dell d-sf-a-24 practice test
Dell Security Foundations Achievement
Question 1
A .R.T.I.E. has an evolving need, which was amplified during the incidents. Their complex and
dispersed IT environments have thousands of users, applications, and resources to manage. Dell
found that the existing Identity and Access Management was limited in its ability to apply expanding
IAM protection to applications beyond the core financial and human resource management
application. A .R.T.I.E. also did not have many options for protecting their access especially in the
cloud. A .R.T.I.E. were also not comfortable exposing their applications for remote access.
Dell recommended adopting robust IAM techniques like mapping out connections between
privileged users and admin accounts, and the use multifactor authentication.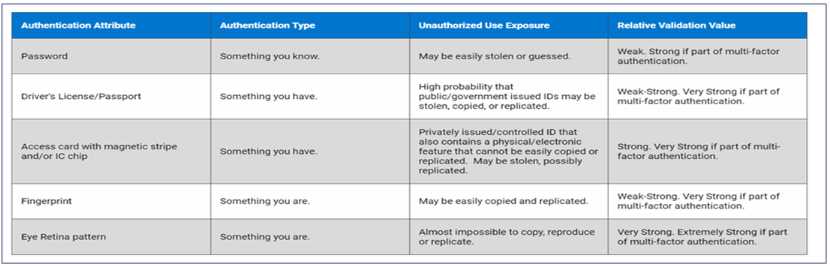
The Dell Services team suggest implementing a system that requires individuals to provide a PIN and
biometric information to access their device.
Which type of multifactor authentication should be suggested?
- A. Something you have and something you are.
- B. Something you have and something you know.
- C. Something you know and something you are.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The recommended multifactor authentication (MFA) type for A .R.T.I.E., as suggested by Dell
Services, is A. Something you have and something you are. This type of MFA requires two distinct
forms of identification: one that the user possesses (something you have) and one that is inherent to
the user (something you are).
Explanation:
Something you have could be a physical token, a security key, or a mobile device that generates
time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs).
Something you are refers to biometric identifiers, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans,
which are unique to each individual.
By combining these two factors, the authentication process becomes significantly more secure than
using any single factor alone. The physical token or device provides proof of possession, which is
difficult for an attacker to replicate, especially without physical access. The biometric identifier
ensures that even if the physical token is stolen, it cannot be used without the matching biometric
input.
Reference:
The use of MFA is supported by security best practices and standards, including those outlined by the
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Dell’s own security framework likely aligns with these standards, advocating for robust
authentication mechanisms to protect against unauthorized access, especially in cloud environments
where the attack surface is broader.
In the context of A .R.T.I.E.'s case, where employees access sensitive applications and data remotely,
implementing MFA with these two factors will help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and
potential data breaches. It is a proactive step towards enhancing the organization’s security posture
in line with Dell’s strategic advice.
Question 2
A Zero Trust security strategy is defined by which of the primary approaches?
- A. IAM and security awareness training
- B. VPNs and IAM
- C. Network segmenting and access control
- D. Micro-segmenting and Multi-factor authentication
Answer:
D
Question 3
To optimize network performance and reliability, low latency network path for customer traffic,
A.R.T.I.E created a modern edge solution. The edge solution helped the organization to analyze and
process diverse data and identify related business opportunities. Edge computing also helped them
to create and distribute content and determine how the users consume it. But as compute and data
creation becomes more decentralized and distributed, A .R.T.I.E. was exposed to various risks and
security challenges inevitably became more complex. Unlike the cloud in a data center, it is physically
impossible to wall off the edge.
Which type of edge security risk A .R.T.I.E. is primarily exposed?
- A. Data risk
- B. Internet of Things risk
- C. Protection risk
- D. Hardware risk
Answer:
A
Explanation:
For the question regarding the type of edge security risk A .R.T.I.E. is primarily exposed to, let’s
analyze the options:
Data risk: This refers to the risk associated with the storage, processing, and transmission of data.
Given that A .R.T.I.E. is a social media company with a platform for sharing content and making in-
app purchases, there is a significant amount of data being handled, which could be at risk if not
properly secured.
Internet of Things (IoT) risk: This involves risks associated with IoT devices, which may not be
applicable in this context as A .R.T.I.E. is described as a social media company rather than one that
specializes in IoT devices.
