cisco 100-160 practice test
Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Cybersecurity
Question 1
How does a honeypot enhance network security?
- A. It monitors network traffic and sends alerts when potential threats are detected.
- B. It acts as a decoy and diverts malicious traffic away from important systems.
- C. It isolates external-facing services from the Internet and protects them from attack.
- D. It detects and prevents identified threats through real-time packet inspection.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Cybersecurity Study Guide, a honeypot is
a security mechanism that appears to be a legitimate system or resource but is intentionally made
vulnerable to attract attackers. Its purpose is not to serve legitimate users but to detect, study, and
sometimes divert malicious activity.
"A honeypot is a decoy system or service designed to attract and engage attackers. By simulating a
target of interest, it allows security teams to monitor attack methods, collect intelligence, and
sometimes divert threats away from production systems. Honeypots do not prevent attacks but help
in identifying them and understanding adversary tactics."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Basic Network Security Concepts, Honeypots and Honey Nets section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
In this context:
Option A describes an IDS (Intrusion Detection System), not a honeypot.
Option C refers to a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone), not a honeypot.
Option D describes an IPS (Intrusion Prevention System).
Option B correctly identifies a honeypot’s role as a decoy to divert or engage attackers.
Question 2
Which data type is protected through hard disk encryption?
- A. Data in process
- B. Data in transit
- C. Data in use
- D. Data at rest
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide explains that hard disk encryption is a method used to protect
data stored on a physical device from unauthorized access.
"Data at rest refers to data stored on a device, such as files on a hard drive, SSD, or removable media.
Hard disk encryption protects data at rest by converting it into an unreadable format unless accessed
with the correct decryption key."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Data States and Protection Methods section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
Data in process refers to data actively being handled by applications in memory (RAM), which is not
the primary target of disk encryption.
Data in transit is protected via encryption methods such as TLS, not disk encryption.
Data in use is accessed and manipulated by programs in real-time, also not the primary scope of disk
encryption.
Data at rest is the correct answer, as hard disk encryption directly safeguards stored files.
Question 3
Your supervisor suspects that someone is attempting to gain access to a Windows computer by
guessing user account IDs and passwords. The supervisor asks you to use the Windows Event Viewer
security logs to verify the attempts.
Which two audit policy events provide information to determine whether someone is using invalid
credentials to attempt to log in to the computer? (Choose 2.)
Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
- A. Object access failure
- B. Account logon failure
- C. Account lockout success
- D. Account logoff success
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
According to the CCST Cybersecurity course, Windows Event Viewer’s Security logs record
authentication-related events that can help identify password-guessing attempts (also known as
brute force attacks).
"The Account logon failure event indicates that an authentication attempt has failed, which may
suggest incorrect credentials were used. Multiple such events in a short time frame can indicate a
brute-force attack. The Account lockout success event confirms that an account has been locked due
to repeated failed logon attempts, which further supports the suspicion of password-guessing
attacks."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Incident Handling, Monitoring and Analyzing Security Events section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
Object access failure relates to unauthorized attempts to open or modify files, not login attempts.
Account logon failure (B) shows failed login attempts due to invalid credentials.
Account lockout success (C) confirms that repeated login failures have triggered a lockout.
Account logoff success is a normal event and does not indicate malicious activity.
Question 4
You are going to perform a penetration test on a company LAN. As part of your preparation, you
access the company’s websites, view webpage source code, and run internet searches to uncover
domain information. You also use social media to gather details about the company and its
employees.
Which type of reconnaissance activities are you performing?
- A. Passive
- B. Active
- C. Offline
- D. Invasive
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide explains that reconnaissance is the process of collecting
information about a target before attempting exploitation.
"Passive reconnaissance is conducted without directly engaging with the target systems. Examples
include reviewing public websites, examining HTML source code, querying public DNS records, and
using social media to gather information. Since no packets are sent directly to the target system, it
reduces the risk of detection."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Management, Reconnaissance Techniques
section, Cisco Networking Academy)
Passive (A) is correct because all actions described — viewing public pages, searching online, and
checking social media — involve no direct interaction that could alert the target.
