Adobe ad0-e718 practice test
Adobe Commerce Architect Master
Question 1
A company wants to build an Adobe Commerce website to sell their products to customers in their
country. The taxes in their country are highly complex and require customization to Adobe
Commerce. An Architect is trying to solve this problem by creating a custom tax calculator that will
handle the calculation of taxes for all orders in Adobe Commerce.
How should the Architect add the taxes for all orders?
- A. Write a before plugin to \Magento\Quote\Model\QuoteManagement::placeOrder() and add the custom tax to the quote
- B. Declare a new total collector in "etc/sales.xml" in a custom module
- C. Add a new observer to the event 'sales_quote_collect_totals_before" and add the custom tax to the quote
Answer:
B
Explanation:
you can create tax rules in Magento 2 by going to Stores > Taxes > Tax Rules and choosing or adding
tax rates. However, this may not be enough for complex tax scenarios that require customization.
https://amasty.com/knowledge-base/how-to-configure-tax-calculation-in-magento-2.html
To add a new total to the order, the Architect should declare a new total collector in the
“etc/sales.xml” file of a custom module. This file defines the order of calculation and rendering of
totals.
The
Architect
should
also
implement
a
model
class
that
extends
\Magento\Quote\Model\Quote\Address\Total\AbstractTotal and overrides the collect() and fetch()
methods to handle the logic of adding the custom tax to the quote and order. Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/howdoi/checkout/checkout_new_total.html
Question 2
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to log the result of a ServiceClass : : ge-Dara method execution
after all plugins have executed. The method is public, and there are a few plugins declared for this
method. Among those plugins are after and around types, and all have sortOrder specified.
Which solution should be used to meet this requirement?
- A. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value higher than the highest declared plugin sortOrder and implement afterGetData method.
- B. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value lower than the lowest declared plugin sortOrder and implement aroundGetData method
- C. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value higher than the highest declared plugin sortOrder and implement aroundGetData method
Answer:
C
Explanation:
the sortOrder property from the plugin node declared in di.xml determines the plugin’s
prioritization when more than one plugin is observing the same method. The
Magento\Framework\Interception\PluginListInterface
which
is
implemented
by
Magento\Framework\Interception\PluginList\PluginList is responsible to define when to call the
before, after, and around methods for each plugin.
Therefore, to log the result of a ServiceClass::getData method execution after all plugins have
executed, the solution should be:
C. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value higher than the highest declared plugin sortOrder
and implement aroundGetData method.
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.3/extension-dev-guide/plugins.html
Question 3
An Adobe Commerce Architect is asked by a merchant using B2B features to help with a
configuration issue.
The Architect creates a test Company Account and wants to create Approval Rules for orders. The
Approval Rules tab does not appear in the Company section in the Customer Account Menu when
the Architect logs in using the Company Administrator account.
Which two steps must be taken to fix this issue? (Choose two.)
- A. Set 'Enable Purchase Orders' in the B2B Admin to TRUE
- B. Merchant needs to log out of frontend and then log back in to load new permissions
- C. Set Enable Purchase Orders' on the Company Record to TRUE
- D. Make sure that the 'Purchase Order' payment method is active
- E. Set 'Enable B2B Quote" in the B2B Admin to TRUE
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
Enabling Purchase Orders at both the B2B Admin and the Company Record levels is necessary for
Approval Rules to appear in the Company section of the Customer Account Menu. When 'Enable
Purchase Orders' is set to TRUE, the system assumes that the company will be making purchases
using purchase orders, and the Approval Rules tab becomes visible.
To create Approval Rules for orders, the Architect needs to enable Purchase Orders both in the B2B
Admin and on the Company Record. This will allow the Company Administrator to access the
Approval Rules tab in the Customer Account Menu and create rules based on various criteria. The
Purchase Order payment method and the B2B Quote feature are not required for this functionality.
Reference:
https://docs.magento.com/user-guide/customers/account-dashboard-approval-rules.html
Question 4
An external system integrates functionality of a product catalog search using Adobe Commerce
GraphQL API. The Architect creates a new attribute my_attribute in the admin panel with frontend
type select.
