Huawei h12-351-v1-0 practice test
HCIE-WLAN (Written) V1.0
Question 1
Assume that a large enterprise needs to deploy a WLAN to provide wireless access for both
employees and guests. However, guest data may pose security threats on the network. Which of the
following networking modes is applicable to this scenario?
- A. Navi WAC Networking
- B. Leader AP networking
- C. Mesh networking
- D. Fat AP networking
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Navi WAC networking is a networking mode that uses a WLAN Access Controller (WAC) to manage
and control APs. It can provide different authentication and security policies for different user
groups, such as employees and guests. Guest data is isolated from the internal network to prevent
security threats.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100064352/9aadccc0/navi-wac-
networking
Question 2
Which of the following methods are used in IPsec to ensure secure transmission of service data on
the network through encryption and authentication?
- A. The receiver verifies the identity of the sender.
- B. The receiver rejects old or duplicate packets in order to prevent attacks initiated by malicious users who resend sniffed packets,
- C. The sender verifies the identity of the receiver.
- D. Data integrity is verified.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
IPsec uses authentication headers (AHs) and encapsulating security payloads (ESPs) to ensure secure
transmission of service data on the network. AHs provide authentication and integrity verification for
the sender and the receiver, while ESPs provide encryption and optional authentication for the data.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/ipsec
Question 3
Either of the two APs that have established a mesh connection can send a Mesh Peering Close frame
to the other AP to tear down the
mesh connection.
- A. True
- B. False
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A mesh connection can be torn down by either of the two APs that have established it by sending a
Mesh Peering Close frame to the other AP. This frame indicates that the sender no longer wants to
maintain the mesh connection.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/mesh-
networking
Question 4
DRAG DROP
In mesh networking, APs have different roles. Drag the AP roles on the left to the role descriptions on
the right.
Answer:
Explanation:
MP: Mesh node that uses IEEE 802.11 MAC and PHY protocols for wireless communication. This node
supports automatic topology discovery, automatic route discovery, and data packet forwarding.
It
can provide both mesh service and user access service1
.
MPP: MP node that connects a WMN to MPs on other types of networks.
This node can function as a
portal for communication between internal mesh nodes and external networks1
.
Neighbor MP: Neighboring MP with which an MP prepares to establish a mesh link1
.
Candidate MP: AP that directly communicates with a mesh node2
.
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100064365/90f2391e/configuration-
examples-for-mesh 2
:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100169459/8d79210e/configuring-wireless-
mesh-networking
Question 5
In a VRRP HSB scenario, if the VRRP preemption delay is set to a small value, which of the following
problems may occur after a master/backup switchover? (Select All that apply)
- A. The batch backup process cannot be started.
- B. A master/backup switchback is triggered too quickly.
- C. Backup information is incomplete.
- D. Service data on the master and backup WACs is lost.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
According to the Huawei documents and resources, the VRRP preemption delay is the time that an
AC waits before preempting another AC with a lower priority. If the VRRP preemption delay is set to
a small value, the following problems may occur after a master/backup switchover:
B. A master/backup switchback is triggered too quickly. If the master AC recovers soon after a
switchover, it may preempt the backup AC again and become the master AC.
This may cause
frequent switchovers and affect network stability1
.
C. Backup information is incomplete. If the backup AC takes over services from the master AC too
quickly, it may not have received all the data synchronized from the master AC through HSB.
This may
cause service interruption or data loss2
.
Therefore,
B
and
C
are
the
correct
answers.
Reference: 1:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100064368/80fc2ebd/example-for-
configuring-vrrp-hsb 2
:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100096325/1a753937/vrrp-hsb-configuration
Question 6
The display sync-configuration compare command is executed on the backup WAC in HSB to check
wireless configuration synchronization. Based on the command output, which of the following
statements are true? (Select All that apply)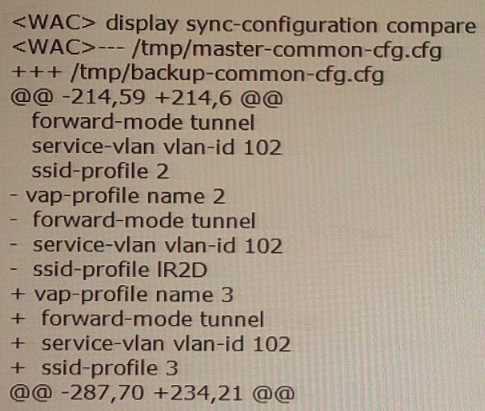
- A. This command is used to check whether the public configurations on two WACs are consistent after wireless configuration synchronization.
