.
Create a list of names to assign to the systems on the network and decide whether to use NIS, LDAP,
DNS, or the network databases in the local /etc directory.
* If necessary, establish administrative subdivisions and design a strategy for subnets.
Decide if your site requires that you divide your network into subnets to service administrative
subdivisions
* Determine where to place routers in the network design.
If your network is large enough to require routers, create a network topology that supports them.
* Decide whether to create virtual networks in the overall network configuration scheme.
You might need to create virtual networks within a system to reduce the hardware footprint of your
network.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Network Planning (Task Map)
Question 7
To upgrade a system from Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris 11, it is necessary to________.
- A. convert all Oracle Solaris 10 packages to Oracle Solaris 11 packages using IPS
- B. use IPS and Live Upgrade to install all updated software
- C. use IPS to replace the Oracle Solaris 10 kernel with the Oracle Solaris 11 kernel
- D. save user data and perform a new Oracle Solaris 11 install; there is no upgrade method
- E. update Oracle Solaris 10 from an Oracle Solaris 11 repository
Answer:
D
Explanation:
There are no upgrade methods or tools available to transition from Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris
11. You cannot use an installer to upgrade from Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris 11.
Oracle Solaris 11 Transition Tools and Features
Note:
* There are no upgrade methods or tools available to transition from Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle
Solaris 11. You cannot use an installer to upgrade from Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris 11.
/ JumpStart Migration Utility (js2ai)
Used to convert Oracle Solaris 10 JumpStart rules and profiles to a format that is compatible with AI
manifest entries.
/ ZFS shadow migration feature
Used to migrate data from an existing file system to a new file system.
/ Oracle Solaris 11 support for Oracle Solaris 10 zones
Used to migrate your Oracle Solaris 10 application environments to an Oracle Solaris 11 system.
/ NFS file sharing and pool migration
Used to access shared files from an Oracle Solaris 10 system on an Oracle Solaris 11 system.
Used to import a ZFS storage pool from an Oracle Solaris 10 system into an Oracle Solaris 11 system.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Transitioning Your Oracle Solaris 10 System to
Oracle Solaris 11
Question 8
When attempting to perform an installation of Oracle Solaris 11, you encounter a failure message
along the lines of "no offers were received." What is the most likely reason for this message and
why?
- A. The system could not obtain a DHCP-based lease so it could not proceed.
- B. The amount of disk space offered by the installer is inadequate so the installer attempted to compress data in memory.
- C. The minimum amount of memory is not sufficient to load the necessary network driver so the installer tried to offer disk as backing store.
- D. An IP address provided is located on a different network segment because the correct RARP server did not respond.
- E. The IP address provided is outside the range of allocatable addresses.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
No DHCP or Proxy DHCP Offers Were Received
If a DHCP server is not responding to an x86 client's request, you see the following messages:
Intel(R) Boot Agent PXE Base Code (PXE-2.1 build 0.86)
Copyright(C) 1997-2007, Intel Corporation
CLIENT MAC ADDR 00 14 4F 29 04 12 GUID FF2000008 FFFF FFFF FFFF 7BDA264F1400
DHCP......... No DHCP or ProxyDHCP offers were received
PXE-MOF: Exiting Intel Boot Agent
The timeout message indicates that the client is sending a DHCP request and not getting a response.
This issue is probably due to an error in the DHCP configuration. Check to see if your client is
configured correctly in the DHCP server.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11, No DHCP or Proxy DHCP Offers Were Received
Question 9
What are the three properties of a business critical cloud infrastructure?
- A. service isolation
- B. flexible, virtual application instances
- C. dedicated, single purpose file servers
- D. easy, intuitive provisioning, chargeback, and capacity planning
- E. rigid, inflexible network design
Answer:
A, B, D
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Overview
* Flexible cloud infrastructure supports dynamic resource pooling, elastic scalability, and rapid
application deployment
* Includes Oracle Enterprise Manager, a complete cloud lifecycle management solution that allows
you to quickly set up, manage, and support enterprise clouds and traditional Oracle IT environments
from applications to disk
* Built-in security and high availability
* Application-aware virtualization and management capabilities
Question 10
Which two actions must be taken to enable IP forwarding on all interfaces yet disable on a specific
interface?
- A. routeadm –r
- B. ipadm set–addrprop
- C. ipadm set–ifprop
- D. routeam –e
- E. dladm set–router
Answer:
A, E
Explanation:
The routeadm command is used to administer system-wide configuration for IP forwarding and
routing. IP forwarding is the passing of IP packets from one network to another; IP routing is the use
of a routing protocol to determine routes.
-e option...
Enable the specified option. The effect is to prepare the associated services (svc:/network/ipv4-
forwarding:default in the case of ipv4-forwarding) for enabling. By means of the routing-svcs
variable, the routing daemons are specified to be enabled on subsequent boot or when routeadm -u
is run.
-d option...
Disable the specified option. The effect is to prepare the associated services (svc:/network/ipv4-
forwarding:default in the case of ipv4-forwarding) for enabling. By means of the routing-svcs
variable, the routing daemons are specified to be disabled on subsequent boot or when routeadm -u
is run.
Reference: System Administration Commands , routeadm
Question 11
A customer has multiple applications and you believe consolidation using Oracle Solaris Zones will
help them. The customer is concerned that consolidating them all on one physic server may cause
adverse interactions between them, causing problems with functionality, security, and performance.
What are the two benefits of Zones that would explain why Zones would be a good choice?
