omg omg ocup2 adv300 practice test
OMG Certified UML Professional 2 (OCUP 2) - Advanced Level
Question 1
Choose the correct answer :
Which feature of a UML model element could NOT be adapted by a Stereotype?
- A. Notation could be changed.
- B. Constraints could be added
- C. Constraints can be removed.
- D. Attributes and Operations could be added.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A stereotype in UML is a powerful extension mechanism that allows developers to tailor UML models
for particular domains or platforms. Stereotypes can adapt UML model elements by adding
constraints, changing notation, and adding attributes and operations.
However, they cannot remove
existing constraints from a model element12
.
Notation Change (A): Stereotypes can indeed change the notation of a model element to make it
more expressive or domain-specific.
For example, a stereotype could be used to visually distinguish
between different kinds of classes in a class diagram1
.
Adding Constraints (B): Stereotypes can add new constraints to a model element to specify
additional rules or requirements that are not defined by the standard UML1
.
Removing Constraints ©: This is not a capability of stereotypes. Constraints define rules that must be
followed, and once they are part of a model element, they cannot be removed by a
stereotype.
Instead, they are an intrinsic part of the model’s definition1
.
Adding Attributes and Operations (D): Stereotypes can be used to add attributes and operations to a
model element, which allows for the specification of additional properties or behaviors that are not
part of the standard UML metamodel1
.
In summary, while stereotypes are versatile and can extend the capabilities of UML model elements
in various ways, they do not have the ability to remove constraints that are already applied to those
elements.
This is because constraints are considered fundamental rules that govern the integrity of
the model, and removing them would potentially violate the model’s correctness or completeness1
.
Question 2
Choose the correct answer :
A framework developer has been given a requirement to create an extensible utility for solution
developers to use to create collections. The framework developer has submitted the following
diagram fragment for review: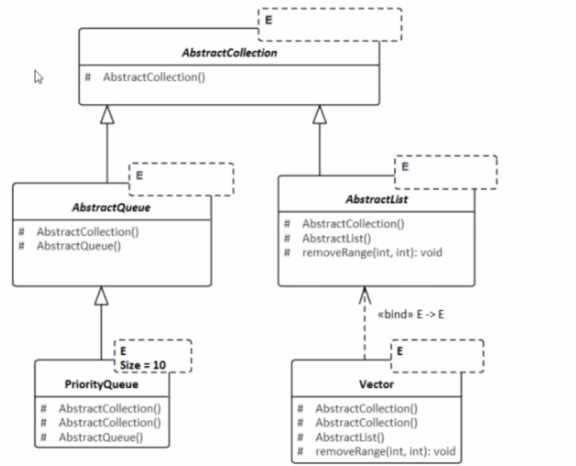
Which review comment is valid and applicable?
- A. The upper limit of 10 for the Size of PhontyQueue is too small and should be increased to at least 20 to accommodate special cases.
- B. The «bind» relationship between the concrete class Vector and the abstract class AbstractList is incorrect. It should be a Generalization relationship.
- C. The Generalization relationship between the concrete class PriorityOueue and the abstract class AbstractQueue is incorrect. It should be a «bmd» relationship.
- D. The template parameter Size cannot be added to a specialized class. It needs to be moved to the top of the hierarchy and added to AbstractCollection and AbstractQueue.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In UML, the «bind» relationship is used to specify that a class is a template instantiation of a
template class, where actual parameters are bound to the formal parameters of the template class1
.
However, in the case of the relationship between a concrete class like Vector and an abstract class
like AbstractList, the correct relationship should be Generalization, not «bind».
Generalization is a taxonomic relationship between a more general classifier and a more specific
classifier.
Each instance of the specific classifier is also an instance of the general classifier1
.
Thus, Vector being a concrete implementation of AbstractList, should inherit from AbstractList, which
is correctly represented by a Generalization relationship in UML.
The other options can be evaluated as follows:
Option A: The upper limit for the size of PhontyQueue is a design decision that should be based on
the requirements and use cases of the application. It is not inherently incorrect in UML to have a
specific upper limit.
Option C: The Generalization relationship is correctly used
between PriorityQueue and AbstractQueue as it represents inheritance in UML.
