Fortinet fcss sdw ar 7 4 practice test
FCSS - SD-WAN 7.4 Architect
Question 1
Exhibit.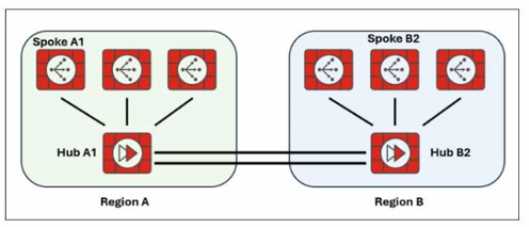
Two hub-and-spoke groups are connected through redundant site-to-site IPsec VPNs between Hub 1
and Hub 2
Which two configuration settings are required for the spoke A1 to establish an ADVPN shortcut with
the spoke B2? (Choose two.)
- A. On hubs, auto-discovery-forwarder must be enabled on the IPsec VPNs to hubs.
- B. On hubs, auto-discovery-receiver must be enabled on the IPsec VPNs to spokes.
- C. On hubs, auto-discovery-forwarder must be enabled on the IPsec VPNs to spokes.
- D. On hubs, auto-diacovery-sender must be enabled on the IPsec VPNs to spokes
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
To allow spokes in different hub-and-spoke groups to establish ADVPN shortcuts, the hubs must be
configured to forward and send ADVPN shortcut offers. The key required settings on the hub are
auto-discovery-forwarder (for VPNs to hubs) and auto-discovery-sender (for VPNs to spokes). This
ensures the hub can facilitate and advertise ADVPN shortcut offers between spokes.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q1]
Fortinet SD-WAN 7.4 ADVPN Guide (Auto-discovery settings for hub-and-spoke topologies)
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.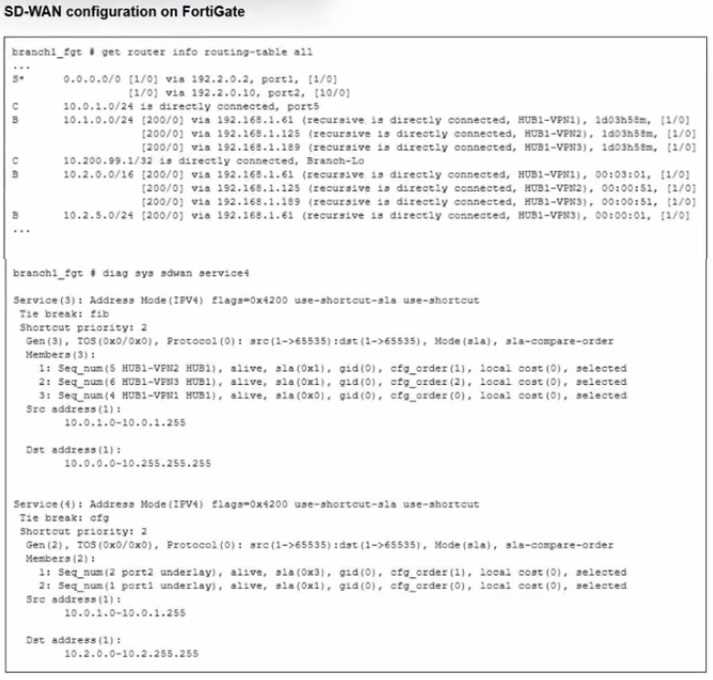
Which SD-WAN rule and interface uses FortiGate to steer the traffic from the LAN subnet 10.0.1.0/24
to the corporate server 10.2.5.254?
- A. SD-WAN service rule 3 and interface HUB1-VPN2.
- B. SD-WAN service rule 3 and interface HUB1-VPN3.
- C. SD-WAN service rule 4 and port1 or port2.