Protection risk: This could refer to the overall security measures in place to protect the company’s
assets. Since A .R.T.I.E. has moved some applications to the public cloud and operates an internal
network accessible via VPN, the protection of these assets is crucial.
Hardware risk: This involves risks related to the physical components of the network. The case study
does not provide specific details about hardware vulnerabilities, so this may not be the primary
concern.
Considering the case study’s focus on data handling, cloud migration, and the need for secure
solutions, Data risk seems to be the most relevant edge security risk A .R.T.I.E. is exposed to. The
decentralization of compute and data creation, along with the inability to physically secure the edge
as one would with a data center, increases the risk to the data being processed and stored at the
edge.
Remember, when preparing for assessments like the Dell Security Foundations Achievement, it’s
important to thoroughly review the study materials provided, understand the key concepts, and
apply them to the scenarios presented in the case studies. Good luck with your preparation!
Question 4
The cybersecurity team performed a quantitative risk analysis on A .R.T.I.E.'s IT systems during the
risk management process.
What is the focus of a quantitative risk analysis?
- A. Rank and handle risk to use time and resources more wisely.
- B. Evaluators discretion for resources.
- C. Knowledge and experience to determine risk likelihood.
- D. Objective and mathematical models to provide risk acumens.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Quantitative risk analysis in cybersecurity is a method that uses objective and mathematical models
to assess and understand the potential impact of risks. It involves assigning numerical values to the
likelihood of a threat occurring, the potential impact of the threat, and the cost of mitigating the risk.
This approach allows for a more precise measurement of risk, which can then be used to make
informed decisions about where to allocate resources and how to prioritize security measures.
The focus of a quantitative risk analysis is to provide risk acumens, which are insights into the level of
risk associated with different threats. This is achieved by calculating the potential loss in terms of
monetary value and the probability of occurrence. The result is a risk score that can be compared
across different threats, enabling an organization to prioritize its responses and resource allocation.
For example, if a particular vulnerability in the IT system has a high likelihood of being exploited and
the potential impact is significant, the quantitative risk analysis would assign a high-risk score to this
vulnerability. This would signal to the organization that they need to address this issue promptly.
Quantitative risk analysis is particularly useful in scenarios where organizations need to justify
security investments or when making decisions about risk management strategies. It provides a clear
and objective way to communicate the potential impact of risks to stakeholders.
In the context of the Dell Security Foundations Achievement, understanding the principles of
quantitative risk analysis is crucial for IT staff and application administrators.
It aligns with the topics
covered in the assessment, such as security hardening, identity and access management, and
security in the cloud, which are all areas where risk analysis plays a key role123
.
Question 5
A R.T.I.E.'s business is forecast to grow tremendously in the next year, the organization will not only
need to hire new employees but also requires contracting with third-party vendors to continue
seamless operations. A .R.T.I.E. uses a VPN to support its employees on the corporate network, but
the organization is facing a security challenge in supporting the third-party business vendors.
To better meet A .R.T.I.E.'s security needs, the cybersecurity team suggested adopting a Zero Trust
architecture (ZTA). The main aim was to move defenses from static, network-based perimeters to
focus on users, assets, and resources. Zero Trust continuously ensures that a user is authentic and the
request for resources is also valid. ZTA also helps to secure the attack surface while supporting
vendor access.
What is the main challenge that ZTA addresses?
- A. Authorization of A .R.T.I.E. employees.
- B. Malware attacks.
- C. Access to the corporate network for third-party vendors.
- D. Proactive defense in-depth strategy.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The main challenge that Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) addresses is the access to the corporate
network for third-party vendors.
ZTA is a security model that assumes no implicit trust is granted to
assets or user accounts based solely on their physical or network location (i.e., local area networks
versus the internet) or based on asset ownership (enterprise or personally owned)12
. It mandates
that any attempt to access resources be authenticated and authorized within a dynamic policy
context.
A .R.T.I.E.'s business model involves contracting with third-party vendors to continue seamless
operations, which presents a security challenge.
The traditional VPN-based approach to network
security is not sufficient for this scenario because it does not provide granular control over user
access and does not verify the trustworthiness of devices and users continuously2
.
Implementing ZTA would address this challenge by:
Ensuring that all users, even those within the network perimeter, must be authenticated and
authorized to access any corporate resources.
Providing continuous validation of the security posture of both the user and the device before
granting access to resources.
