Juniper jn0-363 practice test
Service Provider Routing and Switching, Specialist (JNCIS-SP)
Question 1
Exhibit button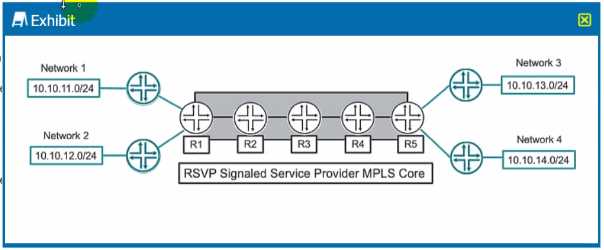
Which two statements are correct about the service provider MPLS network shown in the exhibit?
(Choose two.)
- A. R3 will perform a label pop operation on the transport MPLS label.
- B. Traffic from Network 1 to Network 3 and traffic from Network 1 to Network 4 each need their own unique label-switched path.
- C. Traffic from Network 1 to Network 3 and from Network 1 to Network 4 can share the same label- switched path.
- D. R3 will perform a label swap operation on the transport MPLS label.
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
In MPLS, multiple paths can be merged if they share the same egress router. In the given scenario,
traffic from Network 1 to Network 3 and Network 4 can be engineered to follow the same label-
switched path (LSP) within the MPLS network until they reach the last common point before
diverging to their respective destinations.
As for R3 performing label operations, in a typical MPLS network, intermediate routers (like R3)
perform label swapping. They replace the incoming label with a new label before forwarding the
packet along the LSP. A label pop operation is typically performed by the egress router in the case of
an ultimate hop pop (UHP), where it removes the MPLS label before delivering the packet to the final
destination outside the MPLS domain.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on MPLS
Understanding MPLS Label Operations (Swap, Push, and Pop) - Juniper Networks
Question 2
Which two statements are correct about IS-IS? (Choose two.)
- A. A level 1 only router can never form an adjacency with a level 2 only router.
- B. For level 2 adjacencies, the area IDs can be different.
- C. For level 2 adjacencies, the area IDs must be the same.
- D. A level 1 only router can form an adjacency with a level 2 only router.
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
A Level 1 router can become adjacent with the Level 1 and Level 1-2 (L1/L2) router. A Level 2 router
can become adjacent with Level 2 or Level 1-2 (L1/L2) router. There is no adjacency between L1 only
and L2 only router. HOWEVER: If two routers are in different areas, they can only form a Level 2
adjacency. As such, two routers in different areas can NOT form a Level 1 adjacency. If you want two
routers to form a Level 1 adjacency, they have to be in the same area.
IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) operates at two levels: Level 1 and Level 2. Level
1 routers are only aware of their own area's topology, while Level 2 routers have knowledge of the
topology across areas. A Level 1 router cannot form an adjacency with a Level 2 router unless the
Level 2 router is also operating as a Level 1 router (Level 1-2 router). Level 2 routers can form
adjacencies regardless of their area IDs because Level 2 operates at the domain level and is used to
interconnect different IS-IS areas.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IS-IS
IS-IS Levels and Areas Explanation - Juniper Networks
Question 3
You are adding an IPv6 configuration to an Interface on a Junos device.
In this scenario, which statement is correct?
- A. The link local address must be manually configured within the fdO0::/8 prefix range.
- B. The link local address must be manually configured within the fe80::/10 prefix range.
- C. The link local address is automatically created using the MAC address within the fe80::'l0 prefix range.
- D. The link local address is automatically created using the MAC address within the fd00::/8 prefix range.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
IPv6 link-local addresses are automatically generated for each interface and have a prefix of
fe80::/10. The interface's MAC address is typically used as part of the process to create the Interface
Identifier (IID) in the link-local address, following the EUI-64 format.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IPv6
IPv6 Interface Addresses - Juniper Networks
Question 4
Which statement is correct about IS-IS?
- A. IS-IS is a distance vector routing protocol.
- B. IS-IS is a path vector routing protocol.
- C. IS-IS is a link-state routing protocol.
- D. IS-IS is a classful routing protocol.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
IS-IS is a link-state routing protocol that uses a Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to create a
topology map of the network. It floods link-state advertisements (LSAs) to all nodes within the
network area to ensure each node has a consistent view of the network topology.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IS-IS
Understanding IS-IS - Juniper Networks
Question 5
Which new field is added to an IPv6 header as compared lo IPv4?