Later, the Architect sees that Productinterface already has the field my_atcribute, but returns an mc
value. The Architect wants this field to be a new type that contains both option id and label.
To meet this requirement, an Adobe Commerce Architect creates a new module and file
etc/schema.graphqls that declares as follows:
After calling command setup:upgrade, the introspection of Productlnterface field xy_attribute
remains int. What prevented the value type of field my_attribute from changing?
- A. The fields of Productlnterface are checked during processing schema.graphqls files. If they have a corresponding attribute, then the backendjype of product attribute is set for field type.
- B. The interface Productlnterface is already declared in Magento.CatalogGraphQI module. Extending requires use of the keyword -xceni before a new declaration of Productlnterface.
- C. The Magento.CatalogGraphQI module occurs later in sequence than the Magento.GraphQI module and merging output of dynamic attributes schema reader overrides types declared in schema.graphqls
Answer:
A
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce Developer Guide1
, the fields of ProductInterface are checked
during processing schema.graphqls files. If they have a corresponding attribute, then the
backend_type of product attribute is set for field type. Therefore, the value type of field my_attribute
remains int because it corresponds to the attribute my_attribute that has a frontend type select and
a backend_type int.
Question 5
An Adobe Commerce Architect is creating a new GraphQL API mutation to alter the process of adding
configurable products to the cart. The mutation accepts configurable product ID. If the given product
has only one variant, then the mutation should add this variant to the cart and return not nullable
cart type. If the configurable product has more variants, then the mutation should return not nullable
conf igurableProduct type.
The mutation declaration looks as follows:
How should the Adobe Commerce Architect declare output of this mutation?
A)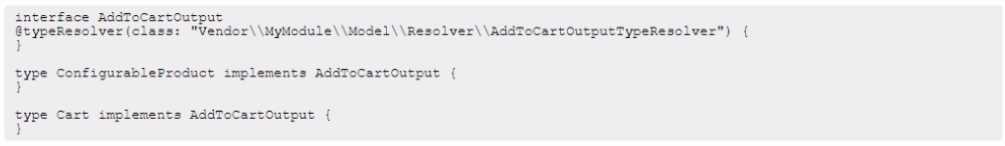
B)
C)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce Developer Guide2
, a union type is a special kind of object that
can be one of several types. It is useful for returning disjoint data types from a single field. In this
case, the output of the mutation can be either Cart or ConfigurableProduct, depending on the
number of variants of the given product. Therefore, a union type should be declared for the output of
this mutation, as shown in option C. The other options are not valid syntax for union types.
Question 6
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to create a new customer segment condition to enable admins
to specify an 'Average sales amount' condition for certain segments.
The
Architect
develops
the
custom
condition
under
vendor\Module\Model\Segment\condition\AverageSalesAmount with all of its requirements: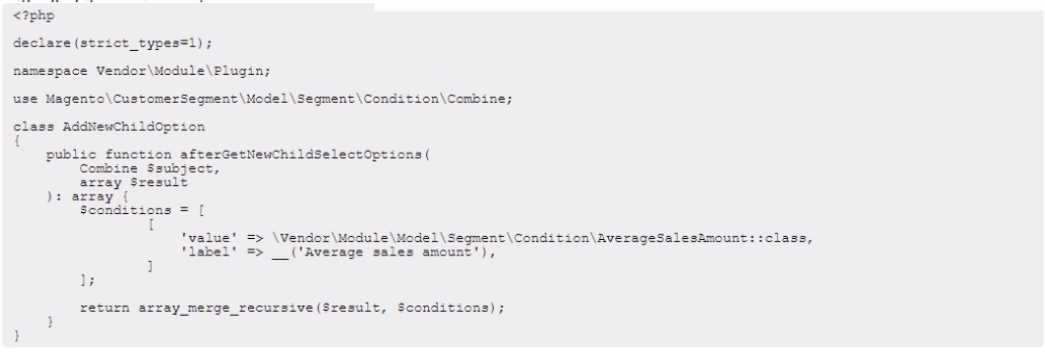
During
testing,
the
following
error
appears:
Which two steps should the Architect complete to fix the problem? (Choose two.)