Active (B) would involve direct probing, like port scans or vulnerability scans.
Offline (C) is not an official reconnaissance classification in this context.
Invasive (D) is a general term and not used as a standard reconnaissance category in CCST material.
Question 5
Your manager asks you to review the output of some vulnerability scans and report anything that
may require escalation.
Which two findings should you report for further investigation as potential security vulnerabilities?
(Choose 2.)
- A. Encrypted passwords
- B. Disabled firewalls
- C. Open ports
- D. SSH packets
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course teaches that vulnerability scan results should be reviewed for
misconfigurations and exposures that can be exploited by attackers.
"Disabled firewalls expose systems to direct network attacks and should be treated as critical
findings. Open ports can indicate unnecessary or unsecured services running, which may provide
entry points for attackers. These findings should be escalated for remediation or further security
hardening."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Management, Analyzing and Responding to
Scan Results section, Cisco Networking Academy)
Encrypted passwords (A) are good practice, not a vulnerability.
Disabled firewalls (B) leave systems defenseless against incoming attacks.
Open ports (C) can be exploited if the services they expose are vulnerable or misconfigured.
SSH packets (D) are normal in secure remote administration and are not inherently a vulnerability.
Question 6
A client cannot connect to the corporate web server. You discover a large number of half-open TCP
connections to the server.
What should you do?
- A. Take action to stop the TCP SYN flood attack.
- B. Change the connection protocol from HTTP to HTTPS.
- C. Ignore the half-open connections because this is a normal part of the TCP three-way handshake.
- D. Flush the DNS cache information.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide identifies SYN flood attacks as a type of Denial of Service (DoS)
attack that exploits the TCP three-way handshake. Attackers send many SYN requests without
completing the handshake, leaving the server with numerous half-open connections and exhausting
resources.
"A TCP SYN flood attack overwhelms a target server by initiating a high volume of TCP connections
but never completing the handshake, resulting in numerous half-open connections that consume
system resources and can render the service unavailable."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Incident Handling, Denial-of-Service Attacks section, Cisco Networking
Academy)
A is correct: The proper action is to stop the SYN flood, often using firewalls, intrusion prevention
systems, or SYN cookies.
B (switching to HTTPS) does not address the flooding issue.
C is incorrect because the excessive number of half-open connections indicates an attack, not normal
operation.
D (flushing DNS cache) is unrelated to this type of attack.
Question 7
Which two basic metrics should be taken into consideration when assigning a severity to a
vulnerability during an assessment? (Choose 2.)
- A. The likelihood that an adversary can and will exploit the vulnerability
- B. The impacts that an exploit of the vulnerability will have on the organization
- C. The time involved in choosing replacement software to replace older systems
- D. The age of the hardware running the software that contains the vulnerability
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course describes that risk scoring for vulnerabilities often involves likelihood
and impact — similar to the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) model.
"When prioritizing vulnerabilities, assess both the likelihood of exploitation and the potential impact
to the organization. Likelihood measures how easy or probable it is for an adversary to exploit the
weakness, while impact measures the consequences to confidentiality, integrity, and availability if
exploitation occurs."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Vulnerability Assessment and Risk Management, Risk Assessment and
Prioritization section, Cisco Networking Academy)
A is correct: Likelihood is a fundamental part of severity assessment.
B is correct: Impact determines how damaging an exploit would be.
C is incorrect: Time to choose replacement software is an operational consideration, not a severity
metric.
D is incorrect: Hardware age may influence performance but does not directly define vulnerability
severity.
Question 8
Which Windows app is a command-line interface that includes a sophisticated scripting language
used to automate Windows tasks?
- A. PowerShell
- B. Microsoft Management Console
- C. Vim
- D. MS-DOS
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course identifies Windows PowerShell as both a command-line interface
(CLI) and a robust scripting environment. It is used by system administrators for automation,
configuration, and task scheduling.