- A. version
- B. checksum
- C. fragment offset
- D. flow label
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The IPv6 header includes a new field that is not found in the IPv4 header, called the flow label. The
flow label in IPv6 is used to identify packets that require special handling by routers for quality of
service (QoS) or other reasons, allowing these packets to be handled efficiently as they move
through the network.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IPv6
IPv6 Header Fields - Juniper Networks
Question 6
Interface ge-0/0/0.0 connecls yout network to your ISP. You want to advertise this interface address
as an Internal route In OSPF without creating a neighbor with your ISP.
In this scenario, how is this task accomplished?
- A. Remove interface ge-0/0/0.0 from OSPF.
- B. Create a generated route for Interface ge-0/0/0.0.
- C. Add ge-0/0/0.0 as a passive interface In OSPF.
- D. Configure a static route for Interface ge-0/0/0.0.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When you want to advertise an interface in OSPF but not form an OSPF adjacency over that interface
(for example, towards an ISP), you can configure the interface as passive. This will advertise the
network on the interface in OSPF without sending OSPF hello packets or forming OSPF neighbor
relationships on that interface.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on OSPF
OSPF Configuration Guide - Juniper Networks
Question 7
What are two types of SlDs used in segment touting? (Choose two.)
- A. node
- B. adjacency
- C. link
- D. interface
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
https://zartmann.dk/sr-intro/
In segment routing, SIDs (Segment Identifiers) are used to identify different types of segments that
can be traversed. A node SID represents an instruction to route a packet to a particular node, and an
adjacency SID represents an instruction to route a packet over a specific link or adjacency between
two nodes.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on Segment Routing
Question 8
Exhibit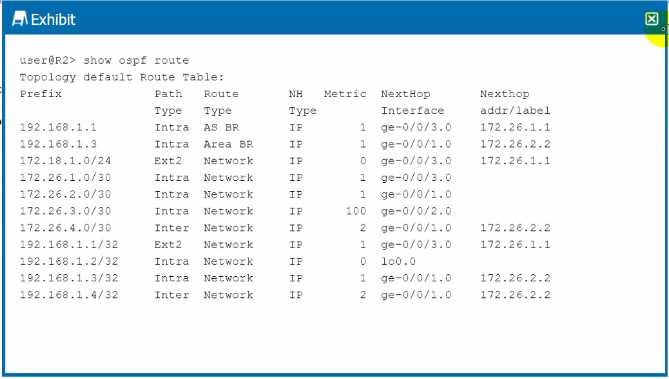
Which prefix in the output shown in the exhibit is an external prefix injected by an OSPF router?
- A. 192.168.1.3
- B. 172.18.1.0/24
- C. 192.108.1.4
- D. 172.26.4.0730
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In the OSPF routing table output, prefixes are marked with different route types. An external prefix
injected into OSPF is marked as 'Ext' (External) followed by a number that indicates whether it's an
E1 or E2 route. The prefix 172.18.1.0/24 is marked as Ext2, which indicates that it is an external route
that has been redistributed into OSPF from another routing protocol or static configuration.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on OSPF
Question 9
Which statement describes integrated routing and bridging (IRB) interfaces?
- A. An IRB interface Is an IP gateway For hosts of a bridge domain.
- B. An IRB interface assigns interfaces to VLANs.
- C. An IRB interface enables Layer 2 switching on the router.
- D. An IRB interface defines a bridge domain.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) interface is used to provide Layer 3 routing services to hosts
within a bridge domain. The IRB acts as a default gateway for hosts in that domain, enabling
communication with other networks.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IRB Interfaces
Question 10
Exhibit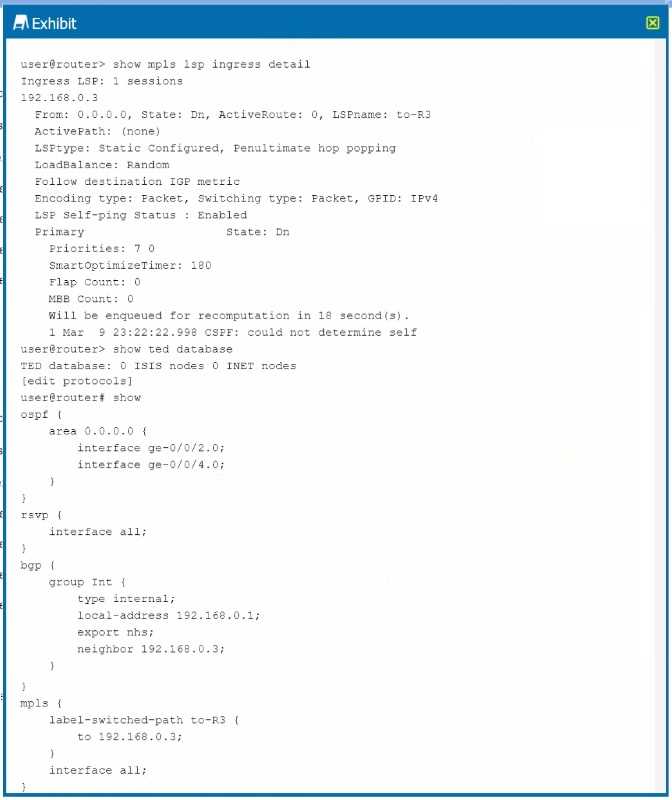
The LSP is not establishing correctly.
