Fortinet fcp fwb ad 7 4 practice test
FCP - FortiWeb 7.4 Administrator
Question 1
Which implementation is most suited for a deployment that must meet PCI DSS compliance criteria?
- A. SSL offloading with FortiWeb in reverse proxy mode
- B. SSL offloading with FortiWeb in PCI DSS mode
- C. SSL offloading with FortiWeb in transparency mode
- D. SSL offloading with FortiWeb in full transparent proxy mode
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) sets forth security requirements to
protect cardholder data. Requirement 6.6 specifically mandates that public-facing web applications
be protected against known attacks by either:
Exclusive Networks+3Gordion+3layer7solutions.com+3
Reviewing applications via manual or automated vulnerability security assessment tools or methods,
at least annually and after any changes.
Installing an automated technical solution that detects and prevents web-based attacks, such as a
web application firewall (WAF), in front of public-facing web applications to continually inspect all
traffic.
FortiWeb, Fortinet's web application firewall, offers various deployment modes to protect web
applications:
Reverse Proxy Mode: FortiWeb acts as an intermediary, terminating client sessions and initiating
sessions to the backend servers. This mode provides comprehensive protection and allows for
features like SSL offloading, URL rewriting, and advanced routing capabilities.
Transparent Mode: FortiWeb operates at Layer 2, inspecting traffic without modifying it, making it
invisible to both clients and servers. This mode simplifies deployment as it doesn't require changes
to the existing network topology.
Full Transparent Proxy Mode: Combines aspects of both reverse proxy and transparent modes,
providing inspection and modification capabilities while remaining transparent to network devices.
PCI DSS Mode: A specialized deployment tailored to meet PCI DSS compliance requirements. This
mode ensures that FortiWeb is configured with security policies and features aligned with PCI DSS
standards, offering robust protection against threats targeting cardholder data.
Given the need to meet PCI DSS compliance criteria, deploying FortiWeb in PCI DSS mode is the most
appropriate choice. This mode is specifically designed to align with PCI DSS requirements, ensuring
that all necessary security measures are in place to protect cardholder data
Question 2
Review the following configuration:
What are two routing behaviors that you can expect on FortiWeb after this configuration change?
(Choose two.)
- A. Non-HTTP traffic routed through the FortiWeb is allowed.
- B. IPv6 routing is enabled.
- C. Non-HTTP traffic destined to the FortiWeb virtual server IP address is dropped.
- D. Only ICMP traffic is allowed. All other traffic is dropped.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
FortiWeb is primarily designed to handle HTTP and HTTPS traffic, protecting web applications from
various threats. By default, when operating in reverse proxy mode, FortiWeb does not forward non-
HTTP/HTTPS protocols to protected servers. However, administrators can configure FortiWeb to
handle non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic differently using the config router setting command. This command
allows enabling IP-based forwarding (routing) for non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic. When enabled, FortiWeb
can route non-HTTP traffic through itself to the appropriate backend servers.
Despite this capability, any non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic that is destined directly for a FortiWeb virtual
server IP address is dropped. This means that while FortiWeb can be configured to forward non-
HTTP/HTTPS traffic to backend servers, it will not process non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic targeted at its own
virtual server IPs.
Regarding IPv6 routing, FortiWeb does support IPv6 in various operation modes, including reverse
proxy, offline inspection, and transparent inspection. However, enabling IPv6 routing requires
specific configurations and is not automatically enabled by default.
Question 3
An attacker attempts to send an SQL injection attack containing the known attack string 'root'; --
through an API call.
Which FortiWeb inspection feature will be able to detect this attack the quickest?
