comptia cnx-001 practice test
CompTIA CloudNetX
Question 1
HOTSPOT
New devices were deployed on a network and need to be hardened.
INSTRUCTIONS
Use the drop-down menus to define the appliance-hardening techniques that provide the most
secure solution.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All
button.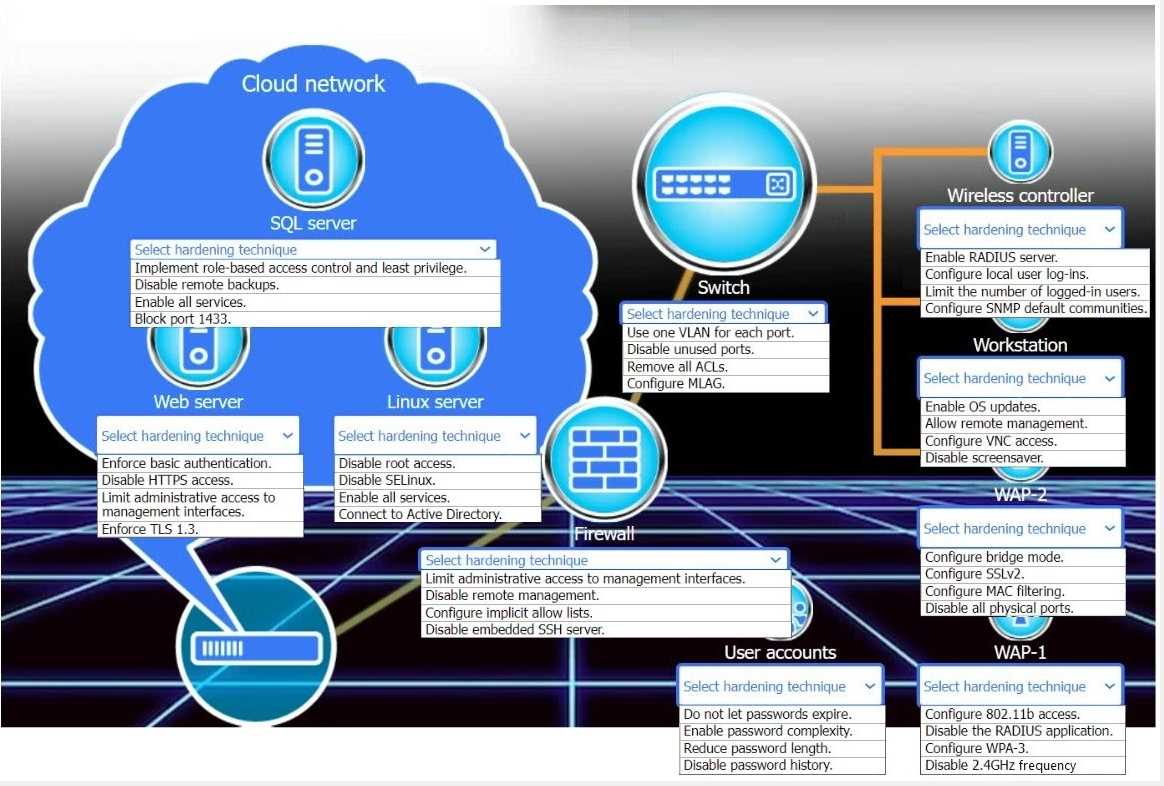
Answer:
