LPI 300-300 practice test
LPIC-3 Mixed Environments
Question 1
Which of the following statements is true about raw printing with Samba?
- A. Print jobs are submitted as vector files, including font files, which are rendered and printed by Samba.
- B. Printing jobs are always submitted to Samba in raw postscript.
- C. Any printed file, e.g. an office document, is submitted to the printer without any further processing in exactly the same bit sequence as it is stored on disk.
- D. Samba converts printer-specific jobs to raw data to make them printable on an arbitrary printer.
- E. Printing jobs are rendered on the client and passed on to the printer by Samba.
Answer:
E
Explanation:
Client-Side Rendering: In Samba, raw printing means that the client machine renders the print job,
which includes converting it to a printer-ready format.
Transmission to Printer: This rendered print job is then sent to the Samba server without further
processing or alteration. Samba acts merely as a pass-through, sending the job directly to the printer.
Advantages: This method offloads the rendering process from the server to the client, which can be
beneficial in environments with diverse printer types and models, reducing the processing load on
the server.
Conclusion: Thus, the correct answer is that printing jobs are rendered on the client and passed on to
the printer by Samba.
Reference:
Samba Printing Documentation
Question 2
The configuration of a Samba share contains the following line:
force directory mode = 0555
If a client creates a new directory with the permissions 0750, which permissions will the resulting
directory have in the Samba server's file system?
- A. 0755
- C. 0750
- D. 0555
- E. 0777
Answer:
D
Explanation:
force directory mode = 0555: This setting in Samba forces the permissions of any newly created
directories to be 0555 regardless of what the client requests.
Client Request: If a client creates a directory with permissions 0750, Samba will override this and set
the directory's permissions to 0555.
Permissions Breakdown:
0: No permissions for owner.
5: Read and execute permissions for the group.
5: Read and execute permissions for others.
Enforcement: Samba applies this mode strictly to ensure consistency and security as defined by the
administrator.
Reference:
Samba Force Directory Mode Documentation
Question 3
Which of the following smb.conf options turns a regular file share into a DFS share?
- A. msdfs root = yes
- B. addfs support = yes
- C. dfs forward = yes
- D. follow symlinks = yes
- E. proxy share = yes
Answer:
A
Explanation:
DFS (Distributed File System): This allows for the organization of shared files on multiple servers in a
distributed file system.
msdfs root = yes: This option in the Samba configuration file (smb.conf) enables a share to be a DFS
root. This means the share can provide access to multiple other shares possibly located on different
servers, creating a single point of access.
Functionality: When enabled, users accessing this DFS root can be redirected transparently to the
actual location of the shared files, which might be spread across different servers.
Setup: To configure a DFS root, add msdfs root = yes to the specific share definition in smb.conf.
Reference:
Samba DFS Configuration
Question 4
FILL BLANK
What option in sms.conf defines where the data of a file share is stored? (Specify ONLY the option
name without any values.)
Answer:
path
Explanation:
path Option: This parameter in smb.conf specifies the directory on the server where the shared data
is stored.
Usage: Within a share definition, the path option points to the actual location on the filesystem that
Samba will share.
Example Configuration:
[example_share] path = /srv/samba/share
Importance: Defining the correct path is crucial for ensuring that the share points to the intended
directory with the appropriate data and permissions.
Reference:
Samba smb.conf man page
Question 5
Which parameter within a share definition in the Samba configuration makes Samba only show files
and directories on a file share which a user can access?
- A. hide unreadable = yes
- B. valid files = read,write
- C. browse mask = 000
- D. browseable = readable
- E. display mode = 100
Answer:
A
Explanation:
hide unreadable: This smb.conf option ensures that only files and directories that the user has
permissions to access are visible in the file share.
Functionality: When set to yes, files and directories that the user cannot read (due to permissions)
will be hidden from their view.
Security and Usability: This helps in enhancing both security and usability by preventing users from
seeing files they cannot access, reducing clutter and potential confusion.
Example Configuration:
[example_share] hide unreadable = yes
Reference:
Samba smb.conf Documentation
Question 6
Which of the following lines is missing in the given [printers] share definition?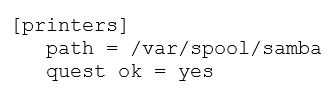
- A. printcap name = cups
- B. printable = yes
- C. print script = /usr/bin/lp -d %P %s
- D. print admin = Administrator, root, @lpadmin
- E. load printers = yes
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In the context of a Samba configuration for printer shares, the [printers] section usually requires the
printable = yes directive to indicate that the share is meant for printing. Without this directive,
Samba would not treat the share as a printer share, even if other settings like path are configured
properly.
The given snippet is:
The line printable = yes is missing and is essential for defining a printer share.
Reference:
Samba Official Documentation - Printer Sharing
Question 7
The [homes] section of smb.conf contains the parameter browseable = no. What are the resulting
consequences? (Choose two.)
- A. When browsing the Samba server, there is no visible share named after the current user.
- B. If the Samba server is part of an Active Director/ Domain, only users in the qroup Se3rowsingUsers can browse the homes share.
- C. When browsing the Samba server, users can open the homes share but they cannot see the content of their home directories.
- D. The homes share can be directly accessed by specifically opening this share by its UNC path.
- E. When browsing the Samba server, there is no visible share called homes.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
When browseable = no is set in the [homes] section of smb.conf, it prevents the share from
appearing in the list of available shares when users browse the server. However, users can still access
their home directories if they specify the correct UNC path directly.
