cisco 300-620 practice test
Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (DCACI)
Question 1
An engineer is implementing a Cisco ACI data center network that includes Cisco Nexus 2000 Series
10G fabric extenders. Which physical topology is supported?
A)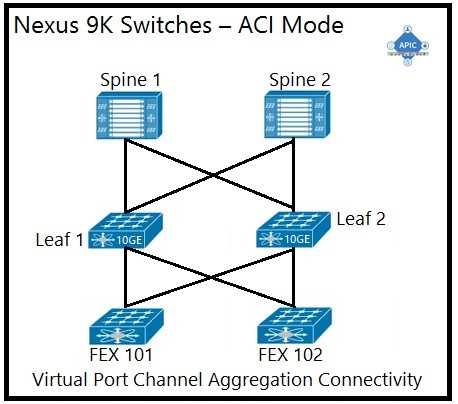
B)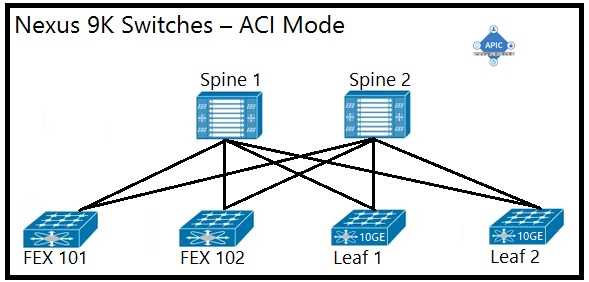
C)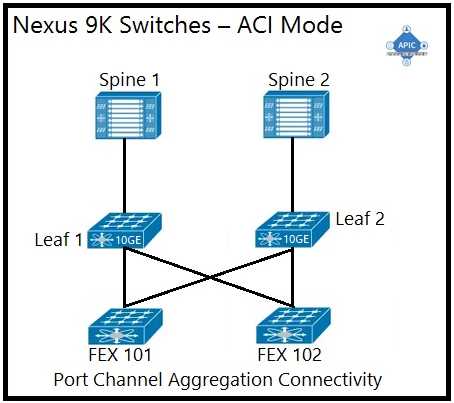
D)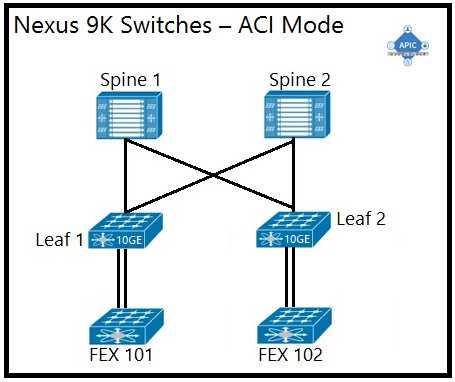
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The supported physical topology for a Cisco ACI data center network that includes Cisco Nexus 2000
Series 10G fabric extenders is depicted in Option A. This topology illustrates a pair of spine switches
connected to leaf switches, which are then connected to the fabric extenders. The Cisco Nexus 2000
Series Fabric Extenders act as remote line cards for a parent Cisco Nexus switch, extending the
network fabric. The topology shown is a spine-leaf architecture, which is a scalable, high-bandwidth
framework that is typical in ACI deployments.
Reference:
For a detailed understanding of the ACI fabric and supported topologies, you can refer to the Cisco
Application Centric Infrastructure Design Guide, which provides comprehensive information on
design recommendations and deployment models:
Cisco ACI Design Guide
.
To learn more about the role of fabric extenders in the ACI architecture, the following resource offers
insights into how they integrate with the ACI fabric:
Understanding the ACI Fabric
.
Question 2
An ACI administrator notices a change in the behavior of the fabric. Which action must be taken to
determine if a human intervention introduced the change?
- A. Inspect event records in the APIC UI to see all actions performed by users.
- B. Inspect /var/log/audit_messages on the APIC to see a record of all user actions.
- C. Inspect audit logs in the APIC UI to see all user events.
- D. Inspect the output of show command history in the APIC CLI.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To determine if a change in the behavior of the ACI fabric was due to human intervention, an ACI
administrator should inspect the audit logs in the APIC UI.
The audit logs provide a record of all user
events, which includes actions performed by users, making it possible to trace any changes back to
specific human activities1
.
Question 3
An engineer is creating a configuration import policy that must terminate if the imported
configuration is incompatible with the existing system. Which import mode achieves this result?
- A. merge
- B. atomic
- C. best effort
- D. replace
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The import mode that must be used to ensure that the import process terminates if the imported
configuration is incompatible with the existing system is the ‘atomic’ mode. This mode ignores
shards that contain objects that cannot be imported while proceeding with shards that can be
imported.
If the incoming configuration’s version is incompatible with the existing system, the
import process will terminate2
.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/4-x/aci-fundamentals/Cisco-ACI-Fundamentals-401/Cisco-ACI-Fundamentals-401_chapter_01011.html
Question 4
Which components must be configured for the BGP Route Reflector policy to take effect?