Explanation: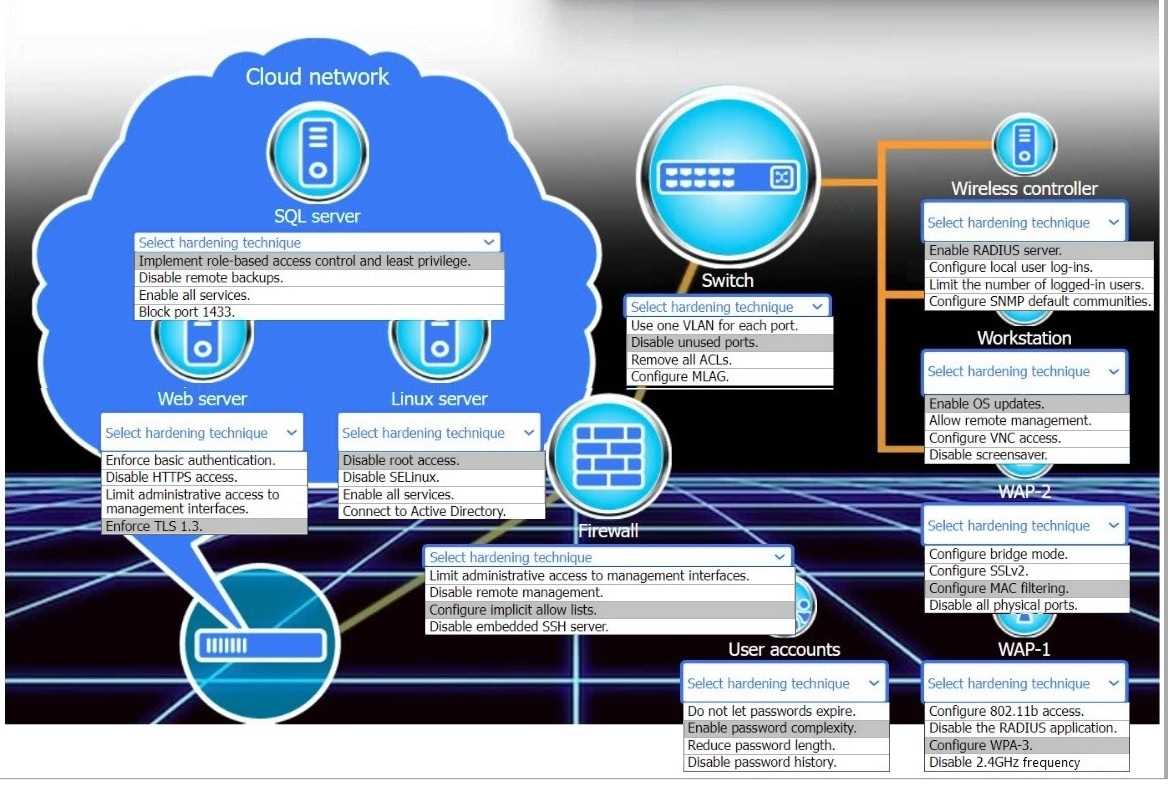
Question 2
SIMULATION
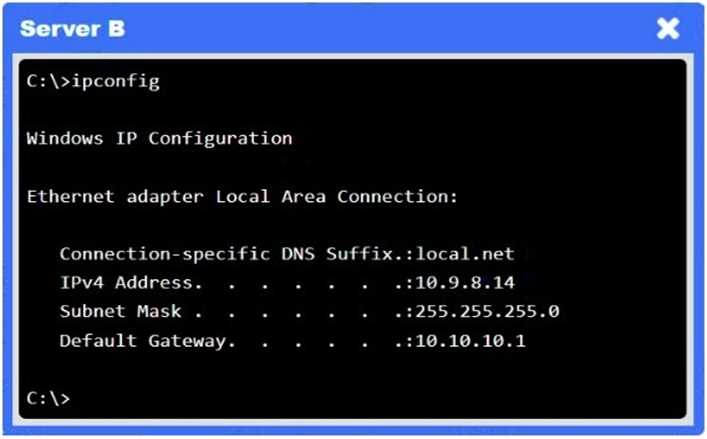
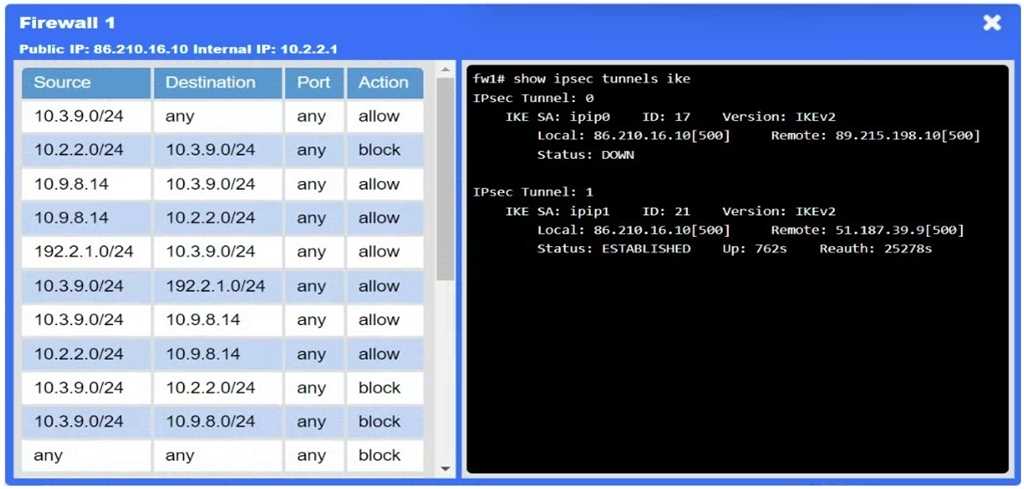
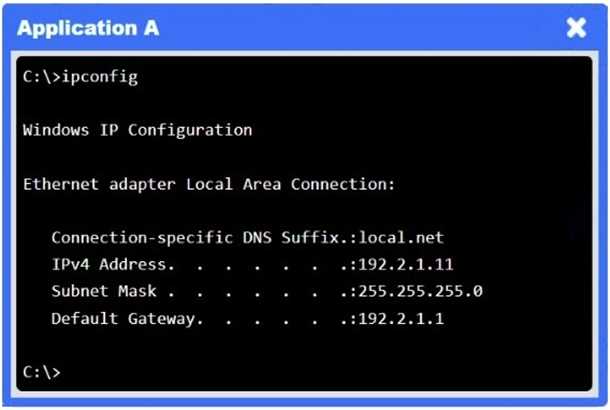
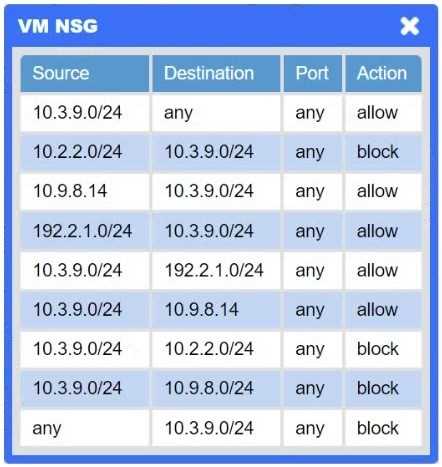
A network administrator needs to resolve connectivity issues in a hybrid cloud setup. Workstations
and VMs are not able to access Application
A. Workstations are able to access Server B.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on workstations, VMs, firewalls, and NSGs to troubleshoot and gather information. Type help in
the terminal to view a list of available commands.
Select the appropriate device(s) requiring remediation and identify the associated issue(s).
