comptia sk0-005 practice test
CompTIA Server+ Certification Exam
Question 1
Which of the following is typical of software licensing in the cloud?
- A. Per socket
- B. Perpetual
- C. Subscription-based
- D. Site-based
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Cloud software licensing refers to the process of managing and storing software licenses in the cloud.
The benefits of cloud software licensing models are vast. The main and most attractive benefit has to
do with the ease of use for software vendors and the ability to provide customizable cloud software
license management based on customer needs and desires1. Cloud-based licensing gives software
developers and vendors the opportunity to deliver software easily and quickly and gives customers
full control over their licenses, their analytics, and more1. Cloud based licensing gives software
sellers the ability to add subscription models to their roster of services1. Subscription models are one
of the most popular forms of licensing today1. Users sign up for a subscription (often based on
various options and levels of use, features, etc.) and receive theirlicenses instantly1.
Reference: 1 Everything You Need to Know about Cloud Licensing | Thales
Question 2
A server administrator wants to run a performance monitor for optimal system utilization. Which of
the following metrics can the administrator use for monitoring? (Choose two.)
- A. Memory
- B. Page file
- C. Services
- D. Application
- E. CPU
- F. Heartbeat
Answer:
A,E
Explanation:
Memory and CPU are two metrics that can be used for monitoring system utilization. Memory refers
to the amount of RAM that is available and used by the system and its processes. CPU refers to the
percentage of processor time that is consumed by the system and its processes. Both memory and
CPU can affect the performance and responsiveness of the system and its applications. Monitoring
memory and CPU can help identify bottlenecks, resource contention, memory leaks, high load, etc.
Question 3
After configuring IP networking on a newly commissioned server, a server administrator installs a
straight- through network cable from the patch panel to the switch. The administrator then returns
to the server to test network connectivity using the ping command. The partial output of the ping
and ipconfig commands are displayed below: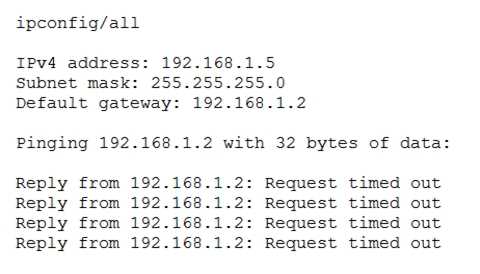
The administrator returns to the switch and notices an amber link light on the port where the server
is connected. Which of the following is the MOST likely reason for the lack of network connectivity?
- A. Network port security
- B. An improper VLAN configuration
- C. A misconfigured DHCP server
- D. A misconfigured NIC on the server
Answer:
D
Explanation:
A misconfigured NIC on the server is the most likely reason for the lack of network connectivity. The
output of the ping command shows that the server is unable to reach its default gateway (10.0.0.1)
or any other IP address on the network. The output of the ipconfig command shows that the server
has a valid IP address (10.0.0.10) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0) but no default gateway
configured. This indicates that there is a problem with the NIC settings on the server, such as an
incorrect IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server, etc. A misconfigured NIC can also
cause an amber link light on the switch port, which indicates a speed or duplex mismatch between
the NIC and the switch.
Question 4
A user cannot save large files to a directory on a Linux server that was accepting smaller files a few
minutes ago. Which of the following commands should a technician use to identify the issue?
- A. pvdisplay
- B. mount
- C. df -h
- D. fdisk -l
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The df -h command should be used to identify the issue of not being able to save large files to a
directory on a Linux server. The df -h command displays disk space usage in human-readable format
for all mounted file systems on the server. It shows the total size, used space, available space,
percentage of use, and mount point of each file system. By using this command, a technician can
check if there is enough free space on the file system where the directory is located or if it has
reached its capacity limit.
Question 5
Following a recent power outage, a server in the datacenter has been constantly going offline and
losing its configuration. Users have been experiencing access issues while using the application on
the server. The server technician notices the data and time are incorrect when the server is online.
All other servers are working. Which of the following would MOST likely cause this issue? (Choose
two.)
- A. The server has a faulty power supply
- B. The server has a CMOS battery failure
- C. The server requires OS updates
- D. The server has a malfunctioning LED panel
- E. The servers do not have NTP configured
- F. The time synchronization service is disabled on the servers
Answer:
B,F
Explanation:
The server has a CMOS battery failure and the time synchronization service is disabled on the
servers. The CMOS battery is a small battery on the motherboard that powers the BIOS settings and
keeps track of the date and time when the server is powered off. If the CMOS battery fails, the server
will lose its configuration and display an incorrect date and time when it is powered on. This can
cause access issues for users and applications that rely on accurate time stamps. The time
synchronization service is a service that synchronizes the system clock with a reliable external time
source, such as a network time protocol (NTP) server. If the time synchronization service is disabled
on the servers, they will not be able to update their clocks automatically and may drift out of sync
with each other and with the network. This can also cause access issues for users and applications
that require consistent and accurate time across the network.
