appian acd101 practice test
Appian Associate Developer
Question 1
A customer wants to display a small toolbar with three icons - a "sad face," a "face with neutral
expression," and a "happy face" - on the bottom of every page in their application.
Users will be instructed to use the icon that best expresses their current experience using the
application. This will allow the customer to collect valuable data about users.
Which object type should be called from each page to implement this feature?
- A. An interface, because the component must render user interface elements.
- B. An expression rule, because the component captures expressions of user sentiment for analysis.
- C. A decision, because the component captures a choice that users select from an array of custom selection components, rather than a standard dropdown or radio button.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Appian, interfaces are used to design and render user interface elements, allowing for the creation
of custom layouts and components that can interact with users. In this scenario, the toolbar with
emotion icons is a UI element that needs to be consistently presented across various pages. Using an
interface ensures that these icons can be interactively used by users to express their sentiments, and
the data collected can be analyzed for user experience insights. Interfaces are capable of embedding
such UI elements and can be invoked or included across multiple pages within an application, making
them the ideal choice for this requirement.
Reference:
Appian Documentation on Interfaces: Provides detailed guidance on how to design and use
interfaces to create user-centric UI components.
Question 2
You select the "Generate groups and folders to secure and organize objects" option while creating a
new application, Acme, with the prefix ACM.
By default, which two groups are generated by Appian? (Choose two.)
- A. ACM Administrators
- B. ACM Designers
- C. ACM Viewers
- D. ACM Users
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
When creating a new application in Appian and opting to generate groups and folders for
organization and security, Appian automatically creates specific groups to facilitate application
development and management. The default groups include "Administrators" and "Designers" with
the application prefix, in this case, ACM. The ACM Administrators group is intended for users who
will have full control over the application, including configuration and deployment aspects. The ACM
Designers group is designated for users primarily involved in the design and development of the
application, granting them necessary permissions to create and modify application components
without full administrative privileges.
Reference:
Appian Documentation on Application Design: Offers insights into best practices for structuring and
securing Appian applications, including the use of groups for effective application management.
Question 3
You need to remove an unused field from an existing record type Product, which has data sync
enabled and is backed by a database table.
What should you do?
- A. Delete the field from the record type and optionally delete the column from the database table.
- B. Delete the field from the product Custom Data Type (CDT) and perform a full resync of the record type.
- C. Delete the column from the database table and perform a full resync of the record type.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Appian, when dealing with a record type that has data sync enabled and is backed by a database
table, changes to the structure of the underlying data model, such as removing a field, should be
carefully managed. The correct approach involves deleting the unused field from the Custom Data
Type (CDT) that defines the structure of the data for the record type. Following this change, a full
resynchronization of the record type is necessary to ensure that the changes in the CDT are reflected
in the record type and its associated data in Appian. This process ensures data integrity and
consistency across the application and the database.
Reference:
Appian Documentation on Data Management: Provides guidelines on managing data structures,
including CDTs and record types, within Appian applications.
Question 4
You have a record action that should only be visible to certain users under conditions specified by an
expression.
How should you configure this?
- A. Set security on the process model.
- B. Set permissions directly on the user object.
- C. Set security on the record action.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To control the visibility of a record action based on certain user conditions or expressions, the
security settings of the record action itself must be configured. This involves defining conditions or
expressions within the record action's security settings that evaluate whether a user meets the
criteria to see and interact with the action. This method allows for dynamic control over the
accessibility of actions based on user roles, specific attributes, or other contextual factors, ensuring
that only authorized users can see and execute the action under specified conditions.
Reference:
Appian Documentation on Record Actions: Details how to configure and secure record actions,
including visibility and permissions, to tailor the user experience within record views.
Question 5
Which Appian feature is used to automate repetitive manual tasks such as extracting data from a
system for which there is no API?
- A. RPA
- B. Process Mining
- C. Connected Systems
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the Appian feature designed to automate repetitive manual
tasks, especially in scenarios where interacting with systems without APIs is necessary. RPA bots can
mimic human actions, such as navigating through system interfaces, extracting data, and entering
information, effectively bridging the gap between digital processes and systems that lack API
integrations. This capability is particularly useful for integrating legacy systems into modern
workflows, streamlining operations that would otherwise require manual intervention.
Reference:
Appian Documentation on RPA: Explains how RPA can be leveraged within Appian to automate tasks,
providing examples and best practices for implementing RPA bots in business processes.
Question 6
Review the following expression rule:
union(ri!fruit, ri!vegetables)
The rule inputs are configured as text arrays.
What is the expected output?
- A. All items in ri!fruit followed by items in ri!vegetables, including duplicate values.
- B. Only items that are in both ri!fruit and ri!vegetables.