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All
button.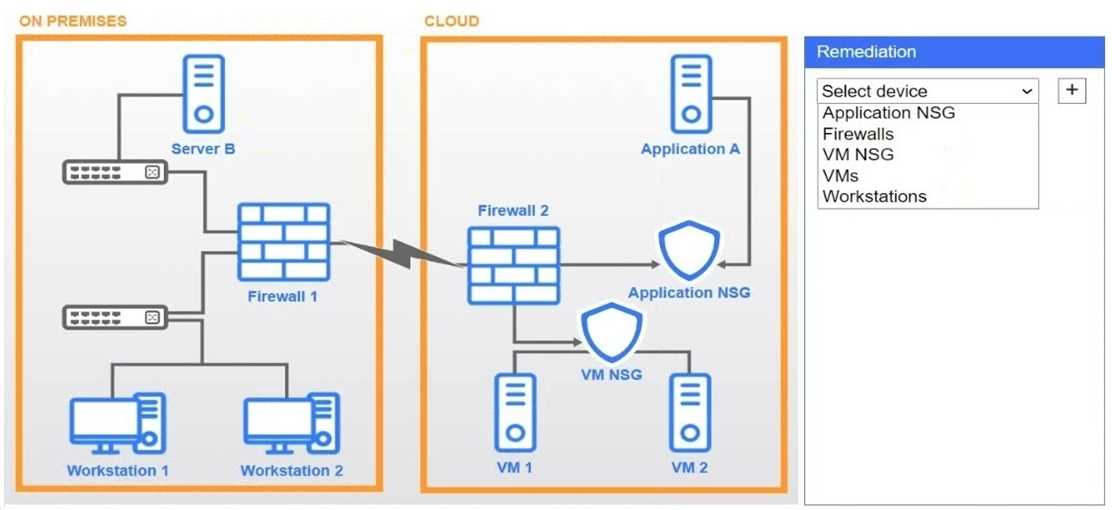
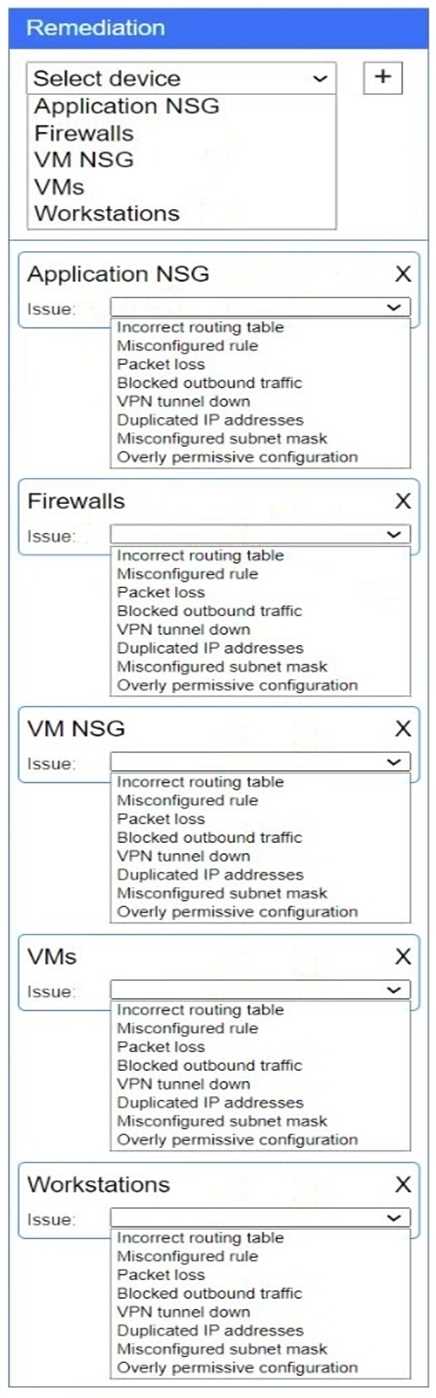


Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation: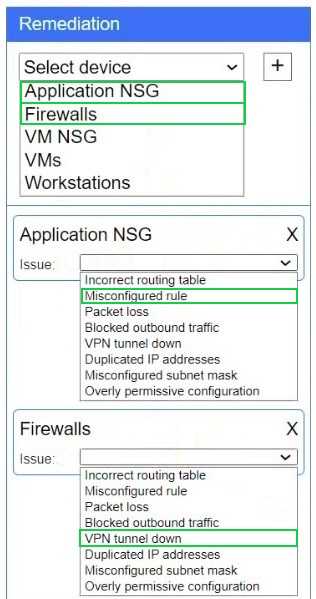
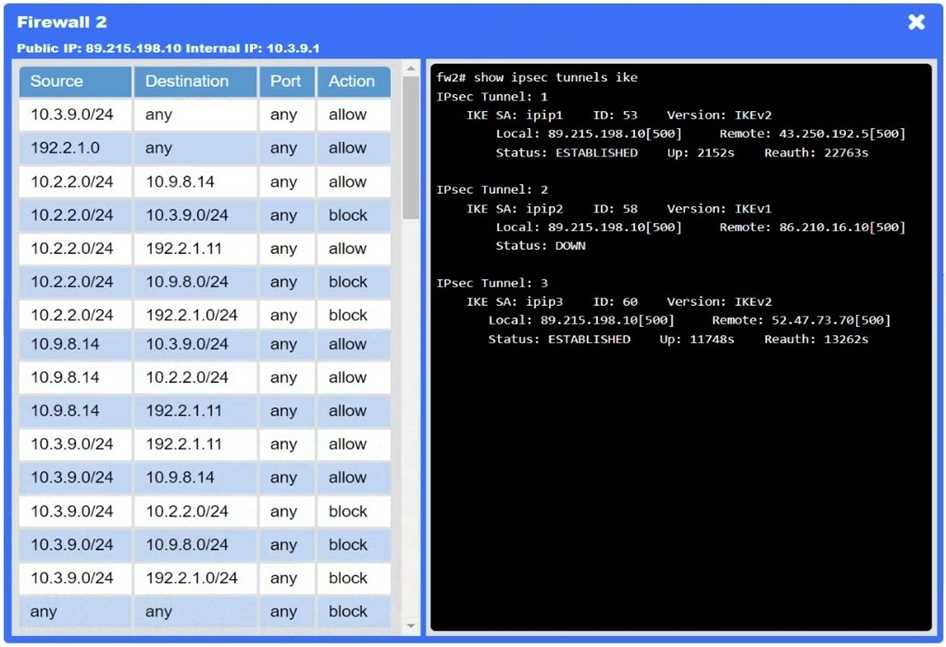
Firewalls → VPN tunnel down
The IPsec tunnel between on-prem Firewall 1 and cloud Firewall 2 (ipip0/ipip2) is down, so no traffic
can traverse to the cloud.
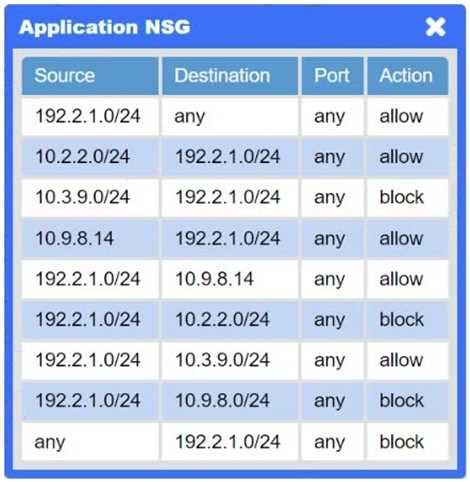
Application NSG → Misconfigured rule
There’s a “block” rule for 10.3.9.0/24 → 192.2.1.0/24, preventing legitimate on-prem clients from
reaching Application A.
Question 3
HOTSPOT
You are designing a campus network with a three-tier hierarchy and need to ensure secure
connectivity between locations and traveling employees.
INSTRUCTIONS
Review the command output by clicking on the server, laptops, and workstations on the network.
Use the drop-down menus to determine the appropriate technology and label for each layer on the
diagram. Options may only be used once.
