linux foundation cks practice test
Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist
Question 1
Create a new ServiceAccount named backend-sa in the existing namespace default, which has the
capability to list the pods inside the namespace default.
Create a new Pod named backend-pod in the namespace default, mount the newly created sa
backend-sa to the pod, and Verify that the pod is able to list pods.
Ensure that the Pod is running.
Answer:
See the
Explanation:
A service account provides an identity for processes that run in a Pod.
When you (a human) access the cluster (for example, using kubectl), you are authenticated by the
apiserver as a particular User Account (currently this is usually admin, unless your cluster
administrator has customized your cluster). Processes in containers inside pods can also contact the
apiserver. When they do, they are authenticated as a particular Service Account (for
example, default).
When you create a pod, if you do not specify a service account, it is automatically assigned
the default service account in the same namespace. If you get the raw json or yaml for a pod you
have created (for example, kubectl get pods/<podname> -o yaml), you can see
the spec.serviceAccountName field has been
automatically set
.
You can access the API from inside a pod using automatically mounted service account credentials, as
described in
Accessing the Cluster
. The API permissions of the service account depend on
the
authorization plugin and policy
in use.
In version 1.6+, you can opt out of automounting API credentials for a service account by
setting automountServiceAccountToken: false on the service account:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: build-robot
automountServiceAccountToken: false
...
In version 1.6+, you can also opt out of automounting API credentials for a particular pod:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
serviceAccountName: build-robot
automountServiceAccountToken: false
...
The pod spec takes precedence over the service account if both specify
a automountServiceAccountToken value.
Question 2
Fix all issues via configuration and restart the affected components to ensure the new setting takes
effect.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the API server:-
a. Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes RBAC
b. Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes Node
c. Ensure that the --profiling argument is set to false
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:-
a. Ensure the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false.
b. Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is set to Webhook.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the ETCD:-
a. Ensure that the --auto-tls argument is not set to true
Hint: Take the use of Tool Kube-Bench
Answer:
See the
Explanation below.
Explanation:
API server:
Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes RBAC
Turn on Role Based Access Control.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) allows fine-grained control over the operations that different
entities can perform on different objects in the cluster. It is recommended to use the RBAC
authorization mode.
Fix - Buildtime
Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
component: kube-apiserver
tier: control-plane
name: kube-apiserver
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- command:
+ - kube-apiserver
+ - --authorization-mode=RBAC,Node
image: gcr.io/google_containers/kube-apiserver-amd64:v1.6.0
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 8
httpGet:
host: 127.0.0.1
path: /healthz
port: 6443
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 15
timeoutSeconds: 15
name: kube-apiserver-should-pass
resources:
requests:
cpu: 250m
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/
name: k8s
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs
name: certs
- mountPath: /etc/pki
name: pki
hostNetwork: true
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes
name: k8s
- hostPath:
path: /etc/ssl/certs
name: certs
- hostPath:
path: /etc/pki
name: pki
Ensure the --authorization-mode argument includes Node
Remediation: Edit the API server pod specification file /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-
apiserver.yaml on the master node and set the --authorization-mode parameter to a value that
includes Node.
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC
Audit:
/bin/ps -ef | grep kube-apiserver | grep -v grep
Expected result:
'Node,RBAC' has 'Node'
Ensure that the --profiling argument is set to false
Remediation: Edit the API server pod specification file /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-
apiserver.yaml on the master node and set the below parameter.
--profiling=false
Audit:
/bin/ps -ef | grep kube-apiserver | grep -v grep
Expected result:
'false' is equal to 'false'
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:-
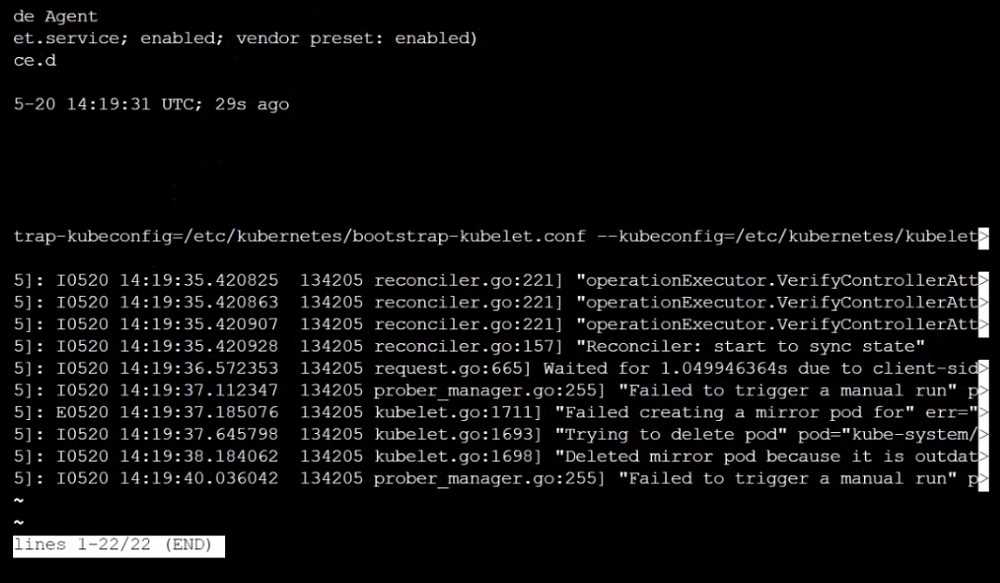
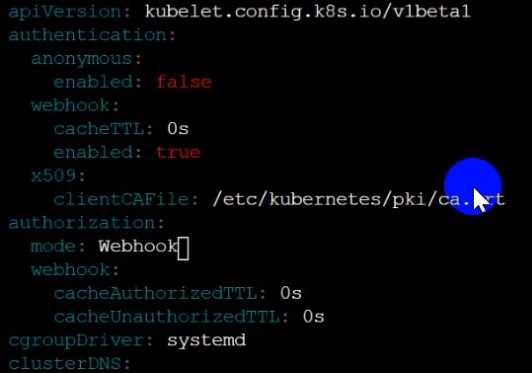
Ensure the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false.