A . When browsing the Samba server, there is no visible share named after the current user.
The share will not appear in the list of shares visible to the user during browsing.
D . The homes share can be directly accessed by specifically opening this share by its UNC path.
Users can still access the share by directly typing the path in the form \\servername\username.
Reference:
Samba Official Documentation - Home Directories
Question 8
Which Samba utility, when launched with the appropriate parameters, generates the following
output?
- A. smbcacls
- B. smbclient
- C. getfacl
- D. smbxattr
- E. smbfacl
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The smbcacls utility is used to manage Windows ACLs on Samba shares. The output format shown in
the image suggests it relates to detailed ACL information, which is typically generated by smbcacls.
Reference:
Samba smbcacls man page
Question 9
Which of the following options can be used to limit access to a Samba share? (Choose two.)
- A. untrusted users
- B. write list
- C. valid groups
- D. valid users
- E. accept list
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
To limit access to a Samba share, the valid users and valid groups options can be used. These
directives specify which users or groups are allowed to access the share.
C . valid groups
This option restricts access to members of specified Unix groups.
D . valid users
This option restricts access to specified Unix users.
Reference:
Samba smb.conf man page
Question 10
In case the following parameters are set in a Samba file share configuration:
create mask = 711
force create mode = 750
What are the effective permissions of a file created with the permissions 777?
- A. 066
- B. 027
- C. 777
- D. 761
- E. 751
Answer:
E
Explanation:
The effective permissions of a file created with the permissions 777 can be calculated considering
the create mask and force create mode.
create mask = 711 implies that the permission bits are ANDed with 0711, i.e., only the owner can
read, write, and execute.
force create mode = 750 implies that certain permission bits are always set, specifically 0750, i.e.,
read, write, and execute for the owner, and read and execute for the group.
The create mask reduces the permissions to 0711, and then force create mode adds the 0750 mask
to the result.
Original permission: 777 AND with create mask (711): 711 OR with force create mode (750): 751
Thus, the effective permission is 751.
Reference:
Samba smb.conf man page - create mask
Question 11
Which of the following are valid Samba backends to store user and group information? (Choose two.)
- A. sdb
- B. smbpasswd
- C. ldapsam
- D. krb
- E. smb
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
smbpasswd: This backend uses the smbpasswd file to store user and group information. It is a simple
plaintext file format that holds password hashes and other account information.
ldapsam: This backend utilizes LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) to store user and group
information. LDAP is a more scalable and flexible option suitable for larger environments.
Other Options:
sdb, krb, smb: These are not valid Samba backends for storing user and group information.
Reference:
Samba User and Group Database Backends
Question 12
How is the Global Catalog of an Active Directory domain accessed?
- A. Through LDAP queries to the ports 3268 (plain text) and 3269 (TLS encrypted).
- B. Through the share GCS SMB which is available on each domain controller.
- C. Through GCS records in the DNS sub zone _gc in the domain's DNS zone.
- D. Through LDAP queries to the base dn CN=GC in the standard LDAP directory.
- E. Through SRV records in the DNS sub zone _msgc in the domain's DNS zone.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Global Catalog: The Global Catalog is a distributed data repository that contains a searchable, partial
representation of every object in every domain in a multi-domain Active Directory forest.
Access Method: It is accessed through LDAP queries to specific ports:
Port 3268: For plain text (unencrypted) LDAP queries.
Port 3269: For LDAP queries encrypted with TLS.
Other Options:
GCS SMB share, GCS records, SRV records, CN=GC in LDAP: These do not provide the correct method
to access the Global Catalog.
Reference:
Microsoft Documentation on Active Directory Global Catalog
Question 13
Which of the following Samba commands provides comprehensive information and status flags on
the user candidate?
- A. smbpasswd -l -u candidate
- B. net sam show candidate
- C. pdbedit -v -u candidate
- D. samba-tool user list
- E. getent smbpasswd candidate
Answer:
C
Explanation:
pdbedit: This Samba command is used to manage the user accounts stored in the Samba password
database.
-v: The verbose option provides detailed information.
-u candidate: Specifies the user for which to display the information.
Other Commands:
smbpasswd, net sam show, samba-tool user list, getent smbpasswd: These commands do not
provide the same comprehensive information and status flags as pdbedit.
Reference:
Samba pdbedit Documentation
Question 14
Which service unifies Linux and Windows account management by allowing a Linux system to
include Windows domain users in the Linux user database?
- A. smbpasswdd
- B. sudo
- C. NIS
- D. Winbind
- E. OpenLDAP
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Winbind: This service is used to unify Linux and Windows account management by allowing a Linux
system to include Windows domain users in the Linux user database.
Functionality: Winbind enables Linux systems to retrieve user and group information from a
Windows NT-based domain or Active Directory.
Other Services:
smbpasswdd, sudo, NIS, OpenLDAP: These services do not provide the same functionality for
unifying account management between Linux and Windows.
Reference:
Samba Winbind Documentation
Question 15
Which group of commands manages the directory replication in an active directory domain?
- A. samba-tool repl
- B. samba-tool directory
- C. samba-tool drs
- D. samba-tool domain
- E. samba-tool sync
Answer:
C
Explanation:
samba-tool drs: This set of commands is used to manage directory replication in an Active Directory
domain. DRS stands for Directory Replication Service.
Functionality: It provides various subcommands to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot replication
issues.
Other Commands:
samba-tool repl, directory, domain, sync: These do not specifically manage directory replication in
the same way as samba-tool drs.
Reference:
Samba DRS Command Documentation