Click on the magnifying glass to make additional configuration changes.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All
button.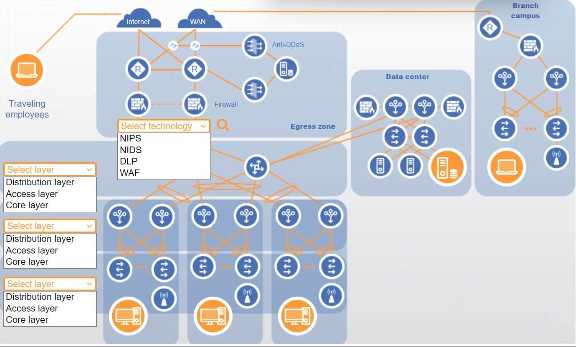
Answer:
Explanation: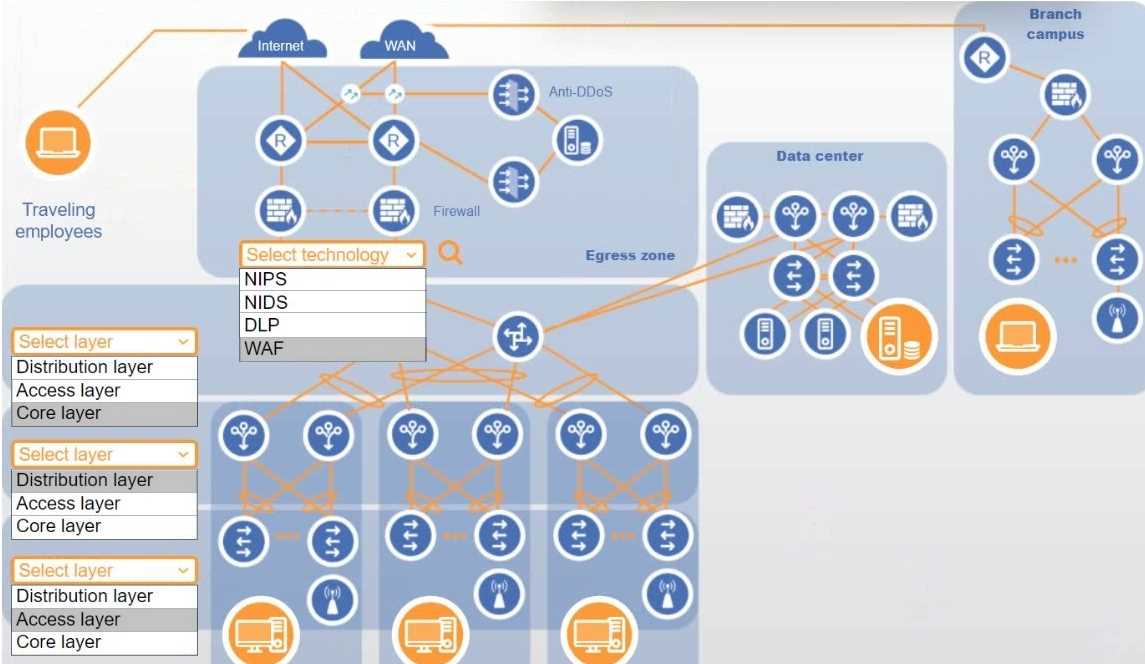
Question 4
As part of a project to modernize a sports stadium and improve the customer service experience for
fans, the stadium owners want to implement a new wireless system. Currently, all tickets are
electronic and managed by the stadium mobile application. The new solution is required to allow
location tracking precision within 5ft (1.5m) of fans to deliver the following services:
Emergency/security assistance
Mobile food order
Event special effects
Raffle winner location displayed on the giant stadium screen
Which of the following technologies enables location tracking?
- A. SSID
- B. BLE
- C. NFC
- D. IoT
Answer:
B
Explanation:
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is a wireless personal area network (WPAN) technology designed for
applications that require lower energy consumption and reduced cost while maintaining a
communication range similar to classic Bluetooth. BLE supports location tracking with an accuracy
range typically between 1 to 2 meters (approximately 3 to 6 feet), making it ideal for applications
that demand fine-grained location services, such as stadium services requiring real-time user
proximity data.