Referring to the exhibit, what should you do to solve the problem?
- A. Enable traffic engineering for the OSPF protocol.
- B. Enable traffic engineering for the IS-IS protocol.
- C. Enable traffic engineering for the BGP protocol.
- D. Enable traffic engineering for the RSVP protocol.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The exhibit shows that the Label Switched Path (LSP) is down. One common reason for this could be
that the IGP is not providing traffic engineering information to the MPLS process. Since the exhibit
shows the OSPF configuration, enabling traffic engineering extensions for OSPF would allow OSPF to
distribute the labels and traffic engineering information necessary for LSP establishment.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on MPLS and OSPF
Question 11
You are bringing a new network online with three MX Series devices enabled for STP. No root bridge
priority has been configured. Which statement is true in this scenario?
- A. The device with the lowest MAC address will be elected as the root bridge.
- B. The device with the highest MAC address will be elected as the root bridge.
- C. The device with the lowest numerical lo0 IP address will be elected as the root bridge.
- D. The device with the highest numerical lo0 IP address will be elected as The bridge.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
https://supportportal.juniper.net/s/article/EX-Identify-the-Root-Bridge-in-a-Spanning-Tree-STP-
network?language=en_US The root bridge in a spanning-tree network is the bridge with the smallest
or the lowest bridge ID.
In the absence of a manually configured priority, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) elects the root
bridge based on the lowest bridge ID, which is a combination of the priority and the MAC address.
The device with the lowest MAC address will have the lowest bridge ID and thus be elected as the
root bridge.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on STP
Question 12
What Is a key differentiator of generate routes from aggregate routes?
- A. Generate routes use a forwarding next hop.
- B. Generate routes have a default next-hop value of reject.
- C. Generate routes have a default preference value of 210.
- D. Generate routes cannot be used as a gateway of last resort.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
https://www.networkfuntimes.com/junos-aggregate-routes-vs-generate-routes-how-to-summarise-
on-juniper-routers/
Generated routes are a type of route that can be created to summarize and generate more specific
routes within the routing table. Unlike aggregate routes, which summarize existing routes and inherit
a next-hop, generated routes do not necessarily have to match an existing route and will have a next-
hop of reject by default unless specified otherwise.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on Routing Policies and Route Generation
Question 13
Which statement is correct about the FE80;:/10 prefix?
- A. This prefix range is used for the link local address.
- B. This prefix range is used on the loopback interface.
- C. This prefix range is reserved for multicast applications
- D. This prefix range is not reserved.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The FE80::/10 prefix is reserved for IPv6 link-local addresses. These addresses are auto-configured on
all IPv6-enabled interfaces and can be used for communication within the local link (subnet) only.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IPv6 Addressing
Question 14
You are asked to create connections between routing instances on the same Junos device and route
between the connected Instances. What are two ways to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
- A. Use physical interfaces.
- B. Use an IRB interface.
- C. Use logical tunnel interfaces.
- D. Use loopback interfaces.
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
To create connections between routing instances on the same Junos device and route between them,
you can use logical tunnel interfaces, which are virtual interfaces that can be used to route traffic
between instances without the need for physical connectivity. Additionally, loopback interfaces,
which represent the device itself, can be used to route traffic between routing instances as they are
always up and can be reached within the device.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on Routing Instances
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on Logical Tunnel Interfaces
Question 15
Which configuration selling prohibits a static route from being redistributed by a dynamic routing
protocol?
- A. route-filter
- B. no-readvertise
- C. qualified-next-hop
- D. passive
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The no-readvertise policy statement is used to prevent a static route from being redistributed into a
dynamic routing protocol. This setting ensures that routes that are configured statically are not
advertised out via dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF or BGP.
Reference:
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on Routing Policy