NetApp ns0-593 practice test
NetApp certified support engineer - ONTAP specialist
Question 1
When you review performance data for a NetApp ONTAP cluster node, there are back-to-back (B2B)
type consistency points (CPs) found occurring on the loot aggregate.
In this scenario, how will performance of the client operations on the data aggregates be affected?
- A. During B2B processing, clients will be unable to write data.
- B. Data aggregates will not be affected by B2B processing on another aggregate.
- C. During B2B processing, all I/O to the node is stopped.
- D. During B2B processing, clients will be unable to read data.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A B2B type consistency point (CP) occurs when a new CP is triggered before the previous CP is
completed, due to the second memory buffer reaching a watermark. This can cause write latency to
increase as user write operations are not replied until a write buffer frees up. However, this only
affects the aggregate that is undergoing the B2B processing, and not the other aggregates on the
same node. Therefore, the performance of the client operations on the data aggregates will not be
affected by B2B processing on the root aggregate. Reference =
What is the Back-to-Back (B2B)
Consistency Point Scenario?
,
What are the different Consistency Point types and how are they
measured in ONTAP 9?
,
What are the different Consistency Point types and how are they measured?
Question 2
Recently, a CIFS SVM was deployed and is working. The customer wants to use the Dynamic DNS
(DDNS) capability available in NetApp ONTAP to easily advertise both data UFs to their clients.
Currently. DNS is only responding with one data LIF. DDNS is enabled on the domain controllers.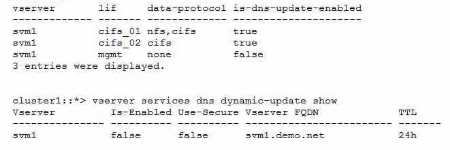
Referring to the exhibit, which two actions should be performed to enable DDNS updates to work?
(Choose two.)
- A. Disable the -vserver-fqdn parameter for the SVM DDNS services.
- B. Remove the NFS protocol from the cifs_01 data LIF.
- C. Enable the -use-secure parameter for the SVM DDNS services.
- D. Enable the -is-enabled parameter for the SVM DDNS services
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
To enable DDNS updates to work, two actions should be performed:
Remove the NFS protocol from the cifs_01 data LIF.
This is because DDNS updates are only supported
for LIFs that have only one data protocol enabled1
. The cifs_01 LIF has both NFS and CIFS protocols
enabled, which prevents it from registering its DNS record dynamically. By removing the NFS protocol
from the cifs_01 LIF, it will become eligible for DDNS updates.
Enable the -is-enabled parameter for the SVM DDNS services.
This is because the -is-enabled
parameter controls whether the SVM sends DDNS updates to the DNS servers2
. The exhibit shows
that the -is-enabled parameter is set to false for the svm1 SVM, which means that it does not send
any DDNS updates. By enabling the -is-enabled parameter, the SVM will start sending DDNS updates
for its eligible LIFs. Reference:
1: Configure dynamic DNS services3
2: Manage DNS/DDNS services with System Manager4
Question 3
A customer is calling you to troubleshoot why users are unable to connect to their CIFS SVM.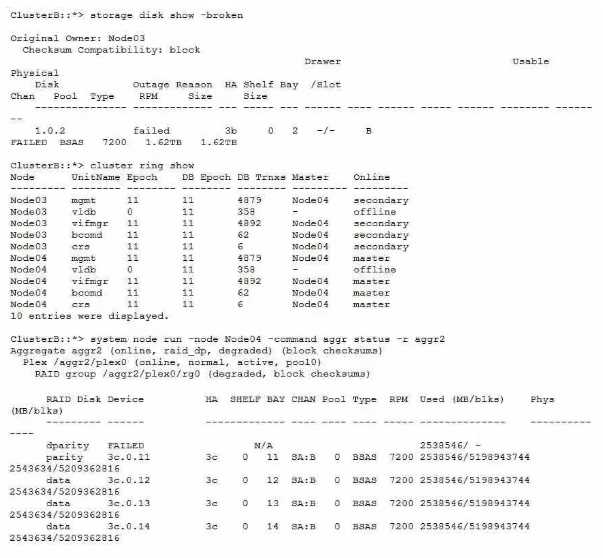
Referring to the Information shown in the exhibit, what Is the source of the problem?