According to the CompTIA CloudNetX CNX-001 Official Objectives, under the Network Architecture
domain, specifically in the subdomain:
"Wireless Technologies: Identify capabilities of BLE, NFC, RFID, and IoT devices within a network
environment," it is outlined that:
"BLE enables proximity-based services and real-time indoor location tracking with high accuracy
when used with beacon infrastructure."
"BLE beacons can be deployed throughout a physical space, transmitting signals received by mobile
applications to determine a user’s location within a few feet."
"BLE is widely adopted for use cases including indoor navigation, asset tracking, and personalized
user engagement, making it a critical technology for modern high-density venues such as stadiums."
In comparison:
SSID merely identifies a wireless network and has no location tracking function.
NFC requires close contact (under 4 cm), and is not suitable for continuous or broad-range tracking.
IoT is an overarching category that includes connected devices and sensors; however, IoT is not a
standalone location tracking technology. It may include BLE as a component, but BLE specifically
provides the precise location tracking functionality.
These distinctions are explicitly addressed in the CompTIA CloudNetX CNX-001 Study Guide, under
the section:
“Emerging Network Technologies and Architectures”, where BLE is described as a key enabling
technology for context-aware and location-based services in enterprise and public environments.
Question 5
A company is experiencing Wi-Fi performance issues. Three Wi-Fi networks are available, each
running on the 2.4 GHz band and on the same channel. Connecting to each Wi-Fi network yields slow
performance. Which of the following channels should the networks be configured to?
- A. Channel 1, Channel 2. and Channel 3
- B. Channel 2. Channel 4, and Channel 9
- C. Channel 1, Channel 6, and Channel 11
- D. Channel 3, Channel 5, and Channel 10
Answer:
C
Explanation:
These are the three non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz band, eliminating co-channel and
adjacent-channel interference for optimal Wi-Fi performance.
Question 6
A company hosts a cloud-based e-commerce application and only wants the application accessed
from certain locations. The network team configures a cloud firewall with WAF enabled, but users
can access the application globally. Which of the following should the network team do?
- A. Reconfigure WAF rules.
- B. Configure a NAT gateway.
- C. Implement a CDN.
- D. Configure geo-restriction.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Geo-restriction lets you block or allow traffic based on the requester’s geographic region, preventing
access from locations you haven’t authorized.
Question 7
A network architect must ensure only certain departments can access specific resources while on
premises. Those same users cannot be allowed to access those resources once they have left
campus. Which of the following would ensure access is provided according to these requirements?
- A. Enabling MFA for only those users within the departments needing access
- B. Configuring geofencing with the IPs of the resources
- C. Configuring UEBA to monitor all access to those resources during non-business hours
- D. Implementing a PKI-based authentication system to ensure access
Answer:
B
Explanation:
By defining an IP-based geofence around the on-premises network addresses where those resources
reside, you ensure that only users connecting from inside the campus IP ranges can reach them. As
soon as the same users leave that network (and thus fall outside the geofenced IP block), access is
automatically denied.
Question 8
A security architect needs to increase the security controls around computer hardware installations.
The requirements are:
Auditable access logs to computer rooms
Alerts for unauthorized access attempts
Remote visibility to the inside of computer rooms
Which of the following controls best meet these requirements? (Choose two.)
- A. Video surveillance
- B. NFC access cards
- C. Motion sensors
- D. Locks and keys
- E. Automated lighting
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
Video surveillance provides continuous, remote visibility into computer rooms and can be integrated
with analytics to generate alerts on unauthorized presence.
NFC access cards enforce controlled entry with a system that logs every card swipe and issues alerts
on failed or out-of-hours attempts, giving you auditable access records and immediate notifications
of any suspicious activity.
Question 9
A network security engineer must secure a web application running on virtual machines in a public
cloud. The virtual machines are behind an application load balancer. Which of the following
technologies should the engineer use to secure the virtual machines? (Choose two.)