Option D: While it is true that template parameters are typically defined at the top of the hierarchy,
the statement is too absolute. In UML, template parameters can be added to specialized classes, but
it depends on the specific design and requirements. Therefore, without additional context, this
statement cannot be deemed universally valid.
In conclusion, the most applicable and valid review comment is option B, which correctly identifies
the misuse of the «bind» relationship in the context of the class diagram provided.
Question 3
Choose the correct answer :
Which statement should be taken into consideration when extending a UML metaclass with a
stereotype?
- A. UML recommends to start extending the metaclass "Class" and then other metaclasses depending on the expected qualities of the profile.
- B. The choice of the extended metaclass is not that important since tools can always apply a profile's filtering rules to hide unneeded metaclasses.
- C. The metaclass and the stereotype that extends it should be semantically related to each other to avoid having to constrain the metamodel excessively.
- D. UML specifies rules on how the mapping between stereotypes and UML metaclasses should be done; these rules must be followed to identify the best metaclasses.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When extending a UML metaclass with a stereotype, it is critical to ensure that the metaclass and the
stereotype are semantically related. This is because a stereotype is a way to extend the UML
metamodel to create new kinds of model elements that can include additional semantics and
constraints, but still adhere to the base behavior defined by the metaclass. The stereotype should be
a meaningful specialization of the metaclass and not contradict its fundamental semantics. By
keeping them semantically related, there is less need for additional constraints on the metamodel,
and the resulting profile is more intuitive for users. This is consistent with the principles described in
the UML 2 Specification, particularly in the sections on profiles and stereotypes.
Question 4
Choose the correct answer :
An organization has determined that they want to add the capability to create and add requirement
elements to their UML models. They also want to create a unique relationship for tracing
requirements to other model elements.
What is the appropriate approach to do this?
- A. Use the requirement element and relationship defined in the UML specification.
- B. Create a profile that stereotypes Class as requirement and Dependency as the relationship.
- C. Create a new MOF metamodel that includes UML and adds the desired requirement element and relationship.
- D. Assign tag values that ascribe the desired requirement type to a UML Requirement and Dependency relationship.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
UML allows the introduction of new concepts that are not part of the standard UML metamodel by
creating a profile. To add capabilities for modeling requirements and tracing relationships in UML, a
profile can be created where a Class is stereotyped to represent a requirement, and a Dependency is
stereotyped to represent the trace relationship. This approach is both practical and conforms to the
UML standard's mechanisms for extending the language. It is a common practice to create such
profiles for requirements engineering within the UML framework. This conforms to the UML 2
Superstructure Specification, which provides guidelines on creating and applying profiles and
stereotypes.
Question 5
Choose the correct answer :
Where does UML explicitly intend String Expression elements to be used?
- A. as (he ValueSpecifications for the nameExpressions of ParameterableElements within Template specifications
- B. as the model the author chooses for the specification of custom dynamically-generated names for any NamedElement
- C. whenever an OpaqueExpression form of a ValueSpecification needs to specify an expression that operates on String instances
- D. The specification has no metaclass StnngExpression and so no use of StringExpression is explicitly intended.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In UML, ValueSpecifications are used to specify the value of an element. The UML 2 Specification
does not define a metaclass named StringExpression. Instead, it provides a metaclass named
OpaqueExpression, which can be used when an expression is written in a language that is not directly
interpretable by the model. Since there is no metaclass called StringExpression in the UML 2
Specification, there is no explicitly intended use for it within the UML metamodel. The absence of
this metaclass suggests that any use of a concept called "StringExpression" would not conform to
standard UML 2 practices and would likely be part of an extension or profile, not the core UML
metamodel.
Question 6
Choose the correct answer :
What does the UML specification say about choosing between a MOF-based metamodel and a UML
profile?
- A. It is not always clear when to use one approach over the other; this decision must be domain- specific
- B. It is always good to opt for metamodeling when the metamodel is large and the domain is inherently complex such as the database domain.
- C. Since UML extends MOF. it is always preferable to start by extending MOF and. if this turns out to be complex, then shift to extending UML.