Remediation: If using a Kubelet config file, edit the file to set authentication: anonymous: enabled
to false. If using executable arguments, edit the kubelet service
file /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf on each worker node and set the
below parameter in KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS variable.
--anonymous-auth=false
Based on your system, restart the kubelet service. For example:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart kubelet.service
Audit:
/bin/ps -fC kubelet
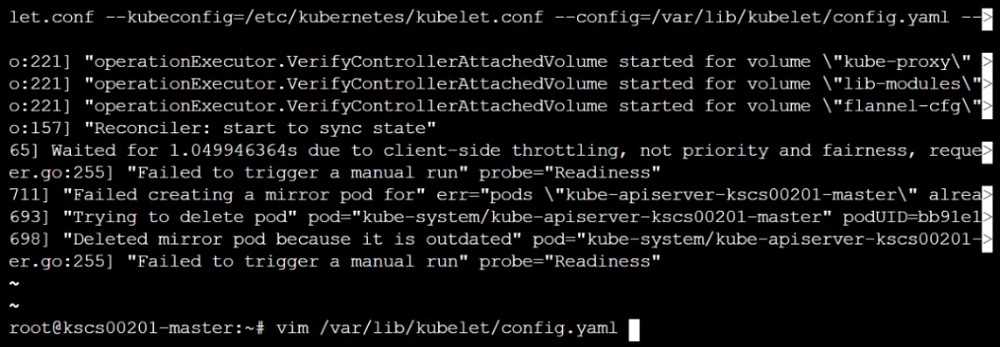
Audit Config:
/bin/cat /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
Expected result:
'false' is equal to 'false'
2) Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is set to Webhook.
Audit
docker inspect kubelet | jq -e '.[0].Args[] | match("--authorization-mode=Webhook").string'
Returned Value: --authorization-mode=Webhook
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the ETCD:-
a. Ensure that the --auto-tls argument is not set to true
Do not use self-signed certificates for TLS. etcd is a highly-available key value store used by
Kubernetes deployments for persistent storage of all of its REST API objects. These objects are
sensitive in nature and should not be available to unauthenticated clients. You should enable the
client authentication via valid certificates to secure the access to the etcd service.
Fix - Buildtime
Kubernetes
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod: ""
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
component: etcd
tier: control-plane
name: etcd
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- command:
+ - etcd
+ - --auto-tls=true
image: k8s.gcr.io/etcd-amd64:3.2.18
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- /bin/sh
- -ec
- ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints=https://[192.168.22.9]:2379 --
cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/healthcheck-client.crt --
key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/healthcheck-client.key
get foo
failureThreshold: 8
initialDelaySeconds: 15
timeoutSeconds: 15
name: etcd-should-fail
resources: {}
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/etcd
name: etcd-data
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
name: etcd-certs
hostNetwork: true
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /var/lib/etcd
type: DirectoryOrCreate
name: etcd-data
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd
type: DirectoryOrCreate
name: etcd-certs
status: {}
Explanation: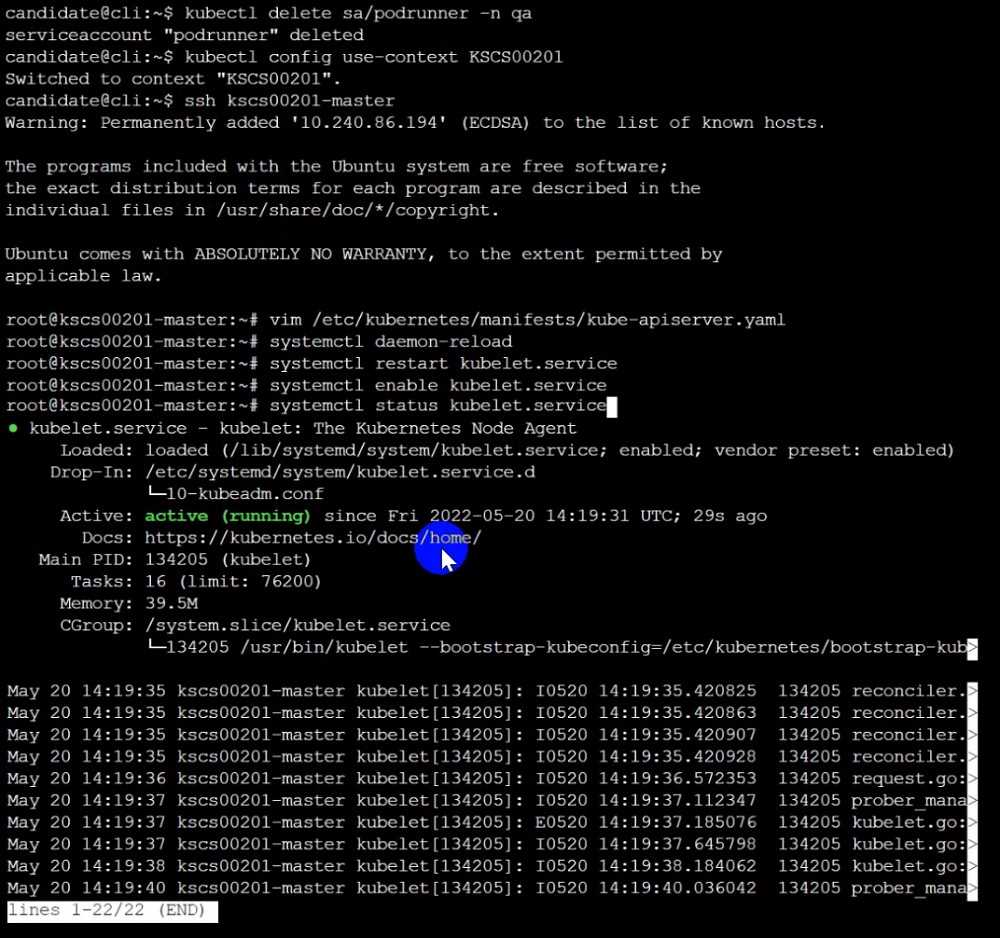
Question 3
Create a PSP that will prevent the creation of privileged pods in the namespace.