- A. API gateway rule
- B. Known signatures
- C. Machine learning (ML)-based API protection—anomaly detection
- D. ML-based API protection—threat detection
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The quickest detection for an SQL injection attack like the one described ('root'; --) would be through
known signatures. FortiWeb utilizes signature-based detection to match incoming traffic against
predefined attack patterns. Since SQL injection attacks are commonly known and have specific
patterns (such as 'root'; --), known signatures would immediately recognize and flag this type of
attack.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.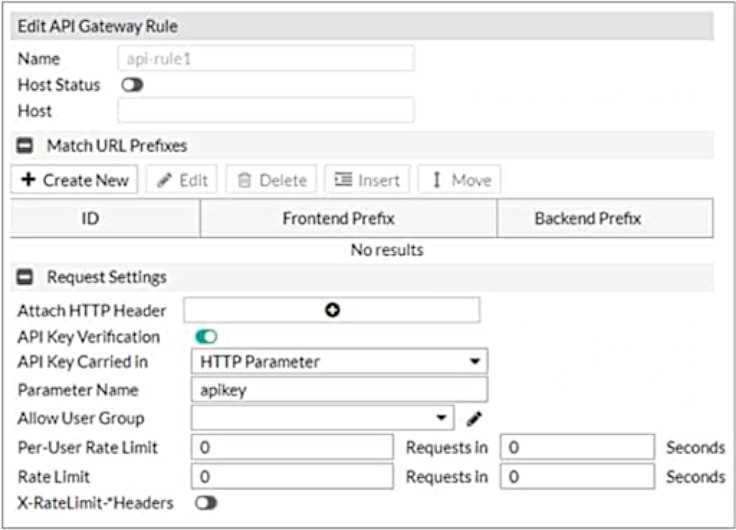
What are two additional configuration elements that you must be configure for this API gateway?
(Choose two.)
- A. You must define rate limits.
- B. You must define URL prefixes.
- C. You must select a setting in the Allow User Group field.
- D. You must enable and configure Host Status.
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
When configuring an API Gateway on a FortiWeb appliance, it's essential to include specific elements
to ensure proper functionality and security. Two critical configuration elements are:
Defining Rate Limits:
Implementing rate limits is crucial to control the number of requests a client can make to the API
within a specified timeframe. This helps prevent abuse, such as denial-of-service attacks, by limiting
excessive requests from clients.
Defining URL Prefixes:
Specifying URL prefixes allows the FortiWeb appliance to identify and manage API requests
accurately. By defining these prefixes, the appliance can route and process API calls correctly,
ensuring that only legitimate traffic reaches the backend services.
These configurations align with Fortinet's best practices for setting up an API Gateway policy. While
the exact steps may vary depending on the FortiWeb firmware version, the general process involves
navigating to the Web Application Firewall section, selecting the API Gateway Policy tab, and
configuring the necessary parameters, including rate limits and URL prefixes.
Question 5
Which would be a reason to implement HTTP rewriting?
- A. To redirect HTTP to HTTPS.
- B. To implement load balancing.
- C. To replace a vulnerable element in a requested URL.
- D. The original page has moved to a new URL.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
HTTP rewriting is a feature in FortiWeb that allows administrators to modify HTTP requests and
responses for various purposes, including security enhancements, user experience improvements,
and application functionality. One common use case for HTTP rewriting is to redirect HTTP traffic to
HTTPS, ensuring that all communications between clients and the server are encrypted and secure.
Explanation of Options:
A . To redirect HTTP to HTTPS: This is a valid reason to implement HTTP rewriting. By rewriting
incoming HTTP requests to HTTPS, administrators can enforce secure connections, protecting data
integrity and confidentiality. FortiWeb supports this functionality, allowing seamless redirection from
HTTP to HTTPS.
B . To implement load balancing: Load balancing is not typically achieved through HTTP rewriting.
Instead, it involves distributing network traffic across multiple servers to ensure availability and
reliability. FortiWeb provides load balancing features, but these are separate from HTTP rewriting
capabilities.
C . To replace a vulnerable element in a requested URL: While HTTP rewriting can modify URLs, its
primary purpose is not to replace vulnerable elements within URLs. Addressing vulnerabilities
typically involves input validation, sanitization, and other security measures rather than rewriting
URLs.
D . The original page has moved to a new URL: This is another valid reason to implement HTTP
rewriting. When a webpage's URL changes, rewriting rules can redirect requests from the old URL to
the new one, ensuring users can still access the content without encountering errors.
