comptia 220-1202 practice test
CompTIA A+ Certification Exam: Core 2
Question 1
SIMULATION
You are configuring a home network for a customer. The customer has requested the ability to access
a Windows PC remotely, and needs all chat and optional functions to work in their game console.
INSTRUCTIONS
Use the drop-down menus to complete the network configuration for the customer. Each option may
only be used once, and not all options will be used.
Then, click the + sign to place each device in its appropriate location.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All
button.
Wireless AP LAN
Firewall Screened Subnet
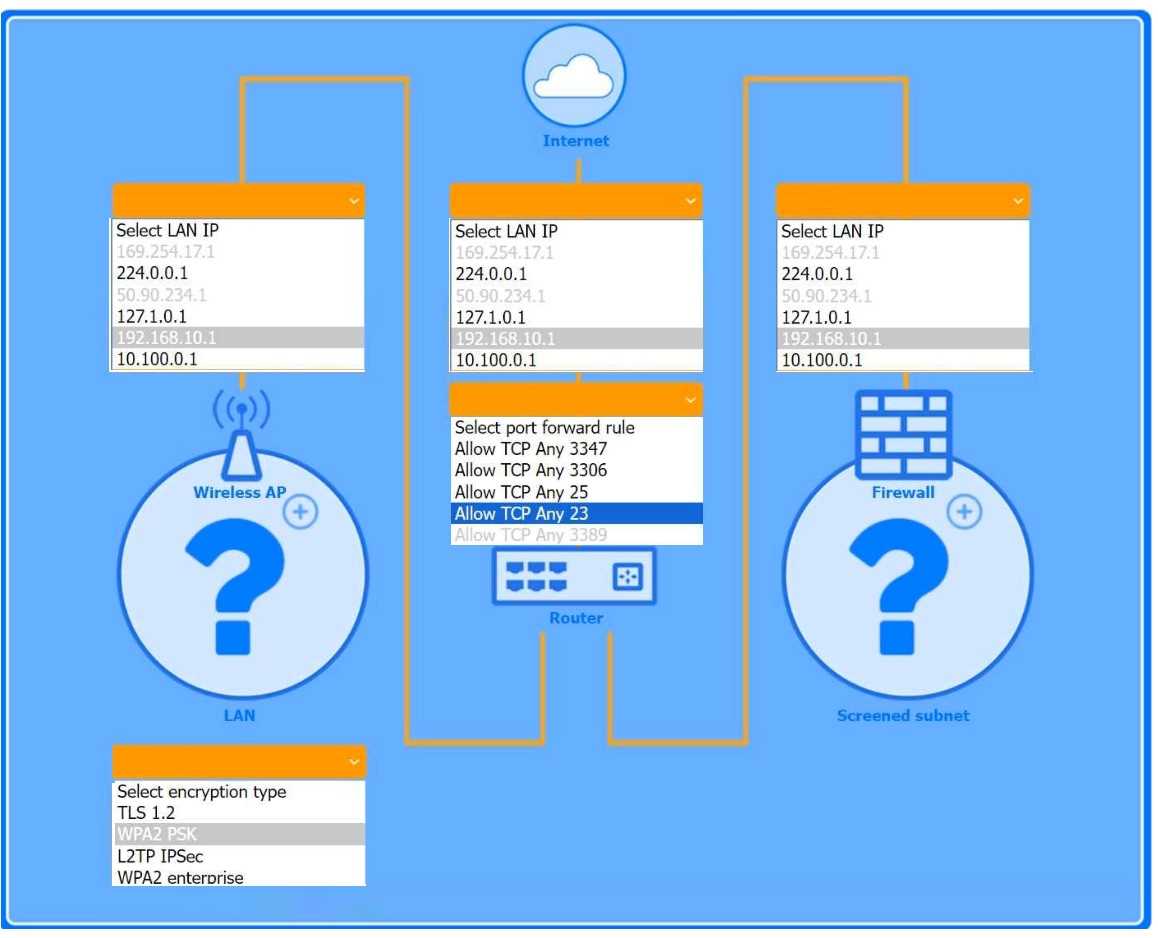
Answer:
See
explanation below.
