nokia 4a0-112 practice test
Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol
Question 1
What do the address resolution protocol (ARP) for IPv4 and the neighbor discovery procedures for
IPv6 have in common?
- A. Both detect duplicate MAC address assignments.
- B. Both detect duplicate IP address assignments.
- C. Both resolve a host device's MAC address using its IP address.
- D. Both resolve a host device's IP address using its MAC address.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
ARP for IPv4 and Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) for IPv6 are both used to map a device's IP
address to its MAC address. This is essential for communication within a local network.
ARP is used in IPv4 networks, and NDP performs a similar function in IPv6 networks, ensuring
devices can communicate effectively on the same network segment.
Question 2
Which of the following statements about the IP forwarding process on a router is TRUE?
- A. It uses the routing table to find a match for the source IP address.
- B. It uses the routing table to find a match for the destination IP address.
- C. It uses the ARP table to find a match for the source MAC address.
- D. It uses the ARP table to find a match for the destination MAC address.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
During the IP forwarding process, routers use the routing table to determine the next hop based on
the destination IP address. The source IP address is not directly involved in the lookup process for
forwarding.
The ARP table is used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, specifically for resolving the MAC
address of the next hop (destination MAC address) for forwarding packets within the local network.
Question 3
When multiple routing protocols offer a route for the same prefix, what part of the router is in charge
of deciding which route to make active?
- A. The routing information base (RIB)
- B. The routing table manager (RTM)
- C. The equal cost multipath configuration
- D. The forwarding information base (FIB)
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The routing table manager (RTM) is responsible for selecting the best route when multiple routing
protocols provide a route for the same destination prefix. It makes the decision on which route to
add to the routing table based on the administrative distance, metric, and other criteria.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.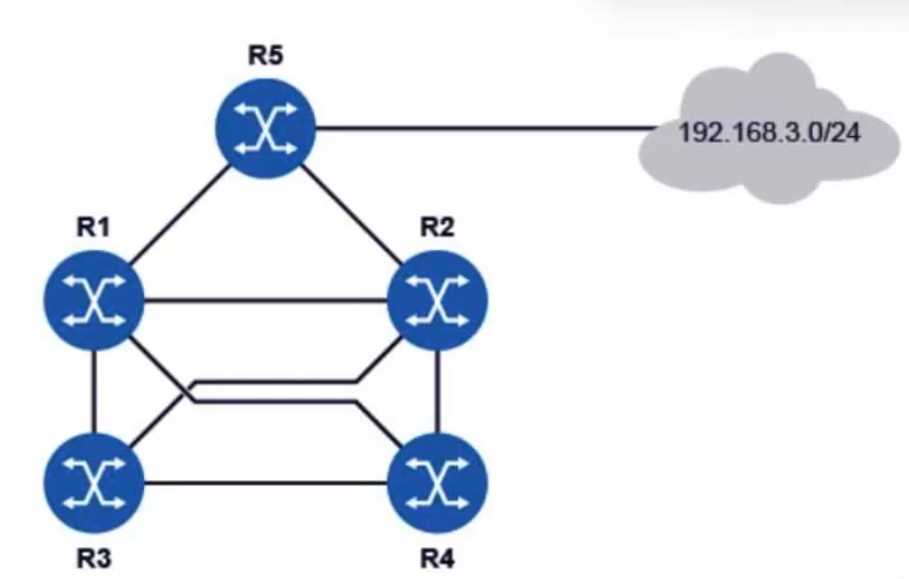
All routers in the diagram are running an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and have been configured
with an ECMP value of 4. Router R5 advertises the prefix 192.168.3.0/24 using the IGP. Assuming all
links have the same cost, how many entries for prefix 192.168.3.0/24 will be in router R3’s routing
table?
- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In this scenario, the routers are configured with an Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) value of 4, meaning
they can utilize up to 4 equal-cost paths to reach a destination. Since Router R5 is advertising the
192.168.3.0/24 prefix and all links have the same cost, router R3 will receive multiple routes to reach
this destination.
Given that all the routers (R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5) are connected in a way that can support multiple
equal-cost paths, and assuming ECMP is set to 4, the routing table on Router R3 will have up to 4
entries for the prefix 192.168.3.0/24.
Thus, Router R3's routing table will contain 4 entries for the prefix 192.168.3.0/24.
Question 5
Which component of the Nokia 7750 SR is in charge of performing the longest prefix match lookup
on packets that arrive on the physical interfaces?
- A. Control Processing Module (CMP)
- B. Media Dependent Adapter (MDA)
- C. Switch Fabric (SF)
- D. Input/Output Module (IOM)
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Input/Output Module (IOM) is responsible for performing the longest prefix match (LPM) lookup
on packets that arrive at the physical interfaces. The IOM performs this function by examining the
destination IP address of incoming packets and using the routing table to determine the best match.
Question 6
What is the replacement for ARP in IPv6?
- A. Duplicate address detection procedures.
- B. Router discovery procedures.
- C. Neighbor discovery procedures.
- D. Stateless address auto-configuration procedures.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In IPv6, the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) replaces the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) used
in IPv4. NDP is responsible for several functions, including resolving IP addresses to MAC addresses
(similar to ARP), detecting duplicate IP addresses, and discovering other devices on the network.
Question 7
Which of the following definitions best describes route redistribution?
- A. It is the process of deciding at line-rate speed which packets will be dropped and which ones will be forwarded.
- B. It is the process of redirecting packets to be processed by an intermediate network function before allowing them to be forwarded to their intended final destination.
- C. It is the process of passing routing information from one routing domain to another, which usually means from one routing protocol to another.
