Adobe ad0-e722 practice test
Adobe Commerce Architect Master
Question 1
A company wants to build an Adobe Commerce website to sell their products to customers in their
country. The taxes in their country are highly complex and require customization to Adobe
Commerce. An Architect is trying to solve this problem by creating a custom tax calculator that will
handle the calculation of taxes for all orders in Adobe Commerce.
Following best practices, how should the Architect add the taxes for all orders?
- A. Add a new observer to the event sales.quote.collecLtotals.before'' and add the custom tax to the quote
- B. Write a before plugin to \Magento\Quote\Model\QuoteManagement::placeOrder() and add the custom tax to the quote
- C. Declare a new total collector in "etc/sales.xmr in a custom module
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, the best way to add a custom tax calculation to
all orders is to declare a new total collector in the “etc/sales.xml” file of a custom module. This way,
the custom tax logic can be implemented in a separate class that extends the
\Magento\Quote\Model\Quote\Address\Total\AbstractTotal class and overrides the collect() and
fetch() methods. The collect() method is responsible for calculating the tax amount and adding it to
the quote address, while the fetch() method is responsible for displaying the tax amount in the cart
and checkout pages. The new total collector can be assigned to any area of the order totals, such as
before or after the subtotal, shipping, or grand total.
Reference:
Customizing order totals
How to add custom fee or discount to order totals in Magento 2
Question 2
An Adobe Commerce Architect is creating a new GraphQL API mutation to alter the process of adding
configurable products to the cart. The mutation accepts configurable product ID. If the given product
has only one variant, then the mutation should add this variant to the cart and return not nullable
Cart type. If the configurable product has more variants, then the mutation should return not
nullable Conf igurableProduct type.
The mutation declaration looks as follows:
How should the Adobe Commerce Architect declare output of this mutation?
A)
B)
C)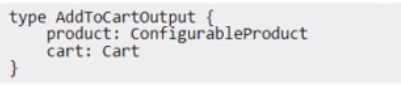
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, the output of a GraphQL mutation is declared by
specifying the type of the data returned by the mutation. The type can be either a scalar type (such
as String, Int, Boolean, etc.), an object type (such as Cart, Product, Customer, etc.), or a union type
(such as SearchResult, which can be either Product or Category). A union type is used when the
mutation can return more than one possible type of data, depending on the input or the logic of the
mutation. In this case, the mutation can return either a Cart type or a ConfigurableProduct type,
depending on the number of variants of the configurable product. Therefore, the output of the
mutation should be declared as a union type that includes both Cart and ConfigurableProduct types.
Option B is the only option that correctly declares a union type using the pipe symbol (|) to separate
the possible types. Option A and Option C are incorrect because they use brackets ([ ]) and curly
braces ({ }), which are used for declaring list types and input object types, respectively.
Reference:
GraphQL API - Adobe Inc.
Schema language with GraphQL | Adobe Commerce
Question 3
A third-party company needs to create an application that will integrate the Adobe Commerce
system to get orders data for reporting. The integration needs access to the GET /Vl/orders endpoint.
It will call this endpoint automatically every hour around the clock. The merchant wants the ability to
restrict or extend access to resources as well as to revoke the access using Admin Panel.
Which type of authentication available in Adobe Commerce should be used and implemented in a
third-party system for this integration?
- A. Use token-based authentication to obtain the Admin Token. The third-party system will utilize the REST endpoint using the admin username and password to get the Admin Token, which will be used as the Bearer Token to authorize.
- B. Use token-based authentication to obtain an integration Token, integration will be created and activated in the admin panel using default integration token settings to get access to the token, which will be used as the Bearer Token to authorize.
- C. Use OAuth-based authentication to provide access to system resources. Integration will be registered by the merchant in the admin panel with an OAuth handshake during activation. The third- party system should follow OAuth protocol to authorize.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, OAuth-based authentication is the
recommended method for integrations that need access to system resources, such as orders,
customers, products, etc. OAuth-based authentication allows the merchant to control the access
level and scope of the integration, as well as to revoke the access at any time using the admin panel.
