nokia 4a0-d01 practice test
Nokia Data Center Fabric Fundamentals
Question 1
Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons why BGP is used as the routing protocol in the data
center?
- A. It is more efficient than link-state protocols like IS-IS and OSPF.
- B. BGP neighbors automatically discover each other.
- C. It is a well understood and mature routing protocol.
- D. It supports both IPv4 and IPv6.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
BGP is not chosen because it is more efficient than link-state protocols; in fact, link-state protocols
like IS-IS and OSPF generally provide faster convergence and more efficient route calculation. BGP is
used in data centers mainly because it is mature, well understood, supports both IPv4 and IPv6, and
offers flexible policy control.
Question 2
Which of the following statements about the data center’s leaf-spine topology (clos network) is
FALSE?
- A. Each leaf router is connected to all the spine routers in the cluster.
- B. It provides a consistent path for east-west traffic.
- C. It uses the spanning tree protocol to avoid forwarding loops.
- D. It uses ECMP to distribute traffic across duplicate links.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The leaf-spine (Clos) topology does not use the spanning tree protocol because it relies on equal-cost
multipath (ECMP) routing to prevent loops and efficiently utilize all available paths. Spanning tree is
typically avoided in modern data center fabrics to enable full bandwidth utilization.
Question 3
Which of the following is NOT a function of Nokia’s SR Linux application manager?
- A. It monitors the health of all applications.
- B. It manages the SR Linux and customer-defined applications.
- C. It reads the application’s configuration information and starts each application.
- D. It translates the application’s YANG model into protobufs for the IDB.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The SR Linux application manager does not perform the function of translating an application's YANG
model into protobufs for the Interface DataBase (IDB). Its primary roles are managing applications,
reading their configuration, and monitoring their health.
Question 4
Which of the following statements about the YANG model used in Nokia’s SR Linux is FALSE?
- A. All configuration and state information is defined as a YANG model.
- B. The YANG model uses a tree structure with “leafs” as the branches and “containers” as the data components.
- C. The YANG model can be converted into other formats such as JSON or XML.
- D. The YANG model provides a standardized way for applications to retrieve SR Linux configuration and state information.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In YANG models, "leafs" are the data nodes (not branches), and "containers" group related data
nodes. The statement incorrectly reverses their roles by calling leafs branches and containers data
components.
Question 5
Which of the following is NOT one of the characteristics of Nokia’s SR Linux?
- A. It uses an unmodified Linux kernel that simplifies the use of third party applications.
- B. It uses a modular, state-driven architecture that gives applications efficient access to system information.
- C. It includes a NetOgs development kit that supports the integration of third-party applications.
- D. It uses mature and stable SNMP protocol to access the command line interface.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Nokia’s SR Linux does not rely on the SNMP protocol for accessing the command line interface;
instead, it uses modern, programmable interfaces aligned with its modular architecture.
Question 6
Which of the following statements about Nokia’s Fabric Services System is FALSE?
- A. Data center fabric configuration is represented as the fabric intent in a declarative YAML format.
- B. Digital sandbox provides notification of performance issues in the data center fabric.
- C. Telemetry data is provided in a context that is relevant to the fabric intent.
- D. Cloud-native design enables easy integration with the customer's environment.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The Digital Sandbox in Nokia’s Fabric Services System is primarily used for simulation and validation
of fabric intent, not for providing notifications of performance issues.
Question 7
Which of the following statements about configuration checkpoints in Nokia SR Linux is FALSE?
- A. Checkpoint 0 is always the oldest checkpoint.
- B. The current running configuration can be saved as a JSON-formatted checkpoint file.
- C. The operator can revert to any existing checkpoint.
- D. The operator can generate a new checkpoint when committing configuration changes.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Nokia SR Linux, checkpoint numbering is dynamic. The system assigns the lowest available number
to the most recent checkpoint, not necessarily "0." When the number of saved checkpoints exceeds
the configured maximum, the oldest checkpoint is removed, and the remaining checkpoints are
renumbered accordingly. Therefore, checkpoint "0" is not always the oldest checkpoint.
Question 8
Which of the following statements about the CLI modes in Nokia’s SR Linux is FALSE?
- A. The state mode displays the current configuration and operational information.
- B. The show mode uses pre-defined reports to display operational information.
- C. The running mode is used to make configuration changes.
- D. Users can switch from one mode to another using the enter command.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Nokia SR Linux, users switch between CLI modes using specific commands like configure or exit,
not an enter command. The enter command is not used for mode switching.
Question 9
Which of the following statements about SR Linux interfaces is FALSE?
- A. Only one management interface is allowed.
- B. Network interfaces are associated with physical ports on the linecards.
- C. The loopback interface is a physical interface directly connected to another interface on the same chassis.
- D. Layer 2 parameters such as MTU are configured at the SR Linux interface level while Layer 3 parameters are configured at the subinterface level.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The loopback interface in SR Linux is a logical, virtual interface used for management and routing
purposes; it is not a physical interface directly connected to another interface on the same chassis.
Question 10
Which of the following statements about the IRB subinterface configuration in Nokia SR Linux is
FALSE?
- A. An IP address is configured under the IRB’s subinterface.
- B. An IRB subinterface is configured in an IP-VRF network instance.
- C. One IRB subinterface is configured for each interface within a MAC-VRF network instance.