- C. All items in ri!fruit and ri!vegetables combined, with duplicates removed.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The union() function in Appian combines the elements of two or more arrays into a single array,
removing any duplicate values. Given that the rule inputs ri!fruit and ri!vegetables are configured as
text arrays, the expected output of union(ri!fruit, ri!vegetables) would be an array containing all
unique items from both ri!fruit and ri!vegetables, with any duplicates removed. This function is
useful for combining lists without repetition, ensuring a clean, unique set of elements.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Expression Functions
Question 7
You need to pass data into a process from other parts of your Appian application.
Which configuration is required in your process model?
- A. Toggle the Parameter field to 'True" on the configuration of a process variable.
- B. Create process variables on the Data Management tab of Process Model Properties.
- C. Add an interface as a Process Start Form.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To pass data into a process from other parts of an Appian application, you need to configure process
variables. This is done on the Data Management tab within the Process Model Properties. Here, you
can define process variables that can receive data from external sources, such as interfaces, other
processes, or direct user input, when the process is started. These variables serve as placeholders for
the data that will be used throughout the execution of the process.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Process Model Properties
Question 8
HOTSPOT
Match each node to the correct description for the node.
Note: Each description will be used once. To change your responses, you may deselect your response
by clicking the blank space at the top of the selection list.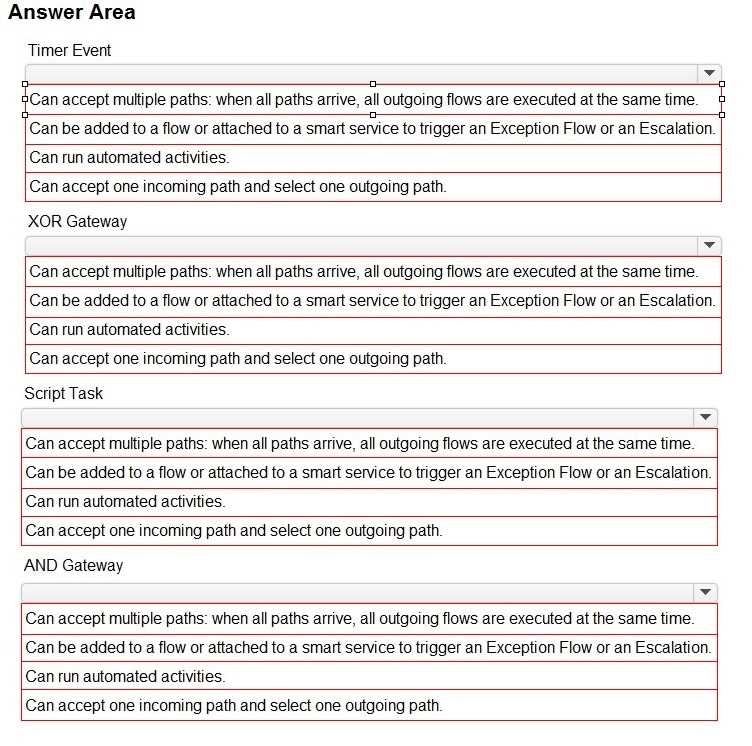
Answer:
Explanation:
Timer Event: Can accept one incoming path and select one outgoing path.
XOR Gateway: Can accept multiple paths; when all paths arrive, all outgoing flows are executed at
the same time.
Script Task: Can run automated activities.
AND Gateway: Can accept multiple paths; when all paths arrive, all outgoing flows are executed at
the same time.
Timer Events in a process model are used to delay the process flow until a specific time condition is
met. They are configured to have one input and one output.
XOR Gateways are decision points that can diverge the process into different paths based on
conditions. If used to converge, they bring together different paths but will continue as soon as one
of the incoming paths is activated.
Script Tasks are automated activities within a process that run scripts or expressions without user
intervention.
AND Gateways are used to synchronize parallel flows in a process. When used to converge parallel
paths, they wait for all incoming paths to complete before continuing.
Reference:
Appian Documentation: Process Modeler Objects
Question 9
You have a record type, ABC_Author, backed by a database table.
You need to retrieve the total number of authors without loading all the data.
According to Appian best practices, which code snippet accomplishes this goal in the most efficient
way?
A)
B)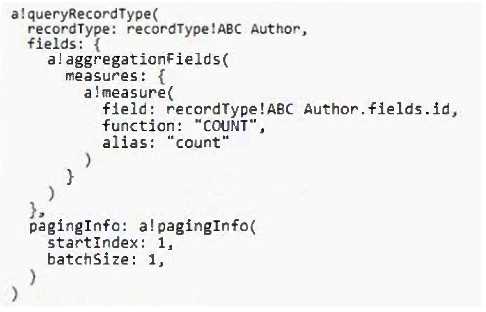
C)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to Appian best practices, the most efficient way to retrieve the total number of authors
without loading all the data is to use a query that includes an aggregation function. Option B uses an
aggregation field with a COUNT function, which is designed to return the number of rows that match
a query without the need to retrieve and load all row data, thus optimizing performance.