- B. The configuration of ssid-profile 2 exists on both the master and backup WACs.
- C. The configuration of vap-profile name 3 exists on the master WAC but not on the backup WAC.
- D. The configuration of vap-profile name 2 exists on the backup WAC but not on the master WAC.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
The display sync-configuration compare command is used to check whether the public configurations
on two WACs are consistent after wireless configuration synchronization. The command output
shows the differences between the configurations on the master and backup WACs. In this case, the
configuration of vap-profile name 3 exists on the master WAC but not on the backup WAC.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/display-
sync-configuration-compare
Question 7
In a dual-link backup scenario, the active/standby link switchover mode is set to priority. When the
active link recovers, the AP detects that the original active link has a higher priority and triggers a
switchback. How many Echo intervals does the AP wait for before switching back to the original
primary WAC?
- A. 20
- B. 10
- C. 15
- D. 5
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a dual-link backup scenario, when the active link recovers, the AP waits for 15 Echo intervals
before switching back to the original primary WAC. This prevents frequent link switchovers caused by
unstable links.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/dual-link-
backup
Question 8
In a dual-link HSB scenario, after an AP sets up CAPWAP links with the active and standby WACs,
which of the following types of packets does the AP periodically send to the WACs to detect link
status?
- A. DTLS
- B. Join
- C. Echo
- D. Keepalive
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a dual-link HSB scenario, after an AP sets up CAPWAP links with the active and standby WACs, the
AP periodically sends Echo packets to the WACs to detect link status. The Echo packets are sent every
30 seconds by default.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/dual-link-
hsb
Question 9
Which of the followings is not a roaming optimization solution?
- A. Proactive roaming
- B. Smart roaming
- C. Fast roaming using PMK caching
- D. 802.11r roaming
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Smart roaming is not a roaming optimization solution, but a feature that allows an AP to
automatically adjust its transmit power based on signal strength and interference level. The other
options are all roaming optimization solutions that can reduce roaming latency and packet loss.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/smart-
roaming
Question 10
DRAG DROP
802. 11r fast roaming (over-the-air) is enabled on the WLAN shown in the figure. A STA roams from
AP1 to AP2. Sort the steps in chronological order during the 802.11r fast roaming process between
WACs.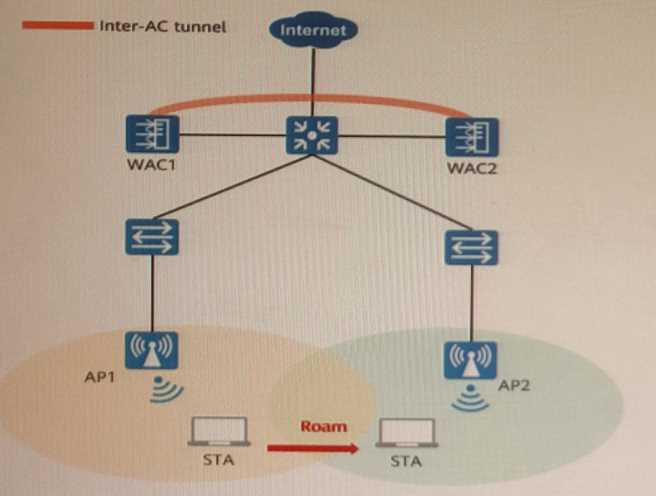

Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Huawei documents and resources, the chronological order during the 802.11r fast
roaming process between WACs is as follows:
2.The STA accesses the network through API. This is the initial association process before roaming.
1.The STA initiates an 802.11 FT authentication request to AP2. This is the first step of the roaming
process when the STA moves to a new AP.
3.AP2 starts the reassociation timer, and sends an 802.11 FT authentication response to the ST
A. This is the second step of the roaming process when AP2 responds to the STA’s request and sets a
timer for reassociation.