- A. spine fabric interface overrides and profiles
- B. access policies and profiles
- C. pod policy groups and profiles
- D. leaf fabric interface overrides and profiles
Answer:
D
Explanation:
For the BGP Route Reflector policy to take effect, the components that must be configured are the
leaf fabric interface overrides and profiles.
These configurations are necessary to establish the route
reflector relationships within the BGP protocol on the leaf switches
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/4-x/L3-configuration/Cisco-APIC-Layer-3-Networking-Configuration-Guide-401/Cisco-APIC-Layer-3-Networking-Configuration-Guide-401_chapter_01.html
Question 5
Which type of policy configures the suppression of faults that are generated from a port being down?
- A. fault lifecycle assignment
- B. event lifecycle assignment
- C. fault severity assignment
- D. event severity assignment
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The type of policy that configures the suppression of faults generated from a port being down is the
‘fault severity assignment’ policy.
This policy allows administrators to change the severity of a fault
or suppress it altogether, which can be useful for managing expected faults and reducing noise from
non-critical events
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/all/faults/guide/b_APIC_Faults_Errors/b_IFC_Faults_Errors_chapter_01.html
Question 6
Which type of profile needs to be created to deploy an access port policy group?
- A. attachable entity
- B. Pod
- C. module
- D. leaf interface
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To deploy an access port policy group within Cisco ACI, an attachable entity profile (AEP) needs to be
created.
An AEP is a policy construct that groups together various domains and allows them to be
attached to the fabric access layer
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/1-x/Operating_ACI/guide/b_Cisco_Operating_ACI/b_Cisco_Operating_ACI_chapter_0110.html
Question 7
A situation causes a fault to be raised on the APIC. The ACI administrator does not want that fault to
be raised because it is not directly relevant to the environment. Which action should the
administrator take to prevent the fault from appearing?
- A. Under System -> Faults, right-click on the fault and select Acknowledge Fault so that acknowledged faults will immediately disappear.
- B. Create a stats threshold policy with both rising and falling thresholds defined so that the critical severity threshold matches the squelched threshold.
- C. Under System -> Faults, right-click on the fault and select Ignore Fault to create a fault severity assignment policy that hides the fault.
- D. Create a new global health score policy that ignores specific faults as identified by their unique fault code.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To prevent a fault from appearing that is not directly relevant to the environment, the ACI
administrator should create a fault severity assignment policy that hides the fault.
This can be done
by selecting “Ignore Fault” under System -> Faults in the APIC UI2
Question 8
A RADIUS user resolves its role via the Cisco AV Pair. What object does the Cisco AV Pair resolve to?
- A. tenant
- B. security domain
- C. primary Cisco APIC
- D. managed object class
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Cisco AV Pair resolves to a managed object class.
In the context of Cisco ACI, the AV Pair is used
to define specific attributes for RADIUS users, which then map to managed objects within the ACI
fabric3
.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/2-x/Security_config/b_Cisco_APIC_Security_Configuration_Guide/b_Cisco_APIC_Security_Guide_chapter_01011.html
Question 9
DRAG DROP
An engineer is configuring a VRF for a tenant named Cisco. Drag and drop the child objects on the left
onto the correct containers on the right for this configuration.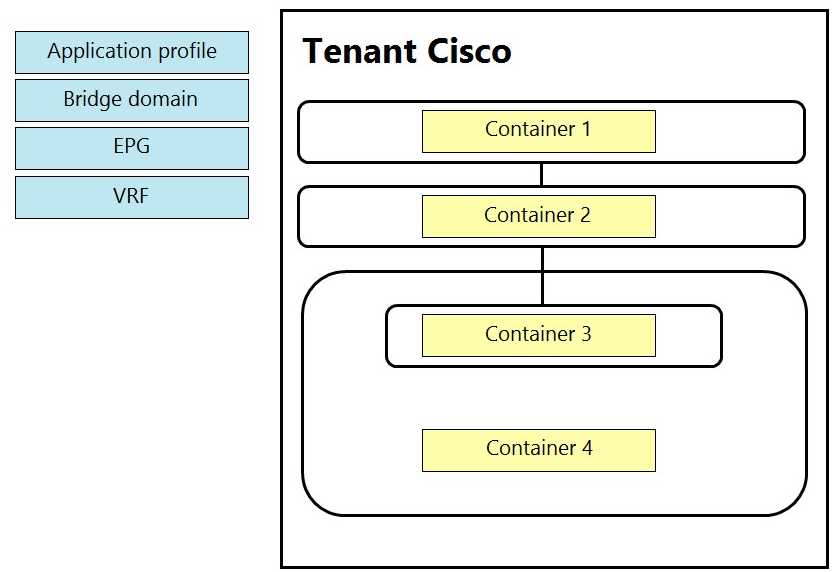
Answer:
Explanation: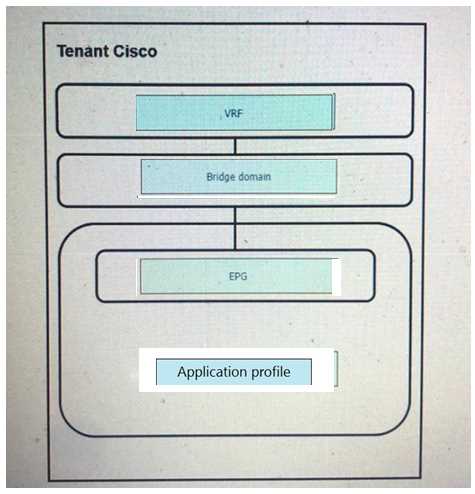
Question 10
Which feature dynamically assigns or modifies the EPG association of virtual machines based on
their attributes?
