cisco 300-440 practice test
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC)
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
While troubleshooting an IPsec connection between a Cisco WAN edge router and an Amazon Web
Services (AWS) endpoint, a network engineer observes that the security association status is active,
but no traffic flows between the devices What is the problem?
- A. wrong ISAKMP policy
- B. identity mismatch
- C. wrong encryption
- D. IKE version mismatch
Answer:
B
Explanation:
An identity mismatch occurs when the local and remote identities configured on the IPsec peers do
not match. This can prevent the establishment of an IPsec tunnel or cause traffic to be dropped by
the IPsec policy. In this case, the network engineer should verify that the local and remote identities
configured on the Cisco WAN edge router and the AWS endpoint match the values expected by each
peer. The identities can be an IP address, a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), or a distinguished
name (DN). The identities are exchanged during the IKE phase 1 negotiation and are used to
authenticate the peers. If the identities do not match, the peers will reject the IKE proposal and the
IPsec tunnel will not be established or will be torn down. Reference :=
Configure IOS-XE Site-to-Site VPN Connection to Amazon Web Services
, Topic: Troubleshooting
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
, Module 3: Implementing Cloud
Connectivity, Lesson 2: Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Cloud OnRamp for IaaS, Topic: Troubleshooting
Cisco SD-WAN Cloud OnRamp for IaaS
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 15M&T
, Chapter: Configuring IPsec Network
Security, Topic: Configuring IPsec Identity and Peer Addressing
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.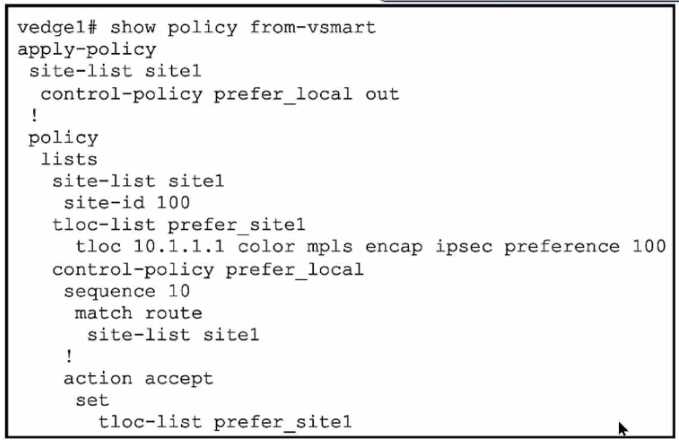
A network engineer discovers that the policy that is configured on an on-premises Cisco WAN edge
router affects only the route tables of the specific devices that are listed in the site list. What is the
problem?
- A. An inbound policy must be applied.
- B. The action must be set to deny
- C. A localized data policy must be configured.
- D. A centralized data policy must be configured
Answer:
D
Explanation:
A centralized data policy is a policy that is applied to all devices in the overlay network, regardless of
the site list. A localized data policy is a policy that is applied only to the devices that are listed in the
site list. In this case, the network engineer wants to apply the policy to all devices in the overlay
network, not just the specific devices in the site list. Therefore, a centralized data policy must be
configured on the on-premises Cisco WAN edge router. Reference :=
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
, Module 3: Implementing Cloud
Connectivity, Lesson 3: Implementing Cisco SD-WAN Cloud OnRamp for Colocation, Topic:
Centralized Data Policy
[Cisco SD-WAN Cloud OnRamp for Colocation Deployment Guide], Chapter: Configuring Centralized
Data Policy
Question 3
A company with multiple branch offices wants a connectivity model to meet its network architecture
requirements. The company focuses on ensuring low latency and efficient routing for its critical
business applications. Which connectivity model meets these requirements?
- A. hub-and-spoke topology with SD-WAN technology, using dynamic routing and OSPF as the routing protocol
- B. fully meshed topology with SD-WAN technology, using dynamic routing and BGP as the routing protocol
- C. point-to-point topology using dedicated leased lines and static routing
- D. star topology with internet-based VPN connections and static routing
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A fully meshed topology with SD-WAN technology, using dynamic routing and BGP as the routing
protocol, meets the requirements of the company because it provides the following benefits:
It allows direct and secure connectivity between any two branch offices, without the need for a
central hub or intermediary devices12
. This reduces the latency and improves the performance of
the critical business applications.
