asq cqe practice test
Certified Quality Engineer
Question 1
The primary characteristic of risk management is being
- A. simple
- B. reactive
- C. unnatural
- D. all-inclusive
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Risk management in software quality engineering aims to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that
could affect project outcomes. The primary characteristic of effective risk management is that it
should be all-inclusive. This means it should encompass all potential risk areas, including technical,
project management, resource allocation, and external factors. An all-inclusive approach ensures
that no significant risk is overlooked and that comprehensive strategies are in place to manage
identified risks effectively.
Reference:
Software Quality Assurance: Principles and Practice by Nina S. Godbole.
ASQ Software Quality Engineer Handbook.
Question 2
Short-run SPC should be used in which of the following situations?
- A. The coded data being used do not show significant shifts in the process.
- B. Regular SPC charts show the process to be out of control.
- C. Many different parts are made in small lots.
- D. The number of charts currently used needs to be increased to control the process better.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Short-run Statistical Process Control (SPC) is particularly useful in situations where many different
parts are made in small lots. This is because traditional SPC methods may not be effective when
production runs are short and the volume of data for individual parts is limited. Short-run SPC
techniques allow for effective monitoring and control of processes that produce a variety of parts in
small quantities by standardizing and coding data to detect shifts and trends over multiple short
runs.
Reference:
Montgomery, D. C. (2009). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control.
ASQ Quality Press: The Certified Quality Engineer Handbook.
Question 3
Which of the following tools is used to plan for and avoid situations that might interfere with project
implementation?
- A. Affinity diagram
- B. Matrix diagram
- C. Interrelationship digraph
- D. Process decision program chan
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) is a tool used to anticipate potential problems that could
interfere with project implementation and to develop countermeasures to prevent or mitigate those
problems. It is a structured method for mapping out every conceivable event and contingency that
can occur in the course of a project, thus allowing project managers to plan for and avoid disruptions
effectively.
Reference:
ASQ Quality Press: The Quality Toolbox.
Total Quality Management by Dale H. Besterfield.
Question 4
Failure to cite the significant contributions of other individuals in a final manuscript for publication
violates which category of the ASQ Code of Ethics?
- A. Fundamental Principles
- B. Relations with the Public
- C. Relations with Employers and Clients
- D. Relations with Peers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Failing to cite the significant contributions of other individuals in a final manuscript for publication
violates the category of "Relations with Peers" in the ASQ Code of Ethics. This category emphasizes
the importance of acknowledging and respecting the contributions of colleagues and collaborators in
professional work. Proper citation practices are essential for maintaining professional integrity and
fostering a collaborative environment within the professional community.
Reference:
ASQ Code of Ethics.
Professional Ethics in Engineering by Mike W. Martin and Roland Schinzinger.
Question 5
The following data sets were presented to top management.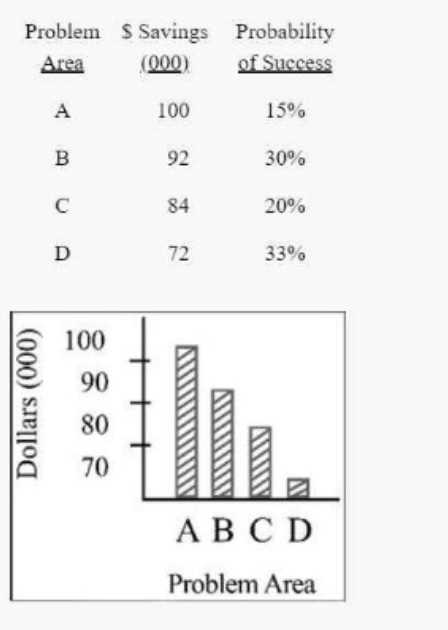
Which problem area should be targeted for improvement first?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To determine which problem area should be targeted for improvement first, we need to consider
both the dollar savings and the probability of success. Calculating the expected savings (dollar
savings multiplied by the probability of success) for each problem area gives us a clear picture:
A: 100,000 * 0.15 = 15,000
B: 92,000 * 0.30 = 27,600
C: 84,000 * 0.20 = 16,800
D: 72,000 * 0.33 = 23,760
Problem Area B has the highest expected savings (27,600), making it the best target for initial
improvement efforts based on the given data. Reference:
Quality Management for Organizational Excellence by David L. Goetsch and Stanley Davis.