In summary, both options A and D are correct reasons to implement HTTP rewriting. However, in the
context of FortiWeb's functionalities, redirecting HTTP to HTTPS (option A) is a common and
significant use case, as it enhances security by ensuring encrypted connections.
Question 6
What is the difference between an API gateway protection schema and a machine learning (ML) API
protection schema?
- A. An API gateway protection schema does not allow authentication.
- B. An API gateway protection schema handles response bodies.
- C. An API gateway protection schema supports data types other than string.
- D. An API gateway protection schema cannot change without administrator intervention.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In FortiWeb's API protection mechanisms, there are distinctions between the traditional API gateway
protection schema and the machine learning (ML) based API protection schema:
Data Type Support: The API gateway protection schema has the capability to support various data
types beyond just strings, allowing for more comprehensive validation and enforcement of API
schemas.
Schema Adaptability: The ML-based API protection schema is designed to automatically learn and
adapt to changes in the API structure without requiring manual intervention from administrators.
This dynamic learning process enables FortiWeb to identify and protect against anomalies and
potential threats in real-time.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibits.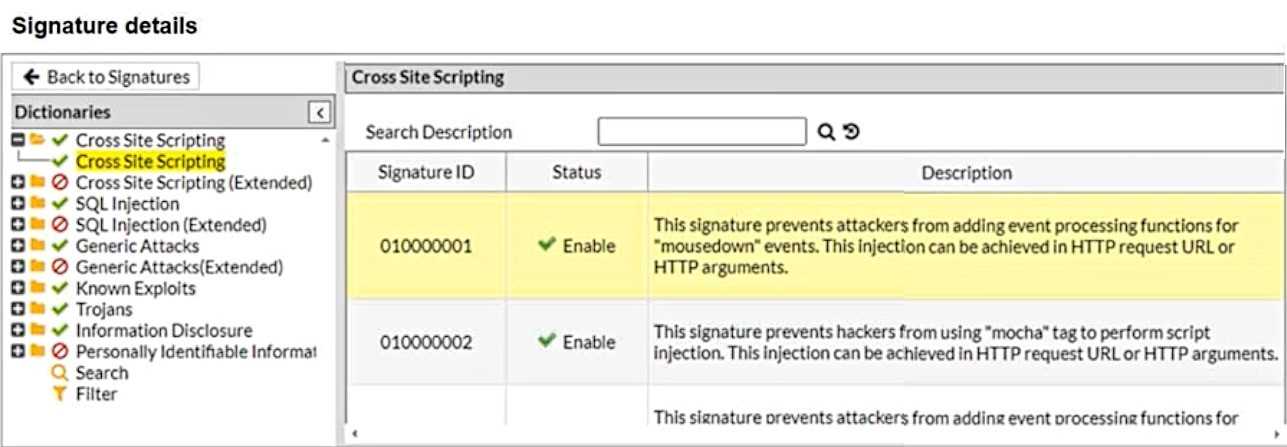
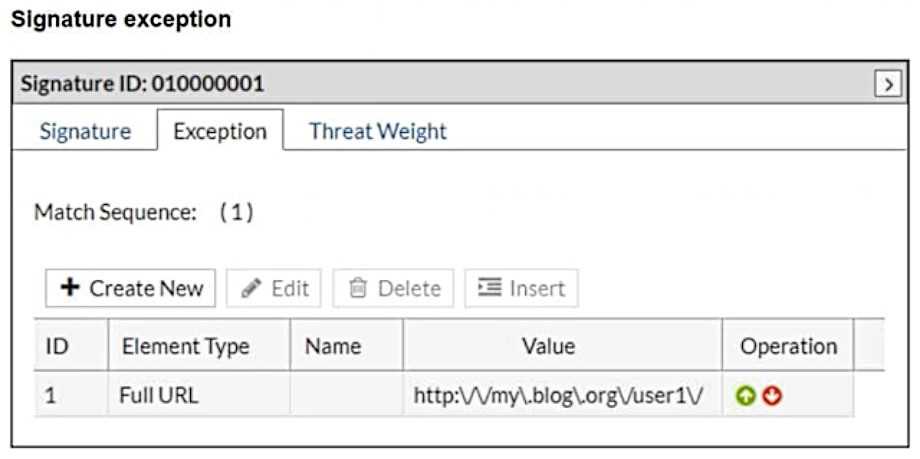
What will happen when a client attempts a mousedown cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against the
site http://my.blog.org/userl1/blog.php and FortiWeb is enforcing the highlighted signature?