It leverages SD-WAN technology to optimize the traffic flow and application quality of service (QoS)
across the WAN13
.
SD-WAN can dynamically select the best path for each application based on the
network conditions and policies13
.
SD-WAN can also provide redundancy, security, and visibility for
the WAN13
.
It uses dynamic routing and BGP as the routing protocol to exchange routing information and
establish connectivity between the branch offices14
.
BGP is a scalable and flexible protocol that can
support multiple address families, such as IPv4 and IPv6, and multiple routing policies, such as local
preference and route filtering14
.
BGP can also enable seamless integration with the cloud service
providers (CSPs) and internet service providers (ISPs)14
.
Reference :=
: Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC, Track 1 of 5) (Cisco U. login required)
: Cisco SD-WAN Design Guide
Question 4
DRAG DROP
An engineer signs in to Cisco vManage and needs to configure a custom application with a Cisco SD-
WAN centralized policy. Drag and drop the steps from the left onto the order on the right to complete
the configuration.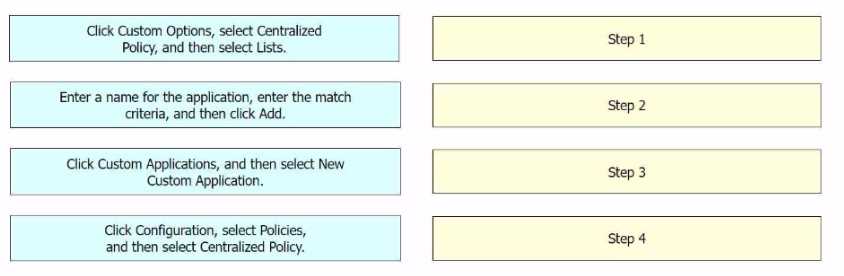
Answer:
Explanation:
To configure a custom application with Cisco SD-WAN centralized policy, you need to follow these
steps25
:
Click Configuration, select Policies, and then select Centralized Policy.
Click Custom Options, select Centralized Policy, and then select Lists.
Click Custom Applications, and then select New Custom Application.
Enter a name for the application, enter the match criteria, and then click Add.
The process of configuring a custom application with a Cisco SD-WAN centralized policy using Cisco
vManage involves several steps1
.
Click Configuration, select Policies, and then select Centralized Policy: This is the first step where you
navigate to the Policies section in the Configuration menu of Cisco vManage1
.
Click Custom Options, select Centralized Policy, and then select Lists: In this step, you select the
Custom Options, then select Centralized Policy, and finally select Lists1
.
Click Custom Applications, and then select New Custom Application: After setting up the Lists, you
click on Custom Applications and then select New Custom Application1
.
Enter a name for the application, enter the match criteria, and then click Add: Finally, you enter a
name for the application, specify the match criteria, and then click Add to complete the
configuration1
.
Reference :=
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Policies Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE
Question 5
Which Microsoft Azure service enables a dedicated and secure connection between an on-premises
infrastructure and Azure data centers through a colocation provider?