Enabling the organization to apply more granular security controls, which is particularly important
when dealing with third-party vendors who require access to certain parts of the network31
.
This approach aligns with the case study’s emphasis on securing the attack surface while supporting
vendor access, as it allows A .R.T.I.E.
to grant access based on the principle of least privilege,
reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems4
.
Question 6
During the analysis, the threat intelligence team disclosed a possible threat which went unnoticed
when an A .R.T.I.E. employee sent their friend a slide deck containing the personal information of a
colleague. The exposed information included employee first and last names, date of birth and
employee ID.
What kind of attack occurred?
- A. Ransomware
- B. Data breach
- C. Advance Persistent Threat
- D. Supply chain attack
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A data breach occurs when confidential information is accessed or disclosed without authorization.
In the scenario described, an employee unintentionally sent out a slide deck containing personal
information of a colleague. This incident falls under the category of a data breach because it involves
the exposure of personal data.
The Dell Security Foundations Achievement covers a broad range of topics, including the NIST
Cybersecurity Framework, ransomware, and security hardening.
It aims to validate knowledge on
various risks and attack vectors, as well as the techniques and frameworks used to prevent and
respond to possible attacks, focusing on people, process, and technology1
.
In the context of the Dell Security Foundations Achievement, understanding the nature of different
types of cyber threats is crucial. A data breach, as mentioned, is an incident where information is
accessed without authorization. This differs from:
A ransomware attack (A), which involves malware that encrypts the victim’s files and demands a
ransom for the decryption key.
An advanced persistent threat ©, which is a prolonged and targeted cyberattack in which an intruder
gains access to a network and remains undetected for an extended period.
A supply chain attack (D), which occurs when a malicious party infiltrates a system through an
outside partner or provider with access to the system and its data.
Therefore, based on the information provided and the context of the Dell Security Foundations
Achievement, the correct answer is B. Data breach.
Question 7
A .R.T.I.E. is planning to deploy some of their applications in a public cloud. A major concern is how
to share and protect data off premises. Also, how data can be used in decision making without
exposing it to anyone who should not have access. Dell Services briefed them about various control
mechanisms to secure data in the public cloud.
Which control mechanism should be selected in this scenario?
- A. Proactive control mechanism
- B. Detective control mechanism
- C. Corrective control mechanism
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Control Mechanism Selection:
For A .R.T.I.E.'s scenario, where the concern is about sharing and protecting data off-premises and
ensuring that data can be used in decision-making without exposing it to unauthorized access, the
most suitable control mechanism would be:
A . Proactive control mechanism
Proactive control mechanisms are designed to prevent security incidents before they occur.
They
include measures such as strong authentication, encryption, and access controls, which align with A
.R.T.I.E.'s requirements for secure migration to the public cloud and maintaining data confidentiality
during decision-making processes1234
.
Data Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit ensures that even if data is intercepted or
accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and secure2
.
Access Control: Implementing robust access control measures, such as role-based access control
(RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), restricts data access to authorized personnel only34
.
Firewalls and Network Security: Deploying firewalls and other network security measures helps to
protect the cloud environment from unauthorized access and potential breaches2
.
Security Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the cloud environment allows for the early detection
of potential security threats and vulnerabilities2
.
Security Patching and Upgrades: Regularly updating and patching systems ensures that security
measures are up-to-date and can defend against the latest threats2
.
These proactive controls are essential for A .R.T.I.E.
as they provide a comprehensive approach to
securing data in the public cloud, align with the Dell Security Foundations Achievement’s focus on
security hardening, and support the Zero Trust model, which assumes no implicit trust and verifies
each request as though it originates from an open network5
.
Question 8
Which framework should be recommended to A .R.T.I.E. to enhance the overall security and
resilience of their critical infrastructure, and outline methods to reduce their cybersecurity risk?
- A. NIST CSF
- B. COBIT
- C. PCIDSS
- D. HIPAA
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Based on the case study provided and the requirements for A .R.T.I.E., the most suitable framework
to enhance the overall security and resilience of their critical infrastructure, and to outline methods
to reduce their cybersecurity risk would be:
A . NIST CSF
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is recommended for A .R.T.I.E. to enhance security and
resilience.
The NIST CSF provides guidelines for organizations to manage cybersecurity risks in a
structured and prioritized manner12
.
