HP hpe6-a78 practice test
Aruba Certified Network Security Associate Exam
Question 1
What is a vulnerability of an unauthenticated Dime-Heliman exchange?
- A. A hacker can replace the public values exchanged by the legitimate peers and launch an MITM attack.
- B. A brute force attack can relatively quickly derive Diffie-Hellman private values if they are able to obtain public values
- C. Diffie-Hellman with elliptic curve values is no longer considered secure in modem networks, based on NIST recommendations.
- D. Participants must agree on a passphrase in advance, which can limit the usefulness of Diffie- Hell man in practical contexts.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The vulnerability of an unauthenticated Diffie-Hellman exchange, particularly when it comes to the
risk of a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, is a significant concern. In this scenario, a hacker can
intercept the public values exchanged between two legitimate parties and substitute them with their
own. This allows the attacker to decrypt or manipulate the messages passing between the two
original parties without them knowing. This answer is based on the fundamental principles of how
Diffie-Hellman key exchange works and its vulnerabilities without authentication mechanisms.
Reference materials from cryptographic textbooks and security protocols detail these vulnerabilities,
such as those found in standards and publications by organizations like NIST.
Question 2
What is a difference between radius and TACACS+?
- A. RADIUS combines the authentication and authorization process while TACACS+ separates them.
- B. RADIUS uses TCP for Its connection protocol, while TACACS+ uses UDP tor its connection protocol.
- C. RADIUS encrypts the complete packet, white TACACS+ only offers partial encryption.
- D. RADIUS uses Attribute Value Pairs (AVPs) in its messages, while TACACS+ does not use them.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
RADIUS and TACACS+ are both protocols used for networking authentication, but they handle the
processes of authentication and authorization differently. RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In
User Service) combines authentication and authorization into a single process, whereas TACACS+
(Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus) separates these processes. This separation
in TACACS+ allows more flexible policy enforcement and better control over commands a user can
execute. This difference is well-documented in various network security resources, including Cisco's
technical documentation and security protocol manuals.
Question 3
A company has an Aruba solution with a Mobility Master (MM) Mobility Controllers (MCs) and
campus Aps. What is one benefit of adding Aruba Airwave from the perspective of forensics?
- A. Airwave can provide more advanced authentication and access control services for the AmbaOS solution
- B. Airwave retains information about the network for much longer periods than ArubaOS solution
- C. Airwave is required to activate Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP) services on the ArubaOS solution
- D. AirWave enables low level debugging on the devices across the ArubaOS solution
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Adding Aruba Airwave to an Aruba solution that includes a Mobility Master (MM), Mobility
Controllers (MCs), and campus APs offers several benefits, notably in the realm of network forensics.
One of the significant advantages is that Airwave can retain detailed information about the network
for much longer periods than what is typically possible with just ArubaOS solutions. This extensive
data retention is crucial for forensic analysis, allowing network administrators and security
professionals to conduct thorough investigations of past incidents. With access to historical data,
professionals can identify trends, pinpoint security breaches, and understand the impact of specific
changes or events within the network over time.
:
Aruba's official product documentation and user guides for Airwave and ArubaOS, which outline
features, benefits, and use cases related to network management and forensic capabilities.
Industry case studies and whitepapers that discuss the implementation and advantages of
integrating Airwave into existing network infrastructure for enhanced monitoring and security.
Question 4
What role does the Aruba ClearPass Device Insight Analyzer play in the Device Insight architecture?
- A. It resides in the cloud and manages licensing and configuration for Collectors
- B. It resides on-prem and provides the span port to which traffic is mirrored for deep analytics.
- C. It resides on-prem and is responsible for running active SNMP and Nmap scans
- D. It resides In the cloud and applies machine learning and supervised crowdsourcing to metadata sent by Collectors
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Aruba ClearPass Device Insight Analyzer plays a crucial role within the Device Insight architecture
by residing in the cloud and applying machine learning and supervised crowdsourcing to the
metadata sent by Collectors. This component of the architecture is responsible for analyzing vast
amounts of data collected from the network to identify and classify devices accurately. By utilizing
machine learning algorithms and crowdsourced input, the Device Insight Analyzer enhances the
accuracy of device detection and classification, thereby improving the overall security and
management of the network.
:
Aruba ClearPass official documentation and whitepapers that detail the functionality and
deployment of the Device Insight Analyzer.
Technical articles and presentations on network security solutions that discuss the use of machine
learning and data analytics in device management.
Question 5
What is a correct guideline for the management protocols that you should use on ArubaOS-Switches?
- A. Disable Telnet and use TFTP instead.
- B. Disable SSH and use https instead.