- A. The v1db database is offline.
- B. The aggregate aggr2 has a failed disk.
- C. The databases On Node03 must be Switched from secondary to master.
- D. The broken disk in Node03 is the source of the problem.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The broken disk in Node03 is causing the cluster ring to be offline, which prevents the CIFS SVM from
being accessible. The cluster ring is a distributed database that stores cluster configuration
information and enables communication between cluster nodes. If the cluster ring is offline, the
cluster cannot function properly and the CIFS SVM cannot serve data to clients. The other options are
not relevant to the CIFS SVM connectivity issue. Reference =
https://www.netapp.com/support-and-
training/netapp-learning-services/certifications/support-engineer/
https://mysupport.netapp.com/site/docs-and-kb
Question 4
You have a customer who is concerned with high CPU and disk utilization on their SnapMirror
destination system. They are worried about high CPU and disk usage without any user operations.
In this situation, what should you tell the customer?
- A. Suggest that the customer manually cancel any scanners on the destination to reduce CPU usage.
- B. Explain that background tasks such as SnapMirror throttle up in the absence of user workload.
- C. Suggest that the customer throttle their SnapMirror relationships to reduce resource consumption.
- D. Explain that only user workload should use the CPU and Investigate further.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
SnapMirror is a data replication technology that allows efficient and flexible data protection and
disaster recovery for NetApp ONTAP storage systems1
SnapMirror transfers data between source and destination volumes using a network
connection.
SnapMirror can use storage efficiency features such as compression and deduplication to
reduce the amount of data transferred and stored1
SnapMirror transfers are scheduled and controlled by policies that define the frequency, retention,
and priority of the transfers.
SnapMirror policies can also specify the network bandwidth limit for the
transfers2
SnapMirror transfers are considered background tasks that run in the absence of user
workload.
SnapMirror transfers can consume CPU and disk resources on both source and destination
systems, depending on the amount and type of data being replicated3
SnapMirror transfers can throttle up or down depending on the availability of system resources and
network bandwidth. SnapMirror transfers will throttle up when there is no user workload, and
throttle down when there is user workload.
This is to ensure that SnapMirror transfers do not impact
the performance of user operations3
Therefore, if a customer is concerned with high CPU and disk utilization on their SnapMirror
destination system, the best answer is to explain that background tasks such as SnapMirror throttle
up in the absence of user workload.
This is normal and expected behavior, and it does not indicate a
problem with the system3
Reference:
1: ONTAP 9 Data Protection - SnapMirror - The Open Group 2: ONTAP 9 Data Protection - SnapMirror
Policies - The Open Group 3
: SnapMirror storage efficiency configurations and behavior - Resolution
Guide - NetApp Knowledge Base
Question 5
You are attempting to connect a NetApp ONTAP cluster to a very complex network that requires LIFs
to fail over across subnets.
How would you accomplish this task?
- A. Configure an equal number of UFs on each subnet.
- B. Configure VIP LIFs using OSPF.
- C. Configure VIP LIFs using BGP.
- D. Configure a I IF failover policy for each subnet inside a single broadcast domain.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A LIF (Logical Interface) is a logical entity that represents a network connection point on a node1
.
A VIP LIF (Virtual IP LIF) is a LIF that can fail over across subnets within an IPspace2
.
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a routing protocol that enables VIP LIFs to advertise their IP
addresses to external routers and to update the routing tables when a failover occurs3
.
To connect a NetApp ONTAP cluster to a complex network that requires LIFs to fail over across
subnets, you need to configure VIP LIFs using BGP on the cluster and on the external routers3
.
This way, you can ensure that the network traffic is routed to the optimal node and port for each VIP
LIF, and that the network connectivity is maintained in the event of a node or port
failure3
. Reference:
: Logical Interfaces, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: VIP LIFs, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Configuring BGP on a cluster, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
Question 6
Which two statements about NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP licenses ate true? (Choose two.)
- A. Having an Essentials package enables you to convert to another licensing option.
- B. Capacity-based license packages support only single-node configurations.
- C. BYOL licenses are purchased directly from NetApp.
