dell d-pdd-dy-23 practice test
Dell PowerProtect DD Deploy 2023
Question 1
What is the maximum number of PowerProtect DD systems that can be used in a Smart Scale data
center?
- A. 64
- B. 32
- C. 128
- D. 256
Answer:
B
Explanation:
By enabling Smart Scale services from DDMC, the Smart Scale architecture pools together a set of
DD series appliances into a group under the data center in which they are coordinated with each
other for space balancing. Smart Scale supports up to 32 systems in a system pool and four system
pools in a data center.
Question 2
What needs to be configured when implementing LACP on a PowerProtect DD appliance to gain
access to the underlying aggregated link connection?
- A. NIC Teams
- B. DD Boost Interface Groups
- C. Virtual network interface
- D. Physical network interface
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When implementing Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on a PowerProtect DD appliance, a
virtual network interface is created to aggregate the physical interfaces into a single logical link. This
configuration is essential to enable LACP functionality, as it allows the system to balance network
traffic effectively across multiple physical connections, enhancing redundancy and throughput. By
aggregating these physical interfaces, the appliance can better handle high data volumes, providing
stable and efficient access to the underlying network resources.
The virtual network interface manages the logical grouping, ensuring seamless failover and load
balancing between the physical links that comprise the aggregated connection.
Question 3
What is the maximum number of snapshots per MTree that can be stored on a PowerProtect DD?
- A. 750
- B. 100
- C. 32
- D. 128
Answer:
A
Explanation:
PowerProtect DD allows up to 750 snapshots per MTree, supporting efficient data protection and
recovery with minimal impact on storage resources. This feature provides extensive backup
versioning options for granular data recovery.
Question 4
An administrator is migrating their old cloud tier-enabled Data Domain to a new PowerProtect DD
appliance with cloud tier. During migration, the administrator recognizes that file system cleaning on
the source system is not possible. What is the most likely cause of this behavior?
- A. Migration will restrict all activities on both systems
- B. Source system is running in restricted mode
- C. Filesystem is disabled on the source system
- D. Migration will restrict all activities on the source system
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When a source system is in restricted mode, certain maintenance tasks, like file system cleaning, are
unavailable. This restriction is typically applied during migrations to prevent data inconsistencies,
ensuring a smooth transfer of data to the new system.
During the migration process from an older Data Domain system with cloud tier capabilities to a new
PowerProtect DD appliance, the source system operates in a "restricted mode." This restricted mode
limits specific functionalities, including file system cleaning. File system cleaning is a maintenance
operation that reclaims storage by deduplication and cleaning up obsolete data. However, to prevent
data inconsistency or interference during migration, this functionality is temporarily disabled on the
source system, thus ensuring data integrity until the migration process is completed.
The restricted mode ensures that all critical operations remain stable and predictable on the source
system, which is essential for a smooth migration to the new environment.
Question 5
What is the maximum backup speed of PowerProtect DD Virtual Edition using DD Boost?
- A. 4.2TB/h
- B. 7.0TB/h
- C. 9.0TB/h
- D. 2.5TB/h
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The maximum backup speed of the PowerProtect DD Virtual Edition (DDVE) when utilizing DD Boost
is 4.2TB per hour. DD Boost is a feature that enhances the speed and efficiency of data transfers
between the backup application and the Data Domain appliance by performing deduplication
operations closer to the source, thus reducing network traffic and improving throughput. DDVE’s
performance capabilities are optimized for virtualized environments, and the 4.2TB/h rate represents
the upper limit under ideal conditions, maximizing data protection performance in virtual setups.
Question 6
What is a characteristic of Dell Cloud Tier?
- A. NFS, HTTPS, and CIFS are supported for data movement.
- B. The VTL vault cannot be stored in cloud tier storage.
- C. Managed through a single namespace.
- D. Scales to the maximum capacity of the active tier.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Dell Cloud Tier is designed to extend storage to cloud environments while maintaining a single
namespace for management simplicity. This feature enables seamless data management across local
and cloud storage tiers, preserving data accessibility and integrity.
Question 7
An administrator must display the compression statistics for all files and directories in the file system
for the last 7 days and the last 24 hours. Which command is used to gather this information?
- A. storage show
- B. mtree show
- C. filesys report
- D. quota show
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The filesys report command provides detailed compression statistics, essential for administrators to
monitor storage efficiency over time. This insight into compression ratios aids in storage optimization
and management planning on PowerProtect DD systems.
Question 8
Which backup application uses BoostFS?
- A. IBM Spectrum Protect
- B. Quest vRanger
- C. Veritas NetBackup
- D. Dell Avamar
Answer:
D
Explanation:
BoostFS (Boost File System) is a specialized Dell EMC technology that integrates with backup
applications to enable optimized data transfers to Dell EMC Data Domain systems. BoostFS works
effectively with Dell's Avamar backup software, leveraging the Data Domain Boost technology to
provide deduplication and improve backup efficiency. The BoostFS integration enables Avamar to
utilize features like client-side deduplication, reducing data that needs to be transferred and stored
on Data Domain systems, and enhancing performance and storage efficiency.