- A. Azure Private Link
- B. Azure ExpressRoute
- C. Azure Virtual Network
- D. Azure Site-to-Site VPN
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Azure ExpressRoute is a service that enables a dedicated and secure connection between an on-
premises infrastructure and Azure data centers through a colocation provider. A colocation provider
is a third-party data center that offers network connectivity services to multiple customers. Azure
ExpressRoute allows customers to bypass the public internet and connect directly to Azure services,
such as virtual machines, storage, databases, and more. This provides benefits such as lower latency,
higher bandwidth, more reliability, and enhanced security. Azure ExpressRoute also supports hybrid
scenarios, such as connecting to Office 365, Dynamics 365, and other SaaS applications hosted on
Azure. Azure ExpressRoute requires a physical connection between the customer’s network and the
colocation provider’s network, as well as a logical connection between the customer’s network and
the Azure virtual network. The logical connection is established using a Border Gateway Protocol
(BGP) session, which exchanges routing information between the two networks. Azure ExpressRoute
supports two models: standard and premium. The standard model offers connectivity to all Azure
regions within the same geopolitical region, while the premium model offers connectivity to all
Azure regions globally, as well as additional features such as increased route limits, global reach, and
Microsoft peering. Reference:
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
,
Learning
Plan: Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity v1.0 (ENCC 300-440) Exam Prep
,
ENCC |
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity | Netec
Question 6
An engineer must enable the OMP advertisement of BGP routes for a specific VRF instance on a Cisco
IOS XE SD-WAN device. What should be configured after the global address-family ipv4 is
configured?
- A. Set the VRF-specific route advertisements.
- B. Enable bgp advertisement.
- C. Enter sdwan mode.
- D. Disable bgp advertisement.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To enable the OMP advertisement of BGP routes for a specific VRF instance on a Cisco IOS XE SD-
WAN device, the engineer must first configure the global address-family ipv4 and then enable bgp
advertisement under the vrf definition.
This will allow the device to advertise the BGP routes learned
from the cloud provider to the OMP control plane, which will then distribute them to the other SD-
WAN devices in the overlay network1
Reference := 1
: Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0, Module 3:
Implementing Cloud Connectivity, Lesson 3: Configuring IPsec VPN from Cisco IOS XE to AWS, Topic:
Configuring BGP on the Cisco IOS XE Device, Page 3-24.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit.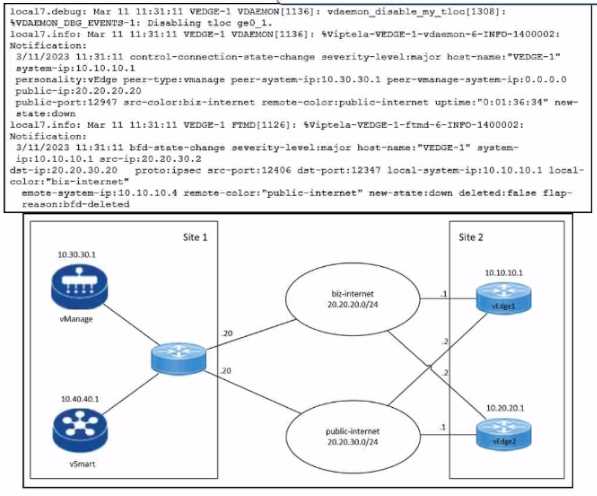
Refer to the exhibits. An engineer troubleshoots a Cisco SD-WAN connectivity issue between an on-
premises data center WAN Edge and a public cloud provider WAN Edge. The engineer discovers that
BFD is Dapping on vEdge1. What is the problem?
- A. The remote Edge device BFD is down.
- B. The remote Edge device failed to respond BFD keepalives.
- C. The remote Edge device has a duplicate IP address.
- D. The control plane deleted the BFD session.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is a protocol that detects failures in the overlay tunnel
between Cisco SD-WAN devices. BFD packets are sent and received periodically by each device to
check the liveliness and quality of the connection. If a device does not receive a BFD packet from its
peer within a specified timeout interval, it considers the peer to be unreachable and reports a BFD
down event. This event triggers a control connection state change and a possible route change in the
SD-WAN fabric.
