Fortinet fcp fct ad 7 2 practice test
FCP - FortiClient EMS 7.2 Administrator
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit, which shows FortiClient EMS deployment, profiles.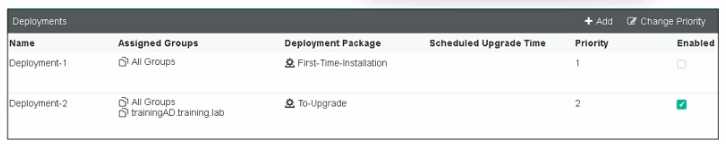
When an administrator creates a deployment profile on FortiClient EMS. which statement about the
deployment profile is true?
- A. Deployment-2 will upgrade FortiClient on both the AD group and workgroup.
- B. Deployment-1 will install FortiClient on new AO group endpoints.
- C. Deployment-2 will install FortiClient on both the AD group and workgroup.
- D. Deployment-1 will upgrade FortiClient only on the workgroup.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Deployment Profiles Analysis:
Deployment-1 has the "First-Time-Installation" package and is assigned to "All Groups" with a priority
of 1 but is not enabled.
Deployment-2 has the "To-Upgrade" package, is assigned to both "All Groups" and
"trainingAD.training.lab," with a priority of 2 and is enabled.
Evaluating Deployment-2:
Deployment-2 will upgrade FortiClient on both "All Groups" and "trainingAD.training.lab" since it is
enabled and assigned to these groups. This includes both AD (Active Directory) groups and
workgroups.
Conclusion:
Since Deployment-2 is set to upgrade FortiClient on all the assigned groups and workgroups, the
correct answer is A.
Reference:
FortiClient EMS deployment and profile documentation from the study guides.
Question 2
Exhibit.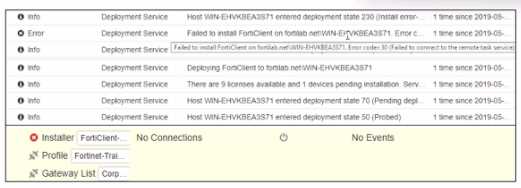
Based on the logs shown in the exhibit, why did FortiClient EMS tail to install FortiClient on the
endpoint?
- A. The FortiClient antivirus service is not running.
- B. The Windows installer service is not running.
- C. The remote registry service is not running.
- D. The task scheduler service is not running.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiClient/Technical-Note-FortiClient-fails-to-install-from-
FortiClient-EMS/ta-p/193680
The deployment service error message may be caused by any of the following. Try eliminating them
all, one at a time.
1. Wrong username or password in the EMS profile
2. Endpoint is unreachable over the network
3. Task Scheduler service is not running
4. Remote Registry service is not running
5. Windows firewall is blocking connection
Question 3
Which two statements are true about ZTNA? {Choose two.)
- A. ZTNA manages access for remote users only.
- B. ZTNA provides role-based access.
- C. ZTNA provides a security posture check.
- D. ZTNA manages access through the client only.
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access) is a security architecture that is designed to provide secure access
to network resources for users, devices, and applications. It is based on the principle of "never trust,
always verify," which means that all access to network resources is subject to strict verification and
authentication.
Two functions of ZTNA are:
ZTNA provides a security posture check: ZTNA checks the security posture of devices and users that
are attempting to access network resources. This can include checks on the device's software and
hardware configurations, security settings, and the presence of malware.
ZTNA provides role-based access: ZTNA controls access to network resources based on the role of the
user or device. Users and devices are granted access to only those resources that are necessary for
their role, and all other access is denied. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and minimize the
risk of data breaches.
Question 4
When site categories are disabled in FortiClient web filter, which feature can be used to protect the
endpoint from malicious web access?
- A. Real-time protection list
- B. Block malicious websites on antivirus
- C. FortiSandbox URL list
- D. Web exclusion list
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Web Filter Functionality:
When site categories are disabled in the FortiClient web filter, the endpoint still requires protection
from malicious web access.
Alternative Protection Features:
The web exclusion list can be used to manage and block specific URLs that are known to be
malicious, providing a way to control and secure web access even without site categories being
enabled.
Conclusion:
The correct feature that can be used to protect the endpoint in this scenario is the web exclusion list
(D).
Reference:
FortiClient web filter configuration and features from the study guides.
Question 5
Exhibit.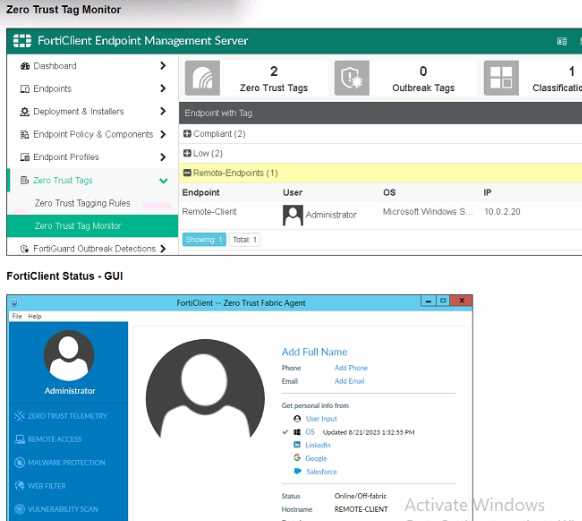
Refer to the exhibits, which show the Zero Trust Tag Monitor and the FortiClient GUI status.