"PowerShell is a Windows command-line shell and scripting language built on the .NET framework. It
allows administrators to automate administrative tasks, manage system configurations, and execute
complex scripts for system management."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Endpoint Security Concepts, System Administration Tools section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A is correct: PowerShell provides both interactive command execution and scripting capabilities.
B (MMC) is a GUI-based management console, not a CLI.
C (Vim) is a text editor, not a Windows-native CLI.
D (MS-DOS) is a legacy command shell with no advanced scripting features comparable to
PowerShell.
Question 9
Why is it necessary to update firmware to the latest version?
- A. To support the latest operating systems and applications
- B. To patch firmware in the kernel of the operating system
- C. To correct security holes and weaknesses
- D. To explore new hardware features
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide, firmware updates are a critical security
maintenance task because vulnerabilities in firmware can be exploited by attackers to gain persistent
control over hardware.
"Keeping firmware up to date is necessary to patch security vulnerabilities and weaknesses that
could be exploited by threat actors. Vendors release firmware updates to correct security flaws,
enhance stability, and ensure compatibility with updated security protocols."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Endpoint Security Concepts, System and Firmware Maintenance section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A is partially true but not the primary security reason for updates.
B is incorrect because firmware is not part of the OS kernel; it’s embedded in the hardware.
C is correct: patching vulnerabilities in firmware is essential for endpoint protection.
D may occur as a side benefit, but it’s not the main reason from a cybersecurity perspective.
Question 10
How do threat actors launch ransomware attacks on organizations?
- A. They implant malware to collect data from the corporation’s financial system.
- B. They deface an organization’s public-facing website.
- C. They lock data and deny access to the data until they receive money.
- D. They secretly spy on employees and collect employees’ personal information.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course describes ransomware as a form of malicious software that encrypts
or locks access to an organization’s data, demanding payment for its release.
"Ransomware is a type of malware that denies access to data by encrypting it and demands payment
from the victim to restore access. Threat actors may deliver ransomware through phishing emails,
malicious downloads, or exploiting vulnerabilities in exposed systems."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Malware Types and Threats section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A describes spyware or information-stealing malware.
B is website defacement, which is vandalism, not ransomware.
C is correct: locking/encrypting data and demanding payment is the defining behavior of
ransomware.
D is more aligned with insider threat or espionage activities.
Question 11
Which macOS security feature encrypts the entire macOS volume?
- A. FileVault
- B. Gatekeeper
- C. System Integrity Protection (SIP)
- D. XProtect
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide highlights FileVault as the macOS full-disk encryption tool.
"FileVault is macOS’s built-in full-disk encryption feature. It encrypts the contents of the entire
startup disk to help prevent unauthorized access to the information stored on the drive, even if the
device is lost or stolen."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Endpoint Security Concepts, Disk Encryption section, Cisco Networking
Academy)
A is correct: FileVault provides complete volume encryption.
B (Gatekeeper) controls app installation by verifying code signatures.
C (System Integrity Protection) protects system files from modification.
D (XProtect) is macOS’s built-in malware detection system.
Question 12
You are reviewing your company’s disaster recovery plan.
Which two daily data backup actions should the plan include? (Choose 2.)
- A. Back up the data to removable media and store it off-site.
- B. Back up each department’s data to a separate local server.
- C. Back up the data by using cloud services.
- D. Back up the data by using RAID on a local external hard drive with a secondary power source.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide emphasizes that backups should be stored off-site or in the
cloud to ensure recovery even if the primary location is damaged or compromised.
"A comprehensive disaster recovery plan includes performing regular backups and ensuring copies
are stored in locations not subject to the same physical risks as the primary site. Off-site storage and
cloud-based backups provide resilience against local disasters."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Backup and Disaster Recovery section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A is correct: Off-site removable media ensures recovery even if the main site is destroyed.
B is incorrect: Local-only backups are vulnerable to the same risks as production systems.
C is correct: Cloud services provide geographically separate storage with automated redundancy.
D is incorrect: RAID is for hardware fault tolerance, not a complete backup solution.
Question 13
Which two passwords follow strong password policy guidelines? (Choose 2.)