A)
B)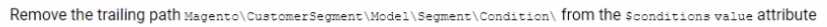
C)
D)
E)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
- E. Option E
Answer:
B, E
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce Developer Guide1
, to create a new customer segment condition,
the
custom
condition
class
must
implement
the
Magento\CustomerSegment\Model\Segment\Condition\Combine\Interface interface. The class
must also have a constructor that accepts an array of data and a context object that contains the
required dependencies. Therefore, option B is correct because the constructor is missing the context
object parameter. Option E is also correct because the class does not implement the required
interface. The other options are not relevant for this problem.
Question 7
An Architect working on a headless Adobe Commerce project creates a new customer attribute
named my_attribure. Based on the attribute value of the customer, the results of GraphQI queries
are modified using a plugin. The frontend application is communicating with Adobe Commerce
through Varnish by Fastly, which is already caching the queries that will be modified. The Adobe
Commerce Fastly extension is installed, and no other modifications are made to the application.
Which steps should the Architect take to make sure the vcl_hash function of Varnish also considers
the newly created attribute?
A)
B)
C)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Option B is the correct way to make sure the vcl_hash function of Varnish also considers the newly
created attribute. The Architect should create a new module that depends on Magento_Fastly and
declare a plugin for \Magento\Fastly\Model\Config::getVclSnippets() method. The plugin should add
a new snippet to the result array with the type ‘recv’ and the content ‘set req.http.my_attribute =
req.http.X-Magento-Vary;’. This will append the value of the customer attribute to the hash key used
by Varnish for caching. Option A is incorrect because it modifies the core file of Magento_Fastly
module, which is not recommended and can cause issues during upgrades. Option C is incorrect
because it uses the wrong type and content for the snippet, which will not affect the vcl_hash
function. Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/cloud/cdn/fastly-vcl-bypass-to-origin.html
According to the Adobe Commerce Developer Guide2
, to make sure the vcl_hash function of Varnish
also considers the newly created attribute, the Architect should use a plugin for
Magento\Customer\Model\Context::getVaryString method and add the attribute value to the vary
string. This will ensure that Varnish caches different versions of GraphQL queries based on the
attribute value of the customer. Therefore, option B is correct. Option A is not correct because it does
not affect the vcl_hash function. Option C is not correct because it does not use a plugin for the
getVaryString method.
Question 8
A company has an Adobe Commerce store. An attribute named "my.attribute" (type "text") is created
to save each product's global ID that is shared between multiple systems.
Several months after going live, the values of "my.attribute" are all integer. This causes a problem for
the other systems when those systems receive this data.
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to recommend a solution to change the type of "my.attribute"
from textXo int
Which two steps should the Architect take to achieve this? (Choose two.)
- A. Migrate data from table "catalog_product_entity_text" to "catalog.producLentityjnt" for the attribute.id
- B. Go to Admin > Stores > Attributes > Product, edit "my.attribute" and update type from "text' to "inf
- C. Write a plugin for \Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attrlbute\Backend\AbstractBackend::afterLoad() and load data from "catalog_product_entity_int"
- D. Create a Data Patch and update 'my.attribute' type from "text" to "inf
- E. Run the Command bin/magentc indexer: reset catalog_product_attribute
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
Option A is correct because it will migrate data from one table to another based on the attribute id,
which is required when changing the attribute type14
.
Option D is correct because it will create a
data patch that will update ‘my.attribute’ type from “text” to “int”, which is a recommended way of
changing the attribute type programmatically4
.
To change the type of “my.attribute” from text to int, the Architect should take two steps: A) Migrate
data from table “catalog_product_entity_text” to “catalog_product_entity_int” for the attribute_id.
This step will move the existing values of the attribute from the text table to the int table, which
corresponds to the new type. D) Create a Data Patch and update ‘my.attribute’ type from “text” to
“int”. This step will update the attribute metadata in the database and reflect the new type. Option B
is incorrect because the Admin panel does not allow changing the type of an existing attribute.
Option
C
is
incorrect
because
writing
a
plugin
for
\Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Backend\AbstractBackend::afterLoad() will not change the
type of the attribute, but only load data from a different table. Option E is incorrect because running
the command bin/magento indexer:reset catalog_product_attribute will not change the type of the
attribute,
but
only
reset
the
indexer
status.
Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/attributes.html
Question 9
A merchant is using a unified website that supports native Adobe Commerce B2B and B2C with a
single store view.
The merchant wants to show the B2B account features like negotiable quotes and credit limits in the
header of the site on every page for the logged-in users who are part of a B2B company account.
Each B2B company has its own individual shared catalog and customer group, and many customer
groups for non B2B customers change. The merchant requests that this should not be tied to
customer groups.
Which two solutions should the Architect recommend considering public data and caching? (Choose
two.)
- A. Create a plugin that switches the theme when a user is part of a B2B company so the output can be modified accordingly in the alternate theme.
- B. Check if the current user is part of a B2B company within a block class and modify the output accordingly.
- C. Create a new custom condition for customer segments that allow for choosing whether a user is part of a B2B company and then use this segment to modify the output accordingly.
- D. Set whether the current user is part of a B2B company in the customer session and use that data directly to modify the output accordingly.
- E. Create a new HTTP Context variable to allow for separate public content to be cached for users in B2B companies where the output can be modified accordingly.
Answer:
C, E
Explanation:
C would involve creating a new custom condition for customer segments that allow for choosing if a
user is part of a B2B company, and then use this segment to modify the output accordingly. E would
involve creating a new HTTP Context variable to allow for separate public content to be cached for
users in B2B companies, where the output can be modified accordingly.
To show the B2B account features in the header of the site on every page for the logged-in users who
are part of a B2B company account, the Architect should recommend two solutions: C) Create a new
custom condition for customer segments that allow for choosing whether a user is part of a B2B
company and then use this segment to modify the output accordingly. This solution will allow the
merchant to create a customer segment based on the custom condition and use it to display different
content in the header for B2B users. E) Create a new HTTP Context variable to allow for separate
public content to be cached for users in B2B companies where the output can be modified
accordingly. This solution will ensure that the public content cache is varied based on the custom
HTTP Context variable, which can be set based on whether the user is part of a B2B company or not.
Option A is incorrect because switching the theme based on the user’s B2B status is not a scalable or
maintainable solution, and it will also affect the entire site’s appearance, not just the header. Option
B is incorrect because checking the user’s B2B status within a block class will not work with public
content cache, as it will not vary the cache based on that condition. Option D is incorrect because
setting the user’s B2B status in the customer session will not work with public content cache, as it
will
not
vary
the
cache
based
on
that
data.
Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/segmentation.html
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/cache/page-caching/public-content.html
Question 10
An Architect is reviewing a custom module that is logging customer activity data on storefront using
observers. The client reports that logs were recorded while the client was previewing storefront
catalog pages from Admin Panel for a future scheduled campaign, using Adobe Commerce staging
preview functionality.
What should the Architect check first to address this issue9
A.
The
plugin
for
the
public
method
isAllowedObserver()
from
\Magento\Staging\Model\Event\Manager that alters the return value
B. The logging observers being copied from etc\events.xml to etc\adminhtml\events.xml with the
attribute disabled=’’true"
C.
The
list
of
logging
observers
in
bannedObservers
parameter
of
\Magento\staging\Model\Event\Managertype in di.xml
Answer:
C
Explanation:
It will allow you to exclude logging observers from being executed during staging preview
functionality
by
adding
them
to
bannedObservers
parameter
of
\Magento\staging\Model\Event\Manager type in di.xml file. This will prevent customer activity data
from being logged while previewing storefront catalog pages from Admin Panel for a future
scheduled campaign.
The Architect should check the list of logging observers in bannedObservers parameter of
\Magento\Staging\Model\Event\Manager type in di.xml. This parameter defines the list of observers
that should not be executed during staging preview. The Architect should add the logging observers
to this list to prevent them from recording customer activity data while previewing the storefront
catalog pages from Admin Panel. Reference: https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/staging.html
Question 11
An Adobe Commerce Architect gets a request to change existing payment gateway functionality by
allowing voided transactions only for a certain range of paid amounts.