4.The STA generates and installs a P TK based on the information contained in the response frame.
This is the third step of the roaming process when the STA derives a new pairwise key for encryption.
5.The STA sends a reassociation request to AP2. This is the fourth step of the roaming process when
the STA requests to reassociate with AP2.
6.AP2 generates and installs a PTK according to PMK-RI and information contained in the request
frame. This is the fifth step of the roaming process when AP2 derives the same pairwise key as the
STA.
7.After receiving the reassociation request, AP2 disables the reassociation timer, and then sends a
reassociation reg onse to the STA. This is the sixth step of the roaming process when AP2 confirms
the reassociation with the STA and stops the timer.
8.The STA receives the response frame of AP2. The roaming process is complete. This is the final step
of the roaming process when the STA completes the handover to AP2.
Therefore,
2,
1,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
is
the
correct
answer.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100169459/8d79210e/configuring-wireless-
mesh-networking
Question 11
In Huawei's smart roaming solution, which of the following methods can be used by a WAC to
discover and maintain neighboring AP entries of STAs? (Select All that Apply)
- A. The WAC obtains such entries using 802. 11v.
- B. The AP listens to the Probe frames sent by STAs.
- C. The AP periodically and proactively scans neighboring APs of STAs.
- D. STAs proactively report neighboring AP information.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
In Huawei’s smart roaming solution, the WAC can discover and maintain neighboring AP entries of
STAs by using two methods: passive listening and active scanning. Passive listening means that the
AP listens to the Probe frames sent by STAs and reports them to the WAC. Active scanning means
that the AP periodically and proactively scans neighboring APs of STAs and reports them to the WAC.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/smart-
roaming
Question 12
Which of the following statements about the home agent are true? (Select All that Apply)
- A. The home agent communicates with the gateway on the STAs1 home network at Layer 2.
- B. The home agent communicates with the gateway on the STAs' home network at Layer 3.
- C. A home AP can function as a home agent of STAs.
- D. A home WAC can function as a home agent of STAs.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
The home agent is a device that communicates with the gateway on the STAs’ home network at Layer
3 and maintains the binding entries of STAs’ home addresses and care-of addresses. A home WAC
can function as a home agent of STAs, while a home AP cannot.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/mobile-ip
Question 13
Which of the following types of non-Wi-R devices can be identified by Huawei APs? (Select All that
Apply)
- A. Bluetooth device
- B. ZigBee device
- C. Game controller
- D. 2.4 GHz wireless video and audio transmitter
Answer:
ABD
Explanation:
Huawei APs can identify non-Wi-Fi devices that operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band, such as
Bluetooth devices, ZigBee devices, game controllers, wireless video and audio transmitters,
microwave ovens, cordless phones, and baby monitors.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/non-wi-fi-
device-identification
Question 14
Which of the following advantages does BSS coloring provide in Wi-Fi 6? (Select All that Apply)
- A. Higher packet rate on the air interface
- B. Enhanced encryption on the air interface
- C. More efficient channel use
- D. Higher concurrency in high-density scenarios
Answer:
ACD
Explanation:
BSS coloring is a feature introduced in Wi-Fi 6 that assigns different colors to different BSSs to reduce
co-channel interference. BSS coloring provides the following advantages:
Higher packet rate on the air interface: BSS coloring reduces collisions between packets from
different BSSs on the same channel, improving packet transmission efficiency.
More efficient channel use: BSS coloring allows spatial reuse of channels by different BSSs, increasing
channel utilization.
Higher concurrency in high-density scenarios: BSS coloring reduces interference among neighboring
APs and improves network performance in high-density scenarios.
Reference:
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/bss-
coloring
Question 15
An AP may preferentially use the BTM mode to steer some STAs. With which of the following
protocols are such STAs compliant?
- A. 802.11k
- B. 802.11i
- C. 802.11r
- D. 802.11v
Answer:
D
Explanation:
An AP may preferentially use the BTM mode to steer some STAs that are compliant with 802.11v
protocol. BTM stands for BSS Transition Management, which is a feature defined in 802.11v protocol
that allows an AP to send a request to a STA to switch to another BSS.
Reference: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100058940/8a8f1c9b/btm