- D. SD-WAN service rule 4 and interface port2.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Traffic steering in Fortinet SD-WAN is based on defined rules and the corresponding outgoing
interfaces. The exhibit (not shown here) would indicate that the traffic from the LAN subnet
10.0.1.0/24 to the server 10.2.5.254 is matched by SD-WAN rule 3 and sent out via the HUB1-VPN3
interface.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q2]
FortiOS 7.4 SD-WAN Concept Guide – Rule Matching
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.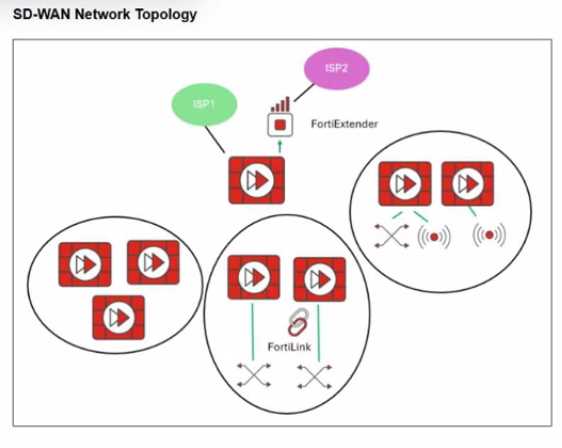
Refer to the exhibit.
You want to configure SD-WAN on a network as shown in the exhibit.
The network contains many FortiGate devices. Some are used as NGFW, and some are installed with
extensions such as FortiSwitch. FortiAP. or Forti Ex tender.
What should you consider when planning your deployment?
- A. You can build an SD-WAN topology that includes all devices. The hubs can be FortiGate devices with Forti Extender.
- B. You can build an SD-WAN topology that includes all devices. The hubs must be devices without extensions.
- C. You must use FortiManager to manage your SD-WAN topology.
- D. You must build multiple SD-WAN topologies. Each topology must contain only one type of extension.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Fortinet SD-WAN, hubs should not have extensions like FortiSwitch, FortiAP, or FortiExtender
installed, as these can affect hub functionality and scalability. While all device types can be included
in the topology, the hubs must be "clean" FortiGate devices without such extensions to ensure
proper ADVPN and overlay management.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q3]
Fortinet SD-WAN Reference Architecture Guide 7.4 – Hub requirements
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
Refer to the exhibit that shows event logs on FortiGate.
Based on the output shown in the exhibit, what can you say about the tunnels on this device?
- A. The master tunnel HU82-VPN3 cannot accept ADVPN shortcuts.
- B. The device steers voice traffic through the VPN tunnel HUB1-VPN3.
- C. The VPN tunnel HUB1-VPN1_0 is a shortcut tunnel.
- D. There is one shortcut tunnel built from master tunnel VPN4.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Event logs (from the exhibit) show how traffic is matched to SD-WAN rules and routed. The log
output indicates that voice traffic is being routed through the HUB1-VPN3 tunnel. This matches SD-
WAN's application-aware steering, which uses dynamic performance metrics to select the optimal
path.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q4]
FortiOS 7.4 SD-WAN Application-Aware Routing Documentation
Question 5
Exhibit.
Which action will FortiGate take if it detects SD-WAN members as dead?
- A. FoftiGate bounces port5 after it detects all SD-WAN members as dead.
- B. FortiGate fails over to the secondary device after it detects port5 as dead.
- C. FortiGate sends alert messages through poft5 when it detects all SD-WAN members as dead
- D. FortiGate brings down port5 after it detects all SD-WAN members as dead.
Answer:
C
Question 6
You are planning a large SD-WAN deployment with approximately 1000 spokes and want to allow
ADVPN between the spokes. Some remote sites use FortiSASE to connect to the company's SD-WAN
hub. Which overlay routing configuration should you use?
- A. BGP on loopback with dynamic BGP for ADVPN shortcut routing.
- B. BGP on loopback with IPsec phase2 selectors for ADVPN shortcut routing.
- C. BGP per overlay with dynamic BGP for ADVPN shortcut routing.