In this scenario, the engineer discovers that BFD is flapping on vEdge1, which means that the BFD
session between vEdge1 and the remote Edge device is going up and down repeatedly. This indicates
a connectivity issue between the two devices, such as network congestion, packet loss, or
misconfiguration. The most likely cause of the problem is that the remote Edge device failed to
respond BFD keepalives within the timeout interval, which resulted in a BFD timeout event on
vEdge1. This event caused vEdge1 to mark the remote Edge device as down and notify the control
plane. The control plane then tried to establish a new BFD session with the remote Edge device,
which may have succeeded or failed depending on the network condition. This cycle of BFD session
creation and deletion caused the BFD flapping on vEdge1.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of the problem. Option A is incorrect because if the
remote Edge device BFD was down, vEdge1 would not receive any BFD packets from it and would not
flap. Option C is incorrect because if the remote Edge device had a duplicate IP address, vEdge1
would not be able to establish a BFD session with it in the first place. Option D is incorrect because
the control plane does not delete the BFD session unless there is a configuration change or a port-
hop event on the device. Reference:
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection Flap-Reason Definitions on
Cisco vEdge Routers
,
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN BFD
,
Cisco SD WAN: BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding
Detection)
Question 8
An engineer is implementing a highly secure multitier application in AWS that includes S3. RDS, and
some additional private links. What is critical to keep the traffic safe?
- A. VPC peering and bucket policies
- B. specific routing and bucket policies
- C. EC2 super policies and specific routing policies
- D. gateway load balancers and specific routing policies
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A highly secure multitier application in AWS that includes S3, RDS, and some additional private links
requires specific routing and bucket policies to keep the traffic safe. The reasons are as follows:
Specific routing policies are needed to ensure that the traffic between the tiers is routed through the
private links, which provide secure and low-latency connectivity between AWS services and on-
premises resources12
.
The private links can also prevent the exposure of the data and the application
logic to the public internet12
.
Bucket policies are needed to control the access to the S3 buckets that store the application
data34
.
Bucket policies can specify the conditions under which the requests are allowed or denied,
such as the source IP address, the encryption status, the request time, etc.34
.
Bucket policies can
also enforce encryption in transit and at rest for the data in S334
.
Reference :=
: AWS PrivateLink
: AWS PrivateLink FAQs
: Using Bucket Policies and User Policies
: Bucket Policy Examples
Question 9
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the commands from the left onto the purposes on the right to identify issues on a
Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN device.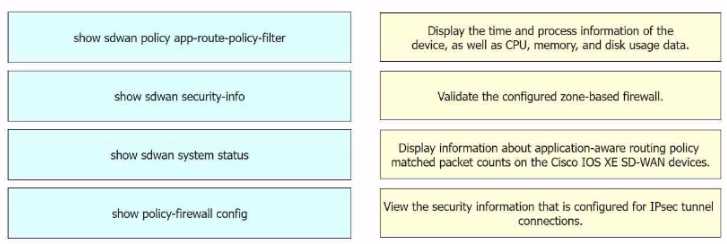
Answer:
Explanation: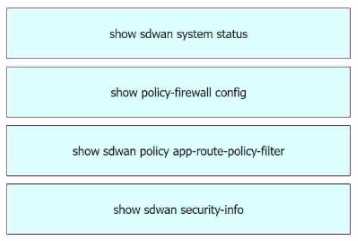
Display the time and process information of the device, as well as CPU, memory, and disk usage dat
a.
= show sdwan system status1
Validate the configured zone-based firewall.
= show policy-firewall config1
Display information about application-aware routing policy matched packet counts on the Cisco IOS
XE SD-WAN devices.
= show sdwan policy app-route-policy-filter1
View the security information that is configured for IPsec tunnel connections.
= show sdwan security-
info
The commands used to identify issues on a Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN device are as follows1
:
show sdwan system status: This command is used to display the time and process information of the
device, as well as CPU, memory, and disk usage data1
.
show policy-firewall config: This command is used to validate the configured zone-based firewall1
.
show sdwan policy app-route-policy-filter: This command is used to display information about
application-aware routing policy matched packet counts on the Cisco IOS XE SD-WAN devices1
.
show sdwan security-info: This command is used to view the security information that is configured
for IPsec tunnel connections1
.