- A. CDN
- B. DLP
- C. IDS
- D. WAF
- E. SIEM
- F. NSG
Answer:
D, F
Explanation:
WAF: Protects the web application by inspecting incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests at the load balancer,
blocking SQL injection, XSS, and other common web attacks.
NSG: Enforces network-layer controls on the VMs’ subnets or interfaces, allowing only approved
ports and IP ranges to reach the application servers.
Question 10
A company is expanding operations and opening a new facility. The executive leadership team
decides to purchase an insurance policy that will cover the cost of rebuilding the facility in case of a
natural disaster. Which of the following describes the team's decision?
- A. Business continuity
- B. Disaster recovery
- C. Risk transference
- D. Memorandum of understanding
Answer:
C
Explanation:
By purchasing an insurance policy, the company shifts the financial burden of rebuilding after a
natural disaster to the insurer, which is the essence of risk transference.
Question 11
A network engineer is establishing a wireless network for handheld inventory scanners in a
manufacturing company's warehouse. The engineer needs an authentication mechanism for these
scanners that uses the Wi-Fi network and works with the company's Active Directory. The business
requires that the solution authenticate the users and authorize the scanners. Which of the following
provides the best solution for authentication and authorization?
- A. TACACS+
- B. RADIUS
- C. LDAP
- D. PKI
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Using a RADIUS server with 802.1X on the Wi-Fi infrastructure allows the scanners (and their users)
to be authenticated against Active Directory and mapped to the correct authorization policies.
TACACS+ is geared toward device management, LDAP alone doesn’t handle the Wi-Fi 802.1X
handshake, and PKI by itself wouldn’t provide the user-to-device authorization flow needed. RADIUS
gives you both authentication and authorization tied into AD.
Question 12
A company is migrating an application to the cloud for modernization. The engineer needs to provide
dependencies between application and database tiers in the environment. Which of the following
should the engineer reference in order to best meet this requirement?
- A. Internal knowledge base article
- B. CMDB
- C. WBS
- D. Diagram of physical server locations
- E. SOW
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) explicitly maps and documents the relationships and
dependencies among configuration items, such as your application and database tiers, making it the
ideal reference when migrating to the cloud.
Question 13
A network administrator recently deployed new Wi-Fi 6E access points in an office and enabled 6GHz
coverage. Users report that when they are connected to the new 6GHz SSID, the performance is
worse than the 5GHz SSID. The network administrator suspects that there is a source of 6GHz
interference in the office. Using the troubleshooting methodology, which of the following actions
should the network administrator do next?
- A. Test to see if the changes have improved network performance.
- B. Use a spectrum analyzer and check the 6GHz spectrum.
- C. Document the list of channels that are experiencing interference.
- D. Change the channels being used by the 6GHz radios in the APs.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Before making configuration changes, you should verify and pinpoint the suspected interference
source by analyzing the 6 GHz band. A spectrum analyzer will reveal any non-Wi-Fi transmissions or
overlapping noise that’s degrading performance, allowing you to target your remediation effectively.
Question 14
A SaaS company is launching a new product based in a cloud environment. The new product will be
provided as an API and should not be exposed to the internet. Which of the following should the
company create to best meet this requirement?
- A. A transit gateway that connects the API to the customer's VPC
- B. Firewall rules allowing access to the API endpoint from the customer's VPC
- C. A VPC peering connection from the API VPC to the customer's VPC
- D. A private service endpoint exposing the API endpoint to the customer's VPC
Answer:
D
Explanation:
AWS PrivateLink (a private service endpoint) lets you expose your API over an interface endpoint
directly into each customer’s VPC without ever traversing the public internet, ensuring the service
remains fully private.
Question 15
A network administrator is configuring firewall rules to lock down the network from outside attacks.
Which of the following should the administrator configure to create the most strict set of rules?
- A. URL filtering
- B. File blocking
- C. Network security group
- D. Allow List
Answer:
D
Explanation:
By explicitly permitting only known, approved traffic and blocking everything else by default, an
allow-list policy enforces the strictest firewall posture.