Question 6
A company has implemented a requirement to encrypt all the hard drives on its servers as part of a
data loss prevention strategy. Which of the following should the company also perform as a data loss
prevention method?
- A. Encrypt all network traffic
- B. Implement MFA on all the servers with encrypted data
- C. Block the servers from using an encrypted USB
- D. Implement port security on the switches
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The company should also implement MFA on all the servers with encrypted data as a data loss
prevention method. MFA stands for multi-factor authentication, which is a method of verifying a
user’s identity by requiring two or more pieces of evidence, such as something they know (e.g., a
password), something they have (e.g., a token), or something they are (e.g., a fingerprint). MFA adds
an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, even if the user’s
password is compromised or stolen. Encrypting the hard drives on the servers protects the data from
being read or copied if the drives are physically removed or stolen, but it does not prevent
unauthorized access to the data if the user’s credentials are valid.
Question 7
A systems administrator is setting up a server on a LAN that uses an address space that follows the
RFC 1918 standard. Which of the following IP addresses should the administrator use to be in
compliance with the standard?
- A. 11.251.196.241
- B. 171.245.198.241
- C. 172.16.19.241
- D. 193.168.145.241
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The administrator should use 172.16.19.241 as an IP address to be in compliance with RFC 1918
standard. RFC 1918 defines three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for private internets,
meaning they are not globally routable on the public Internet and can be used within an enterprise
without any risk of conflict or overlap with other networks. These ranges are:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix) 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix) 192.168.0.0 -
192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
Out of these ranges, only 172.16.19.241 falls within one of them (172.16/12 prefix). The other
options are either public IP addresses that belong to other organizations or networks
(11.251.196.241, 171.245.198.241) or invalid IP addresses that do not conform to any standard
(193.168.145.241).
Reference: https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/RFC-1918
Question 8
An administrator needs to perform bare-metal maintenance on a server in a remote datacenter.
Which of the following should the administrator use to access the server’s console?
- A. IP KVM
- B. VNC
- C. A crash cart
- D. RDP
- E. SSH
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The administrator should use an IP KVM to access the server’s console remotely for bare-metal
maintenance. An IP KVM stands for Internet Protocol Keyboard Video Mouse, which is a device that
allows remote control of a server’s keyboard, video, and mouse over a network connection, such as
LAN or Internet. An IP KVM enables an administrator to perform tasks such as BIOS configuration,
boot sequence selection, operating system installation, etc., without being physically present at the
server location.
The other options are not suitable for bare-metal maintenance because they require either physical
access to the server (a crash cart) or an operating system running on the server (VNC, RDP, SSH). A
crash cart is a mobile unit that contains a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and cables that can be plugged
into a server for direct access to its console. VNC stands for Virtual Network Computing, which is a
software that allows remote desktop sharing and control over a network connection using a
graphical user interface (GUI). RDP stands for Remote Desktop Protocol, which is a protocol that
allows remote desktop access and control over a network connection using a GUI or command-line
interface (CLI). SSH stands for Secure Shell, which is a protocol that allows secure remote login and
command execution over a network connection using a CLI.
Question 9
A technician needs to provide a VM with high availability. Which of the following actions should the
technician take to complete this task as efficiently as possible?
- A. Take a snapshot of the original VM
- B. Clone the original VM
- C. Convert the original VM to use dynamic disks
- D. Perform a P2V of the original VM
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Cloning the original VM is the most efficient way to provide a VM with high availability. Cloning is the
process of creating an exact copy of a VM, including itsconfiguration, operating system, applications,
and data. A cloned VM can be used as a backup or a replica of the original VM, and can be powered
on and run independently. Cloning can be done quickly and easily using vSphere tools or other third-
party software. By cloning the original VM and placing it on a different host server or availability
zone, the technician can ensure that if the original VM fails, the cloned VM can take over its role and
provide uninterrupted service to the users and applications.
Question 10
A server administrator receives a report that Ann, a new user, is unable to save a file to her home
directory on a server. The administrator checks Ann’s home directory permissions and discovers the
following:
dr-xr-xr-- /home/Ann
Which of the following commands should the administrator use to resolve the issue without granting
unnecessary permissions?
- A. chmod777/home/Ann
- B. chmod666/home/Ann
- C. chmod711/home/Ann
- D. chmod754/home/Ann
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The administrator should use the command chmod 754 /home/Ann to resolve the issue without
granting unnecessary permissions. The chmod command is used to change the permissions of files
and directories on a Linux server. The permissions are represented by three numbers, each ranging
from 0 to 7, that correspond to the read ®, write (w), and execute (x) permissions for the owner,
group, and others respectively. The numbers are calculated by adding up the values of each
permission: r = 4, w = 2, x = 1. For example, 7 means rwx (4 + 2 + 1), 6 means rw- (4 + 2), 5 means r-x
(4 + 1), etc. In this case, Ann’s home directory has the permissions dr-xr-xr–, which means that only
the owner (d) can read ® and execute (x) the directory, and the group and others can only read ® and
execute (x) but not write (w) to it. This prevents Ann from saving files to her home directory. To fix
this issue, the administrator should grant write permission to the owner by using chmod 754
/home/Ann, which means that the owner can read ®, write (w), and execute (x) the directory, the
group can read ® and execute (x) but not write (w) to it, and others can only read ® but not write (w)
or execute (x) it. This way, Ann can save files to her home directory without giving unnecessary
permissions to others.