Create a new PodSecurityPolicy named prevent-privileged-policy which prevents the creation of
privileged pods.
Create a new ServiceAccount named psp-sa in the namespace default.
Create a new ClusterRole named prevent-role, which uses the newly created Pod Security Policy
prevent-privileged-policy.
Create a new ClusterRoleBinding named prevent-role-binding, which binds the created ClusterRole
prevent-role to the created SA psp-sa.
Also, Check the Configuration is working or not by trying to Create a Privileged pod, it should get
failed.
Answer:
See the
Explanation below.
Explanation:
Create a PSP that will prevent the creation of privileged pods in the namespace.
$ cat clusterrole-use-privileged.yaml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: use-privileged-psp
rules:
- apiGroups: ['policy']
resources: ['podsecuritypolicies']
verbs: ['use']
resourceNames:
- default-psp
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: privileged-role-bind
namespace: psp-test
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: use-privileged-psp
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: privileged-sa
$ kubectl -n psp-test apply -f clusterrole-use-privileged.yaml
After a few moments, the privileged Pod should be created.
Create a new PodSecurityPolicy named prevent-privileged-policy which prevents the creation of
privileged pods.
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: example
spec:
privileged: false # Don't allow privileged pods!
# The rest fills in some required fields.
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
- '*'
And create it with kubectl:
kubectl-admin create -f example-psp.yaml
Now, as the unprivileged user, try to create a simple pod:
kubectl-user create -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pause
spec:
containers:
- name: pause
image: k8s.gcr.io/pause
EOF
The output is similar to this:
Error from server (Forbidden): error when creating "STDIN": pods "pause" is forbidden: unable to
validate against any pod security policy: []
Create a new ServiceAccount named psp-sa in the namespace default.
$ cat clusterrole-use-privileged.yaml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: use-privileged-psp
rules:
- apiGroups: ['policy']
resources: ['podsecuritypolicies']
verbs: ['use']
resourceNames:
- default-psp
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: privileged-role-bind
namespace: psp-test
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: use-privileged-psp
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: privileged-sa
$ kubectl -n psp-test apply -f clusterrole-use-privileged.yaml
After a few moments, the privileged Pod should be created.
Create a new ClusterRole named prevent-role, which uses the newly created Pod Security Policy
prevent-privileged-policy.
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
name: example
spec:
privileged: false # Don't allow privileged pods!
# The rest fills in some required fields.
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
- '*'
And create it with kubectl:
kubectl-admin create -f example-psp.yaml
Now, as the unprivileged user, try to create a simple pod:
kubectl-user create -f- <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pause
spec:
containers:
- name: pause
image: k8s.gcr.io/pause
EOF
The output is similar to this:
Error from server (Forbidden): error when creating "STDIN": pods "pause" is forbidden: unable to
validate against any pod security policy: []
Create a new ClusterRoleBinding named prevent-role-binding, which binds the created ClusterRole
prevent-role to the created SA psp-sa.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
# You need to already have a Role named "pod-reader" in that namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
# You can specify more than one "subject"
- kind: User
name: jane # "name" is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
# "roleRef" specifies the binding to a Role / ClusterRole
kind: Role #this must be Role or ClusterRole
name: pod-reader # this must match the name of the Role or ClusterRole you wish to bind to
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
Question 4

Context
A Role bound to a Pod's ServiceAccount grants overly permissive permissions. Complete the
following tasks to reduce the set of permissions.
Task
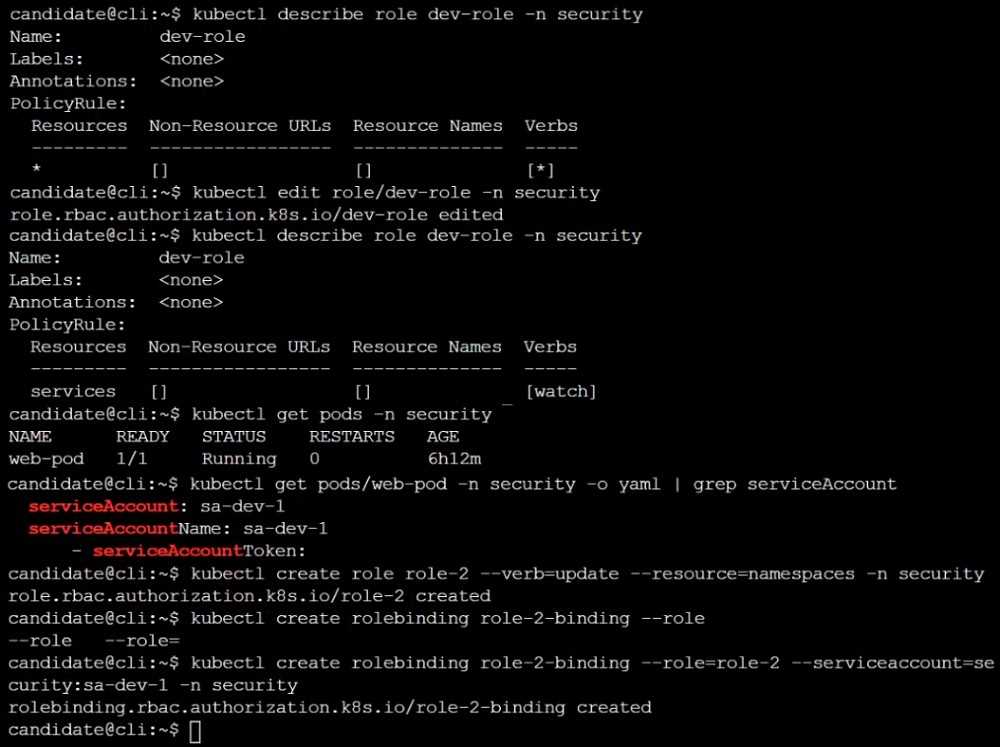
Given an existing Pod named web-pod running in the namespace security.
