giac gced practice test
GIAC Certified Enterprise Defender
Question 1
When an IDS system looks for a pattern indicating a known worm, what type of detection method is
it using?
- A. Signature-based
- B. Anomaly-based
- C. Statistical
- D. Monitored
Answer:
A
Question 2
Why would an incident handler acquire memory on a system being investigated?
- A. To determine whether a malicious DLL has been injected into an application
- B. To identify whether a program is set to auto-run through a registry hook
- C. To list which services are installed on they system
- D. To verify which user accounts have root or admin privileges on the system
Answer:
C
Question 3
Which could be described as a Threat Vector?
A. A web server left6 unpatched and vulnerable to XSS
B. A coding error allowing remote code execution
C. A botnet that has infiltrated perimeter defenses
D. A wireless network left open for anonymous use
Answer:
A
A threat vector is the method (crafted packet) that would be used to exercise a vulnerability
(fragmentation to bypass IDS signature). An unpatched web server that is susceptible to XSS simply
describes a vulnerability (unpatched) paired with a specific threat (XSS) and does not touch on the
method to activate the threat. Similarly, the coding error that allows remote code execution is simply
describing the pairing of a vulnerability with a threat, respectively. The botnet is an unspecified
threat; there is no indication of how the threat was activated (or it’s intention/capabilities; the
threat).
Question 4
A security device processes the first packet from 10.62.34.12 destined to 10.23.10.7 and recognizes a
malicious anomaly. The first packet makes it to 10.23.10.7 before the security devices sends a TCP
RST to 10.62.34.12. What type of security device is this?
A. Host IDS
B. Active response
C. Intrusion prevention
D. Network access control
Answer:
B
An active response device dynamically reconfigures or alters network or system access controls,
session streams, or individual packets based on triggers from packet inspection and other detection
devices. Active response happens after the event has occurred, thus a single packet attack will be
successful on the first attempt and blocked in future attempts. Network intrusion prevention devices
are typically inline devices on the network that inspect packets and make decisions before
forwarding them on to the destination. This type of device has the capability to defend against single
packet attacks on the first attempt by blocking or modifying the attack inline.
Question 5
Which tool uses a Snort rules file for input and by design triggers Snort alerts?
- A. snot
- B. stick
- C. Nidsbench
- D. ftester
Answer:
C
Question 6
Network administrators are often hesitant to patch the operating systems on CISCO router and
switch operating systems, due to the possibility of causing network instability, mainly because of
which of the following?
A. Having to rebuild all ACLs
B. Having to replace the kernel
C. Having to re-IP the device
D. Having to rebuild ARP tables
E. Having to rebuild the routing tables
Answer:
B
Many administrators are hesitant to upgrade the IOS on routers based on past experience with the
code introducing instability into the network. It is often difficult to completely test an IOS software
upgrade in a production environment because the monolithic kernel requires that the IOS be
replaced before the device can be tested. Because of these reasons, IOS upgrades to resolve security
flaws are often left undone in many organizations.
Question 7
A company estimates a loss of $2,374 per hour in sales if their website goes down. Their webserver
hosting site’s documented downtime was 7 hours each quarter over the last two years. Using the
information, what can the analyst determine?
A. Annualized loss expectancy
B. CVSS risk score
C. Total cost of ownership
D. Qualitative risk posture
Answer:
A
The annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is deduced by multiplying the single loss expectancy (SLE) by
the annual rate of occurrence (ARO); in this example $2, 374 × (7 × 4), respectively. This is a form of
Quantitative risk analysis. Qualitative risk posture is deduced by measuring and contrasting the
likelihood (probability of occurrence) with the level of impact and by definition does not address risk
using monetary figures. Total cost of ownership (TCO) is the sum of all costs (technical,
administrative, environmental, et al) that are involved for a specific system, service, etc. CVSS risk
scoring is not based off of this type of loss data.
Question 8
To detect worms and viruses buried deep within a network packet payload, Gigabytes worth of traffic
content entering and exiting a network must be checked with which of the following technologies?
- A. Proxy matching
- B. Signature matching
- C. Packet matching
- D. Irregular expression matching
- E. Object matching
Answer:
C
Question 9
When identifying malware, what is a key difference between a Worm and a Bot?
- A. A Worm gets instructions from an external control channel like an IRC server.
- B. A Worm, unlike a Bot, is installed silently as an add-on to a legitimate program.
- C. A Bot, unlike a Worm, is frequently spread through email attachments.
- D. A Bot gets instructions from an external control channel like an IRC server.