Explanation:
The completed configuration:
1. Wireless AP (LAN side)
1. LAN IP: 192.168.10.1
2. Encryption: WPA2 PSK
2. Router (port-forward rule)
1. Allow TCP Any 3389
This forwards inbound RDP traffic (TCP/3389) from the Internet to the Windows PC, enabling Remote
Desktop access.
3. Firewall (screened subnet side)
1. LAN IP: 10.100.0.1
4. Device placement
1. PC: place behind the router (where the port-forward rule points).
2. Game console: place on the Wireless AP (so it can use chat and extra services over WPA2 PSK).
3. Firewall: place in front of the screened subnet (with its 10.100.0.1 IP facing that subnet).
The Windows PC is placed in the screened subnet (behind the firewall) for enhanced security.
Remote access to this PC requires port forwarding of TCP port 3389 (RDP), which is correctly
configured through the router.
The Game Console is placed on the Wireless AP LAN, using WPA2 PSK for a secure wireless
connection. Game consoles typically use peer-to-peer chat and online services that require open
access without firewall restrictions, which is why the console is not placed behind the firewall.
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Reference Points:
Objective 3.4: Given a scenario, implement best practices associated with data and device security.
Objective 2.4: Given a scenario, use appropriate tools to support and configure network settings.
Study Guide Reference: CompTIA A+ Core 2 guides recommend using screened subnets (a type of
DMZ) for systems needing controlled external access, such as remote desktops, while placing gaming
and media devices on less restricted networks for full functionality.
Question 2
A technician needs to provide remote support for a legacy Linux-based operating system from their
Windows laptop. The solution needs to allow the technician to see what the user is doing and
provide the ability to interact with the user's session. Which of the following remote access
technologies would support the use case?
- A. VPN
- B. VNC
- C. SSH
- D. RDP
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The correct answer isVNC (Virtual Network Computing). VNC is a graphical desktop-sharing system
that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It is
platform-independent and widely supported on Linux, which makes it ideal for providinginteractive
remote support for a Linux-based operating system. It allows the technician not only to view the
remote desktop session but also tocontrol it, fulfilling the need to see and interact with the user’s
session.
A . VPN(Virtual Private Network) creates a secure tunnel to a network but doesnot provide desktop
sharing or session controlby itself.
C . SSH(Secure Shell) provides secure command-line access to Unix/Linux systems but does not
offergraphical desktop interaction, which is a requirement in this case.
D . RDP(Remote Desktop Protocol) is primarily a Microsoft protocol, and although it can be made to
work on Linux, it isnot natively supported on legacy Linux systems, and thusless suitablethan VNC in
this scenario.
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Core 2 Objective Reference:
Objective 1.8 – Given a scenario, use features and tools of the operating system.
Under this objective, candidates are expected to be familiar with remote access technologies,
includingRDP, SSH, and VNC, and understand their appropriate uses and limitations on different
platforms such as Windows and Linux.
Question 3
A technician is attempting to join a workstation to a domain but is receiving an error message stating
the domain cannot be found. However, the technician is able to ping the server and access the
internet. Given the following information:
IP Address – 192.168.1.210
Subnet Mask – 255.255.255.0
Gateway – 192.168.1.1
DNS1 – 8.8.8.8
DNS2 – 1.1.1.1
Server – 192.168.1.10
Which of the following should the technician do to fix the issue?
- A. Change the DNS settings.
- B. Assign a static IP address.
- C. Configure a subnet mask.