- A. better single threaded performance
- B. better software isolation
- C. better hardware isolation
- D. simpler VLAN management
- E. simple, effective resource controls
Answer:
B, E
Explanation:
B (not C): A zone is a virtualized operating system environment that is created within a single
instance of the Oracle Solaris operating system. Oracle Solaris Zones are a partitioning technology
that provides an isolated, secure environment for applications.
Note:
* When you create a zone, you produce an application execution environment in which processes are
isolated from the rest of the system. This isolation prevents a process that is running in one zone
from monitoring or affecting processes that are running in other zones. Even a process running with
root credentials cannot view or affect activity in other zones. A zone also provides an abstract layer
that separates applications from the physical attributes of the machine on which the zone is
deployed. Examples of these attributes include physical device paths and network interface names.
The default non-global zone brand in the Oracle Solaris 11.1 release is the solariszone.
By default, all systems have a global zone. The global zone has a global view of the Oracle Solaris
environment that is similar to the superuser (root) model. All other zones are referred to as non-
global zones. A non-global zone is analogous to an unprivileged user in the superuser model.
Processes in non-global zones can control only the processes and files within that zone. Typically,
system administration work is mainly performed in the global zone. In rare cases where a system
administrator needs to be isolated, privileged applications can be used in a non-global zone. In
general, though, resource management activities take place in the global zone.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11.1 Information Library, Oracle Solaris Zones Overview
Question 12
A zone won't boot. Identify the five causes.
- A. The zone is configured to have its own CPUs, and there aren't enough.
- B. The zone is configured to have exclusive access to an NIC, and the NIC is already up.
- C. The zone is configured to mount a file system, which is already mounted.
- D. The zone is currently running or shutting down.
- E. The zone has been uninstalled.
- F. Your terminal session is missing the SYS_TIME privilege.
Answer:
A, B, C, D, E
Explanation:
A: dedicated-cpu Resource
The dedicated-cpu resource specifies that a subset of the system's processors should be dedicated to
a non-global zone while it is running. When the zone boots, the system will dynamically create a
temporary pool for use while the zone is running.
C: s the global administrator in the global zone, you can import raw and block devices into a non-
global zone. After the devices are imported, the zone administrator has access to the disk. The zone
administrator can then create a new file system on the disk and perform one of the following actions:
Mount the file system manually
Place the file system in /etc/vfstab so that it will be mounted on zone boot
D, E: Booting a zone places the zone in the running state. A zone can be booted from the ready state
or from the installed state. A zone in the installed state that is booted transparently transitions
through the ready state to the running state. Zone login is allowed for zones in the running state.
Incorrect:
Not F: Sys_time not related to booting a zone.
Question 13
Which two statements are true of the GRUB menu?
- A. GRUB is the default boot loader for Oracle Solaris 11 SPARC and x86.
- B. GRUB supports Oracle Solaris and Oracle Linux only.
- C. GRUB loads a kernel based upon the file name, disk, and partition specified.
- D. GRUB uses boot environments for all operating systems.
- E. GRUB is fully compliant with the Multiboot specification.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
A:
* If your system has more than one OS installed on the system or more than one root boot
environment in a ZFS root pool, you can boot from these boot environments for both SPARC and x86
platforms.
* GRUB, the open source boot loader, is the default boot loader in the Solaris OS.
C: With GRUB based booting, the kernel is loaded by specifying its file name, and the drive, and the
partition where the kernel resides. GRUB based booting replaces the Solaris Device Configuration
Assistant and simplifies the booting process with a GRUB menu.
Incorrect:
Not E:
* In this implementation of GRUB, the multiboot module is no longer used.
Question 14
What two features identify Oracle Solaris 11 as being "built for clouds"?
- A. ability to use SSH lo securely connect to Oracle Solaris 11 servers
- B. first fully virtualized operating system featuring built-in virtualization with Zones
- C. secure rapid provisioning and lifecycle management
- D. Oracle Solaris 11 has been designed to provide a robust and easily usable desktop environment for end users
- E. Oracle Solaris 11 is installable from DVD Media
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
B: Built-in Virtualization
Whatever the needs of your cloud infrastructure, Oracle has a comprehensive suite of built-in
virtualization technologies to compliment your business requirements.
Choose from Oracle Solaris Zones, OVM Server for SPARC, OVM Server for x86 and OVM VirtualBox.
With Oracle Solaris Zones, administrators can rapidly provision secure and isolated virtual
environments in which to deploy cloud applications and services.
D:
Oracle Solaris is the best platform for the cloud because it combines key computing elements -
operating system, virtualization, networking, storage management, and user environment - into a
stable, secure, mission-critical foundation that customers can depend on
Question 15
Your installation has completed successfully and the system did not reboot automatically. Which
option would cause this?
- A. Automatic reboots are only allowed when invoked via SMF.
- B. The client never reboots automatically after the successful installation, staying available for manually verification of the install process.
- C. The "auto_reboot" parameter in the Automated Installer manifest has not been set to "true."
- D. The "installation" service needed to be refreshed for the "auto_reboot" setting is to be applied, so all clients being installed from it could reboot.
- E. Post installation reboots are no longer necessary because the Oracle Solaris 11 Automated Installation installs and actives the system's services in the desired state such that there is no need for a reboot.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
auto_reboot Optional. Omitting the auto_reboot attribute is equivalent to setting the value of the
attribute to false. By default, AI does not automatically reboot the client after installation. To request
automatic reboot of the client after successful installation, specify auto_reboot="true".
Note:
* Example 1 Set the auto_reboot Attribute
$ aimanifest set /auto_install/ai_instance@auto_reboot false
Reference: Creating a Custom AI Manifest