Juniper jn0-649 practice test
Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT)
Question 1
You are troubleshooting a BGP connection.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)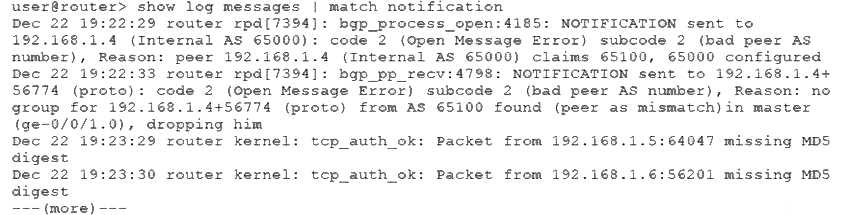
- A. Packet fragmentation is preventing the session from establishing.
- B. The 192.168.1.5 peer has a misconfigured MD5 key.
- C. The ge-0/0/1 interface is disabled.
- D. The 192.168.1.4 peer has a misconfigured autonomous system number.
Answer:
BD
Question 2
Referring to the exhibit, anycast RP is implemented to ensure multicast service availability. The
source is currently sending multicast traffic using group 239.1.1.1 and R3 is receiving PIM register
messages, but R2 does not have active source information.
In this scenario, what are two methods to receive the active source information on R2? (Choose
two.)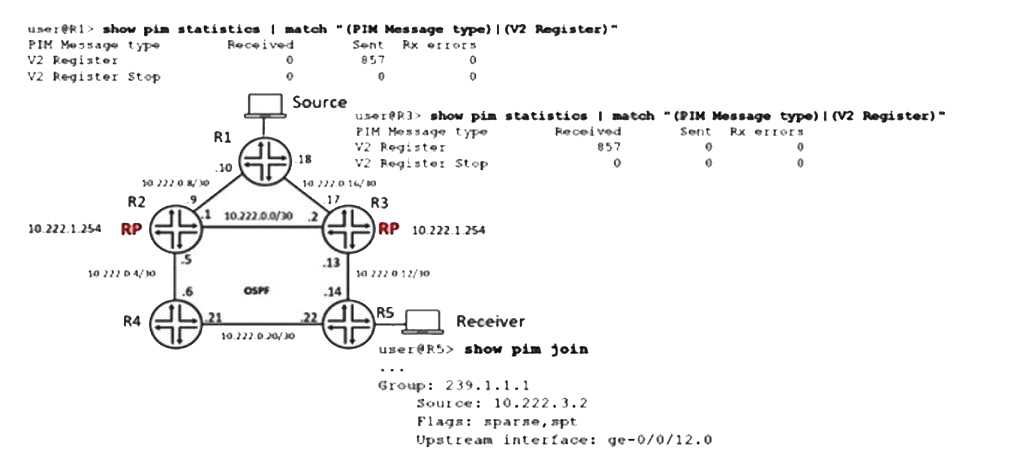
- A. Configure an RP set in PIM on R1, allowing R1 to forward PIM register messages to R2 and R3 in the set.
- B. Configure an MSDP protocol between R2 and R3.
- C. Configure an RP set in PIM on R2 and R3, allowing the RPs to forward PIM register messages to the other RPs in the set.
- D. Configure an MSDP protocol between R1 and R2.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/multicast/topics/ref/statement/rp-set-edit-protocols-pim.html
Question 3
You are asked to establish interface level authentication for users connecting to your network. You
must ensure that only corporate devices, identified by MAC addresses, are allowed to connect and
authenticate. Authentication must be handled by a centralized server to increase scalability.
Which authentication method would satisfy this requirement?
- A. MAC RADIUS
- B. captive portal
- C. 802.1X with single-secure supplicant mode
- D. 802.1X with multiple supplicant mode
Answer:
A
Explanation:
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/user-access/topics/topic-map/mac-radius-authentication-switching-devices.html
You can configure MAC RADIUS authentication on an interface that also allows 802.1X
authentication, or you can configure either authentication method alone.
If both MAC RADIUS and 802.1X authentication are enabled on the interface, the switch first sends
the host three EAPoL requests to the host. If there is no response from the host, the switch sends the
host’s MAC address to the RADIUS server to check whether it is a permitted MAC address. If the MAC
address is configured as permitted on the RADIUS server, the RADIUS server sends a message to the
switch that the MAC address is a permitted address, and the switch opens LAN access to the
nonresponsive host on the interface to which it is connected.
