MuleSoft mcd-level-2 practice test
MuleSoft Certified Developer - Level 2 (Mule 4)
Question 1
The flow is invoicing a target API. The API’s protocol is HTTPS. The TLS configuration in the HTTP
Request Configuration global element is set to None. A web client submits a request to
http:localhost:8081/vehicles.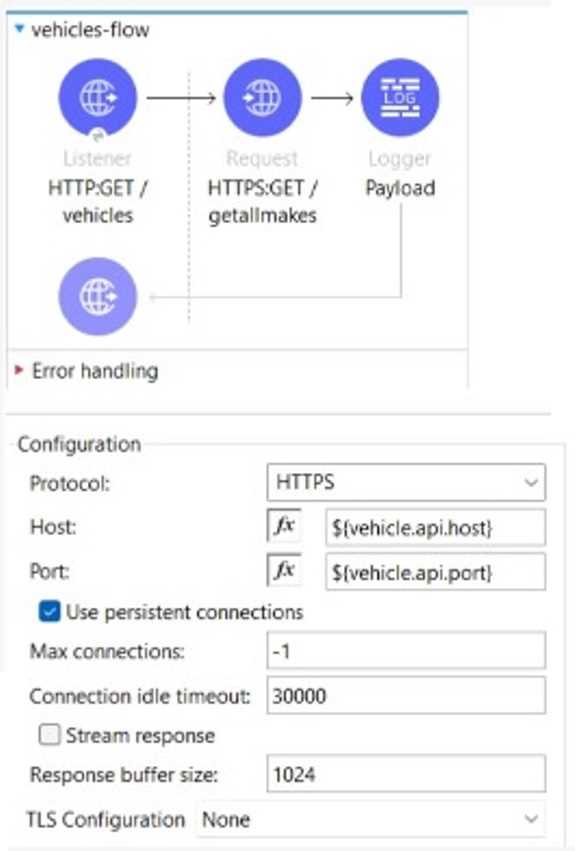
If the certificate of the target API is signed by a certificate authority (CA), what is true about the HTTP
Request operation when the flow executes?
- A. The HTTP Request operation will succeed if the CA’S certificate is present in the JRE’s default keystore
- B. The HTTP Request operation will succeed if the CA’s certificate is present in the JRE’s default truststore.
- C. The HTTP Request operation will always succeed regardless of the CA
- D. The HTTP Request operation will always fail regardless of the CA
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The HTTP Request operation will use the default truststore of the JRE to validate the certificate of the
target API. If the CA’s certificate is present in the truststore, the operation will succeed. Otherwise, it
will fail with a handshake exception. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/tls-
configuration#tls-default
Question 2
When a client and server are exchanging messages during the mTLS handshake, what is being agreed
on during the cipher suite exchange?
- A. A protocol
- B. The TLS version
- C. An encryption algorithm
- D. The Public key format
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A cipher suite is a set of cryptographic algorithms that are used to secure the communication
between a client and a server. A cipher suite consists of four components: a key exchange algorithm,
an authentication algorithm, an encryption algorithm, and a message authentication code (MAC)
algorithm. During the cipher suite exchange, the client and the server agree on which encryption
algorithm
to
use
for
encrypting
and
decrypting
the
data.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/tls-configuration#cipher-suites
Question 3
A custom policy needs to be developed to intercept all cutbound HTTP requests made by Mule
applications.
Which XML element must be used to intercept outbound HTTP requests?
- A. It is not possible to intercept outgoing HTTP requests, only inbound requests
- B. http-policy:source
- C. htt-policy:operation
- D. http-policy:processor
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The http-policy:processor element is used to intercept outbound HTTP requests made by Mule
applications. It allows customizing the request before it is sent to the target API and modifying the
response after it is received from the target API. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-
manager/2.x/policy-mule4-custom-policy#policy-xml-file
Question 4
An API has been built to enable scheduling email provider. The front-end system does very little data
entry validation, and problems have started to appear in the email that go to patients. A validate-
customer’’ flow is added validate the data.
What is he expected behavior of the ‘validate-customer’’ flow?