- D. Update the default gateway.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The issue described—“domain cannot be found” despite the ability to ping the server and access the
internet—indicates aDNS resolution problem, not a network connectivity issue. The workstation is
currently usingpublic DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 1.1.1.1)whichcannot resolve internal domain names,
such as the ones used in Active Directory environments. To resolve this, the technician needs
tochange the DNS settings to point to the internal DNS server, which in most domain setups is
thedomain controller itself (likely 192.168.1.10 in this case).
Here’s the breakdown of the incorrect options:
B . Assign a static IP address: The IP is already assigned and functioning; the device can ping and
reach the network and internet.
C . Configure a subnet mask: The subnet mask is appropriate for the network range (Class C /24).
D . Update the default gateway: The gateway is valid and allows internet access; this is not the issue.
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Core 2 Objective Reference:
Objective 1.8 – Given a scenario, use features and tools of the operating system.
Under this objective, candidates must know how to troubleshoot OS-based network configurations,
includingproper DNS settings in domain environments.
—
Question 4
A network technician notices that most of the company's network switches are now end-of-life and
need to be upgraded. Which of the following should the technician do first?
- A. Implement the change
- B. Approve the change
- C. Propose the change
- D. Schedule the change
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The first step in the IT change management process is to identify and propose the change. In this
case, the technician notices a need (end-of-life network switches), so the appropriate action is to
formally propose a change. This proposal would be documented and submitted for approval before
any planning or implementation occurs.
According to the CompTIA A+ 220-1102 objectives under Operational Procedures (Domain 4.0), the
change management process follows these typical steps:
Submit a change request (Propose the change)
Review and approval (Approve the change)
Planning and scheduling (Schedule the change)
Implementation
Documentation and review
Therefore, proposing the change is the correct first step in accordance with standard ITIL-based
change management practices.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 4.1: Given a scenario, implement best practices associated with
documentation and support systems information management.
Study Guide Section: Change Management Process
===========================
Question 5
MFA for a custom web application on a user's smartphone is no longer working. The last time the
user remembered it working was before taking a vacation to another country. Which of the following
should the technician do first?
- A. Verify the date and time settings
- B. Apply mobile OS patches
- C. Uninstall and reinstall the application
- D. Escalate to the website developer
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) apps, especially time-based one-time password (TOTP) apps (e.g.,
Google Authenticator, Authy), rely on accurate time synchronization between the device and the
authentication server. If the user recently traveled internationally, the device may have incorrect
date/time settings due to time zone changes or failed synchronization, leading to MFA failure.
The most logical and non-intrusive first step is to verify and correct the date and time settings. This
aligns with basic troubleshooting principles—start with the simplest and most likely cause before
taking more drastic action.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 2.6: Given a scenario, apply cybersecurity best practices to secure a
workstation.
Study Guide Section: Authentication technologies and MFA troubleshooting
===========================
Question 6
Which of the following is found in an MSDS sheet for a battery backup?
- A. Installation instructions
- B. Emergency procedures
- C. Configuration steps
- D. Voltage specifications
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
An MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet), now commonly referred to as SDS (Safety Data Sheet), is a
document that provides detailed information on the properties of a particular substance. It includes
safety guidelines and emergency procedures related to handling, exposure, fire hazards, and first
aid—not installation or configuration instructions.
For a battery backup (UPS device), the MSDS would include emergency procedures such as what to
do in case of a chemical spill, exposure to battery acid, or fire hazard due to overheating or chemical
leakage. This ensures the safety of personnel and complies with hazardous materials handling
regulations.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 4.1: Given a scenario, implement best practices associated with
documentation and support systems information management.
Study Guide Section: MSDS/SDS usage and safety documentation
Question 7
The screen of a previously working computer repeatedly displays an OS Not Found error message
when the computer is started. Only a USB drive, a keyboard, and a mouse are plugged into the
computer. Which of the following should a technician do first?