Question 4
Referring to the exhibit, which LSA type is used to advertise 192.168.1.0/24 to R5?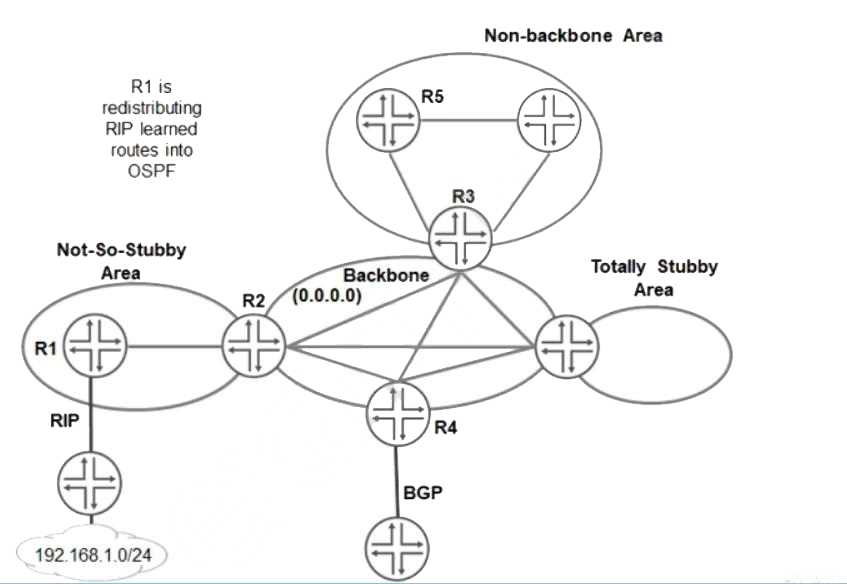
- A. Type 5
- B. Type 4
- C. Type 3
- D. Type 7
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Area-1 has no external connections. However, Area-1 has static route (172.16.31.0/24) that are not
internal OSPF route. You can limit the external route advertisements to the area and advertise the
static routes by designating the area an NSSA. In an NSSA, the ASBR (vMX1) generates NSSA external
(Type 7) LSAs and floods them into the NSSA, where they are contained.
Type-7 LSAs allow an NSSA to support the presence of ASBR and their corresponding external routing
information. The ABR (vMX2) converts Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 External LSAs and leaks them to the
other areas, but external routes from other areas are not advertised within the NSSA.
An admin should check this and change it
https://www.packetswitch.co.uk/configuring-junos-ospf-stub-and-nssa-areas/
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/ospf/topics/ref/statement/nssa-edit-protocols-ospf.html
Question 5
You enable the Multiple VLAN Registration Protocol (MVRP) to automate the creation and
management of virtual LANs.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
- A. The forbidden mode does not register or declare VLANs.
- B. When enabled, MVRP affects all interfaces.
- C. Timers dictate when link state changes are propagated.
- D. MVRP works with RSTP and VSTP.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The forbidden mode does not register or declare VLANs. You can change the registration mode of a
specific interface to forbidden. An interface in forbidden registration mode does not participate in
MVRP even if MVRP is enabled on the switch.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/multicast-l2/topics/topic-map/mvrp.html
MVRP is disabled by default on the switches and, when enabled, affects only trunk interfaces. Once
you enable MVRP, all VLAN interfaces on the switch belong to MVRP (the default normal registration
mode) and those interfaces accept PDU messages and send their own PDU messages. forbidden—
The interface does not register or declare VLANS (except statically configured VLANs).
Question 6
Which address range is used for source-specific multicast?
- A. 239.0.0.0/8
- B. 233.0.0.0/8
- C. 232.0.0.0/8
- D. 224.2.0.0/16
Answer:
C
Explanation:
PIM SSM introduces new terms for many of the concepts in PIM sparse mode. PIM SSM can
technically be used in the entire 224/4 multicast address range, although PIM SSM operation is
guaranteed only in the 232/8 range (232.0.0/24 is reserved). The new SSM terms are appropriate for
Internet
video
applications
and
are
summarized
in
Table
1.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/multicast/topics/concept/multicast-pim-ssm.html
Question 7
Which three configuration parameters must match on all switches within the same MSTP region?
(Choose three.)
