cima cimapra17 ba2 1 practice test
BA2 - Fundamentals of Management Accounting
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
DS is manufacturing company that uses an integrated accounting system. The following payroll data
is available for the month of August:
The Employers' National Insurance for the period was $13,790. An analysis of the wages is as follows:
Which of the following factors affect the budgeted cash flow:
(a) Funds from the issue of share capital
(b) Bank Interest on a long term loan
(c) Depreciation on fixed assets
(d) Bad debt write off
- A. Factors (a), (b), (c) and (d)
- B. Factors (a) and (b) only
- C. Factor (a) only
- D. Factors (b), (c) and (d) only
Answer:
B
Question 2
Which of the following cannot be used to split costs into fixed and variable elements?
- A. Absorption costing
- B. High-low method
- C. Scattergraph
- D. Line of best fit
Answer:
A
Question 3
In order to provide information that is suitable for control purposes, the budget must be:
- A. Computer generated
- B. Fixed
- C. Flexed
- D. Ideal
Answer:
C
Question 4
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the Exhibit.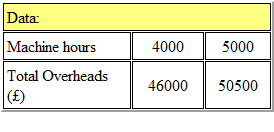
PJ Ltd has forecast that the relationship between total overheads and machine hours will be as
follows:
If the budget is to be based on 4,000 machine hours, the variable overhead absorption rate will be:
*per machine hour.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Answer:
4.46
Question 5
If the fixed costs are increased, the point at which the line plotted on a profit/volume (PV) graph cuts
the horizontal axis will:
- A. Double
- B. Move to the left
- C. Stay the same
- D. Move to the right
Answer:
D
Question 6
Refer to the Exhibit.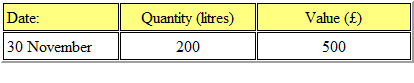
Fabex Ltd manufactures a household detergent called "Clear". The standard data for one of the
chemicals used in production (chemical XTC) is as follows:
(a) 50 litres used per 100 litres of 'Clear' produced
(b) Budgeted monthly production is 1000 litres of 'Clear'.
The closing inventory of chemical XTC for November valued at standard price was as follows:
Actual results for the period during December were as follows:
(a) 500 litres of chemical XTC was purchased for £1300.
(b) 550 litres of chemical XTC was used.
(c) 900 litres of 'Clear' was produced.
It is company policy to extract the material price variance at the time of purchase.
What is the total direct material price variance (to the nearest whole number)?
- A. £50 adverse
- B. £50 favourable
- C. £55 adverse
- D. £55 favourable
Answer:
A
Question 7
Within the relevant range, a variable cost is a cost which:
- A. cannot be forecast with any degree of accuracy because of its variability.
- B. varies in total in proportion to the level of activity.
- C. varies per unit in proportion to the level of activity.
- D. varies in total in proportion to the level of inflation.
Answer:
B
Question 8
Fixed costs can best be described as:
- A. Costs which are difficult to budget accurately
- B. Costs which remain constant, within a relevant range, when activity levels change
- C. Costs which never change
- D. Costs which are uncontrollable
Answer:
B
Question 9
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the Exhibit.
A company operates a batch costing system.
Production overhead costs are absorbed into the cost of batches using a direct labour hour rate.
Other overhead costs are absorbed at a rate of 20% of total production cost. The company adds a
mark-up of 10% to total cost in order to derive its selling prices.
Budgeted production overheads for the period are $44,000 and the budgeted level of activity is
8,800 direct labour hours.
The following data are available for batch number 309:
The required selling price per unit (to two decimal places) is:
Answer:
$28.60
Question 10
Refer to the Exhibit.
A company operates an absorption costing system. The management accounts show that fixed
production overheads were over-absorbed in the period.
Which FOUR combinations could possibly have resulted in this situation?
- A. Combination A
- B. Combination B
- C. Combination C
- D. Combination D
- E. Combination E
- F. Combination F
- G. Combination G
- H. Combination H
Answer:
C, D, E, F
Question 11
The principal budget factor can be defined as:
- A. The factor which has the highest value in the budget
- B. The factor which limits the activities of the organisation
- C. The factor which is most likely to result in an adverse variance
- D. The factor which is least likely to change in the future
Answer:
B
Question 12
Which of the following statements is correct?
i. sector bodies use budgetary planning and control systems
ii. costing cannot be used by public sector bodies because they have no measurable output
iii. in public sector bodies tend to focus on cost management therefore they have no need for non-
financial information
- A. (i) only
- B. (i) and (ii) only
- C. (ii) and (iii) only
- D. (i) and (iii) only
Answer:
A
Question 13
GB Limited operates a standard costing system. During the month 18,500 labour hours were worked
at a standard cost of $6 per hour. The labour efficiency variance was $8,700 favourable.
How many standard hours were produced?
- A. 1,450
- B. 19,950
- C. 17,050
- D. 18,500
Answer:
C
Question 14
Refer to the Exhibit.
AM Ltd. makes and sells a single product for which the standard cost information is as follows:
Budgeted production for the period is 30000 units.
The actual results for the period were as follows: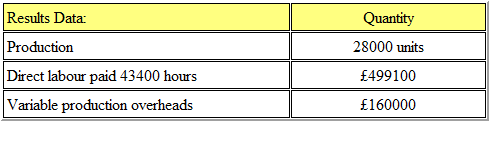
What is the variable overhead expenditure variance?
- A. 13,161 adverse
- B. 13,161 favourable
- C. 13,600 adverse
- D. 13,600 favourable
Answer:
D
Question 15
CORRECT TEXT
Refer to the Exhibit.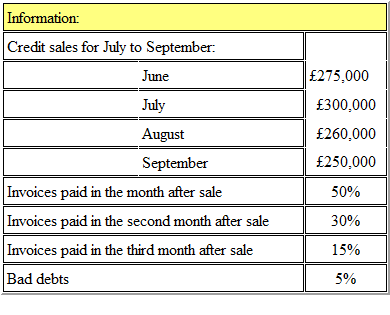
The following details have been extracted from the receivables collection records of SBC:
The amount budgeted to be received in September from credit sales is, to the nearest £000:
Answer:
£257000