Remote-Client is tagged as Remote-User* on the FortiClient EMS Zero Trust Tag Monitor.
What must an administrator do to show the tag on the FortiClient GUI?
- A. Change the FortiClient EMS shared settings to enable tag visibility.
- B. Change the endpoint alerts configuration to enable tag visibility.
- C. Update tagging rule logic to enable tag visibility.
- D. Change the FortiClient system settings to enable lag visibility.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Observation of Exhibits:
The exhibits show the Zero Trust Tag Monitor on FortiClient EMS and the FortiClient GUI status.
Remote-Client is tagged as "Remote-Endpoints" on the FortiClient EMS Zero Trust Tag Monitor.
Enabling Tag Visibility:
To show the tag on the FortiClient GUI, the endpoint alerts configuration must be adjusted to enable
tag visibility.
Verification:
The correct action is to change the endpoint alerts configuration to enable tag visibility, ensuring that
the tag appears in the FortiClient GUI.
Reference:
FortiClient EMS and FortiClient configuration documentation from the study guides.
Question 6
An administrator wants to simplify remote access without asking users to provide user credentials
Which access control method provides this solution?
- A. ZTNA full mode
- B. SSL VPN
- C. L2TP
- D. ZTNA IP/MAC littering mode
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Simplifying Remote Access:
The administrator wants to simplify remote access without asking users to provide user credentials.
Evaluating Access Control Methods:
ZTNA full mode can provide seamless access by leveraging device identity and posture, eliminating
the need for user credentials for each access request.
Other methods like SSL VPN and L2TP typically require user credentials.
Conclusion:
The correct access control method that provides this solution is ZTNA full mode.
Reference:
ZTNA section in the FortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide.
Question 7
A FortiClient EMS administrator has enabled the compliance rule for the sales department Which
Fortinet device will enforce compliance with dynamic access control?
- A. FortiClient
- B. FortiClient EMS
- C. FortiGate
- D. FortiAnalyzer
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Understanding Compliance Rules:
The compliance rule for the sales department needs to be enforced dynamically.
Enforcing Compliance:
FortiGate is responsible for enforcing compliance by integrating with FortiClient EMS to apply
dynamic access control based on compliance status.
Conclusion:
The Fortinet device that will enforce compliance with dynamic access control is the FortiGate.
Reference:
Compliance and enforcement documentation from FortiGate and FortiClient EMS study guides.
Question 8
In a ForliSandbox integration, what does the remediation option do?
- A. Deny access to a tile when it sees no results
- B. Alert and notify only
- C. Exclude specified files
- D. Wait for FortiSandbox results before allowing files
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Understanding FortiSandbox Integration:
In a FortiSandbox integration, various remediation options are available for handling suspicious files.
Evaluating Remediation Options:
The remediation option for alerting and notifying without blocking access or waiting for results is
essential to understand.
Conclusion:
The correct action for the remediation option in this context is to alert and notify only.
Reference:
FortiSandbox integration documentation from the study guides.
Question 9
An administrator needs to connect FortiClient EMS as a fabric connector to FortiGate What is the
prerequisite to get FortiClient EMS lo connect to FortiGate successfully?
- A. Import and verify the FortiClient EMS tool CA certificate on FortiGate.
- B. Revoke and update the FortiClient client certificate on EMS.
- C. Import and verify the FortiClient client certificate on FortiGate.
- D. Revoke and update the FortiClient EMS root CA.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Connecting FortiClient EMS to FortiGate:
The administrator needs to establish a connection between FortiClient EMS and FortiGate as a fabric
connector.
Prerequisites for Connection:
A key prerequisite is the import and verification of the FortiClient EMS tool CA certificate on
FortiGate to ensure a trusted connection.
Conclusion:
The correct prerequisite for a successful connection is to import and verify the FortiClient EMS tool
CA certificate on FortiGate.
Reference:
FortiClient EMS and FortiGate connection and certificate management documentation from the
study guides.
Question 10
An administrator must add an authentication server on FortiClient EMS in a different security zone
that cannot allow a direct connection.
Which solution can provide secure access between FortiClient EMS and the Active Directory server?
- A. Configure and deploy a FortiGate device between FortiClient EMS and the Active Directory server.
- B. Configure Active Directory and install FortiClient EMS on the same VM.
- C. Configure a slave FortiClient EMS on a virtual machine.
- D. Configure an Active Directory connector between FortiClient EMS and the Active Directory server.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Requirement:
The administrator needs to add an authentication server on FortiClient EMS in a different security
zone that cannot allow a direct connection.
Solution Analysis:
The goal is to securely connect FortiClient EMS and the Active Directory server despite being in
different security zones.
