cima cimapro19 p01 1 practice test
P1 Management Accounting
Question 1
You are a trainee management accountant working for a prestigious manufacturing firm. One day
you go to a business meeting a business meeting and the managing director is there. They stand up
and say that the company is losing too much money through wastage and losses and so they have
decided to implement a total quality management system. They go on to say this system will:
1:Allow the company to improve on a consistent and continual basis
2:Allow the company to identify and allocate quality accountability to certain departments
3:Help the company detect error and fraud
Are ALL of these statements correct?
- A. No. (2) is incorrect No. (1) is incorrect
- B. Yes. They ore all correct
- C. No. (1) and (2) are incorrect.
- D. No. (3) and (2) are incorrect.
Answer:
A
Question 2
Christian the management accountant at a car manufacturer has been given a list of costs that have
been incurred due to accidents and errors either occurring or being prevented.
Which of the following are examples of non-conformance costs? Select ALL that apply.
- A. Cost of scrap
- B. Loss of goodwill
- C. Cost of repairs to products
- D. Inspection costs
- E. Cost of repairs to equipment
Answer:
A, B, C
Question 3
You are a management accounting working for a car manufacturer. The company is publicly listed and
has been around for many years.
The company produces 2 products. Car 1 and Car 2. Car 1 sells for £20,000 and Car 2 for £27,000.
Car 1 can be upgraded post production to the 1ZC model for £5,000 and Car 2 to the 2ZC model for
£3,500.
Post production upgrade the 1ZC sells for £25,500 and the 2ZCfor £30,000.
The company sources all of its supplies for the same supplier and has access to a large workforce. As
a result there are no bottlenecks or limiting factors to production.
Based on the information above the company should...
- A. Upgrade both models
- B. Upgrade Car 1 but not Car 2
- C. Upgrade Car 2 but not Car 1
- D. Keep both Cars as base models
Answer:
B
Question 4
Your company want to know how many units they'd have to sell this season to break even. However,
you have some reservations over whether or not breakeven analysis is suitable for the company.
Which of these assumptions over product range limit the accuracy of break even analysis? Select ALL
that apply.
- A. The company only sells one product
- B. The company has a consistent selling ratio across all products
- C. The company sells multiple products
- D. Variable costs remain consistent at any level of production
- E. Fixed costs remain the same regardless of activity
- F. The company has a variable selling ratio across all products
- G. Prices and demand of products will remain steady
Answer:
A, B
Question 5
A manager has not yet used all oh his budget. He is worried that his budget maybe reduced next year
if he is not seen to have needed all the funds. He decides to spend the remaining £1,580 on another
team building exercise as well as a catered lunch for his department.
This example falls under which behavioural aspect of budgetary control?
- A. Irrational spending
- B. Motivation
- C. Budget negotiation
- D. Short term focus
Answer:
A
Question 6
Petco's material price standard was £8 per kg.
When looking over their accounts you calculate that in fact they they purchased 2,000kg at £6 per kg
due to an overly abundant harvest that lowered global pet food prices.
You have been asked by your manager to analyse these figures and come to a conclusion.
With that in mind which of the following statements are correct? Select ALL that apply.
- A. The material price operational variance is £4,000
- B. The material price planning variance is £4,000
- C. Management had control over this variance
- D. Management had no control over this variance
Answer:
B, D
Question 7
A musical instrument manufacturing company is considering a new project that will require 1000 kg
of wood. They have 700 kgs of wood in stock which was purchased last year for £4 per kg. The wood
in stock can be sold back to the supplier for £5 per kg. The wood in stock will have to be replaced if it
is used. The current purchase price of wood is £8 per kg.
Using this information, what is the relevant cost of wood for the manufacturers decision on this
project?