- D. AWS Marketplace contracts cannot be mixed with BYOL.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
Having an Essentials package enables you to convert to another licensing option. This is true because
the Essentials package is a capacity-based licensing option that allows you to pay for Cloud Volumes
ONTAP per TiB of capacity.
You can switch to another capacity-based package or to a Keystone Flex
Subscription at any time1
.
BYOL licenses are purchased directly from NetApp.
This is true because BYOL stands for Bring Your
Own License, which means you need to obtain a license from NetApp before deploying Cloud
Volumes ONTAP systems in any cloud provider2
.
Capacity-based license packages support only single-node configurations.
This is false because
capacity-based license packages support both single-node and HA configurations1
.
AWS Marketplace contracts cannot be mixed with BYOL.
This is false because you can mix AWS
Marketplace contracts with BYOL as long as the license type matches the instance
type3. Reference: 1: Cloud Volumes ONTAP licensing | NetApp Documentation 2: Set up licensing for
Cloud Volumes ONTAP in Google Cloud - NetApp 3
: Set up licensing for Cloud Volumes ONTAP in AWS
- NetApp
Question 7
Your customer complains that u host will constantly report losing a connection to the iSCSl target and
then report that the session was reestablished.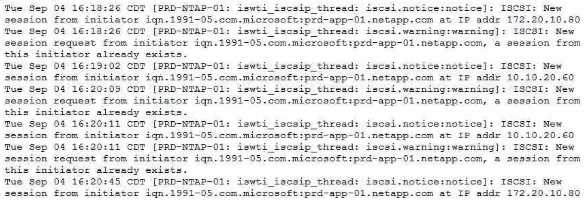
As shown in the exhibit, what is a cause of this flapping?
- A. A host with an IP address of 172.20.10.80 and a second host with an IP address of 10.10.20.60 have the same IQN.
- B. A host with an IP address of 172.20.10.80 and a second host with an IP address of 10.10.20.60 are in different initiator groups.
- C. A host with an IP address of 172.20.10.80 and a second host with an IP address of 10.10.20.60 are accessing the same LUN.
- D. A host with an IP address of 172.20.10.80 and a second IP address of 10.10.20.60 is accessing different LUNs.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
IQN stands for iSCSI Qualified Name, which is a unique identifier for an iSCSI initiator or target1
.
ONTAP uses IQN to authenticate and authorize iSCSI sessions2
.
If two hosts have the same IQN, they will cause a conflict and ONTAP will reject the new session
request from the second host3
.
This will result in the host losing the connection to the iSCSI target and then reporting that the
session was reestablished, as shown in the exhibit.
To avoid this problem, each host should have a unique IQN. Reference:
iSCSI Qualified Name (IQN) - NetApp
iSCSI authentication and authorization - NetApp
Troubleshooting iSCSI issues - NetApp
[Configuring iSCSI initiators - NetApp]
Question 8
A storage administrator reports that a monitoring toot is reporting that the storage controller reads
between 90% to 93% CPU use. You run the sysstat -m command against the node in question.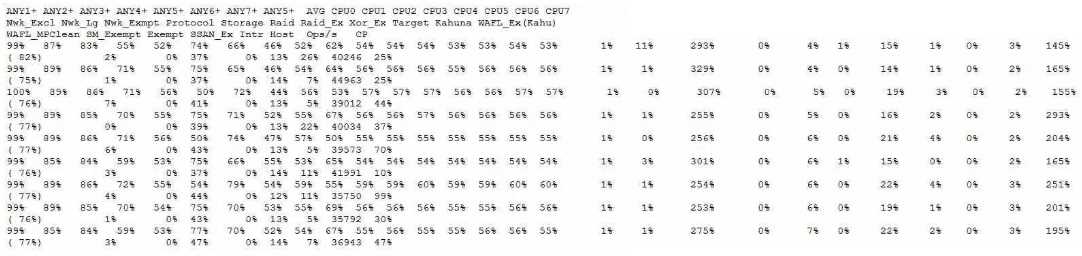
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
- A. The customer should be advised to exclude certain workflows to reduce use.
- B. High network exempt use could be a problem.
- C. You should immediately investigate further by gathering perfstat data and opening a support case.