Evaluating Options:
Installing FortiClient EMS on the same VM as Active Directory (option B) is not practical due to
security zone separation.
Configuring a slave FortiClient EMS on a virtual machine (option C) does not address the need for
secure communication.
Configuring an Active Directory connector (option D) may not be sufficient without secure routing.
Conclusion:
Deploying a FortiGate device between FortiClient EMS and the Active Directory server ensures
secure and controlled access between the two zones.
Reference:
FortiClient EMS and FortiGate configuration and deployment documentation from the study guides.
Question 11
What does FortiClient do as a fabric agent? (Choose two.)
- A. Provides IOC verdicts
- B. Creates dynamic policies
- C. Provides application inventory
- D. Automates Responses
Answer:
CD
Question 12
Exhibit.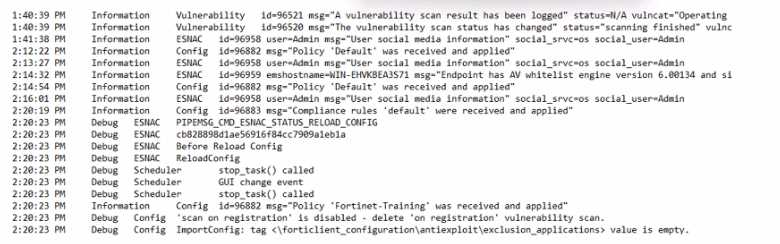
Based on the FortiClient logs shown in the exhibit, which endpoint profile policy is currently applied
lo the ForliClient endpoint from the EMS server?
- A. Fortinet-Training
- B. Default configuration policy c
- C. Compliance rules default
- D. Default
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Observation of Logs:
The logs show a policy named "Fortinet-Training" being applied to the endpoint.
Evaluating Policies:
The log entries indicate that the "Fortinet-Training" policy was received and applied.
Conclusion:
Based on the logs, the currently applied policy on the FortiClient endpoint is "Fortinet-Training".
Reference:
FortiClient EMS policy configuration and log analysis documentation from the study guides.
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit.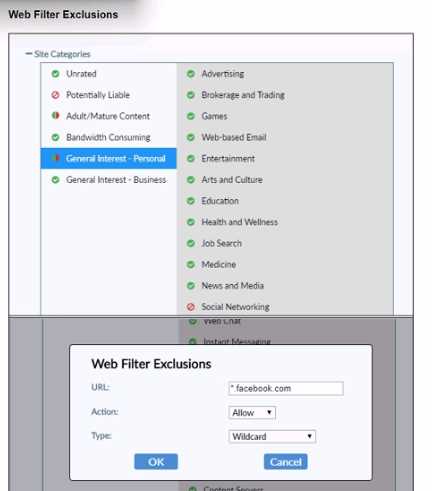
Based on the settings shown in the exhibit, which action will FortiClient take when users try to access
www facebook com?
- A. FortiClient will allow access to Facebook.
- B. FortiClient will block access to Facebook and its subdomains.
- C. FortiClient will monitor only the user's web access to the Facebook website
- D. FortiClient will prompt a warning message to want the user before they can access the Facebook website
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Observation of Web Filter Exclusions:
The exhibit shows a web filter exclusion for "*.facebook.com" with the action set to "Allow."
Evaluating Actions:
This configuration means that FortiClient will allow access to Facebook and its subdomains.
Conclusion:
When users try to access "
www.facebook.com
," FortiClient will allow the access based on the web
filter exclusion settings.
Reference:
FortiClient web filter configuration and exclusion documentation from the study guides.
Question 14
Why does FortiGate need the root CA certificate of FortiCient EMS?
- A. To revoke FortiClient client certificates
- B. To sign FortiClient CSR requests
- C. To update FortiClient client certificates
- D. To trust certificates issued by FortiClient EMS
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Understanding the Need for Root CA Certificate:
The root CA certificate of FortiClient EMS is necessary for FortiGate to trust certificates issued by
FortiClient EMS.
Evaluating Use Cases:
FortiGate needs the root CA certificate to establish trust and validate certificates issued by FortiClient
EMS.
Conclusion:
The primary reason FortiGate needs the root CA certificate of FortiClient EMS is to trust certificates
issued by FortiClient EMS.
Reference:
FortiClient EMS and FortiGate certificate management documentation from the study guides.
Question 15
Which three features does FortiClient endpoint security include? (Choose three.)
- A. DLP
- B. Vulnerability management
- C. L2TP
- D. lPsec
- E. Real-lime protection
Answer:
BDE
Explanation:
Understanding FortiClient Features:
FortiClient endpoint security includes several features aimed at protecting and managing endpoints.
Evaluating Feature Set:
Vulnerability management is a key feature of FortiClient, helping to identify and address
vulnerabilities (B).
IPsec is supported for secure VPN connections (D).
Real-time protection is crucial for detecting and preventing threats in real-time (E).
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) (A) is typically managed by FortiGate or FortiMail.
L2TP (C) is a protocol used for VPNs but is not specifically a feature of FortiClient endpoint security.
Reference:
FortiClient endpoint security features documentation from the study guides.