- D. BGP per overlay with BGP next-hop convergence for ADVPN shortcut routing.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
For a large-scale SD-WAN deployment (such as 1000 spokes) where ADVPN shortcut routing is
required and some remote sites connect via FortiSASE, the recommended overlay routing
configuration is BGP running on loopback interfaces, combined with dynamic BGP for ADVPN
shortcut routing. This design leverages the scalability and resilience of BGP, allowing dynamic
discovery and route exchange necessary for shortcut tunnels between spokes in ADVPN
environments. Using loopback interfaces for BGP peering is considered best practice because it
decouples routing protocol stability from physical link status, ensuring that if a physical underlay
interface fails, the BGP session remains up as long as there’s an alternate path. With dynamic BGP,
each spoke can efficiently learn the routes to other spokes and dynamically establish shortcuts,
which is critical at this scale. This method also integrates smoothly with FortiSASE for remote
connectivity to the SD-WAN hub, providing flexibility and centralized management.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q6]
Fortinet SD-WAN Reference Architecture Guide 7.4, “Scalable Routing with BGP on Loopback and
ADVPN Shortcuts”
Fortinet SD-WAN Concept Guide, “Overlay Routing Designs for Large Deployments”
Question 7
Refer to the exhibits.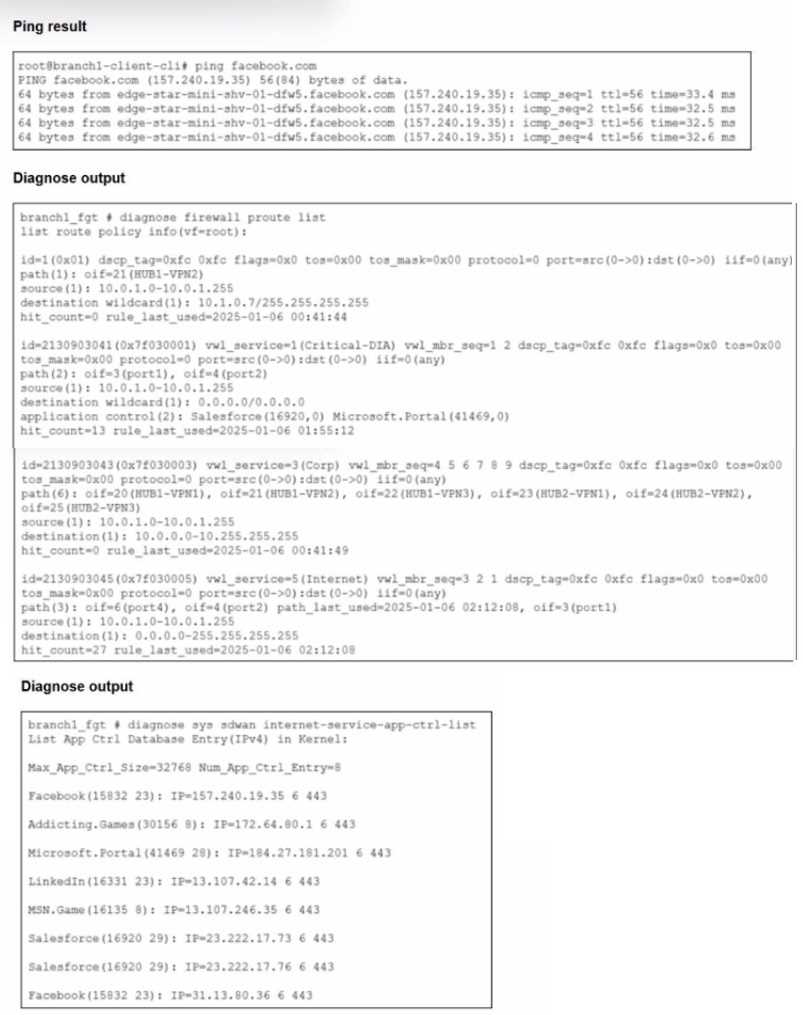
You connect to a device behind a branch FortiGate device and initiate a ping test. The device is part
of the LAN subnet and its IP address is 10.0.1.101.
Based on the exhibits, which interface uses branch 1_fgt to steer the test traffic?
- A. port4
- B. HUB1-VPN1
- C. port1
- D. port2
Answer:
D
Question 8
You manage an SD-WAN topology. You will soon deploy 50 new branches.
Which three tasks can you do in advance to simplify this deployment? (Choose three.)
- A. Update the DHCP server configuration.
- B. Create model devices.
- C. Create a ZTP template.
- D. Define metadata variables value for each device.
- E. Create policy blueprint.