- A. If only the email address Is invalid a VALIDATION.INVALID_EMAIL error is raised
- B. If the email address is invalid, processing continues to see if the appointment data and customer name are also invalid C. If the appointment date and customer name are invalid, a SCHEDULE:INVALID_APPOINTMENT_DATE error is raised D. If all of the values are invalid the last validation error is raised:SCHEDULE:INVALID_CUSTOMER_NAME
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The validate-customer flow uses an until-successful scope to validate each field of the customer data.
The until-successful scope executes its processors until they succeed or exhausts the maximum
number of retries. If any processor fails, it raises an error and stops executing the remaining
processors. Therefore, if only the email address is invalid, a VALIDATION.INVALID_EMAIL error is
raised and the validation of appointment date and customer name is skipped. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/until-successful-scope
Question 5
When implementing a synchronous API where the event source is an HTTP Listener, a developer
needs to return the same correlation ID back to the caller in the HTTP response header.
How can this be achieved?
- A. Enable the auto-generate CorrelationID option when scaffolding the flow
- B. Enable the CorrelationID checkbox in the HTTP Listener configuration
- C. Configure a custom correlation policy
- D. NO action is needed as the correlation ID is returned to the caller in the response header by default
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When implementing a synchronous API where the event source is an HTTP Listener, Mule
automatically propagates some message attributes between flows via outbound and inbound
properties. One of these attributes is correlation ID, which is returned to the caller in the response
header by default as MULE_CORRELATION_ID. Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-
runtime/4.3/about-mule-message#message-attributes
Question 6
Which statement is true about using mutual TLS to secure an application?
- A. Mutual TLS requires a hardware security module to be used
- B. Mutual TLS authenticates the identity of the server before the identity of the client
- C. Mutual TLS ensures only authorized end users are allowed to access an endpoint
- D. Mutual TLS increases the encryption strength versus server-side TLS alone
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Mutual TLS (mTLS) is an extension of TLS that requires both parties (client and server) to present
their certificates to each other during the handshake process. This way, both parties can verify each
other’s identity and establish a secure connection. The authentication of the server happens before
the authentication of the client, as the server sends its certificate first and then requests the client’s
certificate.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/tls-configuration#mutual-
authentication
Question 7
Which statement is true when using XML SDK for creating custom message processors?
- A. Properties are fields defined by an end user of the XML SDK component and serve as a global configuration for the entire Mule project in which they are used
- B. An XML SDK provides both inbound and outbound operations
- C. Operations can be reused in recursive calls
- D. All operations are public
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When using XML SDK for creating custom message processors, all operations are public by default
and can be used by any Mule application that imports them. There is no way to make an operation
private or protected in XML SDK. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-sdk/1.1/xml-
sdk#operations
Question 8
Which type of cache invalidation does the Cache scope support without having to write any
additional code?
- A. Write-through invalidation
- B. White-behind invalidation
- C. Time to live
- D. Notification-based invalidation
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Cache scope supports time to live (TTL) as a cache invalidation strategy without having to write
any additional code. TTL specifies how long the cached response is valid before it expires and needs
to be refreshed. The Cache scope also supports custom invalidation strategies using MEL or
DataWeave
expressions.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/cache-
scope#cache_invalidation
Question 9
What is the MuleSoft recommended method to encrypt sensitive property data?
- A. The encryption key and sensitive data should be different for each environment
- B. The encryption key should be identical for all environments
- C. The encryption key should be identical for all environments and the sensitive data should be different for each environment
- D. The encryption key should be different for each environment and the sensitive data should be the same for all environments
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The MuleSoft recommended method to encrypt sensitive property data is to use the Secure
Properties Tool that comes with Anypoint Studio. This tool allows encrypting properties files with a
secret key and then decrypting them at runtime using the same key. The encryption key and sensitive
data should be different for each environment to ensure security and avoid accidental exposure of
sensitive data. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/secure-configuration-
properties
Question 10
A healthcare portal needs to validate the token that it sends to a Mule API. The developer plans to
implement a custom policy using the HTTP Policy Transform Extension to match the token received in
the header from the heathcare portal.
Which files does the developer need to create in order to package the custom policy?