- D. The CPU Is not a first-order monitoring metric for ONTAP.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
= CPU utilization in ONTAP is not a linear measure of the system load, nor can it be used alone as a
measure of the overall system utilization. ONTAP uses a Coarse Symmetric Multiprocessing (CSMP)
design which partitions system functions into logical processing domains, each with its own
scheduling rules and resource availability. Therefore, a high CPU utilization does not necessarily
indicate a performance problem, unless it is accompanied by other contributing factors such as high
latency, low throughput, or high queue depth. ONTAP has several mechanisms to optimize CPU
usage and balance the workload across the cores, such as WAFL parallelization, exempt processing,
and CPU pinning. The CPU utilization reported by the sysstat command is an average across all cores
and domains, and does not reflect the actual CPU activity or availability for each domain. Therefore,
the CPU is not a first-order monitoring metric for ONTAP, and other metrics such as latency,
throughput, and queue depth should be considered first. Reference =
What is CPU utilization in Data
ONTAP: Scheduling and Monitoring?
,
How to measure CPU utilization
,
What are CPU as a compute
resource and the CPU domains in ONTAP 9?
,
Monitoring CPU utilization before ONTAP upgrade
Question 9
You have a 4-node NetApp ONTAP 9.8 cluster with an AFF A400 HA pair and a FAS8300 HA pair with
16 TB NL-SAS drives. You are asked to automatically tier 150 TB of Snapshot copy data from the AFF
A400 aggregates to the FAS8300.
In this scenario, which ONTAP license must be added to the cluster to accomplish this task?
- A. S3 license
- B. VE license
- C. TPM license
- D. FabricPool license
Answer:
D
Explanation:
FabricPool is an ONTAP feature that enables tiering of cold data from SSD aggregates to low-cost
object storage, either on-premises or in the cloud1
.
FabricPool requires a license to be installed on
the cluster, and the license type depends on the cloud tier being used2
.
In this scenario, the cloud
tier is another ONTAP cluster (FAS8300), which is not supported by the new Cloud Tiering license that
is used for most FabricPool configurations3
.
Therefore, the old FabricPool license that is retained for
dark sites or MetroCluster systems using FabricPool Mirror must be used3
.
The FabricPool license
defines the amount of capacity that can be tiered to the cloud tier, and it can be increased by add-on
orders4
. Reference:
1: FabricPool overview5
2: FabricPool requirements6
3: Install a FabricPool license2
4: ONTAP FabricPool (FP) Licensing Overview1
Question 10
Your customer Informs you about SnapMlrror problems after upgrading NetApp ONTAP software to a
newer version. After investigating the event logs and the SnapMirror history, you see information
about delayed updates of the SnapMirror relationships.
How would your customer prevent such problems in the future?
- A. Quiesce the SnapMirror relationships before upgrading the ONTAP software.
- B. Verify that the cabling of the hardware port that Is responsible for SnapMirror transfers Is correct.
- C. Modify the schedules of the SnapMirror relationships after upgrading the ONTAP software.
- D. Delete the SnapMirror relationships and create them new after upgrading the ONTAP software.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Quiescing the SnapMirror relationships before upgrading the ONTAP software ensures that the data
replication is completed and consistent across the source and destination volumes. This prevents any
data loss or corruption due to the upgrade process. Quiescing also suspends the scheduled updates
until the relationships are resumed, avoiding any delays or failures in the transfers. The other options
are not effective in preventing the SnapMirror problems after the upgrade. Reference =
https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap/upgrade/concept_upgrade_requirements_for_snapmirror.html
https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems-upgrade/upgrade-arl-auto-app/resume_snapmirror_operations.html
Question 11
A customer enabled NFSv4.0 on an SVM and changed the client mount from NFSv3 to NFSv4.
Afterwards, the customer found that the directory owner was changed from root to nobody.
In this scenario, which statement is true?
- A. The customer did not configure name services on the SVM.
- B. The clients must be restarted to start using NFSv4.
- C. The export policy is not configured properly.
- D. The ID mapping domains do not match between the client and server.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
NFSv4 is a network file system protocol that supports security, performance, and scalability
features.
NFSv4 uses ID mapping to ensure that the permissions of files and directories are consistent
across different NFSv4 servers and clients1
ID mapping is the process of translating the user and group identifiers (UIDs and GIDs) of the local
system to the user and group names (user@domain and group@domain) of the remote system, and
vice versa.