- A. The connection will be stripped of the mousedown JavaScript code.
- B. The connection will be blocked as an XSS attack.
- C. FortiWeb will report the new mousedown attack to FortiGuard.
- D. The connection will be allowed.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In the provided configuration, the signature exception has been set for the URL
http://my.blog.org/user1V. This means that any request to this specific URL will bypass the signature
ID 01000001, which is designed to block cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks using the mousedown
event. As the request comes from the URL http://my.blog.org/userl1/blog.php, which does not
match the exception rule for http://my.blog.org/user1V, the attack will be allowed through.
Therefore, the connection will be allowed because the exception rule bypasses protection for the
specified URL.
Question 8
Which high availability mode is commonly used to integrate with a traffic distributer like FortiADC?
- A. Cold standby
- B. Load sharing
- C. Active-Active
- D. Active-Passive
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In Fortinet's high availability (HA) configurations, integrating FortiWeb with a traffic distributor like
FortiADC is best achieved using the Active-Active HA mode. This mode allows multiple FortiWeb
appliances to operate simultaneously, distributing traffic loads and enhancing both performance and
redundancy.
FortiWeb supports several HA modes:
Active-Passive: One appliance actively handles all traffic, while the other remains on standby, ready
to take over if the active unit fails.
Active-Active: Multiple appliances actively process traffic concurrently, sharing the load and
providing redundancy.
High Volume Active-Active: An enhanced version of Active-Active, designed for environments with
exceptionally high traffic volumes.
When integrating with a traffic distributor like FortiADC, the Active-Active mode is particularly
advantageous. FortiADC can intelligently distribute incoming traffic across multiple active FortiWeb
appliances, optimizing resource utilization and ensuring high availability. This setup not only balances
the load but also provides fault tolerance; if one appliance becomes unavailable, FortiADC can
redirect traffic to the remaining active units without service interruption.
This collaborative approach between FortiWeb and FortiADC ensures that web applications remain
secure, performant, and resilient against failures.
Question 9
A customer wants to be able to index your websites for search and advertisement purposes.
What is the easiest way to allow this on a FortiWeb?
- A. Add the indexer IP address to the trusted IP list on the FortiWeb.
- B. Add the indexer IP address to the FortiGuard "Known Search Engines" category.
- C. Create a firewall rule to bypass the FortiWeb entirely for the indexer IP address.
- D. Do not allow any external sites to index your websites.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The easiest way to allow a search engine indexer (such as Googlebot or Bingbot) to index your
website on a FortiWeb is to add the indexer's IP address to the trusted IP list. This ensures that traffic
from trusted indexers is allowed through without being blocked or interfered with by FortiWeb's
security features like bot protection.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
A FortiWeb device is deployed upstream of a device performing source network address translation
(SNAT) or load balancing.
What configuration must you perform on FortiWeb to preserve the original IP address of the client?
- A. Enable and configure the Preserve Client IP setting.
- B. Use a transparent operating mode on FortiWeb.
- C. Enable and configure the Add X-Forwarded-For setting.