Reference :=
Cisco IOS XE Catalyst SD-WAN Qualified Command Reference
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Command Reference
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Systems and Interfaces Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE
SD-WAN Tunnel Interface Commands - Cisco
Question 10
Refer to the exhibits.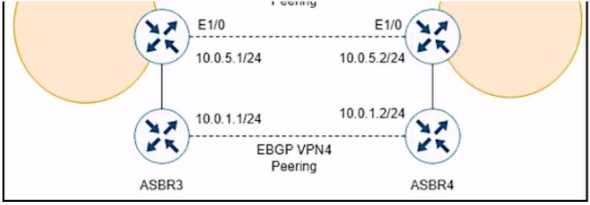
While troubleshooting, a network engineer discovers that the backup path fails between ASBR3 and
ASBR4 for traffic between BGP AS6000 and BGP AS6500 when the connection between ASBR1 and
ASBR2 goes down. The following configurations were performed on ASBR1:
Which command is missing?
- A. bgp additional-paths Install
- B. bgp additional-paths select
- C. redistribute static
- D. bgp advertise-best-external
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The bgp advertise-best-external command is used to enable the advertisement of the best external
path to internal BGP peers. This command is useful when there are multiple exit points from the
local AS to other ASes, and the local AS wants to use the closest exit point for each destination. By
default, BGP only advertises the best path to its peers, and the best path is usually the one with the
lowest IGP metric to the next hop. However, this may not be the optimal path for traffic leaving the
local AS, as it may result in suboptimal hot-potato routing or MED oscillations. The bgp advertise-
best-external command allows BGP to advertise the best external path, which is the path with the
lowest MED among the paths from different neighboring ASes, in addition to the best path. This way,
the internal BGP peers can choose the best exit point based on the MED value, rather than the IGP
metric. In this scenario, ASBR1 is configured to receive additional paths from ASBR2, which is a route
reflector. ASBR2 receives two paths for the same prefix from AS6500, one from ASBR3 and one from
ASBR4. ASBR2 selects the best path based on the IGP metric to the next hop, and advertises it to
ASBR1. However, this path may not be the best external path, as it may have a higher MED value
than the other path. If the connection between ASBR1 and ASBR2 goes down, ASBR1 will not have
any backup path to reach AS6500, as it does not know the other path from ASBR4. To prevent this
situation, ASBR1 should be configured with the bgp advertise-best-external command, so that it can
receive the best external path from ASBR2, along with the best path. This way, ASBR1 will have a
backup path to reach AS6500, in case the primary path fails. Reference :=
IP Routing: BGP
Configuration Guide - BGP Additional Paths … - Cisco
,
BGP Additional Path
s
Question 11
What is the role of service providers to establish private connectivity between on-premises networks
and Google Cloud resources?
- A. facilitate direct, dedicated network connections through Google Cloud Interconnect
- B. enable intelligent routing and dynamic path selection using software-defined networking
- C. provide end-to-end encryption for data transmission using native IPsec
- D. accelerate content delivery through integration with Google Cloud CDN
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The role of service providers to establish private connectivity between on-premises networks and
Google Cloud resources is to facilitate direct, dedicated network connections through Google Cloud
Interconnect. Google Cloud Interconnect is a service that allows customers to connect their on-
premises networks to Google Cloud through a service provider partner. This provides low latency,
high bandwidth, and secure connectivity to Google Cloud services, such as Google Compute Engine,
Google Cloud Storage, and Google BigQuery. Google Cloud Interconnect also supports hybrid cloud
scenarios, such as extending on-premises networks to Google Cloud regions, or connecting multiple
Google Cloud regions together. Google Cloud Interconnect offers two types of connections:
Dedicated Interconnect and Partner Interconnect. Dedicated Interconnect provides physical
connections between the customer’s network and Google’s network at a Google Cloud Interconnect
location. Partner Interconnect provides virtual connections between the customer’s network and
Google’s network through a supported service provider partner. Both types of connections use VLAN
attachments to establish private connectivity to Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
networks. Reference:
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
[Google Cloud Interconnect Overview]
[Google Cloud Interconnect Documentation]
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.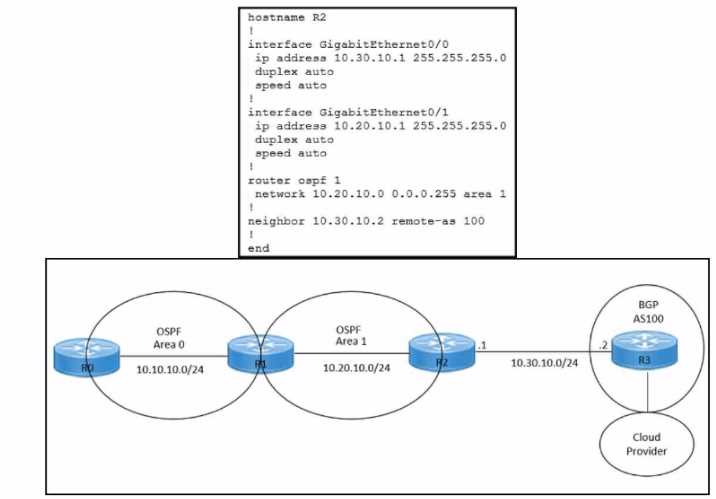
Refer to the exhibits. An engineer must redistribute IBGP routes into OSPF to connect an on-premises
network to a cloud provider. Which command must be configured on router R2?