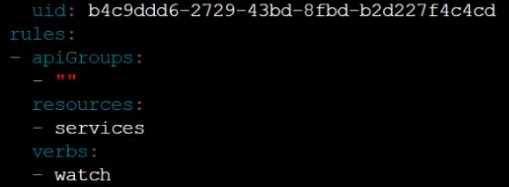
Edit the existing Role bound to the Pod's ServiceAccount sa-dev-1 to only allow performing watch
operations, only on resources of type services.
Create a new Role named role-2 in the namespace security, which only allows performing update
operations, only on resources of type namespaces.
Create a new RoleBinding named role-2-binding binding the newly created Role to the Pod's
ServiceAccount.
Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation: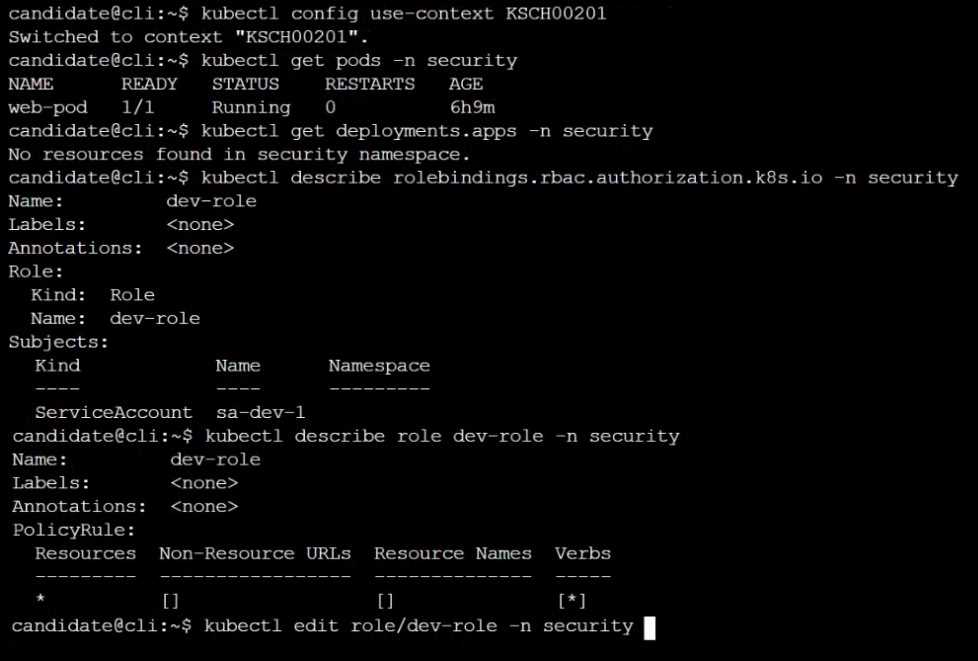
Question 5
Enable audit logs in the cluster, To Do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that
1. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes-logs.txt.
2. Log files are retained for 12 days.
3. at maximum, a number of 8 old audit logs files are retained.
4. set the maximum size before getting rotated to 200MB
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. namespaces changes at RequestResponse
2. Log the request body of secrets changes in the namespace kube-system.
3. Log all other resources in core and extensions at the Request level.
4. Log "pods/portforward", "services/proxy" at Metadata level.
5. Omit the Stage RequestReceived
All other requests at the Metadata level
Answer:
See the
Explanation:
Kubernetes auditing provides a security-relevant chronological set of records about a cluster. Kube-
apiserver performs auditing. Each request on each stage of its execution generates an event, which is
then pre-processed according to a certain policy and written to a backend. The policy determines
what’s recorded and the backends persist the records.
You might want to configure the audit log as part of compliance with the CIS (Center for Internet
Security) Kubernetes Benchmark controls.
The audit log can be enabled by default using the following configuration in cluster.yml:
services:
kube-api:
audit_log:
enabled: true
When the audit log is enabled, you should be able to see the default values at /etc/kubernetes/audit-
policy.yaml
The log backend writes audit events to a file in
JSONlines
format. You can configure the log audit
backend using the following kube-apiserver flags:
--audit-log-path specifies the log file path that log backend uses to write audit events. Not specifying
this flag disables log backend. - means standard out
--audit-log-maxage defined the maximum number of days to retain old audit log files
--audit-log-maxbackup defines the maximum number of audit log files to retain
--audit-log-maxsize defines the maximum size in megabytes of the audit log file before it gets rotated
If your cluster's control plane runs the kube-apiserver as a Pod, remember to mount the hostPath to
the location of the policy file and log file, so that audit records are persisted. For example:
--audit-policy-file=/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml \
--audit-log-path=/var/log/audit.log
Question 6
Analyze and edit the given Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update -y
RUN apt-install nginx -y
COPY entrypoint.sh /
ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]
USER ROOT
Fixing two instructions present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Analyze and edit the deployment manifest file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: security-context-demo-2
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo-2
image: gcr.io/google-samples/node-hello:1.0
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
privileged: True
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
Fixing two fields present in the file being prominent security best practice issues
Don't add or remove configuration settings; only modify the existing configuration settings
Whenever you need an unprivileged user for any of the tasks, use user test-user with the user id
5487
Answer:
See the
Explanation:
FROM debian:latest
MAINTAINER [email protected]
# 1 - RUN
RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils
RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop
RUN apt-get clean
# 2 - CMD
#CMD ["htop"]
#CMD ["ls", "-l"]
# 3 - WORKDIR and ENV
WORKDIR /root
ENV DZ version1
$ docker image build -t bogodevops/demo .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.072kB
Step 1/7 : FROM debian:latest
---> be2868bebaba
Step 2/7 : MAINTAINER [email protected]
---> Using cache
---> e2eef476b3fd
Step 3/7 : RUN apt-get update && DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq apt-utils
---> Using cache
---> 32fd044c1356
Step 4/7 : RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -yq htop
---> Using cache
---> 0a5b514a209e
Step 5/7 : RUN apt-get clean
---> Using cache
---> 5d1578a47c17
Step 6/7 : WORKDIR /root
---> Using cache
---> 6b1c70e87675
Step 7/7 : ENV DZ version1
---> Using cache
---> cd195168c5c7
Successfully built cd195168c5c7
Successfully tagged bogodevops/demo:latest
Question 7
Create a RuntimeClass named gvisor-rc using the prepared runtime handler named runsc.