- A. Run data recovery tools on the disk
- B. Partition the disk using the GPT format
- C. Check boot options
- D. Switch from UEFI to BIOS
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
An "OS Not Found" error typically indicates that the computer is attempting to boot from a drive that
doesn't contain a valid operating system or bootable partition. The presence of a USB drive might be
confusing the boot order. Therefore, the first step a technician should take is to verify and adjust the
boot sequence in the system’s firmware (BIOS or UEFI). It's possible that the USB drive is being
prioritized over the internal hard drive, which may cause the system to miss the OS entirely.
A . Running data recovery tools is premature before confirming boot order.
B . Repartitioning the disk would destroy existing data—this should not be done until confirmed the
OS is actually missing.
D . Switching between UEFI and BIOS (legacy mode) might help in rare cases, but it is not the first
step in standard OS boot issue troubleshooting.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 1.7: Troubleshoot common operating system problems.
Study Guide Section: Boot process and boot order configuration.
===========================
Question 8
A security administrator teaches all of an organization's staff members to use BitLocker To Go. Which
of the following best describes the reason for this training?
- A. To ensure that all removable media is password protected in case of loss or theft
- B. To enable Secure Boot and a BIOS-level password to prevent configuration changes
- C. To enforce VPN connectivity to be encrypted by hardware modules
- D. To configure all laptops to use the TPM as an encryption factor for hard drives
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
BitLocker To Go is a Microsoft encryption feature specifically designed for removable drives such as
USB flash drives and external hard drives. It allows users to protect the data on these devices by
requiring a password to decrypt the contents, thereby preventing unauthorized access in the event
the device is lost or stolen.
A is correct because BitLocker To Go is directly tied to password-protecting removable media.
B and C are unrelated to BitLocker To Go; Secure Boot and VPN encryption are entirely different
security layers.
D applies to BitLocker (not BitLocker To Go) and full disk encryption on internal drives using TPM.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 2.2: Compare and contrast common security measures and tools.
Study Guide Section: Encryption technologies (BitLocker, BitLocker To Go)
===========================
Question 9
Which of the following is used to detect and record access to restricted areas?
- A. Bollards
- B. Video surveillance
- C. Badge readers
- D. Fence
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Badge readers are electronic access control systems that require authorized users to scan a badge
(e.g., RFID or magnetic strip cards) to gain access to restricted physical locations. These systems
typically log all access attempts—successful or denied—providing both detection and recording of
access events.
A . Bollards are physical barriers to prevent vehicle access.
B . Video surveillance can record access visually but does not track identity unless integrated with
access control systems.
D . A fence restricts access but doesn't detect or record who entered.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 2.4: Compare and contrast physical security measures.
Study Guide Section: Physical access controls (e.g., badge readers, mantraps)
Question 10
An administrator received an email stating that the OS they are currently supporting will no longer
be issued security updates and patches. Which of the following is most likely the reason the
administrator received this message?
- A. Support from the computer's manufacturer is expiring
- B. The OS will be considered end of life
- C. The built-in security software is being removed from the next OS version
- D. A new version of the OS will be released soon
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Operating systems periodically reach a status known as "end of life" (EOL), at which point the
developer (e.g., Microsoft, Apple) ceases to provide security updates, patches, or technical support.
When this happens, the OS becomes vulnerable and non-compliant with security best practices,
which is why organizations typically receive advance notifications from vendors or support teams.
A . Manufacturer support expiration only applies to hardware, not OS patching.
C . Security software may be upgraded or removed, but that does not affect patching the OS itself.
D . The release of a new version doesn’t automatically stop updates for the current version.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 1.3: Given a scenario, use appropriate Microsoft operating system
features and tools.
Study Guide Section: OS lifecycle management and vendor support phases (e.g., EOL)
===========================
Question 11
Which of the following is the best way to distribute custom images to 800 devices that include four
device vendor classes with two types of user groups?