- D. Extending UML should be favored because of the fact that there are several tools that support UML profiling, which is not the case for MOF.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The UML (Unified Modeling Language) specification, which is a part of the MOF (Meta-Object
Facility) framework, suggests that the choice between creating a MOF-based metamodel and a UML
profile depends on the specific needs of the domain being modeled. A MOF-based metamodel might
be more appropriate for domains that require defining a completely new set of modeling concepts,
whereas a UML profile is suitable for domains where the extension of existing UML concepts is
sufficient. Since the specification recognizes the variability in modeling requirements across different
domains, it emphasizes the importance of understanding the domain to make an informed decision
on the modeling approach. The UML specification, therefore, does not prescribe a one-size-fits-all
solution but rather leaves the decision to the modeler, based on the domain-specific requirements.
Question 7
Choose the correct answer :
Consider the following diagram fragment: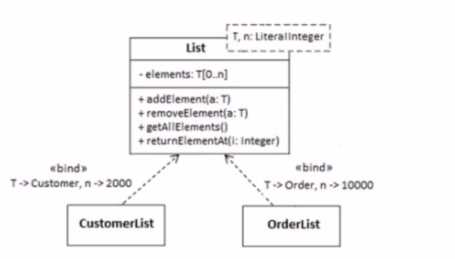
What is the signature of the class template List?
- A. List
- B. T[0..n]
- C. The ordered set {T. n: Integer}
- D. <T -> Customer, n -> 2000> or <T -> Order, n - >10000>
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The class template List shown in the diagram fragment is a parametrized class with two template
parameters: T and n. The signature of the class template includes both of these parameters. The
template parameter T represents a type that can be bound to a specific class when the template is
instantiated, while n represents an integer value that specifies the multiplicity of elements that can
be contained in the list. Therefore, the signature of the class template List is the ordered set {T, n:
Integer}, which includes both the type parameter T and the integer parameter n indicating the
maximum number of elements the list can hold.
Question 8
Choose the correct answer :
Consider the following profile: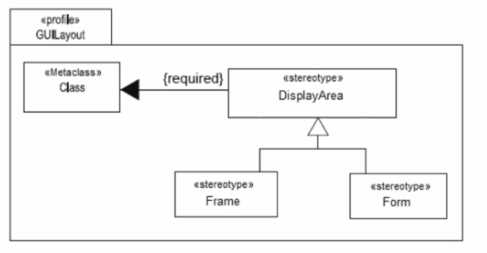
Which statement is true?
- A. Each instance of Class must be linked to exactly one instance of DisplayArea, Frame, or Form.
- B. Each instance of Class must be linked to at most one instance of DisplayArea. Frame, or Form.
- C. Each instance of Class must be linked to exactly one instance of DisplayArea. Frame, and Form.
- D. Instances of Class or its subclasses do not have to be linked to instances of DisplayArea. Frame, or Form.
- E. The diagram is incorrect because a required extension cannot be applied to a stereotype inheritance hierarchy.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The UML diagram fragment provided shows a UML profile with a required extension from the
metaclass Class to the stereotype DisplayArea, which in turn has two subclasses Frame and Form.
The use of {required} indicates that whenever an instance of Class is extended by the DisplayArea
stereotype, it becomes mandatory to do so. However, this does not enforce that every instance of
Class must be linked to DisplayArea or its subclasses (Frame or Form). It only means that if the
DisplayArea stereotype is applied, it is required. Therefore, there is no obligation for every instance
of Class or its subclasses to be stereotyped as DisplayArea, Frame, or Form. It's also worth noting
that the last option (E) could be considered true in some interpretations of UML, but given the
options provided and common UML practices, option D is more accurate.
Question 9
Choose the correct answer :
Which statement is correct about working with multiple profiles?
- A. The only way to integrate profiles is to merge them into one big profile
- B. Only profiles that represent the same domain can be integrated together.
- C. A profile can reuse all or parts of another profile, and extend other profiles.
- D. A profile can reuse all or parts of another profile, but cannot extend other profiles.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In UML, profiles are mechanisms to extend the UML for a specific domain or purpose. The UML
specification allows for one profile to reuse or import elements from another profile. This enables
modularity and encourages reusability of profile elements across different domains. Additionally,
one profile may extend the stereotypes or metaclasses defined in another profile, which allows for
the creation of layered profiles where each layer adds its own specificities. This is a common practice
in software and systems modeling to cater to different aspects of a system within separate profiles,
which are then integrated to form a comprehensive model. The capability to reuse and extend
profiles is defined in the UML 2.x Superstructure Specification, which gives guidelines on how to
define and use profiles within UML.