Create a Pods of image Nginx in the Namespace server to run on the gVisor runtime class
Answer:
See the
Explanation:
Install the Runtime Class for gVisor
{ # Step 1: Install a RuntimeClass
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RuntimeClass
metadata:
name: gvisor
handler: runsc
EOF
}
Create a Pod with the gVisor Runtime Class
{ # Step 2: Create a pod
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-gvisor
spec:
runtimeClassName: gvisor
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
EOF
}
Verify that the Pod is running
{ # Step 3: Get the pod
kubectl get pod nginx-gvisor -o wide
}
Question 8
Task
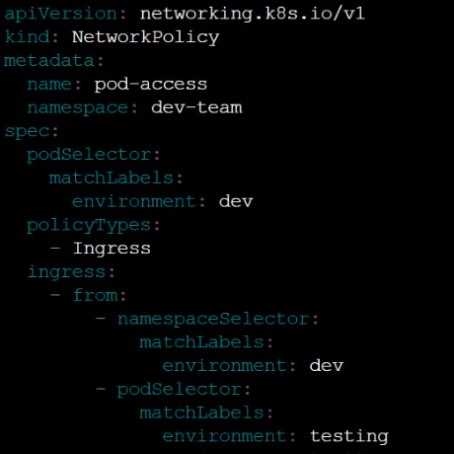
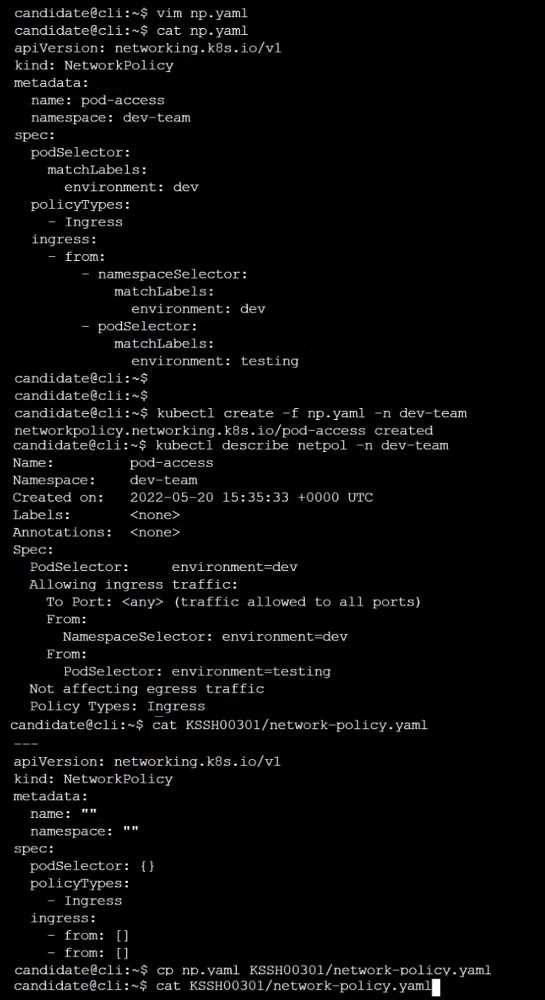
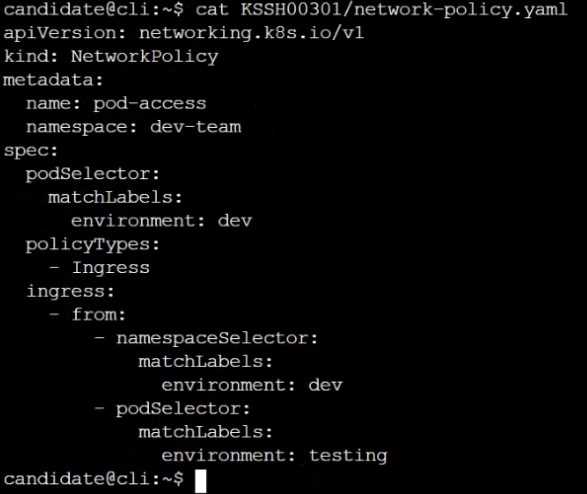
Create a NetworkPolicy named pod-access to restrict access to Pod users-service running in
namespace dev-team.
Only allow the following Pods to connect to Pod users-service:
Pods in the namespace qa
Pods with label environment: testing, in any namespace


Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation: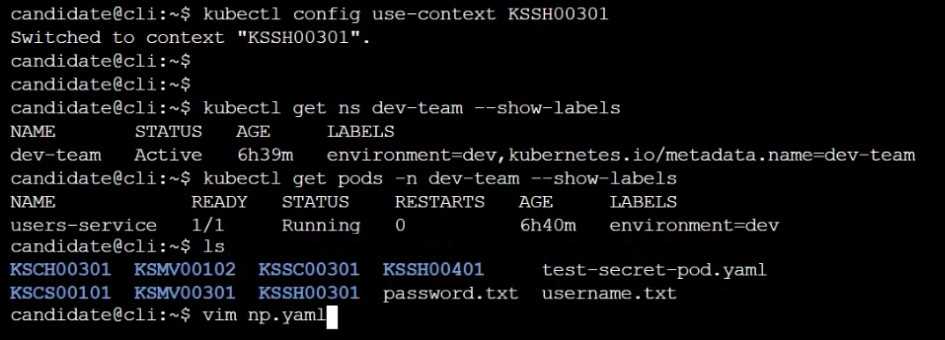
Question 9
A container image scanner is set up on the cluster.
Given an incomplete configuration in the directory
/etc/kubernetes/confcontrol and a functional container image scanner with HTTPS endpoint
https://test-server.local.8081/image_policy
1. Enable the admission plugin.
2. Validate the control configuration and change it to implicit deny.
Finally, test the configuration by deploying the pod having the image tag as latest.
Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation:
ssh-add ~/.ssh/tempprivate
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
cd contrib/terraform/aws
vi terraform.tfvars
terraform init
terraform apply -var-file=credentials.tfvars
ansible-playbook -i ./inventory/hosts ./cluster.yml -e ansible_ssh_user=core -e bootstrap_os=coreos -
b --become-user=root --flush-cache -e ansible_user=core
Question 10
On the Cluster worker node, enforce the prepared AppArmor profile
#include <tunables/global>
profile nginx-deny flags=(attach_disconnected) {
#include <abstractions/base>
file,
# Deny all file writes.
deny /** w,
}
EOF'
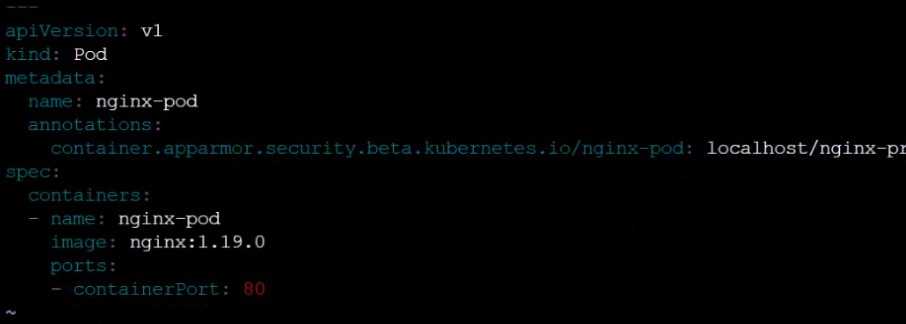
Edit the prepared manifest file to include the AppArmor profile.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: apparmor-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: apparmor-pod
image: nginx
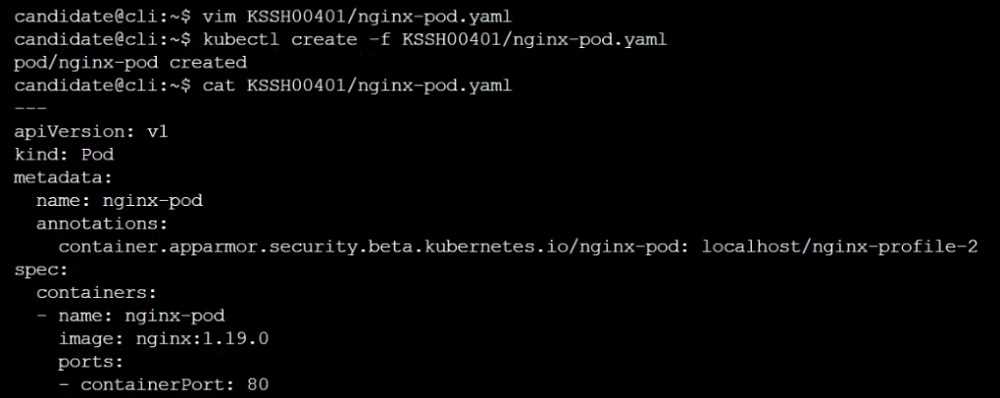
Finally, apply the manifests files and create the Pod specified on it.
Verify: Try to make a file inside the directory which is restricted.
Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation: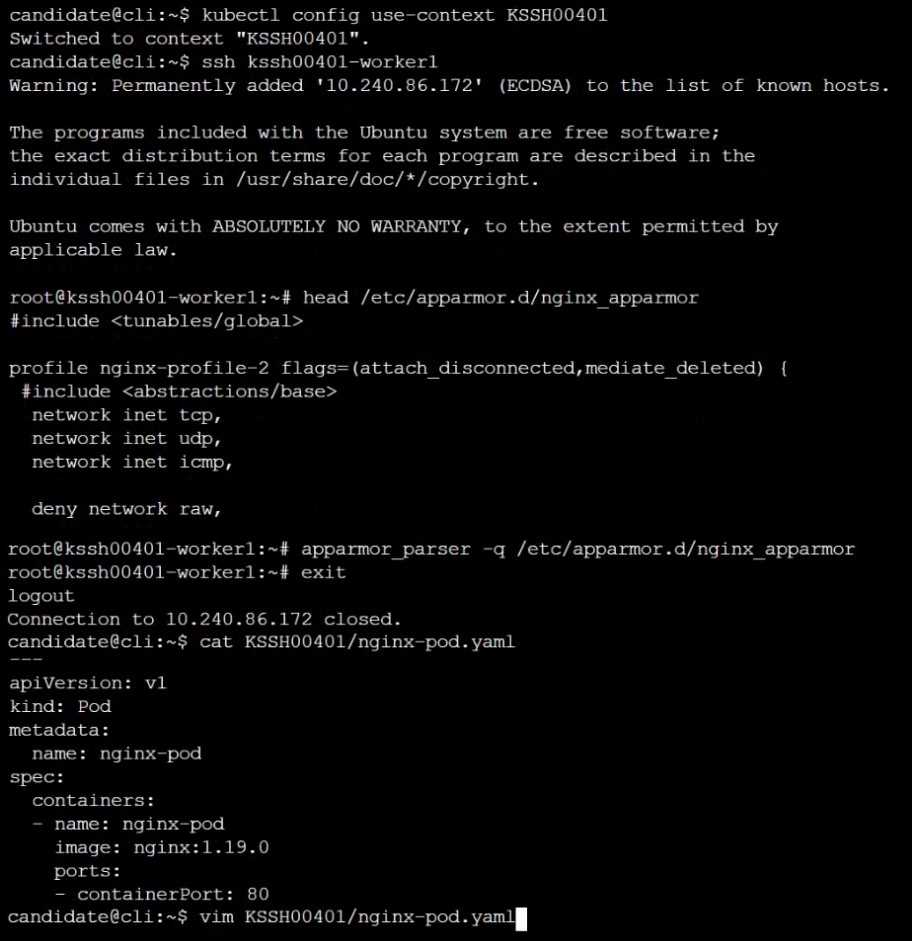
Question 11
Create a new NetworkPolicy named deny-all in the namespace testing which denies all traffic of type
ingress and egress traffic
Answer:
See the
Explanation:
You can create a "default" isolation policy for a namespace by creating a NetworkPolicy that selects
all pods but does not allow any ingress traffic to those pods.