OAuth-based authentication also requires an OAuth handshake between the integration and the
Adobe Commerce system during activation, which ensures a secure exchange of tokens and keys.
The third-party system should follow the OAuth protocol to obtain and refresh the access token,
which will be used as the Bearer Token to authorize the REST API calls.
Reference:
Authentication | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
OAuth-based authentication | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 4
In a custom module, an Architect wants to define a new xml configuration file. The module should be
able to read all the xml configuration files declared in the system, merge them together, and use
their values in PHP class.
Which two steps should the Architect make to meet this requirement? (Choose two.)
- A. Inject a "reader" dependency for "Magento\Framework\Config\Data" in di.xml
- B. Write a plugin for \Magento\Framework\Config\Data::get() and read the custom xml files
- C. Create a Data class that implements "\Magento\Framework\Config\Data"
- D. Append the custom xml file name in "Magento\Config\Model\Config\Structure\Reader" in di.xml
- E. Make a Reader class that implements '\Magento\Framework\Config\Reader\Filesystem"
Answer:
CE
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, to create a new xml configuration file, the
Architect needs to create a Data class and a Reader class for the custom module. The Data class is
responsible for storing and retrieving the configuration data from the cache or the Reader class. The
Data class should implement the “\Magento\Framework\Config\Data” interface or extend the
“\Magento\Framework\Config\Data” class. The Reader class is responsible for reading and validating
the xml configuration files from the file system. The Reader class should implement the
'\Magento\Framework\Config\Reader\Filesystem"
interface
or
extend
the
'\Magento\Framework\Config\Reader\Filesystem" class. The Architect also needs to declare the
Data class and the Reader class in the di.xml file of the custom module, and specify the name of the
xml configuration file, the converter class, and the schema locator class for the Reader class.
Reference:
Configuration types | Adobe Commerce - Experience League
Create configuration types | Adobe Commerce - Experience League
Question 5
An Adobe Commerce Architect creates a stopword for the Italian locale named stopwordsjtJT.csv and
changes
the
stopword
directory
to
the
following:
<magento_root>/app/code/Custo«vendor/Elasticsearch/etc/stopwords/
What is the correct approach to change the stopwords directory inside the custom module?
- A. Add stopwords to the stopwordsDirectory and CustomerVendor_Elasticsearch to the stopword sModule parameter Of the \Magento\Elasticsearch\SearchAdapter\Query\Preprocessor\Stopwords ClflSS Via di.xml
- B. Add a new ClaSS implementing \Magento\Framework\Setup\Patch\PatchInterface to modify the default Value Of elasticsearch\customer\stopwordspath in core.conf ig_data table. C. Add stopwords to the stopwordsDirectory parameter of the\Hagento\Elasticsearch\Model\Adapter\Document\DirectoryBuilder ClaSS Via stopwords/it.xml and Adobe Commerce will automatically detect the current module.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, the correct approach to change the stopwords
directory inside a custom module is to use dependency injection to override the default values of the
stopwordsDirectory
and
stopwordsModule
parameters
of
the
\Magento\Elasticsearch\SearchAdapter\Query\Preprocessor\Stopwords
class.
The
stopwordsDirectory parameter specifies the relative path of the stopwords directory from the
module directory, while the stopwordsModule parameter specifies the name of the module that
contains the stopwords directory. By adding these parameters to the di.xml file of the custom
module, the Architect can change the location of the stopwords files without modifying the core
code or database.
Reference:
To change the directory from your module
Configure Elasticsearch stopwords
Question 6
A client has multiple warehouses where orders can be fulfilled. The cost of shipping goods from each
warehouse varies by day, due to the number of workers available. The Architect needs to make sure
that when an order is shipped, it is shipped from the lowest cost warehouse that is open.
How should this functionality be implemented?
A.
Create
a
new
class
as
a
preference
for
Magento\inventoryShipping\piugin\Sales\shipment\AssignSourceCodeToShipmentPlugin to set the
lowest-cost warehouse on a shipment.