Answer:
B, C, E
Explanation:
When planning to deploy a large number of branches (e.g., 50), Fortinet recommends several
preparatory steps to simplify and automate the rollout. Creating model devices allows you to
predefine configurations and settings that can be cloned or adapted for each branch, saving time and
minimizing manual errors. Preparing a Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) template enables automatic
onboarding and provisioning of new FortiGates as soon as they come online, reducing manual
intervention. Lastly, creating a policy blueprint allows for standardized policy deployment across all
branches, ensuring consistent security and SD-WAN rule enforcement. This holistic approach
streamlines the deployment process, allows for rapid scaling, and ensures that all devices are
configured according to corporate policy from day one.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q8]
Fortinet SD-WAN 7.4 Reference Architecture, “ZTP and Model Device Strategies for Scalable Rollouts”
FortiManager Admin Guide, “Policy Blueprints and Automation for Branch Deployment”
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit.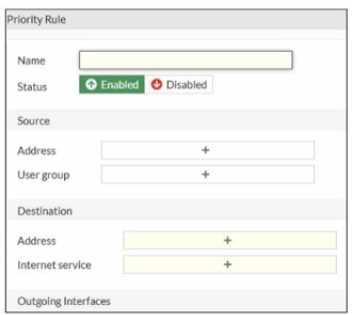
An administrator configures SD-WAN rules for a DIA setup using the FortiGate GUI. The page to
configure the source and destination part of the rule looks as shown in the exhibit. The GUI page
shows no option to configure an application as the destination of the SD-WAN rule Why?
- A. You cannot use applications as the destination when FortiGate is used for a DIA setup.
- B. FortiGate allows the configuration of applications as the destination of SD-WAN rules only on the CLI.
- C. You must enable the feature on the CLI.
- D. You must enable the feature first using the GUI menu System > Feature Visibility.
Answer:
D
Question 10
You are planning a new SD-WAN deployment with the following criteria:
- Two regions
- Most of the traffic is expected to remain within its region
- No requirement for inter-region ADVPN
To remain within the recommended best practices, which routing protocol should you select for the
overlays?
- A. OSPF for the routing within each region and EBGP between the regions.
- B. IBGP with BGP on loopback within each region and EBGP between the regions.
- C. IBGP with BGP per overlays within each region and IBGP with BGP on loopback between the regions.
- D. IBGP within each region and between the regions.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
For SD-WAN deployments that span multiple regions—where most traffic is intra-region and there is
no requirement for inter-region ADVPN—the best practice is to use IBGP with BGP on loopback
interfaces for routing within each region and EBGP between the regions. This approach ensures
robust and scalable routing, isolates regional routing domains, and enables policy control at region
boundaries. BGP on loopback is preferred for its reliability and flexibility, as it enables peering that is
not tied to specific physical interfaces. EBGP between regions allows each region to maintain
independent routing policies and summarization, optimizing performance and manageability. By
separating IBGP (intra-region) and EBGP (inter-region), you create a modular architecture that scales
easily and simplifies fault isolation and troubleshooting.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q10]
Fortinet SD-WAN Reference Architecture Guide 7.4, “Regional Routing Best Practices”
FortiOS 7.4 SD-WAN Overlay Design Guidelines
Question 11
Exhibit.
The administrator configured the IPsec tunnel VPN1 on a FortiGate device with the parameters
shown in exhibit.
Based on the configuration, which three conclusions can you draw about the characteristics and
requirements of the VPN tunnel? (Choose three.)
- A. The tunnel interface IP address on the spoke side is provided by the hub.
- B. The remote end can be a third-party IPsec device.
- C. The administrator must manually assign the tunnel interface IP address on the hub side
- D. The remote end must support IKEv2.
- E. This configuration allows user-defined overlay IP addresses.
Answer:
B, C, E
Explanation:
This configuration demonstrates a typical IPsec setup for SD-WAN overlays where the hub side
requires a manually defined tunnel IP address, and the spoke can be flexibly configured, including
interoperability with third-party IPsec devices. As described in the Fortinet SD-WAN Architect Guide:
“For some overlays, the tunnel interface IP is configured statically on the hub side, which allows
more control over overlay subnetting and facilitates the use of user-defined overlay IP addresses.
This approach is also a requirement for compatibility with non-FortiGate endpoints, such as third-
party IPsec devices that may not support dynamic address assignment via IKE or proprietary
mechanisms.” This enables hybrid SD-WAN environments and advanced designs involving external
partners or cloud services. Overlay IP flexibility is critical for route control and segmentation.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q11]
FortiOS 7.4 SD-WAN Reference Architecture, “Overlay IP Address Management”
SD-WAN 7.4 Concept Guide, Section: "Interoperability with Third-Party Devices"
Question 12
You have a FortiGate configuration with three user-defined SD-WAN zones and two members in each
of these zones. One SD-WAN member is no longer in use in health-check and SD-WAN rules. You
want to delete it.