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: default-deny-ingress
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
You can create a "default" egress isolation policy for a namespace by creating a NetworkPolicy that
selects all pods but does not allow any egress traffic from those pods.
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-all-egress
spec:
podSelector: {}
egress:
- {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
Default deny all ingress and all egress traffic
You can create a "default" policy for a namespace which prevents all ingress AND egress traffic by
creating the following NetworkPolicy in that namespace.
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: default-deny-all
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
This ensures that even pods that aren't selected by any other NetworkPolicy will not be allowed
ingress or egress traffic.
Question 12
a. Retrieve the content of the existing secret named default-token-xxxxx in the testing namespace.
Store the value of the token in the token.txt
b. Create a new secret named test-db-secret in the DB namespace with the following content:
username: mysql
password: password@123
Create the Pod name test-db-pod of image nginx in the namespace db that can access test-db-secret
via a volume at path /etc/mysql-credentials
Answer:
See
the explanation
Explanation:
To add a Kubernetes cluster to your project, group, or instance:
Navigate to your:
Project’s Operations > Kubernetes page, for a project-level cluster.
Group’s Kubernetes page, for a group-level cluster.
Admin Area > Kubernetes page, for an instance-level cluster.
Click Add Kubernetes cluster.
Click the Add existing cluster tab and fill in the details:
Kubernetes cluster name (required) - The name you wish to give the cluster.
Environment scope (required) - The
associated environment
to this cluster.
API URL (required) - It’s the URL that GitLab uses to access the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes exposes
several APIs, we want the “base” URL that is common to all of them. For
example, https://kubernetes.example.com rather than https://kubernetes.example.com/api/v1.
Get the API URL by running this command:
kubectl cluster-info | grep -E 'Kubernetes master|Kubernetes control plane' | awk '/http/ {print $NF}'
CA certificate (required) - A valid Kubernetes certificate is needed to authenticate to the cluster. We
use the certificate created by default.