Reference:
Appian Documentation: a!queryRecordType Function
Question 10
You are creating a new customer onboarding application. Documents are required from customers
for verification and onboarding purposes. You need to store these documents within Appian.
Which two areas in Appian should you configure? (Choose two.)
- A. Knowledge Center
- B. Decision Object
- C. Folder
- D. Feed
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
In Appian, to store documents such as those required for customer onboarding, you should configure
a Knowledge Center and within that, Folders. The Knowledge Center in Appian serves as the top-
level container for storing and organizing documents and folders. Folders within a Knowledge Center
provide a way to categorize and manage access to documents, making them an essential part of
document management in Appian applications. Decision Objects and Feeds are not related to
document storage.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Knowledge Centers and Folders
Question 11
Where can an Appian Developer connect with and share their expertise with other Appian
Developers?
- A. Appian Learning Paths via Appian Academy
- B. Appian Knowledge Base
- C. Appian Community discussions
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Appian Community discussions provide a platform for Appian Developers to connect with, share
expertise, and learn from each other. The community is a vibrant space where developers can ask
questions, share solutions, and discuss best practices related to Appian development. While Appian
Learning Paths via Appian Academy and Appian Knowledge Base are valuable resources for learning
and troubleshooting, the Community discussions specifically facilitate peer-to-peer interaction and
knowledge sharing among developers.
Reference: Appian Community Website
Question 12
You created and published a new process model.
The process model has a start form with two synchronous subprocesses with 40 and 66 nodes each.
All nodes are chained from the start node through the subprocesses to the end node. After the tasks
and subprocesses, there is a second User Input Task in which the user can confirm the entries and
add a comment.
When testing as a normal Acme business user, you see that the confirmation screen is not shown to
you.
What might be the reason for this behavior?
- A. The maximum number of activity chained nodes is exceeded and breaks.
- B. The second User Input Task is assigned to the process initiator.
- C. The second User Input Task is assigned to the Acme business user group.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Appian, there is a limitation on the number of activities that can be chained in a process, known as
the "chaining limit." If a process model exceeds this limit, which includes synchronous subprocesses
and their nodes, the process may break or not behave as expected. In this scenario, with two large
subprocesses chained from start to end, the maximum number of activity chained nodes could be
exceeded, resulting in the confirmation screen not being shown. Adjusting the process model to
reduce chaining or using asynchronous patterns where possible can help mitigate this issue.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Process Model Best Practices
Question 13
Your customer wants to change the name of a field of an existing Custom Data Type (CDT) to match a
renamed database field.
The CDT is backed by a database entity, whose data store has the Automatically Update Database
Schema option disabled. The old column name was BIRTHDATE and the new column name is
DATE_OF_BIRTH.
How should you proceed?
- A. Download the CDT as XSD, make the appropriate changes, and re-upload the XSD. Verify and publish the data store.
- B. Rename the field in the record type in Appian to automatically update the CDT field.
- C. Rename the field in the CDT in Appian. Verify and publish the data store.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When a field name in an existing Custom Data Type (CDT) needs to be changed to match a renamed
database field, and the Automatically Update Database Schema option is disabled, the correct
approach is to rename the field in the CDT within Appian. After renaming the field in the CDT to
match the new database column name (from BIRTHDATE to DATE_OF_BIRTH in this case), you should
verify the changes and publish the data store to reflect the updates. This approach ensures that the
Appian data model remains in sync with the underlying database schema.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Data Types and Data Stores
Question 14
Which step can be critical in passing information from a form back to a process model?
- A. Configure the Data Management tab.
- B. Configure the activity class parameters of a Write to Data Store Entity node, a
- C. Configure inputs on the Data tab of a User Input Task.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The critical step in passing information from a form back to a process model is to configure inputs on
the Data tab of a User Input Task. When you create a User Input Task, it includes a form for users to
interact with. The data entered into this form can be mapped to process variables via the Data tab
configuration. This ensures that the information collected in the form is available to the process for
further use.
Reference: Appian Documentation - User Input Tasks
Question 15
Review the following expression rule:
ri!name is defined as "Maria".
ri!directory is defined as the following:
What is the expected output?
- A. Maria
- B. 0
- C. 1
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Given that ri!name is defined as "Maria" and ri!directory contains two a!map() structures, one of
which includes the name "Maria," the expression wherecontains(ri!name, index(ri!directory,
"name")) will evaluate as follows: The index() function will return a list of values from ri!directory for
the key "name," which will be {"Maria", "Steven"}. The wherecontains() function will then check
where "Maria" is found within this list. Since "Maria" is the first element, the function will return a
list of indices where "Maria" is found, in this case, {1}. Appian lists are 1-indexed, so the first position
is represented by 1, not 0.
Reference: Appian Expression Language Documentation - Functions