- A. VLAN to instance mapping
- B. revision level
- C. configuration name
- D. bridge priority
- E. region name
Answer:
ABE
Explanation:
When enabling MSTP, you define one or more MSTP regions. An MSTP region defines a logical
domain where multiple spanning-tree instances (MSTIs) can be administered independently of MSTIs
in other regions, setting the boundary for bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) sent by one MSTI. An
MSTP region is a group of switches that is defined by three parameters:
Region name—User-defined alphanumeric name for the region.
Revision level—User-defined value that identifies the region.
Mapping table—Numerical digest of VLAN-to-instance mappings.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/stp-l2/topics/topic-map/spanning-tree-configuring-mstp.html
Question 8
Which two statements are correct about the deployment of EVPN-VXLAN on QFX Series devices?
(Choose two.)
- A. Type 1 route advertisements always have the single-active flag set to 1.
- B. Junos OS supports underlay replication for BUM traffic forwarding.
- C. Junos OS supports ingress replication for BUM traffic forwarding.
- D. Type 1 route advertisements always have the single-active flag set to 0.
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
BUM Traffic Forwarding
Junos devices that use MPLS encapsulation for EVPNs can only use ingress replication at this time.
Ingress replication means, to flood traffic to remote PE routers, the traffic has to be replicated, once
for each remote PE router.
The EVPN label for this BUM traffic is learned per PE router from the route type 3, inclusive multicast
Ethernet tag route.
This table shows the format of the inclusive multicast Ethernet tag route.
All-Active Redundancy (4)
This diagram shows the format of the type 1 route, A-D route per ES. The split horizon label is
advertised as part of an extended community attached to the type 1 route. The split horizon label is
also called the ESI label. The extended community also indicates what type of redundancy mode is
used for this given ESI: single-active represented by binary 1 or active-active represented by binary 0.
Question 9
Your enterprise network is running BGP VPNs to support multitenancy. Some of the devices with
which you peer BGP do not support the VPN NLRI. You must ensure that you do not send BGP VPN
routes to the remote peer.
Which two configuration steps will satisfy this requirement? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure an import policy on the remote peer to reject the routes when they are received.
- B. Configure an export policy on the local BGP peer to reject the VPN routes being sent to the remote peer.
- C. Configure a route reflector for the VPN NLRI.
- D. Configure the apply-vpn-export feature on the local BGP peer.
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
Apply both the VRF export and BGP group or neighbor export policies (VRF first, then BGP) before
routes from the vrf or l2vpn routing tables are advertised to other PE routers.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/bgp/topics/ref/statement/vpn-apply-export-edit-protocols-bgp-vp.html
Question 10
You want to create an OSPF area that only contains intra-area route information in the form of Type 1
and Type 2 LSAs.
In this scenario, which area is needed to accomplish this task?
- A. totally non-to-stubby area
- B. totally stubby area
- C. stub area
- D. non-to-stubby area
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A totally stubby area (TSA) is a stub area in which summary link-state advertisement (type 3 LSAs) are
not sent. A default summary LSA, with a prefix of 0.0. 0.0/0 is originated into the stub area by an
ABR, so that devices in the area can forward all traffic for which a specific route is not known, via
ABR.
Question 11
You are implementing the route summarization feature of OSPF.
Which two results do you achieve in this scenario? (Choose two.)
- A. It helps in migrating to future multi-area OSPF network designs.
- B. It reduced the routing table size, enabling devices to store and process less information.
- C. It reduces the impact of topology changes on a device.
- D. It provides optimal routing in the network.
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
OSPF inter-area route summarization reduces the routing information exchanged between areas and
the size of routing tables, and improves routing performance. OSPF inter-area route summarization
enables an ABR to summarize contiguous networks into a single network and advertise the network
to other areas.
Question 12
Your organization has recently acquired another company. You must carry all of the company’s
existing VLANs across the corporate backbone to the existing branch locations without changing
addressing and with minimal configuration.
Which technology will accomplish this task?
- A. Q-in-Q all-in-one bundling
- B. PVLAN isolated VLAN
- C. MVRP registration normal
- D. EVPN-VXLAN anycast gateway
Answer:
A
Question 13
Your enterprise network uses routing instances to support multitenancy. Your Junos devices use BGP
to peer to multiple BGP devices. You must ensure that load balancing is achieved within the routing
instance.
Which two statements would accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure the multipath option at the [edit protocols bgp group <group-name> neighbor] hierarchy.