List the secrets with kubectl get secrets, and one should be named similar to default-token-xxxxx.
Copy that token name for use below.
Get the certificate by running this command:
kubectl get secret <secret name> -o jsonpath="{['data']['ca\.crt']}"
Question 13
use the Trivy to scan the following images,
1. amazonlinux:1
2. k8s.gcr.io/kube-controller-manager:v1.18.6
Look for images with HIGH or CRITICAL severity vulnerabilities and store the output of the same in
/opt/trivy-vulnerable.txt
Answer:
Send us your
suggestion on it.
Question 14

Two tools are pre-installed on the cluster's worker node:
sysdig
falco
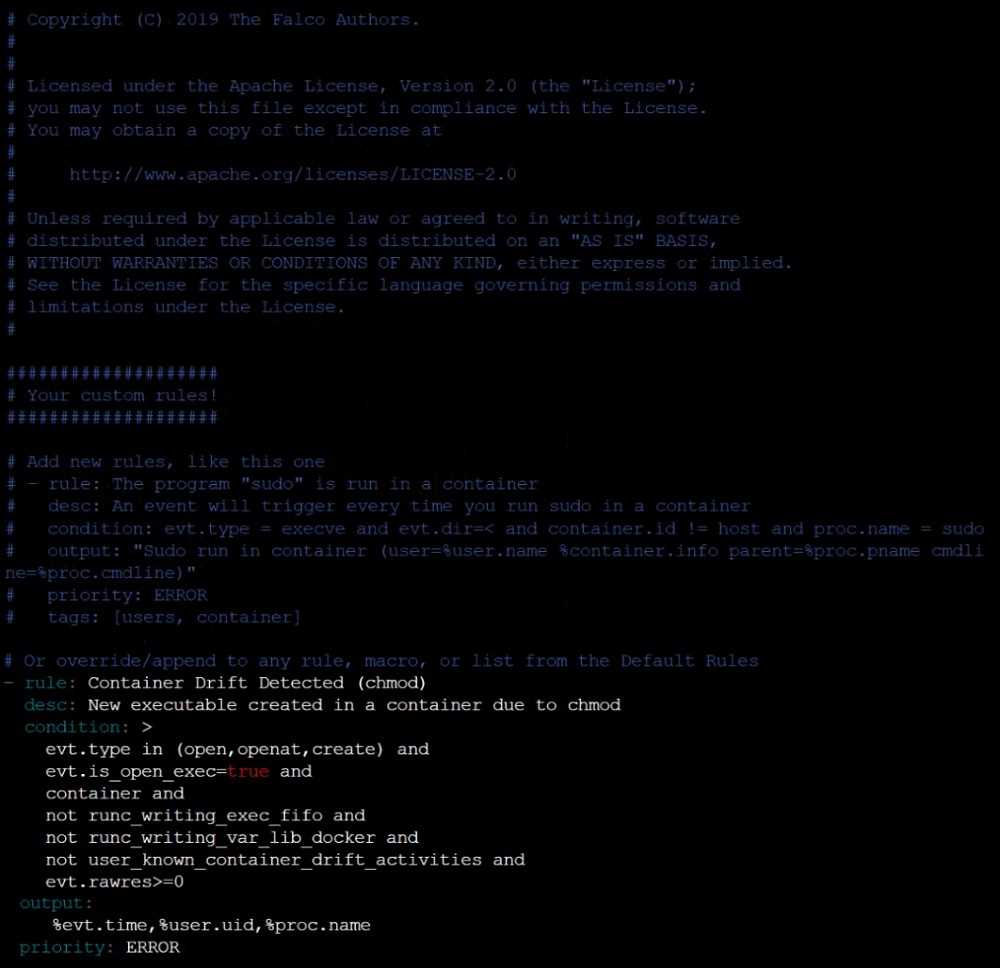
Using the tool of your choice (including any non pre-installed tool), analyze the container's behavior
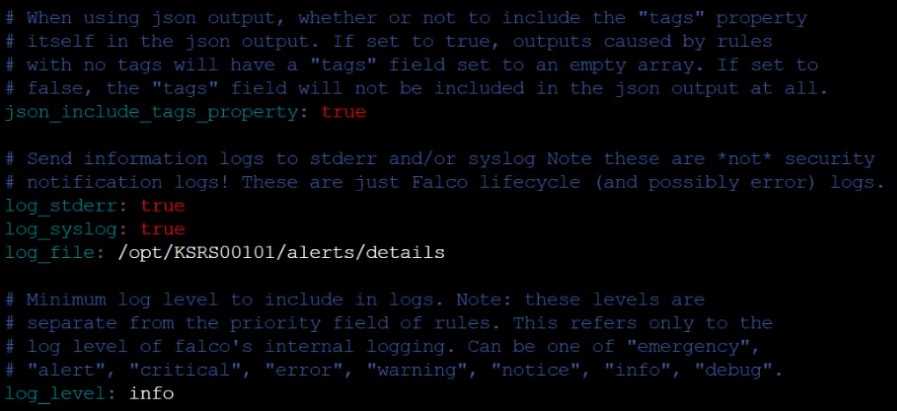
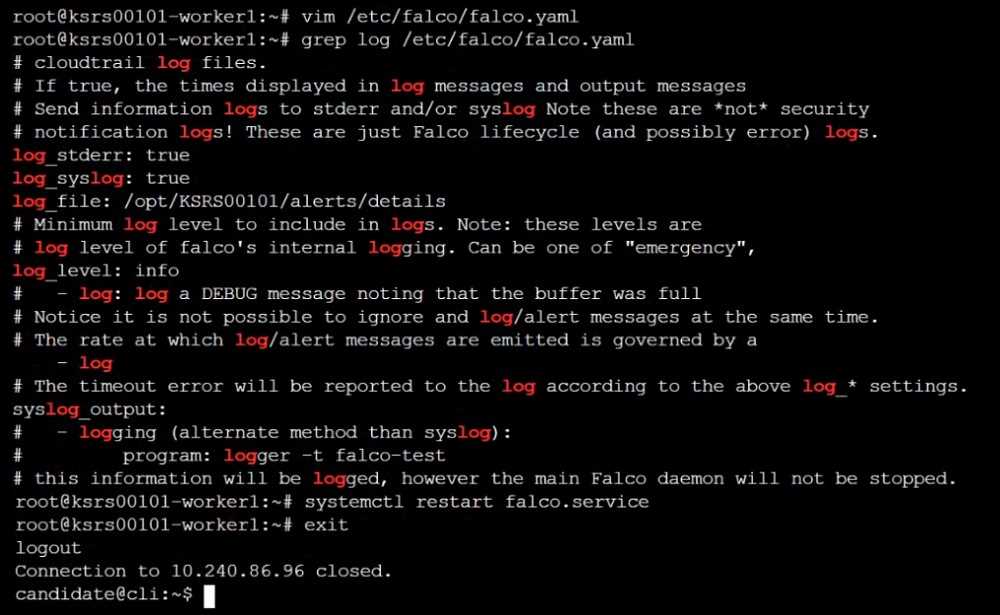
for at least 30 seconds, using filters that detect newly spawning and executing processes.
Store an incident file at /opt/KSRS00101/alerts/details, containing the detected incidents, one per
line, in the following format: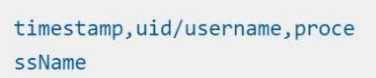
The following example shows a properly formatted incident file:


Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation: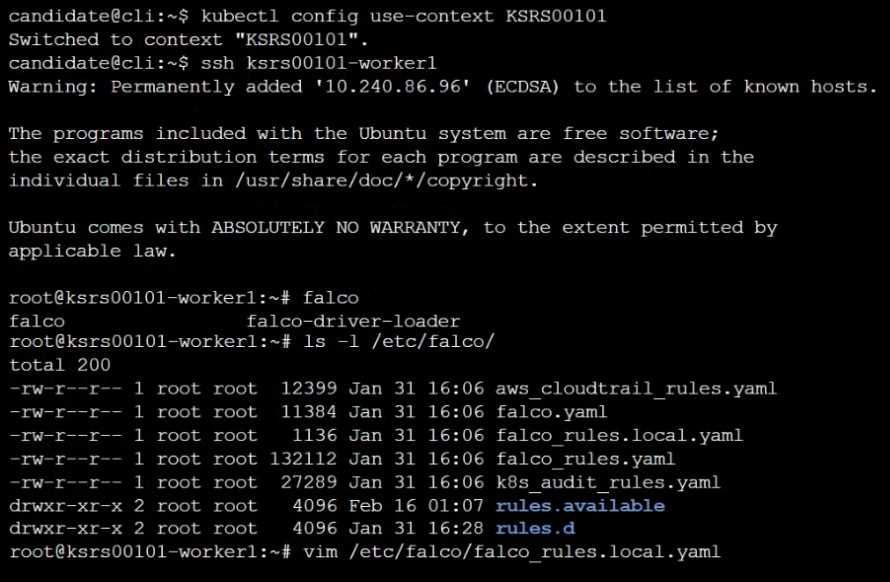
Question 15
Create a User named john, create the CSR Request, fetch the certificate of the user after approving it.
Create a Role name john-role to list secrets, pods in namespace john
Finally, Create a RoleBinding named john-role-binding to attach the newly created role john-role to
the user john in the namespace john.
To Verify: Use the kubectl auth CLI command to verify the permissions.
Answer:
See the
Explanation below.
Explanation:
se kubectl to create a CSR and approve it.
Get the list of CSRs:
kubectl get csr
Approve the CSR:
kubectl certificate approve myuser
Get the certificate
Retrieve the certificate from the CSR:
kubectl get csr/myuser -o yaml
here are the role and role-binding to give john permission to create NEW_CRD resource:
kubectl apply -f roleBindingJohn.yaml --as=john
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/john_external-rosource-rb created
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: john_crd
namespace: development-john
subjects:
- kind: User
name: john
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: crd-creation
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: crd-creation
rules:
- apiGroups: ["kubernetes-client.io/v1"]
resources: ["NEW_CRD"]
verbs: ["create, list, get"]