ASQ Certified Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence Handbook.
Question 6
Which of the following types of planning uses a strategic planning process that relates idealistic goals
to work strategy?
- A. Yoji planning
- B. Hoshin planning
- C. Juran planning
- D. Deining planning
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Hoshin planning, also known as Hoshin Kanri or policy deployment, is a strategic planning process
that aligns an organization's functions and activities with its strategic objectives. It involves setting
idealistic goals and linking them to actionable work strategies through a systematic approach. This
method ensures that all levels of an organization are working harmoniously towards common
objectives.
Reference:
Quality Management and Six Sigma by Shruti Bhat
"Hoshin Kanri: Policy Deployment for Successful TQM" by Yoji Akao
Question 7
Which of the following is most important to shaping the culture of an organization?
- A. Geographic location
- B. Management philosophy
- C. Market share
- D. Implement ISO
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Management philosophy is crucial in shaping the culture of an organization. It defines the values,
beliefs, and principles that guide the behavior of its members. A strong, coherent management
philosophy provides direction, motivates employees, and fosters a sense of identity and purpose
within the organization. It influences decision-making, leadership styles, and the overall work
environment.
Reference:
"Corporate Culture and Performance" by John P. Kotter and James L. Heskett
"The Culture Engine" by S. Chris Edmonds
Question 8
A material review board (MRB) gets its authority to act from which of the following functions?
- A. Executive management
- B. Purchasing
- C. Engineering
- D. National or international standards
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A material review board (MRB) gets its authority to act from executive management. The MRB is
typically composed of representatives from various departments, including engineering, quality, and
production, and is responsible for reviewing and making decisions on non-conforming materials. The
authority given by executive management ensures that the MRB has the power to enforce quality
standards and make necessary decisions.
Reference:
"Quality Control and Management" by James R. Evans and William M. Lindsay
ASQ (American Society for Quality) guidelines
Question 9
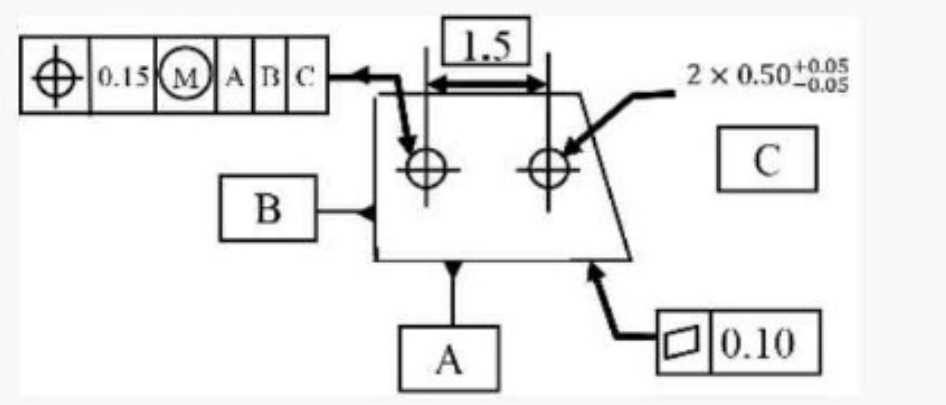
A in this drawing, the symbol is being used to indicate the
- A. reference plane
- B. basic definition
- C. datum
- D. feature
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In the provided drawing, the symbol marked "A" is being used to indicate a datum. A datum is a
reference point, line, or surface used as a basis for measurement and to establish the location or
orientation of other features. It serves as a starting point for dimensional control and ensures
consistency in the manufacturing process.