- C. Disable Telnet and use SSH instead
- D. Disable HTTPS and use SSH instead
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In managing ArubaOS-Switches, the best practice is to disable less secure protocols such as Telnet
and use more secure alternatives like SSH (Secure Shell). SSH provides encrypted connections
between network devices, which is critical for maintaining the security and integrity of network
communications. This guideline is aligned with general security best practices that prioritize the use
of protocols with strong, built-in encryption mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and ensure
data privacy.
Reference: This is a general network management and security practice recommended across various
platforms, including but not limited to ArubaOS-Switch documentation and other network security
resources.
Question 6
Your ArubaoS solution has detected a rogue AP with Wireless intrusion Prevention (WIP). Which
information about the detected radio can best help you to locate the rogue device?
- A. the match method
- B. the detecting devices
- C. the match type
- D. the confidence level
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When an ArubaOS solution detects a rogue AP with Wireless Intrusion Prevention (WIP), the most
crucial information that can help locate the rogue device is the detecting devices.
This is because the
detecting devices can provide the physical location or the network topology context where the rogue
AP has been detected1
.
The detecting devices are typically the Air Monitors (AMs) or Access Points (APs) in the network that
have identified the rogue AP’s presence. These devices can provide information such as the signal
strength and the direction from which the rogue AP’s signals are being received.
By triangulating this
information from multiple detecting devices, it becomes possible to pinpoint the physical location of
the rogue AP2
.
Additionally, the detecting devices can log events and alerts that can be reviewed to understand the
rogue AP’s behavior, such as the channels it is operating on and the potential impact on the
authorized wireless network1
. This information is vital for network administrators to quickly and
effectively respond to the threat posed by the rogue AP.
In contrast, the match method (A) and match type © relate to how the rogue AP is classified and
identified by the system, which is useful for classification but not for physical location.
The
confidence level (D) indicates the system’s certainty in the classification but does not aid in locating
the device2
.
Question 7
What is a benefit of deploying Aruba ClearPass Device insight?
- A. Highly accurate endpoint classification for environments with many devices types, including Internet of Things (loT)
- B. visibility into devices' 802.1X supplicant settings and automated certificate deployment
- C. Agent-based analysts of devices' security settings and health status, with the ability to implement quarantining
- D. Simpler troubleshooting of ClearPass solutions across an environment with multiple ClearPass Policy Managers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Aruba ClearPass Device Insight offers a significant benefit by providing highly accurate endpoint
classification. This feature is particularly useful in complex environments with a wide variety of
device types, including IoT devices. Accurate device classification allows network administrators to
better understand the nature and behavior of devices on their network, which is crucial for
implementing appropriate security policies and ensuring network performance and security.
Reference: This feature is highlighted in Aruba ClearPass Device Insight literature and is a major
selling point of the product as it addresses the challenges posed by diverse and growing device
environments in modern networks.
Question 8
What is a benefit or using network aliases in ArubaOS firewall policies?
- A. You can associate a reputation score with the network alias to create rules that filler traffic based on reputation rather than IP.
- B. You can use the aliases to translate client IP addresses to other IP addresses on the other side of the firewall
- C. You can adjust the IP addresses in the aliases, and the rules using those aliases automatically update
- D. You can use the aliases to conceal the true IP addresses of servers from potentially untrusted clients.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In ArubaOS firewall policies, using network aliases allows administrators to manage groups of IP
addresses more efficiently. By associating multiple IPs with a single alias, any changes made to the
alias (like adding or removing IP addresses) are automatically reflected in all firewall rules that
reference that alias. This significantly simplifies the management of complex rulesets and ensures
consistency across security policies, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing the risk of
errors.
Reference: This functionality is part of the ArubaOS firewall management features, designed to
enhance the usability and flexibility of network security configurations in dynamic network
environments.
Question 9
What is a guideline for managing local certificates on an ArubaOS-Switch?
- A. Before installing the local certificate, create a trust anchor (TA) profile with the root CA certificate for the certificate that you will install
- B. Install an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) certificate to simplify the process of enrolling and re-enrolling for certificate
- C. Generate the certificate signing request (CSR) with a program offline, then, install both the certificate and the private key on the switch in a single file.
- D. Create a self-signed certificate online on the switch because ArubaOS-Switches do not support CA- signed certificates.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When managing local certificates on an ArubaOS-Switch, a recommended guideline is to create a
trust anchor (TA) profile with the root CA certificate before installing the local certificate. This step
ensures that the switch can verify the authenticity of the certificate chain during SSL/TLS
communications. The trust anchor profile establishes a basis of trust by containing the root CA
certificate, which helps validate the authenticity of any subordinate certificates, including the local
certificate installed on the switch. This process is essential for enhancing security on the network, as
it ensures that encrypted communications involving the switch are based on a verified certificate
hierarchy.