ID mapping is done by the idmapd service, which uses the /etc/idmapd.conf file to
determine the domain name of the system2
ID mapping requires that the NFSv4 server and client have the same domain name configured in the
/etc/idmapd.conf file.
If the domain names do not match, the idmapd service cannot map the UIDs
and GIDs to the user and group names, and the permissions of the files and directories will be shown
as nobody:nobody, which is the default anonymous user3
Therefore, if a customer enabled NFSv4.0 on an SVM and changed the client mount from NFSv3 to
NFSv4, and found that the directory owner was changed from root to nobody, the most likely cause is
that the ID mapping domains do not match between the client and server.
The customer should
check and correct the /etc/idmapd.conf file on both systems, and restart the idmapd service and
remount the NFSv4 share4
Reference:
1: ONTAP 9 - Network File System (NFS) - The Open Group 2: ONTAP 9 - NFSv4 and NFSv4.1
Enhancements - The Open Group 3: NFSv4 mount incorrectly shows all files with ownership as
nobody:nobody - Red Hat Customer Portal 4
: NFSv4 mountpoint shows incorrect ownerships as
nobody:nobody in CentOS/RHEL - The Geek Diary
Question 12
You have a NetApp ONTAP cluster consisting of four NetApp FAS8200 controllers with two NetApp
CN1610 cluster switches running ONIAP 9.8 software. You are receiving several alert messages
stating that the cluster network has degraded. After troubleshooting, you determine that the errors
are being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
In this scenario, what should you do first to solve this problem?
- A. Replace the Twinax cable between Node 2, Interface e0b. and the NetApp CN1610 switch.
- B. Replace the motherboard on Node 2.
- C. Replace both NetApp CN1610 switches.
- D. Replace the NetApp CN1610 switch that connects to Node 2, interface e0b.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A Twinax cable is a type of copper cable that is used to connect cluster ports to cluster switches1
.
A cluster port is a network port that is configured for cluster communication and data access2
.
A cluster switch is a network switch that is used to interconnect the nodes in a cluster and provide
redundancy and load balancing3
.
A cluster network is a network that enables cluster communication and data access between the
nodes in a cluster and external clients4
.
A cluster network can be degraded due to various reasons, such as misconfiguration, malfunction, or
excessive link errors on the cluster ports or the cluster switches.
Link errors are errors that occur on the physical layer of the network, such as CRC errors, length
errors, alignment errors, or dropped packets.
Link errors can indicate a problem with the cable, the switch port, the network interface card (NIC),
or the cable connector.
In this scenario, the alert messages state that the cluster network has degraded and the errors are
being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
The first step to solve this problem is to replace the Twinax cable between Node 2, interface e0b and
the NetApp CN1610 switch, as this could be the source of the link errors.
Replacing the cable could resolve the issue and restore the cluster network to a healthy state.
If replacing the cable does not solve the problem, then other steps may be required, such as checking
the switch port, the NIC, or the cable connector, or replacing the switch or the
motherboard. Reference:
: Cluster network cabling, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster ports, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster switches, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster network, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
[5]: How to troubleshoot CLUSTER NETWORK DEGRADED error messages, NetApp Knowledge Base
[6]: Cluster network degraded due to high CRC errors on cluster ports, NetApp Knowledge Base
Question 13
Your customer has mounted an NFS SVM from a Linux client unci performance is very poor. The
customer is certain that they have jumbo frames enabled. They have verified an MTU of 9000 on
both the Linux client and the broadcast domain on the NetApp ONTAP 9.8 cluster.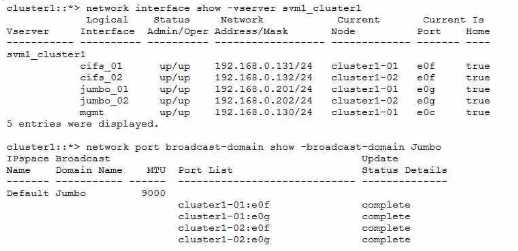
Referring to the exhibit, which ONTAP command will help isolate a possible MTU mismatch?
A.