- A. redistribute ospf 1
- B. redistribute bgp 100 ospf 1
- C. redistribute bgp 100 subnets
- D. bgp redistrlbute-lnternal
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This command redistributes the routes learned from BGP AS100 into OSPF Area 1, which allows
router R2 to advertise those routes to router R1 and connect the on-premises network to the cloud
provider.
The other options are incorrect because they either redistribute the wrong routes or use
the wrong syntax5
.
I hope this helps you understand the question and the answer. If you have any other questions or
requests, please let me know. I am always happy to help.
Reference: 1
:
Learning Plan: Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity v1.0 (ENCC 300-440)
Exam Prep 2
:
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0 3
:
Cisco Multiprotocol
Label Switching 4
:
Exploring Cisco Cloud OnRamp for Colocation 5
:
ENCC: Configuring IPsec VPN from
Cisco IOS XE to AWS
: [Deploying Cisco IOS VTI-Based Point-to-Point IPsec VPNs]
Question 13
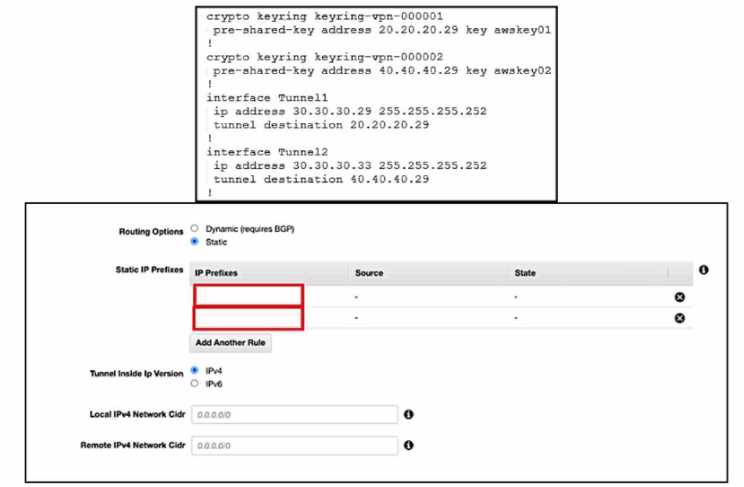
Refer to the exhibits. An engineer needs to configure a site-to-site IPsec VPN connection between an
on premises Cisco IOS XE router and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Which two IP prefixes should be
used to configure the AWS routing options? (Choose two.)