:
ArubaOS-Switch security configuration guides that detail the process of certificate management,
including the creation of trust anchor profiles.
Security best practices and SSL/TLS implementation guidelines that emphasize the importance of
establishing trusted certificate chains for secure communications.
Question 10
What distinguishes a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack from a traditional Denial or service
attack (DoS)?
- A. A DDoS attack originates from external devices, while a DoS attack originates from internal devices
- B. A DDoS attack is launched from multiple devices, while a DoS attack is launched from a single device
- C. A DoS attack targets one server, a DDoS attack targets all the clients that use a server
- D. A DDoS attack targets multiple devices, while a DoS Is designed to Incapacitate only one device
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The main distinction between a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack and a traditional Denial of
Service (DoS) attack is that a DDoS attack is launched from multiple devices, whereas a DoS attack
originates from a single device. This distinction is critical because the distributed nature of a DDoS
attack makes it more difficult to mitigate. Multiple attacking sources can generate a higher volume of
malicious traffic, overwhelming the target more effectively than a single source, as seen in a DoS
attack. DDoS attacks exploit a variety of devices across the internet, often coordinated using botnets,
to flood targets with excessive requests, leading to service degradation or complete service denial.
:
Cybersecurity texts and resources that differentiate between types of denial of service attacks.
Technical documentation and analysis of DDoS tactics, which illustrate how botnets and other
distributed systems are employed to execute attacks.
Question 11
You have an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC). for which you are already using Aruba ClearPass Policy
Manager (CPPM) to authenticate access to the Web Ul with usernames and passwords You now want
to enable managers to use certificates to log in to the Web Ul CPPM will continue to act as the
external server to check the names in managers' certificates and tell the MC the managers' correct
rote
in addition to enabling certificate authentication. what is a step that you should complete on the
MC?
- A. Verify that the MC has the correct certificates, and add RadSec to the RADIUS server configuration for CPPM
- B. install all of the managers' certificates on the MC as OCSP Responder certificates
- C. Verify that the MC trusts CPPM's HTTPS certificate by uploading a trusted CA certificate Also, configure a CPPM username and password on the MC
- D. Create a local admin account mat uses certificates in the account, specify the correct trusted CA certificate and external authentication
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To enable managers to use certificates to log into the Web UI of an Aruba Mobility Controller (MC),
where Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) acts as the external server for authentication, it is
essential to ensure that the MC trusts the HTTPS certificate used by CPPM. This involves uploading a
trusted CA certificate to the MC that matches the one used by CPPM. Additionally, configuring a
username and password for CPPM on the MC might be necessary to secure and facilitate
communication between the MC and CPPM. This setup ensures that certificate-based authentication
is securely validated, maintaining secure access control for the Web UI.
:
Aruba Mobility Controller configuration guides that detail the process of setting up certificate-based
authentication.
Best practices for secure authentication and certificate management in enterprise network
environments.
Question 12
A company has Aruba Mobility Controllers (MCs). Aruba campus APs. and ArubaOS-CX switches. The
company plans to use ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) to classify endpoints by type The ClearPass
admins tell you that they want to run Network scans as part of the solution
What should you do to configure the infrastructure to support the scans?
- A. Create a TA profile on the ArubaOS-Switches with the root CA certificate for ClearPass's HTTPS certificate
- B. Create device fingerprinting profiles on the ArubaOS-Switches that include SNMP. and apply the profiles to edge ports
- C. Create remote mirrors on the ArubaOS-Swrtches that collect traffic on edge ports, and mirror it to CPPM's IP address.
- D. Create SNMPv3 users on ArubaOS-CX switches, and make sure that the credentials match those configured on CPPM
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To configure the infrastructure to support network scans as part of the ClearPass Policy Manager
(CPPM) solution, creating SNMPv3 users on ArubaOS-CX switches is necessary. Ensuring that the
credentials for these SNMPv3 users match those configured on CPPM is crucial for enabling CPPM to
perform network scans effectively. SNMPv3 provides a secure method for network management by
offering authentication and encryption, which are essential for safely conducting scans that classify
endpoints by type. This configuration allows CPPM to communicate securely with the switches and
gather necessary data without compromising network security.
:
ArubaOS-CX configuration manuals that discuss SNMP settings.
Network management and security guidelines that emphasize the importance of secure SNMP
configurations for network scanning and monitoring.
Question 13
You have deployed a new Aruba Mobility Controller (MC) and campus APs (CAPs). One of the WLANs
enforces 802.IX authentication lo Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager {CPPM) When you test connecting
the client to the WLAN. the test falls You check Aruba ClearPass Access Tracker and cannot find a
record of the authentication attempt You ping from the MC to CPPM. and the ping is successful.