B.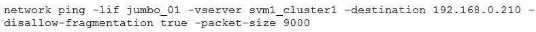
C.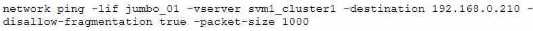
D.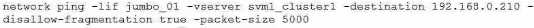
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The ONTAP command that will help isolate a possible MTU mismatch is network ping -lif jumbo_01 -
vserver svm1_cluster1 -destination 192.168.0.210 -disallow-fragmentation true -packet-size 5000.
This command will send a ping packet of 5000 bytes from the logical interface (LIF) jumbo_01 to the
destination IP address 192.168.0.210, without allowing fragmentation. If the ping fails, it means that
there is an MTU mismatch somewhere along the path.
If the ping succeeds, it means that the MTU is
consistent and the problem is elsewhere12. Reference: 1: Check the MTU network setting on the
storage system | NetApp Documentation 2
: How to adjust the MTU for an ONTAP interface - NetApp
Knowledge Base
Question 14
You have a customer complaining of long build times from their NetApp ONTAP-based datastores.
They provided you packet traces from the controller and client. Analysis of these traces shows an
average service response time of 1 ms. QoS output confirms the same. The client traces are reporting
an average of 15 ms in the same time period.
In this situation, what would be your next step?
- A. The cluster is responding slowly and requires further investigation using performance archives.
- B. The client that reports high latency should be investigated.
- C. The cluster interconnects should be investigated.
- D. A sync core should be triggered.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The question describes a scenario where the controller and client have a significant difference in
their reported latency for the same datastores.
The controller’s latency is 1 ms, which is within the normal range for ONTAP-based datastores1
.
The client’s latency is 15 ms, which is much higher than the controller’s latency and could indicate a
performance issue on the client side2
.
Therefore, the next step is to investigate the client that reports high latency and identify the possible
causes, such as network congestion, misconfiguration, resource contention, or application issues23
.
The other options are not relevant or appropriate for this scenario, because:
A) The cluster is not responding slowly, as the controller’s latency is low and QoS output confirms the
same.
C)
The cluster interconnects are not likely to be the cause of the latency difference, as they are used
for communication between nodes within the cluster, not between the controller and the client4
.
D)
A sync core is a diagnostic tool that captures the state of the system at a given point in time, and is
not a troubleshooting step for performance issues5
. Reference:
ONTAP 9 Performance - Resolution Guide - NetApp Knowledge Base
Performance troubleshooting - NetApp
How to troubleshoot performance issues in Data ONTAP 8 7-mode
Cluster interconnect network - NetApp
How to generate a sync core on a node - NetApp
Question 15
Your customer wants to access a LUN on a FAS 8300 system from a VMware ESXi server through the
FC protocol. They already created a new SVM, volume. LUN, and igroup for this purpose. The
customer reports that the server's FC HBA port Is online, but the LUN does not show up.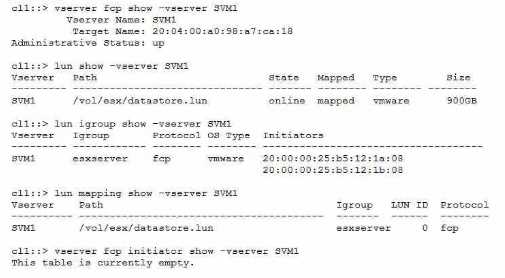
Referring to the exhibit, what is the reason for this problem?
- A. The FC service has not been configured on the SVM.
- B. The zoning on the FC switches Is Incorrect.
- C. The LUN Is not mapped to the correct SCSI ID.
- D. The esxserver igroup contains incorrect IQNs.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To access a LUN on a FAS 8300 system from a VMware ESXi server through the FC protocol, the
customer must configure the FC service on the SVM that owns the LUN. The FC service enables the
SVM to act as an FC target and communicate with the FC initiators on the host. Without the FC
service, the LUN will not be visible to the host, even if the LUN is mapped to an igroup and the FC
LIFs are up. The exhibit shows that the FC service is not configured on the SVM, as the output of the
command vserver fcp initiator show -vserver SVM1 is empty. Therefore, the reason for the problem
is that the FC service has not been configured on the SVM. Reference =
Configure an SVM for
FC
,
Create an FC protocol service
,
Single IQN iSCSI session with ESXi on ONTAP when igroup has two
IQNs