Reference:
https://linuxize.com/post/what-does-chmod-777-mean/
Question 11
Which of the following documents would be useful when trying to restore IT infrastructure
operations after a non-planned interruption?
- A. Service-level agreement
- B. Disaster recovery plan
- C. Business impact analysis
- D. Business continuity plan
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A disaster recovery plan would be useful when trying to restore IT infrastructure operations after a
non-planned interruption. A disaster recovery plan is a document that outlines the steps and
procedures to recover from a major disruption of IT services caused by natural or man-made
disasters, such as fire, flood, earthquake, cyberattack, etc. A disaster recovery plan typically includes:
A list of critical IT assets and resources that need to be protected and restored
A list of roles and responsibilities of IT staff and stakeholders involved in the recovery process
A list of backup and recovery strategies and tools for data, applications, servers, networks, etc.
A list of communication channels and methods for notifying users, customers, vendors, etc.
A list of testing and validation methods for ensuring the functionality and integrity of restored
systems
A list of metrics and criteria for measuring the effectiveness and efficiency of the recovery process
A disaster recovery plan helps IT organizations to minimize downtime, data loss, and financial impact
of a disaster, as well as to resume normal operations as quickly as possible.
Question 12
A systems administrator is setting up a new server that will be used as a DHCP server. The
administrator installs the OS but is then unable to log on using Active Directory credentials.The
administrator logs on using the local administrator account and verifies the server has the correct IP
address, subnet mask, and default gateway. The administrator then gets on another server and can
ping the new server. Which of the following is causing the issue?
- A. Port 443 is not open on the firewall
- B. The server is experiencing a downstream failure
- C. The local hosts file is blank
- D. The server is not joined to the domain
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The server is not joined to the domain is causing the issue. A domain is a logical grouping of
computers that share a common directory database and security policy on a network. Active
Directory is a Microsoft technology that provides domain services for Windows-based computers. To
use Active Directory credentials to log on to a server, the server must be joined to the domain that
hosts Active Directory. If the server is not joined to the domain, it will not be able to authenticate
with Active Directory and will only accept local accounts for logon. To join a server to a domain, the
administrator must have a valid domain account with sufficient privileges and must know the name
of the domain controller that hosts Active Directory.
Question 13
A systems administrator is preparing to install two servers in a single rack. The administrator is
concerned that having both servers in one rack will increase the chance of power issues due to the
increased load. Which of the following should the administrator implement FIRST to address the
issue?
- A. Separate circuits
- B. An uninterruptible power supply
- C. Increased PDU capacity
- D. Redundant power supplies
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The administrator should implement separate circuits first to address the issue of power issues due
to the increased load. Separate circuits are electrical wiring systems that provide independent power
sources for different devices or groups of devices. By using separate circuits, the administrator can
avoid overloading a single circuit with too many servers and reduce the risk of power outages,
surges, or fires. Separate circuits also provide redundancy and fault tolerance, as a failure in one
circuit will not affect the other circuit.
Question 14
Which of the following is a method that is used to prevent motor vehicles from getting too close to
building entrances and exits?
- A. Bollards
- B. Reflective glass
- C. Security guards
- D. Security cameras
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Bollards are an example of a method that is used to prevent motor vehicles from getting too close to
building entrances and exits. Bollards are short, sturdy posts that are installed on sidewalks, parking
lots, or roads to create physical barriers and control traffic flow. Bollards can be used to protect
pedestrians, buildings, or other structures from vehicle collisions or attacks. Bollards can be made of
various materials, such as metal, concrete, or plastic, and can be fixed, removable, or retractable.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bollard
Question 15
A technician is installing a variety of servers in a rack. Which of the following is the BEST course of
action for the technician to take while loading the rack?
- A. Alternate the direction of the airflow
- B. Install the heaviest server at the bottom of the rack
- C. Place a UPS at the top of the rack
- D. Leave 1U of space between each server
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The technician should install the heaviest server at the bottom of the rack to load the rack properly.
Installing the heaviest server at the bottom of the rack helps to balance the weight distribution and
prevent the rack from tipping over or collapsing. Installing the heaviest server at the bottom of the
rack also makes it easier to access and service the server without lifting or moving it. Installing the
heaviest server at any other position in the rack could create instability and safety hazards.