In the vendor module file etc/config.xml, payment method has an option can,_void set to 1.
How should this customization be done?
- A. Extend Magento\Payment\Model\\Method\Adapter and reimplement method void. Use this new class as a new type of payment method facade configuration overriding virtualType type for adapter.
- B. Declare a new plugin for class Magento\Payment\ Gateway\Config\ConfigValueHandler and using the afterHandle method, change the result for Subject can_void.
- C. Add new handler with name can_void to virtualType based on typeMagento payment\Gateway\config\ValueHandlerPool In payment method facade configuration.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Architect should add a new handler with name can_void to virtualType based on type
Magento\Payment\Gateway\Config\ValueHandlerPool in payment method facade configuration.
This handler will be responsible for determining whether the payment method can void transactions
or not, based on the custom logic of the paid amount range. The handler should implement
\Magento\Payment\Gateway\Config\ValueHandlerInterface and override the handle() method to
return true or false depending on the payment amount. Option A is incorrect because extending
Magento\Payment\Model\Method\Adapter and reimplementing method void will not change the
can_void option, but rather the logic of voiding transactions. Option B is incorrect because declaring
a new plugin for class Magento\Payment\Gateway\Config\ConfigValueHandler and using the
afterHandle method will affect all payment methods that use this class, not just the specific one that
needs
customization.
Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/payments-integrations/base-integration/integration-model.html
Question 12
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to customize the workflow of a monthly installments payment
extension. The extension is from a partner that is contracted with the default website PSR which has
its own legacy extension (a module using deprecated payment method).
The installment payment partner manages only initializing a payment, and then hands the capture to
be executed by the PSP. Once the amount is successfully captured, the PSP notifies the website
through an IPN. The goal of the IPN is only to create an "invoice" and save the 'capture information'
to be used later for refund requests through the PSP itself.
The Architect needs the most simple solution to capture the requested behavior without side effects.
Which solution should the Architect implement?
- A. Add a plugin before the $invoice-> () and changes its input to prevent the call of the $payment-> capture()
- B. Change the can_ capture attribute for the payment method under config.xml to be <can_capture>0</can_capture>
- C. Declare a capture command with type Magento\payment\Gateway\Command\NullCommand for the payment method CommandPool in di.zm1
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The best solution for the Adobe Commerce Architect to implement in order to capture the requested
behavior without side effects is to declare a capture command with type
Magento\payment\Gateway\Command\NullCommand for the payment method CommandPool in
di.xml. This will allow the partner to initialize the payment and then hand the capture over to the
PSP, while also preventing the website from calling the $payment->capture() method. It will also
allow the PSP to notify the website through an IPN, which will create an "invoice" and save the
'capture information' to be used later for refund requests through the PSP itself.
The Architect should implement the solution of declaring a capture command with type
Magento\Payment\Gateway\Command\NullCommand for the payment method CommandPool in
di.xml. This command will do nothing when the capture method is called on the payment method,
which is the desired behavior since the capture is handled by the PSP. The NullCommand class
implements \Magento\Payment\Gateway\CommandInterface and overrides the execute() method
to return null. Option A is incorrect because adding a plugin before the $invoice->capture() method
and changing its input will not prevent the call of the $payment->capture() method, but rather
change the invoice object that is passed to it. Option B is incorrect because changing the can_capture
attribute for the payment method under config.xml to be <can_capture>0</can_capture> will not
prevent the capture method from being called, but rather disable the capture option in the Admin
panel.
Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/payments-integrations/base-integration/facade-configuration.html
Question 13
An Architect needs to integrate an Adobe Commerce store with a new Shipping Carrier. Cart data is
sent to the Shipping Carrier's API to retrieve the price and display to the customer. After the feature
is implemented on the store, the API hits its quota and returns the error "Too many requests". The
Shipping Carrier warns the store about sending too many requests with the same content to the API.
In the carrier model, what should the Architect change to fix the problem?
- A. Implement _setCachedQuotes () and_getCachedQuotes() return the data if the request matches.