- D. Turn off NAT on the FortiWeb.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When FortiWeb is deployed upstream of a device performing source network address translation
(SNAT) or load balancing, the original client IP address may be lost. To preserve the original client IP
address, you must enable and configure the Preserve Client IP setting on FortiWeb. This allows
FortiWeb to retain and pass the client's original IP address to the backend servers for accurate
logging and processing.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.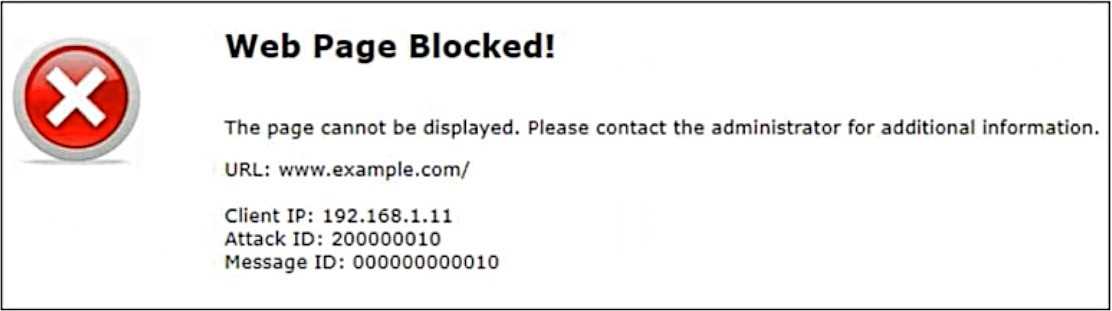
Attack ID 20000010 is brute force logins.
Which statement is accurate about the potential attack?
- A. The attacker has successfully retrieved the credentials to www.example.com.
- B. www.example.com is running attacks against the client 192.168.1.11.
- C. The attack has happened 10 times.
- D. 192.168.1.11 is sending suspicious traffic to FortiWeb.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Attack ID of 20000010 refers to a brute force login attempt, which typically indicates that the
client IP (192.168.1.11) is sending suspicious or malicious traffic to the FortiWeb. FortiWeb detected
and blocked this suspicious activity, which is why the page is shown as blocked.
Question 12
Which three stages are part of creating a machine learning (ML) bot detection algorithm? (Choose
three.)
- A. Model building
- B. Model running
- C. Model verification
- D. Sample collecting
- E. Model Bayesian analysis
Answer:
A, C, D
Explanation:
Model building: In this stage, you design and develop the ML model, which involves selecting
appropriate algorithms and features to detect bot activity.
Model verification: This is where you test and evaluate the model's performance to ensure it can
accurately detect bots without false positives or negatives.
Sample collecting: Gathering relevant data samples (e.g., bot and non-bot traffic) to train the
machine learning model is crucial to ensure it can learn from various scenarios.
Question 13
Under which two circumstances does FortiWeb use its own certificates? (Choose two.)
- A. Connecting to browser clients using SSL
- B. Making a secondary HTTPS connection to a server where FortiWeb acts as a client
- C. Routing an HTTPS connection to a FortiGate
- D. An administrator session connecting to the GUI using HTTPS
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
Making a secondary HTTPS connection to a server where FortiWeb acts as a client: When FortiWeb
needs to connect to an external server via HTTPS (acting as a client), it may use its own certificates
for that connection.
An administrator session connecting to the GUI using HTTPS: FortiWeb uses its own certificates to
secure the HTTPS connection between the administrator and the FortiWeb GUI. This ensures secure
access for management purposes.
Question 14
You are using HTTP content routing on FortiWeb. You want requests for web application A to be
forwarded to a cluster of web servers, which all host the same web application. You want requests
for web application B to be forwarded to a different, single web server.
Which statement regarding this solution is true?
- A. You must chain policies so that all requests go to the virtual server for policy A first, and then redirect requests for web application B to go to the virtual server for policy B
- B. You must create static routes on the FortiWebto allow these requests.
- C. You must put the single web server for application B into a server pool and use it with HTTP content routing.
- D. The server policy always applies the same web protection profile to both web application A and web application B.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To forward requests for web application B to a single web server, you would configure FortiWeb to
use HTTP content routing and create a server pool specifically for web application B. In FortiWeb,
server pools are used to group servers together based on application requirements, and you can
configure the pool to contain only a single web server for application B.
Question 15
What can a FortiWeb administrator do if a client has been incorrectly period blocked?
- A. Allow the period block to expire on its own, you cannot override it.
- B. Manually release the IP address from the blocklist.
- C. Disable and re-enable the server policy.
- D. Force a new IP address to the client.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
If a client has been incorrectly blocked due to a period block, the FortiWeb administrator can
manually release the IP address from the blocklist. This allows the client to access the application
again before the block expires naturally.