- A. vzAny contracts
- B. standard contracts
- C. application EPGs
- D. uSeg EPGs
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The feature that dynamically assigns or modifies the EPG association of virtual machines based on
their attributes is uSeg EPGs.
uSeg EPGs allow for microsegmentation within the Cisco ACI
environment, enabling the dynamic assignment of VMs to EPGs based on attributes such as VM
name, tag, or other identifiers
Question 11
Which feature allows firewall ACLs to be configured automatically when new endpoints are attached
to an EPG?
- A. ARP gleaning
- B. dynamic endpoint attach
- C. hardware proxy
- D. network-stitching
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The feature that allows firewall ACLs to be configured automatically when new endpoints are
attached to an EPG is ARP gleaning.
This feature helps in identifying the endpoints and applying the
necessary ACLs to them as they are discovered
Question 12
An engineer is implementing Cisco ACI at a large platform-as-a-service provider using APIC
controllers, 9396PX leaf switches, and 9336PQ spine switches. The leaf switch ports are configured as
IEEE 802.1p ports. Where does the traffic exit from the EPG in IEEE 802.1p mode in this
configuration?
- A. from leaf ports tagged as VLAN 0
- B. from leaf ports untagged
- C. from leaf ports tagged as VLAN 4094
- D. from leaf ports tagged as VLAN 1
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In a Cisco ACI configuration with IEEE 802.1p ports, the traffic exits from the EPG untagged from leaf
ports.
This means that when the port is configured in Access (802.1p) mode and the access VLAN is
the only VLAN deployed on the port, then traffic will be untagged on egress56
.
Question 13
How is an EPG extended outside of the ACI fabric?
- A. Create an external bridged network that is assigned to a leaf port.
- B. Create an external routed network that is assigned to an EPG.
- C. Enable unicast routing within an EPG.
- D. Statically assign a VLAN ID to a leaf port in an EPG.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
An EPG is extended outside of the ACI fabric by statically assigning a VLAN ID to a leaf port in an
EPG.
This method maps the traffic received on the leaf port to the EPG, and the policy for this EPG is
enforced
Reference: https://www.dclessons.com/l2-external-network-with-aci
Question 14
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the Cisco ACI filter entry options from the left onto the correct categories on the right
indicating what are required or optional parameters.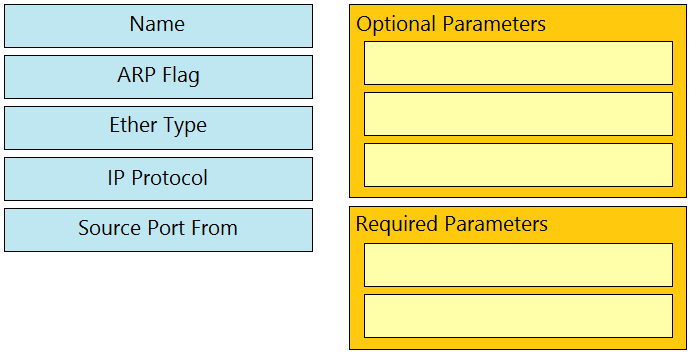
Answer:
Explanation: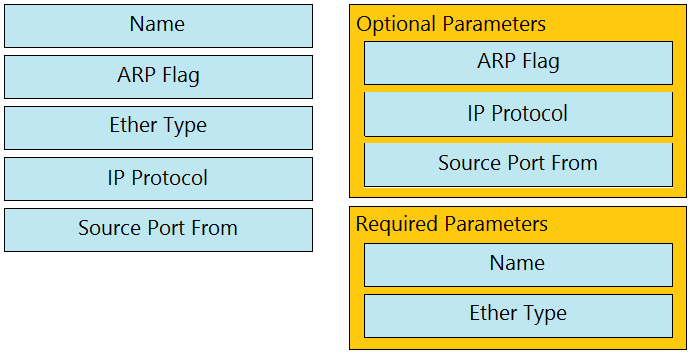
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/aci/apic/sw/1-x/Operating_ACI/guide/b_Cisco_Operating_ACI/b_Cisco_Operating_ACI_chapter_01000.html
Question 15
Where is the COOP database located?
- A. leaf
- B. spine
- C. APIC
- D. endpoint
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The COOP (Council Of Oracle Protocol) database is located on each spine switch within the Cisco ACI
fabric.
The COOP database is responsible for maintaining a consistent copy of endpoint address and
location information across the fabric
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/data-center-virtualization/application-centric-infrastructure/white-paper-c11-739989.html