- A. Use xcopy to clone the hard drives from one to another
- B. Use robocopy to move the files to each device
- C. Use a local image deployment tool for each device
- D. Use a network-based remote installation tool
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
In enterprise environments, network-based deployment solutions (such as Windows Deployment
Services or SCCM) allow administrators to push images across the network to hundreds of devices
efficiently. These tools support hardware-specific drivers (for different vendor classes) and can
accommodate user-group configurations using task sequences or answer files.
A and B (xcopy and robocopy) are file-level tools and not designed for full OS image deployment.
C . Using local tools per device is inefficient for large-scale rollouts (800 devices).
D . Network-based deployment is the industry standard for this scale.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 1.4: Given a scenario, use appropriate Microsoft operating system
installation methods.
Study Guide Section: Deployment methods (including PXE boot, image deployment)
===========================
Question 12
Which of the following types of social engineering attacks sends an unsolicited text message to a
user's mobile device?
- A. Impersonation
- B. Vishing
- C. Spear phishing
- D. Smishing
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Smishing (SMS phishing) is a type of social engineering attack where attackers send fraudulent text
messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware. These
messages often impersonate banks, delivery services, or official institutions to lure the victim into
clicking malicious links.
A . Impersonation is an in-person or voice-based tactic.
B . Vishing refers to voice phishing over phone calls.
C . Spear phishing is a targeted email-based phishing method.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 2.3: Compare and contrast social engineering techniques.
Study Guide Section: Smishing as a type of phishing via SMS or mobile messaging.
===========================
Question 13
A user reports some single sign-on errors to a help desk technician. Currently, the user is able to sign
in to the company's application portal but cannot access a specific SaaS-based tool. Which of the
following would the technician most likely suggest as a next step?
- A. Reenroll the user's mobile device to be used as an MFA token
- B. Use a private browsing window to avoid local session conflicts
- C. Bypass single sign-on by directly authenticating to the application
- D. Reset the device being used to factory defaults
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
SSO issues are often related to cached session data, cookies, or browser artifacts. The fact that the
user can access the company portal but not one specific SaaS tool suggests a session or token
problem. Using a private/incognito browsing window allows a clean session to be initiated, which
often resolves SSO conflicts.
A . Reenrolling MFA is not related unless access issues stem from failed multifactor authentication.
C . Bypassing SSO may not be possible depending on the SaaS tool and company policies.
D . Factory resetting a device is a last resort and unnecessary in this case.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 3.3: Troubleshoot common software, application, and OS security
issues.
Study Guide Section: Troubleshooting login and authentication issues, especially with SSO services.
===========================
Question 14
A technician verifies that a malware incident occurred on some computers in a small office. Which of
the following should the technician do next?
- A. Quarantine the infected systems
- B. Educate the end users
- C. Disable System Restore
- D. Update the anti-malware and scan the computers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Once a malware incident has been confirmed, the immediate next step is to contain the threat.
Quarantining infected systems prevents the malware from spreading to other devices and isolates
the malicious code for further analysis or remediation.
B . Educating end users is important but occurs later in the incident response process.
C . Disabling System Restore is part of cleanup, not containment.
D . Updating and scanning should occur after the system is quarantined to prevent further infection
or spread.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 2.5: Given a scenario, detect, remove, and prevent malware using
appropriate tools and methods.
Study Guide Section: Malware removal best practices — Step 2: Quarantine the infected system
===========================
Question 15
Which of the following is a Linux command that is used for administrative purposes?
- A. runas
- B. cmcl
- C. net user
- D. su
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The su (substitute user) command is used in Linux to switch to another user account, most commonly
to escalate privileges by switching to the root (administrator) account. It allows administrative tasks
to be performed in a terminal session.
A . runas is a Windows command for executing a program under another user's context.
B . cmcl is not a valid Linux or administrative command.
C . net user is a Windows command for managing local user accounts.
Reference:
CompTIA A+ 220-1102 Objective 1.9: Identify common features and tools of the Linux client/desktop
OS.
Study Guide Section: Linux command-line tools — su, sudo
===========================