What happens if you delete the SD-WAN member from the FortiGate GUI?
- A. FodiGate accepts the deletion and removes routes as required.
- B. FortiGate displays an error message. You must use the CLI to delete an SD-WAN member.
- C. FortiGate displays an error message. SD-WAN zones must contain at least two members
- D. FortiGate accepts the deletion and places the member in the default SD-WAN zone.
Answer:
A
Question 13
Refer to the exhibits.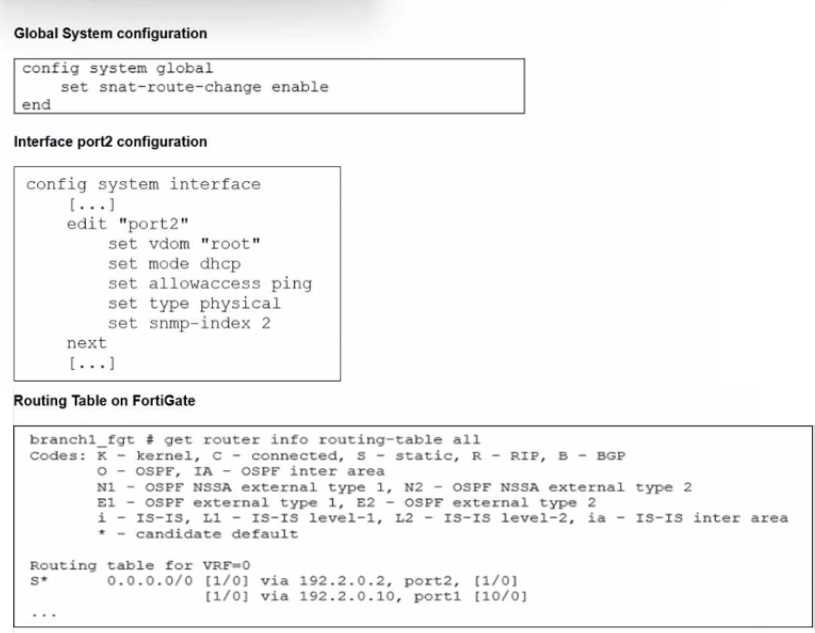
The exhibits show the source NAT (SNAT) global setting. port2 interface settings, and the routing
table on FortiGate.
The administrator increases the member priority on port2 to 20.
Upon configuration changes and the receipt of new packets, which two actions does FortiGate
perform on existing sessions established over port2? (Choose two.)
- A. FortiGate continues routing all existing sessions over port2.
- B. FortiGate routes only new sessions over port2.
- C. FortiGate flags the SNAT session as dirty only if the administrator has assigned an IP pool to the firewall policies with NAT.
- D. FortiGate flags the sessions as dirty.
- E. FortiGate updates the gateway information of the sessions with SNAT so that they use port1 instead of port2.