B.
Create
a
new
class
implementing
Magento\invtntorysourceSelectionApi\Modei\sourceSelectioninterfacece. which returns open
warehouses sorted by cost.
C.
Create
an
after
plugin
On
Hagento\InventoryDistanceBasedSourceSelection\Hodel\Algorithms\DistanceBasedAlgorithto sort
to Warehouse sources by cost
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, the Source Selection Interface is the main
interface for implementing custom source selection algorithms. The interface defines a method
called execute(), which takes a list of items to be shipped and a stock ID as parameters, and returns a
SourceSelectionResultInterface object, which contains the recommended sources and quantities for
each item. The Architect can create a new class that implements this interface and provides the logic
for finding the lowest-cost warehouse that is open for each item. The Architect can then register the
new class as an option for the source selection algorithm in the di.xml file of the custom module.
Reference:
Source Selection Algorithm | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Source Selection Interface | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 7
A merchant is using a unified website that supports native Adobe Commerce B2B and B2C with a
single store view.
The merchant's objective is to display the B2B account features, such as negotiable quotes and credit
limits, in the header of the site on every page for logged-in users who belong to a B2B company
account.
Each B2B company possesses its unique shared catalog and customer group, while numerous
customer groups for non-B2B customers undergo changes. The merchant insists that this association
should not be linked to customer groups.
Which two solutions should the Architect recommend for consideration, taking into account public
data and caching? (Choose two.)
- A. Create a Virtual Type that switches the theme when a user is part of a B2B company so the output can be modified accordingly in the alternate theme.
- B. Create a new HTTP Context variable to allow for separate public content to be cached for users in B2B companies where the output can be modified accordingly.
- C. Set whether the current user is part of a B2B company in the customer session and use that data directly to modify the output accordingly.
- D. Create a new custom condition for customer segments that allow for choosing whether a user is part of a B2B company and then use this segment to modify the output accordingly.
- E. Check if the current user is part of a B2B company within a block class and modify the output accordingly.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
Option B is a valid solution because creating a new HTTP Context variable can allow for
differentiating the public content cache for users who belong to a B2B company account.
The HTTP
Context variable can be used to modify the output of the header block accordingly, without affecting
the performance or scalability of the site1
Option D is also a valid solution because creating a new custom condition for customer segments can
enable targeting users who are part of a B2B company account. The customer segment can be used
to modify the output of the header block accordingly, using layout updates or dynamic blocks.
This
solution can also leverage the existing customer segment functionality and avoid custom coding2
Option A is not a valid solution because switching the theme based on a virtual type can cause
performance issues and increase the complexity of the site maintenance.
Moreover, switching the
theme can affect the entire site appearance, not just the header block3
Option C is not a valid solution because using the customer session data directly to modify the output
of the header block can prevent the public content cache from working properly.
The customer
session data is private and cannot be cached, so this solution can negatively impact the performance
and scalability of the site4
Option E is not a valid solution because checking if the current user is part of a B2B company within a
block class can also prevent the public content cache from working properly.
The block class logic is
executed on every request, so this solution can negatively impact the performance and scalability of
the site5
Reference:
1:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-
guide/architecture/starter-architecture.html?lang=en#http-context 2:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/marketing/customer-segments.html?lang=en 3:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-
guide/design/themes.html?lang=en 4: https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/architecture/starter-architecture.html?lang=en#private-content 5
:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-
guide/architecture/starter-architecture.html?lang=en#public-content
Question 8
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to customize the workflow of a monthly installments payment
extension. The extension is from a partner who is contracted with the default website Payment
Service Provider (PSP), which has its own legacy extension (a module using deprecated payment
method).
The installment payment partner manages only initializing a payment, and then hands the capture to
be executed by the PSP Once the amount is successfully captured, the PSP notifies the website
through a webhook. The goal of the webhook is only to create an "invoice" and save the "capture
information" to be used later for refund requests through the PSP itself.
The Architect needs the most simple solution to capture the requested behavior.
Which solution should the Architect implement?