Answer:
D
Question 10
Monitoring the transmission of data across the network using a man-in-the-middle attack presents a
threat against which type of data?
- A. At-rest
- B. In-transit
- C. Public
- D. Encrypted
Answer:
B
Question 11
Which type of media should the IR team be handling as they seek to understand the root cause of an
incident?
A. Restored media from full backup of the infected host
B. Media from the infected host, copied to the dedicated IR host
C. Original media from the infected host
D. Bit-for-bit image from the infected host
Answer:
A
By imaging the media with tools such as dd or Ghost and analyzing the copy, you preserve the
original media for later analysis so that the results can be recreated by another competent examiner
if necessary.
Question 12
An incident response team is handling a worm infection among their user workstations. They created
an IPS signature to detect and block worm activity on the border IPS, then removed the worm’s
artifacts or workstations triggering the rule. Despite this action, worm activity continued for days
after. Where did the incident response team fail?
A. The team did not adequately apply lessons learned from the incident
B. The custom rule did not detect all infected workstations
C. They did not receive timely notification of the security event
D. The team did not understand the worm’s propagation method
Answer:
B
Identifying and scoping an incident during triage is important to successfully handling a security
incident. The detection methods used by the team didn’t detect all the infected workstations.
Question 13
A legacy server on the network was breached through an OS vulnerability with no patch available.
The server is used only rarely by employees across several business units. The theft of information
from the server goes unnoticed until the company is notified by a third party that sensitive
information has been posted on the Internet. Which control was the first to fail?
A. Security awareness
B. Access control
C. Data classification
D. Incident response
Answer:
C
The legacy system was not properly classified or assigned an owner. It is critical that an organization
identifies and classifies information so proper controls and measures should be put in place. The
ultimate goal of data classification is to make sure that all information is properly protected at the
correct level.
This was not a failure of incident response, access control or security awareness training.
Question 14
Analyze the screenshot below. Which of the following attacks can be mitigated by these
configuration settings?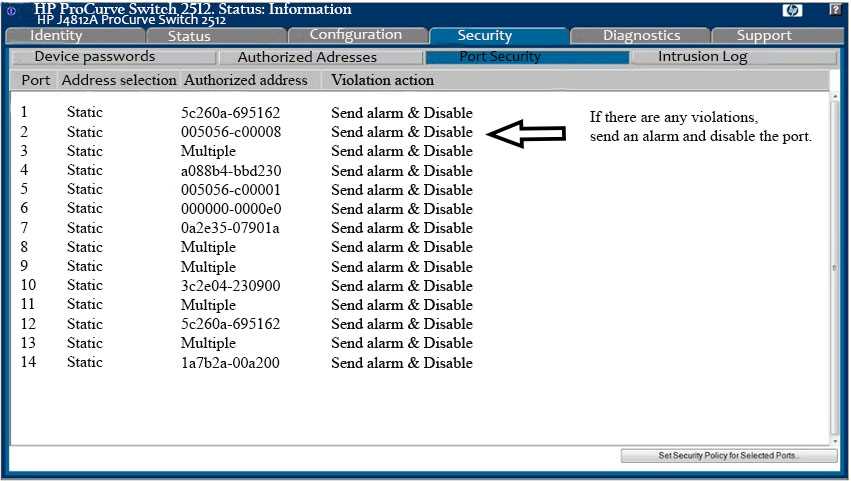
A. A Denial-of-Service attack using network broadcasts
B. A Replay attack
C. An IP masquerading attack
D. A MAC Flood attack
Answer:
D
Both BPDU Guard and Root Guard are used to prevent a new switch from becoming the Root Bridge.
They are very similar but use different mechanisms.
Rootguard allows devices to use STP, but if they send superior BDPUs (i.e. they attempt to become
the Root Bridge), Root Guard disables the port until the offending BPDUs cease. Recovery is
automatic.
If Portfast is enabled on a port, BPDU Guard will disable the port if a BPDU is received. The port stays
disabled until it is manually re-enabled. Devices behind such ports cannot use STP, as the port would
be disabled as soon as they send BPDUs (which is the default behavior of switches).
Question 15
Of the following pieces of digital evidence, which would be collected FIRST from a live system
involved in an incident?
A. Event logs from a central repository
B. Directory listing of system files
C. Media in the CDrom drive
D. Swap space and page files
Answer:
D
Best practices suggest that live response should follow the order of volatility, which means that you
Memory
Swap or page file
Network status and current / recent network connections
Running processes
Open files