Answer:
D, E
Explanation:
When the member priority of a port is increased (e.g., port2 to 20), FortiGate evaluates existing
sessions and applies “dirty” flags where applicable. The SD-WAN session management mechanism is
described in detail: “Upon a change in SD-WAN member priority, all existing sessions using that
member are marked as dirty. For SNAT sessions, the gateway information is updated to ensure future
packets are routed through the newly preferred member, in this case, port1. This automatic re-
evaluation allows SD-WAN to dynamically respond to topology or priority changes, maintaining
optimal routing.” This is fundamental to seamless failover and session persistence in Fortinet SD-
WAN, ensuring active flows are redirected based on updated priorities or health status.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q13]
FortiOS 7.4 SD-WAN Concept Guide, “Session Management During Path Change”
FortiGate CLI Reference: diagnose sys session list
Question 14
Refer to the exhibits.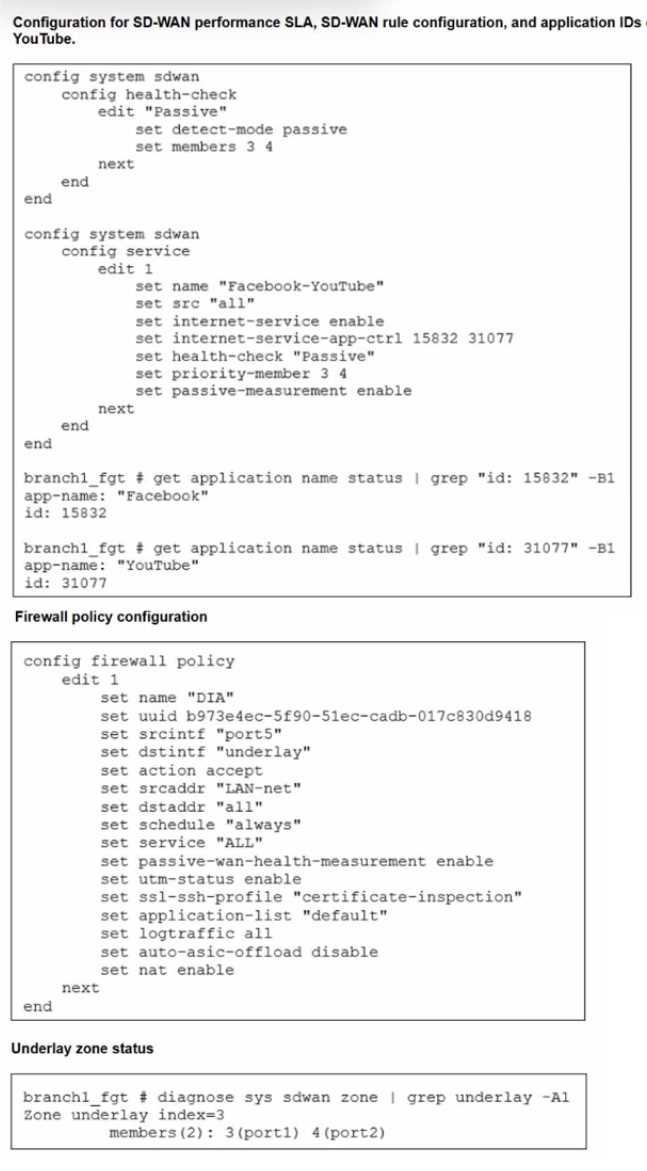
The exhibits show the configuration for SD-WAN performance. SD-WAN rule, the application IDs of
Facebook and YouTube along with the firewall policy configuration and the underlay zone status.
Which two statements are true about the health and performance of SD-WAN members 3 and 4?
(Choose two.)
- A. Only related TCP traffic is used for performance measurement.
- B. The performance is an average of the metrics measured for Facebook and YouTube traffic passing through the member.
- C. Encrypted traffic is not used for the performance measurement.
- D. FortiGate identifies the member as dead when there is no Facebook and YouTube traffic passing through the member.
Answer:
B, D
Question 15
When you use the command diagnose sys session list, how do you identify the sessions that
correspond to traffic steered according to SD-WAN rules?
- A. You identify sessions steered according to SD-WAN rules with the flag vwl.
- B. You cannot identify SD-WAN sessions. You must use the sdwar. session filter.
- C. You identify sessions steered according to SD-WAN rules with the data vwl_mbr_seq.
- D. You identify sessions steered according to SD-WAN rules with the data 3dwan_service_id.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When using the diagnose sys session list command, SD-WAN-specific session steering is indicated by
the presence of the sdwan_service_id field in the session data. This identifier ties the session directly
to a specific SD-WAN rule or service. As noted in the Fortinet documentation: “Sessions that are
handled according to SD-WAN rules will include a service ID tag (sdwan_service_id) in their session
listing. This allows administrators to correlate live sessions with SD-WAN policy matches for
troubleshooting and visibility.” This is a crucial diagnostic tool, as it distinguishes between traffic
managed by traditional routing and that explicitly controlled by SD-WAN steering logic, aiding in
operational insight and troubleshooting.
Reference:
[FCSS_SDW_AR-7.4 1-0.docx Q15]
FortiOS 7.4 CLI Reference, “diagnose sys session list: SD-WAN Service ID Tagging”
SD-WAN 7.4 Concept Guide, Section: "Session Identification for SD-WAN Traffic"