What is a good next step for troubleshooting?
- A. Renew CPPM's RADIUS/EAP certificate
- B. Reset the user credentials
- C. Check CPPM Event viewer.
- D. Check connectivity between CPPM and a backend directory server
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When dealing with a failed 802.1X authentication attempt to a WLAN enforced by Aruba ClearPass
Policy Manager (CPPM) where no record of the attempt is seen in ClearPass Access Tracker, a good
next troubleshooting step is to check the CPPM Event Viewer. Since you are able to successfully ping
from the Mobility Controller to CPPM, this indicates that there is network connectivity between
these two devices. The lack of a record in Access Tracker suggests that the issue may not be with the
RADIUS/EAP certificate or user credentials, but possibly with the ClearPass service itself or its
reception of authentication requests. The Event Viewer can provide detailed logs that might reveal
internal errors or misconfigurations within CPPM that could prevent it from processing
authentication attempts properly.
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit.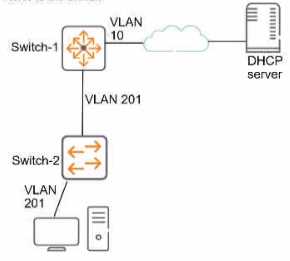
This company has ArubaOS-Switches. The exhibit shows one access layer switch, Swllcn-2. as an
example, but the campus actually has more switches. The company wants to slop any internal users
from exploiting ARP
What Is the proper way to configure the switches to meet these requirements?
- A. On Switch-1, enable ARP protection globally, and enable ARP protection on ail VLANs.
- B. On Switch-2, make ports connected to employee devices trusted ports for ARP protection
- C. On Swltch-2, enable DHCP snooping globally and on VLAN 201 before enabling ARP protection
- D. On Swltch-2, configure static PP-to-MAC bindings for all end-user devices on the network
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To prevent users from exploiting Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) on a network with ArubaOS-
Switches, the correct approach would be to enable DHCP snooping globally and on VLAN 201 before
enabling ARP protection, as stated in option C. DHCP snooping acts as a foundation by tracking and
securing the association of IP addresses to MAC addresses. This allows ARP protection to function
effectively by ensuring that only valid ARP requests and responses are processed, thus preventing
ARP spoofing attacks. Trusting ports that connect to employee devices directly could lead to
bypassing ARP protection if those devices are compromised.
The company’s goal is to prevent internal users from exploiting ARP within their ArubaOS-Switch
network. Let’s break down the options:
Option A (Incorrect): Enabling ARP protection globally on Switch-1 and all VLANs is not the best
approach. ARP protection should be selectively applied where needed, not globally. It’s also not clear
why Switch-1 is mentioned when the exhibit focuses on Switch-2.
Option B (Incorrect): Making ports connected to employee devices trusted for ARP protection is a
good practice, but it’s not sufficient by itself. Trusted ports allow ARP traffic, but we need an
additional layer of security.
Option C (Correct): This is the recommended approach. Here’s why:
DHCP Snooping: First, enable DHCP snooping globally. DHCP snooping helps validate DHCP messages
and builds an IP-MAC binding table. This table is crucial for ARP protection to function effectively.
VLAN 201: Enable DHCP snooping specifically on VLAN 201 (as shown in the exhibit). This ensures
that DHCP messages within this VLAN are validated.
ARP Protection: Once DHCP snooping is in place, enable ARP protection. ARP requests/replies from
untrusted ports with invalid IP-to-MAC bindings will be dropped. This prevents internal users from
exploiting ARP for attacks like man-in-the-middle.
Option D (Incorrect): While static ARP bindings can enhance security, they are cumbersome to
manage and don’t dynamically adapt to changes in the network.
:
ArubaOS-Switch Management and Configuration Guide for WB_16_10 - Chapter 15: IP Routing
Features
Aruba Security Guide
Question 15
Which attack is an example or social engineering?
- A. An email Is used to impersonate a Dank and trick users into entering their bank login information on a fake website page.
- B. A hacker eavesdrops on insecure communications, such as Remote Desktop Program (RDP). and discovers login credentials.
- C. A user visits a website and downloads a file that contains a worm, which sell-replicates throughout the network.
- D. An attack exploits an operating system vulnerability and locks out users until they pay the ransom.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An example of a social engineering attack is described in option A, where an email is used to
impersonate a bank and deceive users into entering their bank login information on a counterfeit
website. Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical hacking
techniques to gain access to systems, data, or personal information. These attacks often involve
tricking people into breaking normal security procedures. The other options describe different types
of technical attacks that do not primarily rely on manipulating individuals through deceptive personal
interactions.