- B. In _doShipmentRequest (), call canCollectRates() before sending request to the API
- C. Override getResponse (), save the response to a variable, check if the response exists, then return.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Implementing setCachedQuotes () andgetCachedQuotes() in the carrier model can allow the store to
store the cart data in a cache, so that repeated requests with the same content can be retrieved from
the cache instead of sending a new request to the API. This can reduce the number of requests and
avoid hitting the quota limit.
Reference:
[1]
https://docs.adobe.com/content/help/en/experience-manager-65/commerce/commerce-payment-shipping-modules/shipping/shipping-carrier-apis.html
[2]
https://docs.adobe.com/content/help/en/experience-manager-
65/commerce/commerce-payment-shipping-modules/shipping/developing-shipping-carrier-
integrations/shipping-carrier-model.html
Question 14
A representative of a small business needs an Adobe Commerce Architect to design a custom
integration of a third-party payment solution. They want to reduce the list of controls identified in
their Self-Assessment Questionnaire as much as possible to achieve PCI compliance for their existing
Magento application.
Which approach meets the business needs?
- A. Utilize the payment provider Iframe system to isolate content of the embedded frame from the parent web page.
- B. Utilize the Advanced Encryption standard (AES-256) algorithm to encrypt all customer-sensitive data from the payment module.
- C. Utilize a trusted signed certificate issued by a Certification Authority (CA) to secure each connection made by the payment solution protocol via HTTPS.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Architect should utilize the payment provider iframe system to isolate content of the embedded
frame from the parent web page. This approach will reduce the list of controls identified in their Self-
Assessment Questionnaire as much as possible to achieve PCI compliance for their existing Magento
application. By using an iframe, the payment provider handles all customer-sensitive data and
Magento does not store or process any cardholder data. This reduces the PCI scope and simplifies the
compliance process. Option B is incorrect because utilizing the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-
256) algorithm to encrypt all customer-sensitive data from the payment module will not reduce the
PCI scope, but rather increase it. Magento will still store and process cardholder data, which requires
more controls and validation. Option C is incorrect because utilizing a trusted signed certificate
issued by a Certification Authority (CA) to secure each connection made by the payment solution
protocol via HTTPS will not reduce the PCI scope, but rather ensure the security of data transmission.
Magento will still store and process cardholder data, which requires more controls and validation.
Reference:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/payments-integrations/payment-gateway/integration.html
Question 15
An Architect is working to implement Adobe Commerce into a pre-built ecosystem in a company.
Communication between different company domains uses event-driven design and is driven via
AMQP protocol with using RabbitMQ.
The Architect needs to establish the data flow between the ERP system and Adobe Commerce.
The ERP system stores only customer data excluding customer addresses.
The role of Adobe Commerce is to provide Customer Address data to the enterprise ecosystem.
Primary Customer data should not be changed from Adobe Commerce side; it should only be
updated by messages data from ERP.
Which three AMQP configurations should be considered to meet these requirements? (Choose
three.)
- A. Create a queue_consumer.xml and communction.xml configuration files for Customer data messages
- B. Create a queue_publisher.xml configuration file for Customer data messages
- C. Create a nueue_publisher.xml configuration file for Customer Address messages
- D. Create a queue_topology.xml configuration file for Customer Address messages
- E. Create a queue_topology.xml configuration file for Customer data messages
- F. Create a queue_customer.xml and communication.xml configuration files for Customer Address messages
Answer:
ACE
Explanation:
To establish the data flow between the ERP system and Adobe Commerce using AMQP protocol with
RabbitMQ, you need to consider the following AMQP configurations:
Create a queue_consumer.xml and communication.xml configuration files for Customer data
messages. These files will define the topics, handlers, and consumers that will receive and process
the messages from the ERP system. The communication.xml file will also specify the schema for the
Customer data messages.
Create a queue_publisher.xml configuration file for Customer Address messages. This file will define
the exchange where the Customer Address messages will be published to. The exchange will route
the messages to the appropriate queues based on the binding rules.
Create a queue_topology.xml configuration file for Customer Address messages. This file will define
the message routing rules and declare the queues and exchanges for the Customer Address
messages. The queue_topology.xml file will also specify the connection name and type for
RabbitMQ.
Reference:
:
https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.3/extension-dev-guide/message-queues/config-mq.html