Question 10
Choose the correct answer :
Which interpretation is valid when NamedElement A is the Supplier in a specialized Dependency
having NamedElement B as the Client, and a Comment indicates that A and B participate in a
transformation?
- A. B is the transformation Realization of A.
- B. A is the transformation Realization of B.
- C. A depends on B.
- D. A and B are part of an economic system where A consumes what B transforms.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In UML, a Dependency is a relationship that signifies that one NamedElement, the client, depends on
another NamedElement, the supplier, meaning that a change in the supplier could affect the client. If
NamedElement A is the supplier and NamedElement B is the client in a Dependency relationship,
and there is a Comment indicating that both participate in a transformation, the interpretation is
that B (the client) depends on A (the supplier) for that transformation. The comment does not
necessarily change the nature of the Dependency relationship; it simply adds additional information
about the nature of their interaction. A transformation could mean that B transforms A's supplied
element in some way, but in terms of UML Dependency relationships, it would still be interpreted as
"A depends on B" or "B requires A for its transformation". This interpretation aligns with the UML 2.x
Infrastructure and Superstructure specifications, which explain Dependencies and their meanings
within the UML metamodel.
Question 11
Choose the correct answer :
Given the following fragment from a profile definition: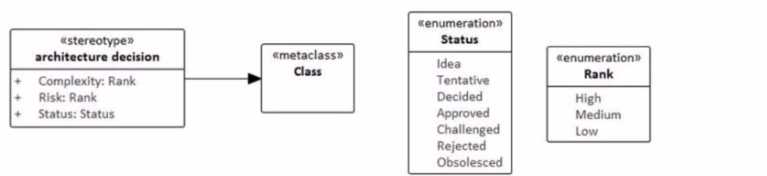
Which statement is correct regarding the application of the profile?
- A. A class stereotyped as an «architecture decision» must contain attributes named Complexity. Risk, and Status with the designated Enumeration types
- B. A class stereotyped as an «architecture decisions will have Stereotype Properties named Complexity. Risk, and Status with the Enumeration types designated in the profile.
- C. A class stereotyped as an «architecture decision» must contain attributes named Complexity. Risk, and Status and they may be any user-defined type.
- D. A class stereotyped as an «architecture decisions must contain exactly three attributes with user- defined names, two of which are of type Rank, and one of type Status.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In UML, a stereotype is a mechanism that extends the vocabulary of the UML in order to create new
model elements. The given profile fragment defines a stereotype «architecture decision» that
extends the metaclass Class. This stereotype includes three properties: Complexity, Risk, and Status,
each typed by specific enumerations: Rank and Status. When a stereotype is applied to a UML
element, it does not create physical attributes on the element; instead, it enables the element to
carry additional information as specified by the stereotype — in this case, as Stereotype Properties.
These properties are effectively tagged values that are associated with the stereotyped element.
Hence, when a class is stereotyped as an «architecture decision», it will have the ability to hold
values for Complexity, Risk, and Status according to the types defined by the enumerations in the
profile. This is consistent with the rules defined in the UML 2.x Superstructure Specification for
profiles and stereotypes.
Question 12
Choose the correct answer :
Which capability Is provided by the Profile mechanism?
- A. storing user-specific configurations of model settings
- B. creating new metamodel elements for specific purposes
- C. adapting existing metamodel elements for specific purposes
- D. configuring model libraries and a set of keywords to be used for a model
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Profile mechanism in UML provides the capability to adapt existing metamodel elements for
specific purposes. Profiles allow modelers to extend the standard UML metamodel with additional
semantics by defining stereotypes, tagged values, and constraints that are specific to a particular
domain, platform, or methodology. This means that profiles tailor the existing UML metamodel
elements to create domain-specific models without changing the underlying metamodel itself. This
adaptation mechanism is described in the UML 2.x Superstructure and Infrastructure Specifications,
which detail how profiles can be used to customize the UML for particular domains or purposes.