- A. Add a plugin before the $invoice->capture() and change Its input to prevent the call of the $Payment->capture()
- B. Change the can_capture attribute for the payment method under config.xml to be <can_capture>0</can_capture>
- C. Declare a capture Command with type Magento\Payment\Gateway\Command\NullCommand for the payment method CommandPool in di.xml
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Option C is the correct solution because declaring a capture command with type
Magento\Payment\Gateway\Command\NullCommand for the payment method command pool in
di.xml will prevent the default capture logic from being executed. The NullCommand class is a
dummy implementation of the CommandInterface that does nothing.
This way, the payment capture
will be handled by the PSP webhook, and the invoice will be created accordingly12
Option A is not a correct solution because adding a plugin before the $invoice->capture() and
changing its input to prevent the call of the $payment->capture() will require modifying the core
Magento code, which is not recommended.
Moreover, this solution will affect all payment methods
that use the invoice capture logic, not just the monthly installments payment extension3
Option B is not a correct solution because changing the can_capture attribute for the payment
method under config.xml to be <can_capture>0</can_capture> will disable the capture functionality
for the payment method entirely.
This means that the invoice cannot be created or captured, even by
the PSP webhook4
Reference:
1:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/payments-integrations/payment-gateway/gateway-command.html?lang=en 2:
https://github.com/magento/magento2/blob/2.4-
develop/app/code/Magento/Payment/Gateway/Command/NullCommand.php 3:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/customization/best-practices.html?lang=en#do-not-modify-core-code 4
:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/payments-
integrations/payment-gateway/payment-gateway-configuration.html?lang=en#payment-method-
configuration
Question 9
An existing Adobe Commerce website is moving to a headless implementation.
The existing website features an "All Brands'' page, as well as individual pages for each brand. All
brand-related pages are cached in Varnish using tags in the same manner as products and categories.
Two new GraphQL queries have been created to make this information available to the frontend for
the new headless implementation: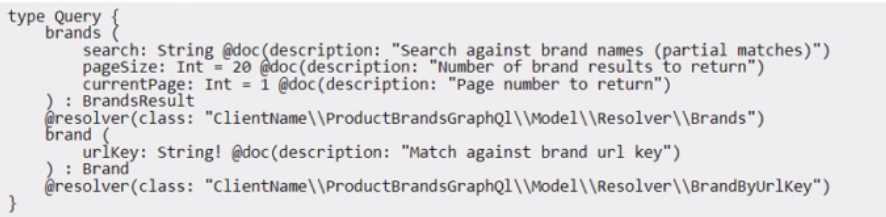
During testing, the queries sometimes return out-of-date information. How should this problem be
solved while maintaining performance?
- A. Specify a @cacgecacheable(cacheable: false) directive for each GraphQL query, making sure that the data returned is not cached, and is up to date
- B. Specify a $cache(cacheidentity: Path\\To\\identityclass) directive for each GraphQL query, corresponding to a class that adds cache tags for relevant brands and associated products C. Each GraphQL query's resolver class should inject \Magento\GraphQlcache\Model\cacheableQuery and call setcachevalidity(true) on it as part of the resolver's resolve function.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This solution ensures that the data returned by the GraphQL queries is up to date, while also
maintaining performance. By specifying a $cache(cacheidentity: Path\To\identityclass) directive for
each GraphQL query, the relevant brands and associated products will be added as cache tags.
Question 10
An Adobe Commerce Architect is investigating a case where some EAV product attributes are no
longer updated.
• The catalog is composed of 20.000 products with 100 attributes each.
• The product updates are run by recurring Adobe commerce imports that happen multiple times a
day.
• The Architect finds an error in the logs that indicates an integrity constraint while trying to insert
row with id 2147483647.
What is causing this error?
- A. Magento framework uses INSERT on DUPLICATE, which leads to reaching the max limit of the increment of the column.
- B. Integrity constraints were dropped after upgrading to the latest version, and the integrity checks were missed.