- A. Wh@tareyouDo1ngtoday4
- B. Feb121978
- C. Fluffy#
- D. 1mPressm3!
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course defines a strong password as one that:
Is at least 8–12 characters long
Uses a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
Avoids dictionary words, personal information, and predictable patterns
"Strong passwords combine length, complexity, and unpredictability, making them resistant to brute
force and dictionary attacks."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Authentication and Access Control section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A is correct: It’s long, mixed case, includes numbers and symbols, and is not easily guessable.
B is incorrect: It’s based on a date, which is predictable.
C is incorrect: Short and based on a dictionary word.
D is correct: Uses complexity and length with leetspeak for added unpredictability.
Question 14
Your home network seems to have slowed down considerably. You look at the home router GUI and
notice that an unknown host is attached to the network.
What should you do to prevent this specific host from attaching to the network again?
- A. Create an IP access control list.
- B. Implement MAC address filtering.
- C. Block the host IP address.
- D. Change the network SSID.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The CCST Cybersecurity course explains that MAC address filtering is a network access control
method that allows only approved device hardware addresses to connect. While not foolproof
against spoofing, it can block a specific device from reconnecting to a small home network.
"MAC address filtering restricts network access to devices whose unique hardware addresses are
explicitly allowed. This can be used to block known unauthorized devices from reconnecting."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Basic Network Security Concepts, Wireless Security Controls section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
A is incorrect: IP ACLs are better for controlling traffic types, not blocking specific devices at the
router level.
B is correct: It prevents the device’s hardware address from reconnecting.
C is temporary since the host can get a new IP via DHCP.
D may hide the network but will not stop a determined attacker who can still detect it.
Question 15
HOTSPOT
For each statement, select True if it is a common motivation to commit cyber attacks or False if it is
not.
Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.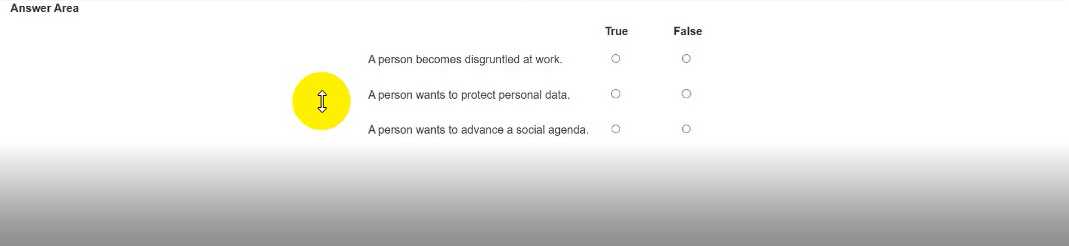
Answer:
Explanation: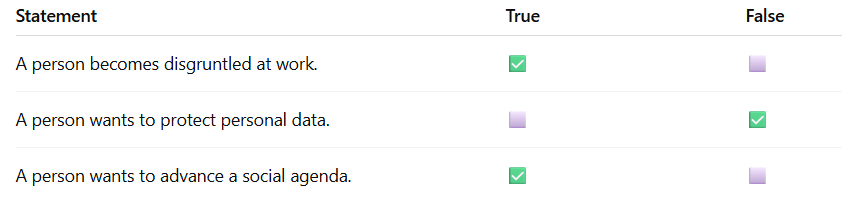
The CCST Cybersecurity Study Guide outlines common motivations for cyberattacks, which include:
Financial gain
Revenge or personal grievance (e.g., disgruntled employees)
Ideological or political purposes (hacktivism)
Espionage and intelligence gathering
"Cyberattack motivations range from financial and competitive advantage to personal vendettas and
advancing political or social causes. Disgruntled insiders may misuse access privileges to harm an
organization, while hacktivists target systems to promote social or political messages."
(CCST Cybersecurity, Essential Security Principles, Threat Actor Motivations section, Cisco
Networking Academy)
Being disgruntled at work → common insider threat motivation (True)
Wanting to protect personal data → defensive action, not a reason to commit an attack (False)
Wanting to advance a social agenda → hacktivist motivation (True)