- A. £8,000
- B. £5,000
- C. £11,500
- D. £5,600
Answer:
A
Question 8
Your company operates using TQM. As the accountant you have been tasked with producing a quality
report so that management can understand how well their new range of products is being received
and how the quality of the products has improved. In order to produce the report you have
requested information from different departments, but you soon realise not all the information is
relevant. You have information regarding the
following:
Cost of downtime Training costs Environmental costs Customer returns and refunds Number of
defects per unit
Which pieces of information are relevant to your report? Select ALL that apply.
- A. Customer returns and refunds
- B. Number of defects per unit
- C. Cost of downtime
- D. Training costs
- E. Environmental costs
Answer:
A, B
Question 9
A company is basing its budget on predicted sales of one of its products. They have tasked you with
forecasting the sales in year 2. The company has found that a fairly accurate prediction can be found
when the trend
is calculated like so:
a = 10,000
b = 2,000
The sales of year 1 were affected by seasonal variation and were as follows:
Q1:12,500
Q2:14,200
Q3:15,400
Q4:19,650
You use a multiplicative model and round percentages to the nearest whole percent.
Select ALL the correct quarterly forecasts of year 2 from the list.
- A. Year 2 Q1 = 20,800
- B. Year 2 Q2 = 22,220
- C. Year 2 Q3 = 24,960
- D. Year 2 Q4 = 27,340
Answer:
A, B
Question 10
A snowboard manufacturer is considering investing in technology that will give a good indication of
how heavy snowfall will be in the future. The predictions tend to be reasonably accurate.
The current budgeted profit for the year is £2,560,000 but if they invest in this technology and it
works, the expected profit will be £2,640,000. The manufacturer is willing to invest a maximum of
£40,000 into the venture.
What is the expected profit if the investment is NOT made?
- A. £2,560,000
- B. £2,640,000
- C. £2,520,000
- D. £2,600,000
Answer:
D
Question 11
According to a decision tree forecasting, there are three possible outcomes of a project requiring
£10,000 capital investment. They are (along with probability of occurring): £20,000 in revenue (45%),
£35,000 (15%),
£10,000 (30%) and -£6,000 (10%).
However, choosing another project (2) requiring the same investment would give us £12,000 and
choosing project 3 would give us a 90% chance of generating revenues of £15,000 but a 5% chance of
revenues of £0.
Project 4 is wildly ambitious and boasts an unlikely (5% chance) of generating revenues of £100,000.
There is a 10% probability of negative revenues.
Which is the risk averse investor more likely to take?
Project 1
Project 2
Project 3
Project 4
Answer:
B
Question 12
Find the weighted average contribution per unit using the following information: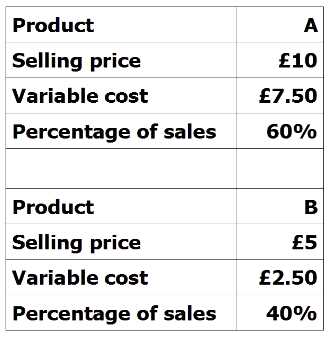
- A. £10
- B. £8
- C. £5.50
- D. £2.50
Answer:
D
Question 13
D3 makes 2 types of toilets - the Executive (Ex) and the Classic (CI). Direct labour costs $6 per hr and
overheads are absorbed on a machine hour basis. The overhead absorption rate for the period is $28
per machine hour. What is the traditional cost per unit for (Ex) and (CI)?
- A. (Ex) 60, (CI) 56
- B. (Ex) 58, (CI) 53
- C. (Ex) 65, (CI) 49
- D. (Ex) 62, (CI) 52
- E. (Ex) 63, (CI) 48
Answer:
C
Question 14
N prepares budgets on an annual basis by using the budget from the previous year, and then
adjusting it for growth and inflation.
This is an example of:
- A. An incremental budget
- B. A rolling budget
- C. A flexed budget
- D. Zero based budgeting
Answer:
A
Question 15
What type of budget is prepared on an annual basis taking current year operating results and
adjusting them for expected growth and inflation?
- A. Rolling budget
- B. Incremental budget
- C. Flexed budget
- D. Zero-based budget
Answer:
B