- A. 30.30.30.0/30
- B. 20.20.20.0/24
- C. 30.30.30.0/24
- D. 50.50.50.0/30
- E. 40.40.40.0/24
Answer:
A, E
Explanation:
The correct answer is A and E because they are the IP prefixes that match the tunnel interfaces on
the Cisco IOS XE router. The AWS routing options should include the local and remote IP prefixes that
are used for the IPsec tunnel endpoints. The other options are either the public IP addresses of the
routers or
the
LAN
subnets that
are
not relevant
for the
IPsec
tunnel
configuration. Reference :=
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
,
Configure
IOS-XE Site-to-Site VPN Connection to Amazon Web Services
,
Site-to-Site VPN with Amazon Web
Services
Question 14
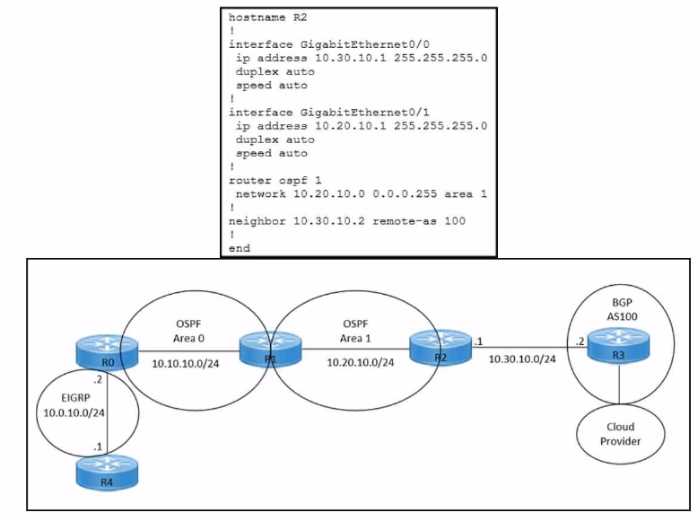
Refer to the exhibits. An engineer must redistribute OSPF internal routes into BGP to connect an on-
premises network to a cloud provider without introducing extra routes. Which two commands must
be configured on router R2? (Choose two.)
- A. router ospf 1
- B. router bgp 100
- C. redistribute ospf 1
- D. redistribute bgp 100
- E. redistribute ospf 1 match internal external
Answer:
B, E
Explanation:
To redistribute OSPF internal routes into BGP, the engineer needs to configure two commands on
router R2. The first command is router bgp 100, which enables BGP routing process and specifies the
autonomous system number of 100. The second command is redistribute ospf 1 match internal
external, which redistributes the routes from OSPF process 1 into BGP, and matches both internal
and external OSPF routes. This way, the engineer can avoid introducing extra routes that are not part
of OSPF process 1, such as the default route or the connected routes. Reference: =
Designing and
Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
, [ENCC: Configuring IPsec VPN from Cisco IOS XE to
AWS], [Deploying Cisco IOS VTI-Based Point-to-Point IPsec VPNs]
Question 15
An engineer must configure an IPsec tunnel to the cloud VPN gateway. Which Two actions send traffic
into the tunnel? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure access lists that match the interesting user traffic.
- B. Configure a static route.
- C. Configure a local policy in Cisco vManage.
- D. Configure an IPsec profile and match the remote peer IP address.
- E. Configure policy-based routing.
Answer:
A E
Explanation:
To send traffic into an IPsec tunnel to the cloud VPN gateway, the engineer must configure two
actions:
Configure access lists that match the interesting user traffic. This is the traffic that needs to be
encrypted and sent over the IPsec tunnel. The access lists are applied to the crypto map that defines
the IPsec parameters for the tunnel.
Configure policy-based routing (PBR). This is a technique that allows the engineer to override the
routing table and forward packets based on a defined policy. PBR can be used to send specific traffic
to the IPsec tunnel interface, regardless of the destination IP address. This is useful when the cloud
VPN gateway has a dynamic IP address or when multiple cloud VPN gateways are available for load
balancing or redundancy. Reference:
Designing and Implementing Cloud Connectivity (ENCC) v1.0
, Module 3: Implementing Cloud
Connectivity, Lesson 3: Implementing IPsec VPNs to the Cloud, Topic: Configuring IPsec VPNs on
Cisco IOS XE Routers
Security for VPNs with IPsec Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE
, Chapter: Configuring IPsec VPNs,
Topic: Configuring Crypto Maps
[Cisco IOS XE Gibraltar 16.12.x Feature Guide], Chapter: Policy-Based Routing, Topic: Policy-Based
Routing Overview