- C. EAV attribute import uses REPLACE, which leads to reaching the max limit of the increment of the column
Answer:
C
Explanation:
EAV attribute import uses the REPLACE statement, which deletes and inserts a new row with the
same primary key value. This causes the auto-increment column to increase by one for each row,
even if the row already exists. If the auto-increment column reaches its maximum value, which is
2147483647 for a signed INT, then any further REPLACE statement will fail with an integrity
constraint violation error. Reference:
EAV and extension attributes | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
GitHub - techdivision/import-attribute: This library provides the functionality for the Magento 2
import of EAV attributes
Data integrity in JSON (B) when replacing EAV - Stack Overflow
Question 11
An Adobe Commerce Architect is planning to create a new action that will add gift registry items to
the customer's quote. What should the Architect do to guarantee that private content blocks are
updated?
- A. Mark the controller by setting no-cache HTTP headers
- B. Invalidate the status of gift registry indexers
- C. Specify a new action in a sections.xml configuration file
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Private content blocks are sections of the page that are specific to each customer and are not cached
by the server. To update these blocks when a customer performs an action, such as adding a gift
registry item to the quote, the Adobe Commerce Architect needs to specify the new action in a
sections.xml configuration file. This file defines which blocks need to be updated for each action and
how often they should be updated. By doing this, the Architect can ensure that the private content
blocks are refreshed with the latest data from the server. Reference:
Private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Configure private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Question 12
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to scope a bespoke news section for a merchants Adobe
Commerce storefront. The merchant's SEO agency requests that the following URL structure:
news/{date}/{article_url_key}, where {date} is the publication date of the article, and
{article_url_key} is the URL key of the article.
The Architect scopes that a news entity type will be created. The date and URL key data will be
stored against each record and autogenerated on save. The values will be able to be manually
overridden.
- A. The Architect needs to manage routing this functionality and adhere to best practice. Which two options should the Architect consider to meet these requirements? (Choose two.)
- B. Create a standard controller route and mapping the internal URLs (such as news/article/view/id/i) to rewrites that are generated on save and then stored in the URL rewrites table.
- C. Create a custom router that runs before the standard router and matches the news portion of the URL, then looks for and loads a news article by matching the date and URL key parts of the URL
- D. Create a plugin that intercepts Magento\Framework\App\Action: :(), looks for the news portion of the URL, and if it matches, loads the relevant news article by matching the URL date and URL key parts.
- E. Create a standard controller route and an index/index controller class that loads the relevant news article by matching the URL date and URL key parts.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
These two options are both valid ways to manage routing for the bespoke news section and adhere
to best practice. Option B leverages the existing URL rewrite functionality of Adobe Commerce,
which allows creating custom URLs for any entity type and storing them in the database. This option
requires creating a standard controller route for the news entity type, such as news/article/view/id/i,
where i is the news article ID. Then, on saving each news article, a rewrite rule is generated that
maps the internal URL to the desired SEO-friendly URL, such as news/{date}/{article_url_key}. The
rewrite rule is stored in the url_rewrite table, which is used by the standard router to match and
redirect requests.
Option
C
involves
creating
a
custom
router
class
that
implements
\Magento\Framework\App\RouterInterface and runs before the standard router in the routing
process. The custom router class can match the news portion of the URL and extract the date and
URL key parts from it. Then, it can look for and load a news article that matches those values using a
model or repository class. If a match is found, it can set the request parameters accordingly and
dispatch the request to a controller action that renders the news article page.
Reference:
Routing | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
URL Rewrites | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Custom Router | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 13
An external system integrates functionality of a product catalog search using Adobe Commerce
GraphQL API. The Architect creates a new attribute my_attribute in the admin panel with frontend
type select-Later, the Architect sees that Productlnterf ace already has the field my_attribute, but
returns an Int value. The Architect wants this field to be a new type that contains both option id and
label.
To meet this requirement, an Adobe Commerce Architect creates a new module and file
etc/schema.graphqls that declares as follows:
After calling command setup:upgrade, the introspection of Productlnterface field my_attribute
remains Int. What prevented the value type of field my_attribute from changing?