Question 13
Choose the correct answer :
Let E be a UML 2.5 NamedElement with a name property of '_name" and with a nameExpression
property of "_expresslon".
Which one presentation or set of presentations of the name of E in a tool conforms to the OMG
specification?
- A. _name
- B. _expression
- C. S_expression$ OR _name
- D. S_expression$ _expression OR _name:_expressk>n
- E. UML 2.5 no longer includes a nameExpression properly within NamedElements.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In UML 2.5, a NamedElement can have a name attribute, which is a string representing the element's
name, and a nameExpression attribute, which is a ValueSpecification used to specify the element's
name in a more dynamic way. The presentation of the name of a NamedElement in a tool that
conforms to the OMG specification could either be the literal name (as specified in the name
attribute) or the evaluated expression from the nameExpression property. Therefore, a tool may
choose to present either the simple name or the evaluated expression or allow toggling between the
two. The specification does not mandate a single fixed presentation, allowing for flexibility in how
tools display the name. This conforms to the OMG's UML 2.5 specification, which describes the
properties of NamedElement and their presentations within tools.
Question 14
Choose the correct answer :
In a model of a commercial transaction, actors might exchange euros, pesos, and dollars
Which figure illustrates compliant use of UML information items for these currency exchanges?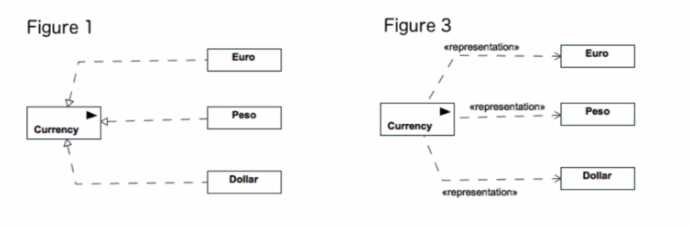
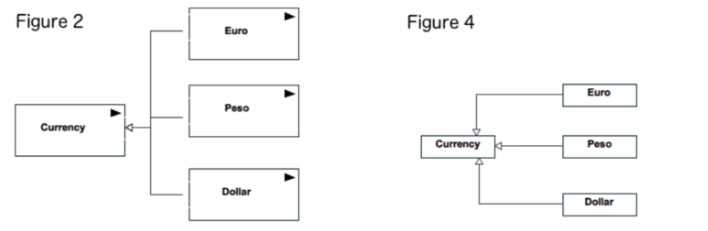
- A. Figure 1
- B. Figure 2
- C. Figure 3
- D. Figure 4
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In UML, an InformationItem represents an abstraction of all those elements in a UML model that
have an information-bearing feature. It is depicted as a classifier with the keyword
«informationItem». An InformationItem does not have direct instances and serves as a mechanism
to handle unspecified, untyped information in a model. In the context of a commercial transaction
model, currencies such as euros, pesos, and dollars can be abstractly represented as
InformationItems to signify that they are used as a form of data exchange but without specifying the
concrete structure or data type. Figure 2 correctly uses InformationItem notation, with the
«informationItem» keyword and the directed association pointing from the Currency
InformationItem to the Euro, Peso, and Dollar, which are likely representations or manifestations of
the Currency. This complies with the UML specification for representing abstract entities in models
that are involved in the exchange or flow of information.
Question 15
Choose the correct answer :
Consider the following diagram fragment:
Which statement is correct about the diagram fragment?
- A. The diagram fragment is a valid UML diagram.
- B. To use the template List. Company must be a bound element to List.
- C. List cannot be used by Company unless Company is also a template.
- D. List cannot be used as a data type, only a bound element to List can.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The provided diagram fragment seems to indicate a situation involving a template. In UML, a
template is a parameterizable element, and a bound element is a specific manifestation of that
template wherein the parameters have been replaced with actual values or types. If 'List' is a
template class, it cannot be directly used as a type. Instead, one must use a bound element of the
List, meaning the template parameters of List must be bound to actual types before it can be used.
For instance, if List is a template expecting a type T, then a concrete class might be List<Customer> or
List<Order>, where Customer or Order are actual types replacing the template parameter T. This use
of templates and bound elements is according to the UML specification, which details how templates
are defined and instantiated within UML models.