Reference:
"Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing" by Alex Krulikowski
ASME Y14.5 - 2009 (Dimensioning and Tolerancing)
Question 10
The producer's risk can be determined from the
- A. acceptance quality limit (AQL)
- B. lot tolerance percent defective (LTPD)
- C. average outgoing quality limit (AOQL)
- D. rejectable quality level (RQL)
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The producer's risk, also known as Type I error or alpha risk, is the risk of rejecting a lot that meets
the acceptance criteria. It can be determined from the acceptance quality limit (AQL), which is the
maximum percentage of defectives that is considered acceptable during random sampling of an
inspection lot. The AQL is used in conjunction with sampling plans to assess the quality of a lot and
make decisions about its acceptance or rejection.
Reference:
"Statistical Quality Control" by Douglas C. Montgomery
ISO 2859-1: Sampling procedures for inspection by attributes
Question 11
The number of runs required by a full-factorial design with three factors each at two levels is equal to
- A. 6
- B. 8
- C. 9
- D. 12
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In a full-factorial design with three factors, each at two levels, the total number of runs required is
calculated by 2n2^n2n, where nnn is the number of factors. For three factors, 23=82^3 = 823=8.
Thus, 8 runs are required to cover all possible combinations of factor levels.
Reference:
"Design and Analysis of Experiments" by Douglas C. Montgomery
ASQ Quality Glossary
Question 12
In a failure mode and effects analysis (FXIEA). the focus should be on
- A. classifying as failures those items with risk priority numbers greater than 100
- B. creating flowchans for the items with high risk priority number or occurrence values
- C. implementing corrective action on items that have high alpha risk values
- D. implementing corrective action on items that have high risk priority number or severity values
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), the focus should be on implementing corrective actions
on items that have high Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) or high severity values. The RPN is calculated by
multiplying the severity, occurrence, and detection ratings, and it helps prioritize which failure
modes need immediate attention.
Reference:
"Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A Guide for Continuous Improvement for the ISO 9000
and QS 9000" by D.H. Stamatis
ASQ guidelines on FMEA
Question 13
Which of the following tools can be used to determine the best option from many choices based on
their importance and merits?
- A. Interrelationship digraph
- B. PERT chart
- C. Tree diagram
- D. Prioritization matrix
Answer:
D
Explanation:
A prioritization matrix is a tool that helps determine the best option from many choices based on
their importance and merits. It evaluates and prioritizes different options using specific criteria and
assigns scores to facilitate decision-making.
Reference:
"The Quality Toolbox" by Nancy R. Tague
ASQ Quality Tools
Question 14
Which of the following statements is true regarding a failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA)?
- A. A FMEA is a pictorial representation of the reliability interdependency of components.
- B. A FMEA should not get updated throughout the life cycle of the product.
- C. The advantage of a FMEA is to communicate the risk with different stakeholders.
- D. The first step in the development of an FMEA is to calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN).
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is used to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in
a system and their effects. The advantage of FMEA is its ability to communicate risk effectively to
different stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aware of potential issues and their impacts,
facilitating better decision-making and risk mitigation.
Reference:
"Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: FMEA from Theory to Execution" by D.H. Stamatis
ASQ guidelines on FMEA
Question 15
If a quality engineer discovers a situation in which unlabeled finished product could be shipped to
customers, what would be an appropriate preventive action to take?
- A. Train the shipping department staff in quality tools and techniques
- B. Identify the unlabeled product and have it labeled
- C. Form a team to error-proof the process
- D. Conduct a backward trace of the process
Answer:
C
Explanation:
If a quality engineer discovers a situation where unlabeled finished product could be shipped to
customers, the appropriate preventive action is to form a team to error-proof the process. This
involves identifying and eliminating the root causes of the issue to prevent recurrence, ensuring that
processes are robust and error-free.
Reference:
"The Lean Six Sigma Pocket Toolbook" by Michael L. George, David Rowlands, Mark Price, and John
Maxey
ASQ guidelines on preventive actions