- A. The Magento_CatalogGraphQI module occurs later in sequence than the Magento_GraphQI module and merging output of dynamic attributes schema reader overrides types declared in schema.graphqls
- B. The fields of Productlnterface are checked during processing schema.graphqls files. If they have a corresponding attribute, then the backendjype of product attribute is set for field type.
- C. The interface Productlnterface is already declared in Magento.CatalogGraphQI module. Extending requires use of the keyword extend before a new declaration of Productlnterface.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, to extend an existing GraphQL interface, the
keyword extend must be used before the interface name. This indicates that the new declaration is
adding or modifying fields to the existing interface, rather than redefining it. If the keyword extend is
omitted, the new declaration will be ignored and the original interface will be used. In this case, the
Architect wants to change the type of the my_attribute field in the ProductInterface interface, which
is already declared in the Magento.CatalogGraphQl module. Therefore, the Architect should use the
keyword extend before declaring the ProductInterface interface in the schema.graphqls file of the
custom module. This will allow the Architect to override the type of the my_attribute field from Int
to MyAttributeType.
Reference:
Extend existing schema | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Schema language with GraphQL | Adobe Commerce
Question 14
An Adobe Commerce store owner sets up a custom customer attribute "my.attribute".
An Architect needs to display additional content on the home page, which should display only to
Customers with "my.attribute" of a certain value and be the same content for all of them. The
website is running Full Page Cache.
With simplicity in mind, which two steps should the Architect take to implement these
requirements? (Choose two.)
- A. Add a new context value of "my_attribute" to Magento\Framework\App\Http\Context
- B. Create a Customer Segment and use 'my.attribute' in the conditions
- C. Add a custom block and a pHTML template with the content to the cmsjndexjndex.xml layout
- D. Add a dynamic block with the content to the Home Page
- E. Use customer-data JS library to retrieve "my.attribute" value
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
To display additional content on the home page based on a custom customer attribute, the Architect
needs to do the following steps:
Add a new context value of “my_attribute” to Magento\Framework\App\Http\Context. This will
allow the Full Page Cache to generate different versions of the page for customers with different
values of “my.attribute”. The context value can be set using a plugin on the
Magento\Customer\Model\Context class.
Add a dynamic block with the content to the Home Page. A dynamic block is a type of content block
that can be configured to display only to specific customer segments or conditions. The Architect can
use the ‘my.attribute’ in the conditions of the dynamic block and assign it to the Home Page in the
Content > Blocks section of the Admin Panel. Reference:
Private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Dynamic Blocks | Adobe Commerce 2.3 User Guide - Magento
Question 15
An Adobe Commerce Architect designs a data flow that contains a new product type with its own
custom pricing logic to meet a merchant requirement. Which three steps are required when adding a
product type with custom pricing? (Choose three.)
- A. Content of the etc/product_types.xml file
- B. Data patch to register the new product type
- C. Hydrator for attributes belonging to the new product type
- D. New price model extending \Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\Price
- E. Custom type model extended from the abstract Product Type model
- F. A new class with custom pricing logic, extending the abstract Product model class
Answer:
ADE
Explanation:
To add a product type with custom pricing, the Architect needs to do the following steps:
Create a content of the etc/product_types.xml file that defines the new product type, its label,
model, index priority, and price model.
This file is used to register the new product type and its
associated classes in Magento1
.
Create a new price model that extends \Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\Price and
implements the custom pricing logic for the new product type.
The price model is responsible for
calculating the final price of the product based on various factors, such as special price, tier price,
catalog price rules, etc2
.
Create a custom type model that extends from the abstract Product Type model
(\Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\AbstractType) and overrides the methods related to the
product type behavior, such as prepareForCart, getAssociatedProducts, etc.
The type model defines
how the product type interacts with other components, such as quote, order, cart, etc3
. Reference:
How to add a new product type in Magento 2? (MageStackDay mystery question 1) - Magento Stack
Exchange
Magento 2: How to create custom product types - BelVG Blog
Magento 2: How to create custom product types - BelVG Blog