- B. Configure the multipath option at the [edit protocols bgp group] hierarchy.
- C. Configure a load-balance per-packet policy and apply it at the [edit routing-options forwarding- table] hierarchy.
- D. Configure the multipath option at the [edit routing-instances <instance-name> routing-options] hierarchy.
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
Fortunately, the Juniper Networks BGP implementation supports the notion of a bandwidth
community. This extended community encodes the bandwidth of a given next hop, and when
combined with multipath, the load-balancing algorithm distributes flows across the set of next hops
proportional to their relative bandwidths. Put another way, if you have a 10-Mbps and a 1-Mbps next
hop, on average nine flows will map to the high-speed next hop for every one that uses the low
speed.
Use of BGP bandwidth community is supported only with per-packet load balancing.
The configuration task has two parts:
Configure the external BGP (EBGP) peering sessions, enable multipath, and define an import policy
to tag routes with a bandwidth community that reflects link speed.
Enable per-packet (really per-flow) load balancing for optimal distribution of traffic.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/bgp/topics/topic-map/load-balancing-bgp-session.html
Question 14
You are asked to enforce user authentication using a captive portal before users access the corporate
network.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
- A. HTTPS is the default protocol for a captive portal.
- B. A captive portal can be bypassed using an allowlist command containing a device’s IP address.
- C. When enabled, a captive portal must be applied to each individual interface.
- D. All Web browser requests are redirected to the captive portal until authentication is successful.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
You can set up captive portal authentication on your switch to redirect all Web browser requests to a
login page that requires users to input a username and password before they are allowed access.
Upon successful authentication, users are allowed access to the network and redirected to the
original page requested. Junos OS provides a customizable template for the captive portal window
that allows you to easily design and modify the look of the captive portal login page. You can modify
the design elements of the template to change the look of your captive portal login page and to add
instructions or information to the page. You can also modify any of the design elements of a captive
portal login page. The first screen displayed before the captive login page requires the user to read
the terms and conditions of use. By clicking the Agree button, the user can access the captive portal
login page.
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/us/en/software/junos/user-access/topics/topic-map/user-authentication-captive-portal.html
Question 15
Referring to the exhibit, ServerA sends a single IP packet destined to 10.0.0.127.
Which two statements correctly describe the behavior of the resulting outbound VXLAN packets that
contain the original packet destined to 10.0.0.127? (Choose two.)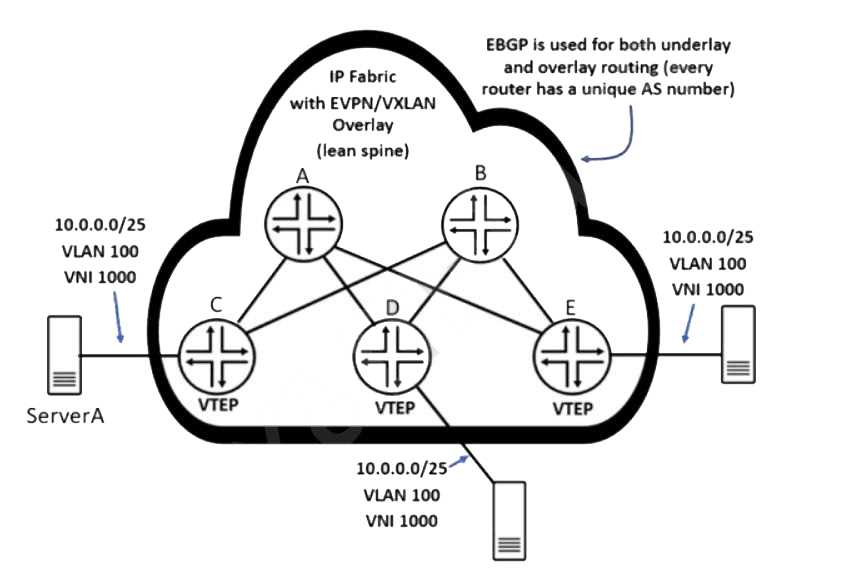
- A. Router E will replicate and send a copy of the received VXLAN packet to router D.
- B. Router C will send a VXLAN packet destined only to router D and router E.
- C. Router D will not replicate and send a copy of the received VXLAN packet to router E.
- D. Router C will send a single VXLAN packet to one remote VTEP.
Answer:
A, D