- D. One IRB subinterface is configured in a MAC-VRF network instance.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In Nokia SR Linux, IRB subinterfaces are configured one per MAC-VRF network instance, not one for
each interface within that instance. Multiple IRB subinterfaces per interface are not typical.
Question 11
Which of the following statements about IP-VRFs in Nokia’s SR Linux is FALSE?
- A. An IP-VRF is a Layer 3 network instance.
- B. Packets in an IP-VRF are forwarded based on the destination IP address.
- C. The router maintains a distinct route table for each IP-VRF instance.
- D. Multiple servers can be connected to the same subnet in an IP-VRF.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Multiple servers connected to the same subnet typically reside within the same Layer 2 domain or
MAC-VRF. IP-VRFs operate at Layer 3 and segment routing and forwarding by separate routing tables,
so multiple servers on the same subnet are not a function of IP-VRF.
Question 12
Which of the following statements about the MAC table shown in the exhibit output is FALSE?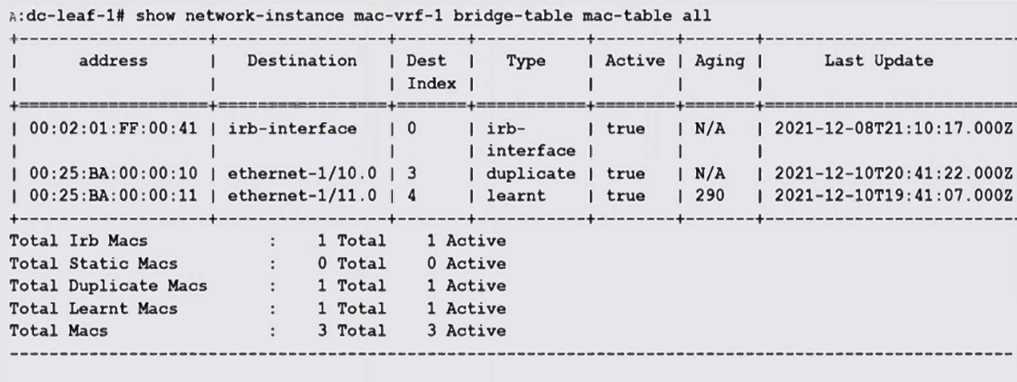
- A. The MAC address 00:25: BA:00:00:10 is learnt on more than one interface.
- B. The MAC re-learning rate has exceeded the threshold within the specified time frame.
- C. [interface ethernet-1/10 is configured with the MAC address 00:25:BA:00:00:10.
- D. Mac-duplication detection is enabled in mac-vrf-1.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The MAC address 00:25:BA:00:00:10 is listed as "duplicate," but it appears only once associated with
interface ethernet-1/10. Therefore, it is not learned on more than one interface.
Question 13
Which of the following statements about a MAC-VRF is FALSE?
- A. A MAC-VRF is a Layer 2 network instance.
- B. Bridge table entries contain an exit interface for each destination address.
- C. Packets received in a MAC-VRF are forwarded based on destination IP address.
- D. Multiple devices can be connected to the same IP subnet using a MAC-VRF.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a MAC-VRF, packets are forwarded based on Layer 2 information such as destination MAC
addresses, not on destination IP addresses.
Question 14
Which of the following statements about resilient ECMP load balancing is TRUE?
- A. The hash value used to distribute traffic is calculated as a modulo function on specific fields of the packet header.
- B. Hash buckets are used to ensure that flows egressing the same interface on one router use different egress interfaces on downstream routers.
- C. A different hash seed is used on downstream routers to ensure that flows are randomly distributed across all eligible router interfaces.
- D. When one of the next-hops fail, only flows currently egressing to that next-hop are impacted.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In resilient ECMP load balancing, when a next-hop fails, only the flows that were using that specific
next-hop are affected and need to be redistributed, minimizing disruption to other flows.
Question 15
Examine the exhibit. Which of the following statements is TRUE?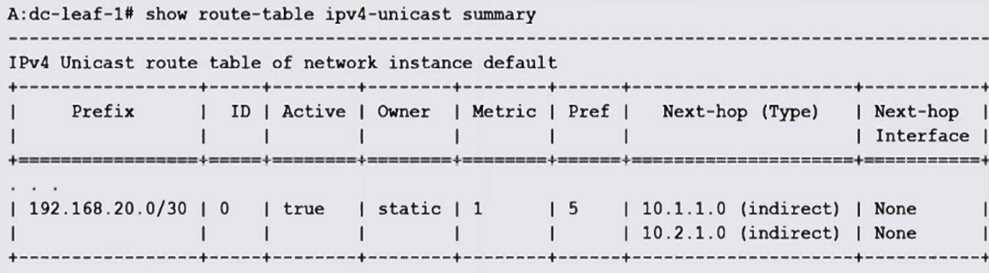
- A. A recursive lookup is performed to resolve 10.2.1.0 to use 10.1.1.0.
- B. A recursive lookup is performed to resolve 10.1.1.0 to use 10.2.1.0.
- C. The next-hop group for this static route is configured with two next-hops.
- D. The next-hop selected for this route will be based on the preference value configured for each next-hop.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The static route shows two next-hop IP addresses (10.1.1.0 and 10.2.1.0) listed, indicating that a
next-hop group with multiple next-hops is configured for load balancing or redundancy.