- D. It is the process of controlling which route advertisements received from routing peers are accepted and/or deciding which locally known prefixes are advertised to routing peers.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Route redistribution is the process of sharing routing information between different routing
protocols or routing domains. For example, a router might redistribute routes learned via OSPF into a
BGP routing table or vice versa. This enables routers to exchange routing information even when
they are using different routing protocols.
Question 8
Which of the following is NOT a function of the control plane a router?
- A. To exchange signaling messages with other routers.
- B. To determine the best way to forward packets.
- C. To establish routing paths to deliver packets from source to destination and to reestablish them in case of failure.
- D. To utilize the forwarding tables to forward data packets towards their destination.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The data plane (or forwarding plane) is responsible for actually forwarding the data packets. It uses
the information stored in the forwarding table to determine how to move packets from one interface
to another toward their destination.
Question 9
Which of the following is a valid alternative representation of the IPv6 address
2001:0da8:0000:0000:0024:0000:4ab9:0300?
- A. 2001:0da8::0024:0000:4ab9:03
- B. 2001:da8::0:24::4ab9:300
- C. 2001:da8::24::4ab9:300
- D. 2001:da8::24:0:4ab9:300
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In IPv6, consecutive sections of zeros can be abbreviated with a double colon (::) once in an address.
Also, leading zeros in each hextet (group of four hexadecimal digits) can be removed.
The original address is 2001:0da8:0000:0000:0024:0000:4ab9:0300.
Removing leading zeros and applying the abbreviation:
0da8 becomes da8.
0000 becomes 0 (and multiple consecutive 0000 sections can be represented by ::).
The final result becomes 2001:da8::24:0:4ab9:300, which matches option A when properly
formatted.
Question 10
Which of the following statements about router interfaces on a Nokia 7750 SR is FALSE?
- A. They can be used in pairs on the same subnet for redundancy.
- B. They can be assigned IPv4 and/or IPv6 addresses.
- C. They can be logical or physical.
- D. The system interface exists by default.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Typically, interfaces on a Nokia 7750 SR router are not configured in pairs on the same subnet for
redundancy. Instead, redundancy is achieved through mechanisms like Virtual Router Redundancy
Protocol (VRRP) or other high availability protocols, not by simply using interfaces in pairs on the
same subnet.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.
A static route has been configured on router R1 to reach the PC at 139.120.121.2.
What might be causing the ping to fail?
- A. Router R2 needs a static route to the PC.
- B. Router R1 needs a static route to router R2.
- C. The configured next hop does not belong to a subnet adjacent to R1.
- D. The configured static route needs to be a default route.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In the configuration on router R1, the static route is defined with the next-hop IP address of
139.120.121.1.
However, the next-hop IP address 139.120.121.1 does not belong to the same subnet as the directly
connected interface on R1, which is 172.31.1.1/30. For the static route to work properly, the next-
hop IP address must be reachable via a directly connected interface, meaning it must be within the
same subnet.
Therefore, this mismatch in subnet adjacency is likely causing the failure to reach the destination
(139.120.121.2).
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.
All routers in the diagram are running a link-state routing protocol. Before the link failure, all routers
have operational adjacencies with each other and there is a BFD session between routers R1 and R3.
After the link failure, which of the following affects the routing protocol’s convergence time?
- A. The value of the Ethernet hello timers on the switches.
- B. The value of the routing protocol hello timers on routers R1 and R3.
- C. The value of the BFD transmit interval, receive interval and multiplier settings on routers R1 and R3.
- D. The time taken by the switches to detect that the physical ports are down.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is used to detect link failures quickly and helps improve
convergence time in link-state routing protocols. The BFD session between routers R1 and R3 allows
them to detect the failure of the link between them more quickly than the regular routing protocol
hello timers. The transmit interval, receive interval, and multiplier settings determine how fast BFD
detects a failure and triggers the routing protocol to converge, which directly impacts the
convergence time.
Question 13
When a router performs the SPF calculation, which router is used as the root of the shortest path
tree?
- A. The router with the fewest links.
- B. The router with the lowest router ID.
- C. The router's closest neighbor.
- D. The router doing the calculation.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When a router performs the SPF (Shortest Path First) calculation, it uses itself as the root of the
shortest path tree (SPT). This router computes the shortest paths to all other routers in the network,
treating itself as the origin and calculating the paths based on its view of the network.
Question 14
A routing domain is using a single-area link-state routing protocol. Which of the following is NOT
information that a router can share with other routers in the domain using protocol-specific
messages?
- A. The IP prefixes of subnets directly attached to the router.
- B. IP prefixes known by the router because it is running ad additional routing protocol.
- C. A copy of the local routing table.
- D. The local router ID and the router IDs of neighboring routers.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a single-area link-state routing protocol (such as OSPF), routers share specific information about
the network topology, not their entire routing table. They exchange link-state advertisements (LSAs)
that contain information about their directly connected interfaces and their state, allowing other
routers to build a consistent view of the network.
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit.
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP
addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach
subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as
shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in
this case?
- A. Router R1 drops the echo request because address 10.10.10.3 does not belong to an adjacent router.
- B. Router R2 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- C. Router R3 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- D. The echo request arrives at the server but there is no path for the echo response to return to router R1.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The static route configured on router R1 uses an indirect next-hop, which is 10.10.10.3 (R3). While
the echo request from R1 reaches the server through the IGP, the problem lies in the return path for
the echo response.
The route 10.4.100.0/24 is reachable through R3, but there is no reciprocal route in R3's routing table
that allows the response to flow back towards R1. This results in a failure to return the echo response
to R1, causing the ping to fail.