Identify: A .R.T.I.E.
can use the NIST CSF to identify its digital assets, cybersecurity policies, and the
current threat landscape1
.
Protect: Implement protective technology to ensure that critical infrastructure services are not
disrupted1
.
Detect: Use the framework to implement advanced detection processes to quickly identify
cybersecurity events1
.
Respond: Develop and implement appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected
cybersecurity incident1
.
Recover: Plan for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a
cybersecurity incident1
.
The NIST CSF aligns with A .R.T.I.E.'s need for a secure migration to the public cloud and addresses
the need for a holistic security capability that ensures security across the organization2
.
It also
supports the Zero Trust model, which is crucial for A .R.T.I.E.'s open platform nature1
.
Question 9
In the cloud, there are numerous configuration options for the services provided. If not properly set,
these configurations can leave the environment in an unsecure state where an attacker can read and
modify the transmitted data packets and send their own requests to the client.
Which types of attack enable an attacker to read and modify the transmitted data packets and send
their own requests to the client?
- A. Data loss
- B. Shared technology
- C. TCP hijacking
- D. Dumpster diving
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Verified Answer:
The type of attack that enables an attacker to read and modify the transmitted data packets and send
their own requests to the client is:
C . TCP hijacking
TCP Hijacking Definition: TCP hijacking is a type of cyber attack where an attacker takes control of a
communication session between two entities12
.
Attack Mechanism: The attacker intercepts and manipulates data packets being sent over the
network, allowing them to read, modify, and insert their own packets into the communication
stream1
.
Impact on Security: This attack can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems, and it
can be used to impersonate the victim, resulting in data breaches and other security incidents1
.
Prevention Measures: Implementing security measures such as encryption, using secure protocols,
and monitoring network traffic can help prevent TCP hijacking attacks1
.
TCP hijacking is particularly relevant to cloud environments where misconfigurations can leave
systems vulnerable. It is crucial for A .R.T.I.E.
to ensure proper security configurations and adopt
measures to protect against such attacks as part of their migration to the public cloud and overall
cybersecurity strategy12
.
Question 10
During the analysis, the threat intelligence team disclosed that attackers not only encrypted files, but
also attempted to encrypt backups and shared, networked, and cloud drives.
Which type of ransomware is used for this attack?
- A. Cryptolocker
- B. Double extortion
- C. Crypto
- D. Locker
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Double Extortion Ransomware: This type of ransomware not only encrypts files but also attempts to
encrypt backups and shared, networked, and cloud drives1
.
Attack Method: Attackers first exfiltrate sensitive data before encrypting it, then threaten to release
the data if the ransom is not paid, hence the term 'double extortion’1
.
Impact on Organizations: This method increases the pressure on the victim to pay the ransom, as
they face the risk of their sensitive data being published or sold1
.
Prevention and Response: Organizations should implement robust backup strategies, including offsite
and offline backups, and have an incident response plan that includes dealing with ransomware and
data breaches1
.
Double extortion ransomware attacks are particularly dangerous because they combine the threat of
data encryption with the threat of data exposure, significantly increasing the potential damage to the
victim organization1
.
Question 11
An external A .R.T.I.E. user requires access to sensitive resources and data.
Which authentication technique should be best recommended to provide access to this business
user?
- A. Two-factor
- B. Privileged Access Management
- C. Multifactor
- D. Single Sign-On
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Multifactor Authentication (MFA) Definition: MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of
identification before gaining access to a resource1
.
Security Enhancement: MFA enhances security by combining something the user knows (like a
password), something the user has (like a smartphone), and something the user is (like a
fingerprint)1
.
Protection Against Unauthorized Access: This method protects against unauthorized access by
ensuring that even if one factor (like a password) is compromised, the attacker still needs the other
factors to gain access1
.
Compliance with Regulations: MFA helps organizations comply with various regulations and cloud
security controls, which is essential for A .R.T.I.E.
as they move to the public cloud1
.
Dell’s Commitment to MFA: Dell’s own security guidelines emphasize the importance of MFA,
reflecting their commitment to safeguarding data integrity and providing an additional layer of
security during the sign-in process1
.
MFA is particularly suitable for A .R.T.I.E.'s scenario because it provides robust security for accessing
sensitive resources and data, which is crucial for external users who may not be within the secure
internal network1
.