By using BoostFS with Dell Avamar, users benefit from enhanced backup speeds, optimized network
bandwidth, and reduced load on the Data Domain system. The BoostFS integration also supports
streamlined management and more effective use of storage resources, which aligns well with Dell
EMC's strategy for comprehensive data protection.
Question 9
What is a use case of BoostFS?
- A. To increase DD Boost throughput
- B. To enable snapshot on DD Boost data
- C. To protect applications that do not support DD Boost
- D. To implement DD Boost over Fibre Channel
Answer:
C
Explanation:
BoostFS allows applications without native DD Boost support to leverage DD Boost’s deduplication
benefits. It provides a seamless data protection layer across various backup applications by
streamlining storage and data transfer processes. BoostFS, or Boost File System, is used to enable
backup functionality for applications that do not natively support DD Boost. It allows these
applications to leverage Data Domain storage efficiency by providing a file system interface. BoostFS
essentially provides a method for applications without DD Boost integration to still utilize
deduplication and other Data Domain benefits, making it highly effective for environments that want
to standardize their storage approach but have a mix of applications with and without DD Boost
support.
Question 10
DRAG DROP
Which is the correct implementation order for a VTL environment?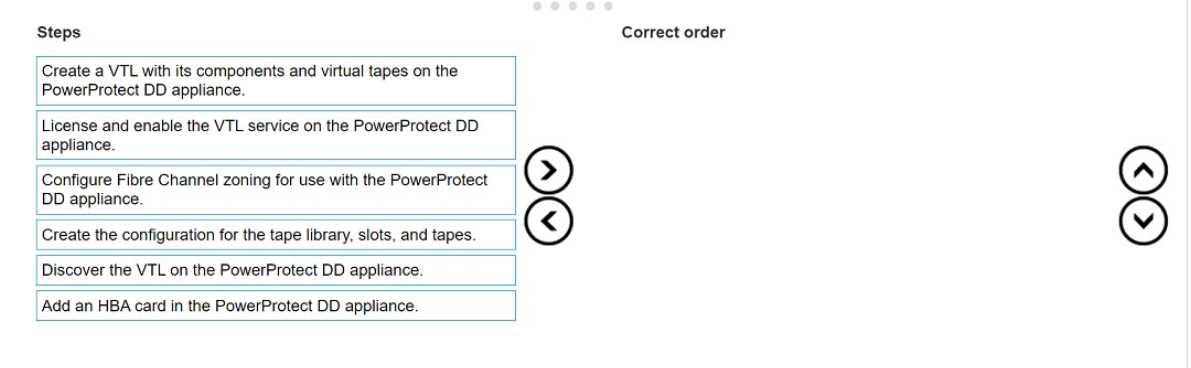
Answer:
Explanation:
The correct order for implementing a Virtual Tape Library (VTL) environment on a PowerProtect DD
appliance is as follows:
Add an HBA card in the PowerProtect DD appliance.
License and enable the VTL service on the PowerProtect DD appliance.
Create a VTL with its components and virtual tapes on the PowerProtect DD appliance.
Create the configuration for the tape library, slots, and tapes.
Configure Fibre Channel zoning for use with the PowerProtect DD appliance.
Discover the VTL on the PowerProtect DD appliance.
Add an HBA Card: The Host Bus Adapter (HBA) card is required to connect the PowerProtect DD
appliance to the Fibre Channel network, which is essential for the VTL configuration.
License and Enable VTL Service: The VTL functionality needs to be licensed and enabled on the
PowerProtect DD appliance to allow the configuration of virtual tape drives and libraries.
Create the VTL: This involves setting up the virtual tape library components and creating virtual tapes
on the appliance, establishing a simulated tape environment.
Configure Tape Library Settings: Set up the logical structure of the tape library, including the number
of slots, tape drives, and tapes, as this information is critical for the backup application.
Configure Fibre Channel Zoning: Proper zoning must be configured in the Fibre Channel environment
to ensure the backup servers can access the virtual tape drives and libraries on the PowerProtect DD
appliance.
Discover the VTL: After setting up the environment, discover the VTL on the PowerProtect DD
appliance to make it available for backup operations.
This ordered process ensures a structured and functional VTL setup within the PowerProtect DD
environment, enabling optimized data protection workflows.
Question 11
A PowerProtect DD administrator wants to enable encryption on one of two existing cloud units.
Which statement is true regarding the encryption?
- A. Cloud tier encryption is provided only by the cloud storage
- B. Encryption can be enabled on each cloud unit individually
- C. Encryption license is not required to enable cloud tier encryption
- D. Active tier encryption is required to enable encryption on the cloud tier
- E. Once data is in the cloud, you cannot change the encryption status
Answer:
E
Explanation:
Once data is stored in the cloud tier, changing its encryption status is not possible due to data
integrity and compliance constraints. Ensuring encryption settings are configured correctly before
data migration is essential to secure storage in cloud environments. When data is moved to the cloud
tier in a PowerProtect DD environment, the encryption status is locked in for that data. This means
that once data has been stored in the cloud with encryption either enabled or disabled, this setting
cannot be altered retroactively for that data. Cloud tier encryption provides secure data storage in
the cloud, but any modification to encryption preferences would only apply to new data moved to
the cloud after the change. This constraint ensures data consistency and integrity within the cloud
storage environment.