- A. Deployable ZIP file, YAML configuration file
- B. JSON properties file, YAML configuration file
- C. JSON properties file, XML template file
- D. XML template file, YAML configuration file
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To package a custom policy using the HTTP Policy Transform Extension, the developer needs to
create an XML template file and a YAML configuration file. The XML template file defines the policy
logic using Mule components and placeholders for user-defined properties. The YAML configuration
file defines the metadata of the policy, such as its name, description, category, parameters, and
dependencies.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/http-policy-
transform#packaging-the-policy
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.
What action must be performed to log all the errors raised by the VM Connector?
- A. Add <AsyncLOgger name=’orgroute.extensions vm’ level=ERROR’I> inside the Logger tag
- B. Add <AsyncLOgger name=’orgroute.extensions vm’ level=ERROR’/> inside the Appenders tag
- C. Configure <Logger level-‘ERROR’/> inside the VM Connector configuration
- D. Nothing, as error-level events are automatically logged
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To log all the errors raised by the VM Connector, the developer needs to add an async logger with the
name ‘org.mule.extension.vm’ and the level ‘ERROR’ inside the appenders tag of the log4j2.xml file.
This will enable logging all error-level events generated by the VM Connector to the console
appender. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/logging-in-mule#configuring-
custom-logging-settings
Question 12
A developer deploys an API to CloudHub and applies an OAuth policy on API Manager. During
testing, the API response is slow, so the developer reconfigures the API so that the out-of-the-box
HTTP Caching policy is applied first, and the OAuth API policy is applied second.
What will happen when an HTTP request is received?
- A. In case of a cache hit, both the OAuth and HTTP Caching policies are evaluated; then the cached response is returned to the caller
- B. In case of a cache it, only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluating; then the cached response is returned to the caller
- C. In case of a cache miss, only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluated; then the API retrieves the data from the API implementation, and the policy stores the data to be cached in Object Store
- D. In case of a cache miss, both the OAuth and HTTP Caching policies are evaluated; then the API retrieves the data from the API implementation, and the policy does not store the data in Object Store
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When an HTTP request is received and the HTTP Caching policy is applied first, it checks if there is a
cached response for that request in Object Store. If there is a cache hit, meaning that a valid cached
response exists, then only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluated and the cached response is returned
to the caller without invoking the OAuth policy or the API implementation. If there is a cache miss,
meaning that no valid cached response exists, then both the HTTP Caching policy and the OAuth
policy
are
evaluated
before
invoking
the
API
implementation.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/http-caching-policy#policy-ordering
Question 13
A system API that communicates to an underlying MySQL database is deploying to CloudHub. The
DevOps team requires a readiness endpoint to monitor all system APIs.
Which strategy should be used to implement this endpoint?
- A. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and reachability of the underlying systems
- B. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and health of the server
- C. Use an existing resource endpoint of the API
- D. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status only
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To implement a readiness endpoint to monitor all system APIs, the developer should create a
dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and reachability of the underlying systems.
This way, the DevOps team can check if the system API is ready to receive requests and if it can
communicate with its backend systems without errors. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-
runtime/4.3/deployment-strategies#readiness-probes
Question 14
The HTTP Request operation raises an HTTP CONNECTIVITY error.
Which HTTP status code and body are returned to the web client?
- A. HTTP Status Code:200. Body ‘Error in processing your request
- B. HTTP Status Code:500. Body ‘The HTTP CONNECTIVITY Error description
- D. HTTP Status Code:500. Body ‘Error in processing your request
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When the HTTP Request operation raises an HTTP CONNECTIVITY error, it triggers an on-error-
continue handler that sets a payload with ‘Error in processing your request’. Since no status code is
explicitly set in this handler, it defaults to 500 (INTERNAL SERVER ERROR). Therefore, the web client
receives an HTTP response with status code 500 and body ‘Error in processing your request’.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/error-handling#on-error-continue
Question 15
A Mule application defines as SSL/TLS keystore properly ‘tis,keystore.keyPassword’’ as secure.
How can this property be referenced to access its value within the application?
- A. #{secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
- C. ${secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
- D. p{secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
Answer:
B
Explanation:
∗∗
secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd
ShortExplanationofCorrectAnswerOnly:Toreferenceasecureproper
tyvaluewithintheapplication,thedeveloperneedstousethesyntax{secure::}. In this case, the property
name is tiskeystore,keyPassword, so the correct syntax is ${secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/secure-configuration-
properties#referencing-secure-properties