Question 12
During analysis, the Dell Services team found outdated applications and operating systems with
missing security patches. To avert potential cyberattacks, Dell recommends application and operating
system hardening measures.
Why is security hardening important for A.R.T.I.E .?
- A. Enhance operational cost.
- B. Decrease attack surface.
- C. Enhance productivity.
- D. Remove redundancy.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Security Hardening Definition: Security hardening involves implementing measures to reduce
vulnerabilities in applications and operating systems1
.
Reducing Attack Surface: By updating and patching outdated applications and operating systems, A
.R.T.I.E.
can minimize the number of potential entry points for attackers1
.
Preventing Cyberattacks: Hardening is a proactive measure to protect against potential cyberattacks
by eliminating as many security risks as possible1
.
Compliance with Best Practices: Security hardening aligns with industry best practices and regulatory
requirements, which is essential for A .R.T.I.E.'s operations in the public cloud1
.
Dell’s Recommendation: Dell’s Security Foundations Achievement emphasizes the importance of
security hardening as a fundamental aspect of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy1
.
Security hardening is crucial for A .R.T.I.E.
because it directly contributes to the robustness of their
cybersecurity posture, ensuring that their systems are less susceptible to attacks and breaches1
.
Question 13
The cybersecurity team must create a resilient security plan to address threats. To accomplish this,
the threat intelligence team performed a thorough analysis of the A .R.T.I.E. threat landscape. The
result was a list of vulnerabilities such as social engineering, zero-day exploits, ransomware, phishing
emails, outsourced infrastructure, and insider threats.
Using the information in the case study and the scenario for this question, which vulnerability type
exposes the data and infrastructure of A.R.T.I.E .?
- A. Malicious insider
- B. Zero day exploit
- C. Ransomware
- D. Social engineering
Answer:
D
Question 14
The security team recommends the use of User Entity and Behavior Analytics (UEBA) in order to
monitor and detect unusual traffic patterns, unauthorized data access, and malicious activity of A
.R.T.I.E. The monitored entities include A .R.T.I.E. processes, applications, and network devices
Besides the use of UEBA, the security team suggests a customized and thorough implementation
plan for the organization.
What are the key attributes that define UEBA?
- A. User analytics, threat detection, and data.
- B. User analytics, encryption, and data.
- C. Encryption, automation, and data.
- D. Automation, user analytics, and data.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
User Analytics: UEBA systems analyze user behavior to establish a baseline of normal activities and
detect anomalies12
.
Threat Detection: By monitoring for deviations from the baseline, UEBA can detect potential security
threats, such as compromised accounts or insider threats12
.
Data Analysis: UEBA solutions ingest and analyze large volumes of data from various sources within
the organization to identify suspicious activities12
.
Behavioral Analytics: UEBA uses behavioral analytics to understand how users typically interact with
the organization’s systems and data12
.
Machine Learning and Automation: Advanced machine learning algorithms and automation are
employed to refine the analysis and improve the accuracy of anomaly detection over time12
.
UEBA is essential for A .R.T.I.E.
as it provides a comprehensive approach to security monitoring,
which is critical given the diverse and dynamic nature of their user base and the complexity of their
IT environment12
.
Question 15
An A .R.T.I.E. employee received an email with an invoice that looks official for $200 for a one-year
subscription. It clearly states: "Please do not reply to this email," but provides a Help and Contact
button along with a phone number.
What is the type of risk if the employee clicks the Help and Contact button?
- A. People
- B. Technology
- C. Operational
- D. Strategic
Answer:
A
Explanation:
People Risk Definition: People risk involves the potential for human error or intentional actions that
can lead to security incidents1
.
Phishing and Social Engineering: The scenario described is typical of phishing, where attackers use
seemingly official communications to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or
accessing malicious links1
.
Employee Actions: Clicking on the button could potentially lead to the employee inadvertently
providing access to the company’s systems or revealing personal or company information1
.
Dell’s Security Foundations Achievement: Dell’s Security Foundations Achievement emphasizes the
importance of recognizing and minimizing phishing exploits as part of managing people risk21
.
Mitigation Measures: Training employees to recognize and respond appropriately to phishing
attempts is a key strategy in mitigating people risk1
.
In this context, the risk is categorized as ‘people’ because it directly involves the potential actions of
an individual employee that could compromise security1
.