Question 12
DRAG DROP
What is the correct order of operations for the Data Invulnerability Architecture (DIA) elements?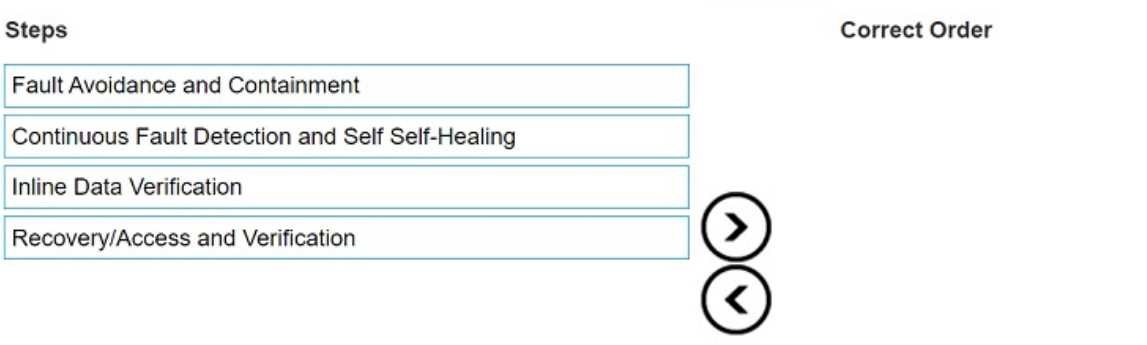
Answer:
Explanation:
The correct order of operations for the Data Invulnerability Architecture (DIA) elements is as follows:
Fault Avoidance and Containment
Continuous Fault Detection and Self-Healing
Inline Data Verification
Recovery/Access and Verification
The Data Invulnerability Architecture (DIA) in Dell PowerProtect DD systems is designed to ensure
data integrity and resiliency throughout the data storage process. Here’s how each element plays a
role in this ordered sequence:
Fault Avoidance and Containment: This is the first layer of protection. DIA focuses on preventing
faults before they occur and containing any potential issues, ensuring that faults do not propagate
within the system. This stage is critical as it forms the foundational protection layer.
Continuous Fault Detection and Self-Healing: After implementing containment, the system
continuously monitors for faults. It actively identifies and mitigates issues through self-healing
mechanisms, addressing any detected errors autonomously to maintain data integrity.
Inline Data Verification: As data is written to storage, the inline data verification checks data integrity
on the fly. This step ensures that any corruption or errors in data are detected immediately, enabling
early intervention before data is permanently stored.
Recovery/Access and Verification: The final step ensures that, during data recovery, the integrity of
the data is verified before it is accessed or restored. This stage completes the DIA cycle by confirming
that data retrieved from storage is accurate and intact.
This ordered approach in DIA is designed to provide robust protection against data loss or corruption,
making Dell PowerProtect DD appliances highly reliable for data protection needs.
Question 13
If ES40 SAS shelves are on the same chain as a DS60, what is the maximum number of possible
shelves on that chain?
- A. 3
- B. 5
- C. 7
- D. 4
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When configuring a chain with ES40 SAS shelves and DS60 shelves in a PowerProtect DD
environment, the maximum allowable number of shelves on that chain is three. This limitation is due
to compatibility and bandwidth requirements for maintaining optimal performance and reliability
across the SAS chain. Mixing different shelf models (ES40 and DS60) in a single chain affects the
maximum supported configuration, and following this limitation ensures that the data transfer
speeds and stability are not compromised.
Question 14
Which command is used to verify the state of the disks in an expansion shelf attached to a
PowerProtect DD system?
- A. disk show stats
- B. disk show state
- C. disk rescan
- D. disk status
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The disk show state command provides the current state of each disk in an expansion shelf, allowing
administrators to monitor disk health and operational status effectively, which is crucial for
maintaining data integrity.
Question 15
Which condition exists for a backup infrastructure based on PowerProtect DD?
- A. Compressed files must be decompressed before being sent to PowerProtect DD.
- B. Backup clients can write data directly to the PowerProtect DD appliance.
- C. VTL can be used to move physical tapes to a DR location.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
PowerProtect DD appliances allow direct data writing from backup clients, which improves efficiency
and data transfer rates, leveraging DD Boost and other protocols for optimized backup performance
without intermediate processing. In a PowerProtect DD backup infrastructure, backup clients are
designed to write data directly to the appliance. This direct write capability is supported by protocols
like DD Boost, which enhances the backup performance by offloading deduplication to the client
side, reducing network bandwidth usage and speeding up backups. PowerProtect DD systems are
optimized to handle direct data ingestion from backup clients, streamlining the data protection
process without requiring intermediate storage or decompression steps. This feature simplifies the
backup architecture and improves data protection efficiency.